Advanced Stem Cell Therapy
Pioneering Treatments for Complex Conditions
Stem cell therapy is transforming regenerative medicine by offering new options for patients with complex or previously untreatable conditions. Across the United States, ongoing research and clinical programs are expanding how clinicians use stem cells to address areas such as oncology, neurology, orthopedics, and autoimmune disorders.
This article helps patients understand the landscape of stem cell therapy options, what to expect from different treatment pathways, and how to evaluate reputable providers.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Clinical Applications

Embryonic Stem Cells
Cells that can become almost any type of tissue.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Adult cells from bone marrow, fat, or umbilical cord that help repair tissues.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Adult cells reprogrammed to act like embryonic stem cells, with wide healing potential.
See advanced medical technologies transformed into quality
healthcare with expert physicians!
Our Hospitals
Liv Hospital Ulus
Main focus of Liv Hospital Ulus is a personalized and scientific approach that embraces its guests with a 360-degree multidisciplinary structure. While high-level health services are produced, scientific studies and research are carried out.
Liv Hospital Vadistanbul
Bringing a new and modern perspective to the health sector by bringing together a patient-oriented approach and experienced physician staff with a multidisciplinary working style in Vadistanbul.
İSÜ Liv Hospital Bahçeşehir
Opened its doors in December 2016, İSÜ Liv Hospital Bahçeşehir was established with the contribution of MLP Care’s quarter-century knowledge and experience in the field of healthcare.
Liv Hospital Ankara
Liv Hospital Ankara, equipped with world class medical infrastructure and technology, is now serving international patients in 25,000 square-meter indoor area.
Liv Hospital Samsun
Liv Hospital Samsun, which adds Turkish hospitality to its special architecture and international quality standards, aims to be indispensable in the sector while promising comfort with its privileged hospitality services.
Liv Hospital Gaziantep
Liv Hospital Gaziantep has a team of experienced physicians, a multidisciplinary diagnostic and therapeutic approach, innovative medical technologies, and patient-oriented, personalized diagnostic and treatment programs.
Liv Duna Medical Center
LIV Hospital Duna Medical Center, established in 2015, is one of the most well-equipped private healthcare facilities in Hungary, offering outpatient services, inpatient care, and diagnostics.
Liv Bona Dea Hospital Bakü
As “Liv Hospital”, we came to Baku in 2022 to provide high-level service in the field of healthcare under the “Liv Bona Dea” brand name. Our professional team provides high-quality emergency medical services 24/7.
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy
The Foundation of Regenerative Medicine
Stem cells are the body’s raw materials — unspecialized cells that can divide, renew, and develop into specialized cell types. These cells play a central role in tissue maintenance and repair: they can self-renew, differentiate into multiple lineages, and migrate to areas of damage where they support healing through direct replacement of cells and by releasing signaling factors that reduce inflammation and modulate immune responses.
- Self-renewal capacity — the ability to divide and create more stem cells for long-term tissue maintenance
- Differentiation potential — the ability to become specialized cells such as bone, cartilage, nerve, or insulin-producing cells
- Homing and migration to damaged tissues where repair is needed
- Anti-inflammatory effects that can reduce local tissue injury
- Immunomodulatory functions that influence immune responses in autoimmune and inflammatory conditions


Get in touch
Speak to someone today, we’re ready for your enquiry. Book an appointment or ask for advice.
Neurodegenerative Diseases and Stem Cell Therapy
Neurological conditions are among the most complex clinical challenges, and regenerative approaches using stem cells are an active area of clinical research and early‑phase treatment programs across the United States. These programs investigate whether stem cells can reduce inflammation, promote neural repair, and support functional recovery after events such as stroke or spinal cord injury.
Parkinson’s Disease
Loss of dopamine neurons causes tremors and movement issues. Stem cells may help replace neurons and support brain function.
Alzheimer’s Disease
Neuron loss leads to memory decline. Stem cells could help replace neurons and reduce inflammation, still under study.
Ataxia
Affects balance due to brain cell loss. Stem cells may help repair and slow progression.
Huntington’s Disease
Inherited neuron loss causes movement and thinking issues. Stem cell therapy is experimental but promising.
Meet Our Doctor in Regenerative Medicine
Your treatment is guided by the expertise of Prof. Dr. Erdal Karaöz, one of Turkey’s most distinguished scientists and a pioneer in regenerative medicine. With a career dedicated to cellular therapies and tissue engineering, his mission is to provide patients with safe, effective, and personalized therapies grounded in cutting-edge scientific research.
📖 You can explore Prof. Dr. Karaöz’s full list of scientific articles on PubMed.
- World-Class Scientific Authority
- GMP-Certified Quality & Safety
Types of Stem Cells Used in Diseases

Autoimmune Diseases
Stem cells are studied for conditions like Lupus, Multiple Sclerosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, and Hashimoto’s, aiming to reset the immune system.
Orthopedic Applications
Used for joint degeneration and tendon injuries, stem cells may offer less invasive repair and pain relief. Results vary.

Diabetes Research
Studies explore restoring insulin production and immune balance, aiming for more than symptom control.

Cardiac Applications
Stem cells are being explored to repair heart tissue after attacks, though this is still experimental.

Get in touch
Speak to someone today, we’re ready for your enquiry. Book an appointment or ask for advice.
Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases
Resetting the Immune System
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own healthy cells. This loss of immune tolerance leads to chronic inflammation and progressive organ damage. Examples include Lupus Erythematosus, Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Systemic Sclerosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, and Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. While conventional medicine mainly offers symptom control through immunosuppressive drugs, these do not address the root cause or provide a cure.

Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT)
A process that renews the immune system using new stem cells to help the body regain balance and health.

Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC)
Special cells that travel to areas of inflammation, calm immune responses, and help repair damaged tissues naturally.
Clinical trials and expert guidelines now support stem cell therapies for select severe and treatment-resistant autoimmune conditions, but the treatment requires careful risk assessment and specialist oversight.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
A condition that causes joint inflammation and pain. Stem cell therapy may help calm inflammation and support joint repair.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
An autoimmune disorder affecting the nervous system. Stem cell transplants, like HSCT, may help reset the immune system and ease symptoms.
Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma)
A rare disease that hardens skin and organs. Stem cell treatments may slow its progress and encourage healing.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Affects spine joints, leading to pain and stiffness. Stem cell therapies, especially MSCs, are being explored to reduce damage and improve mobility.

Get in touch
Speak to someone today, we’re ready for your enquiry. Book an appointment or ask for advice.
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy
The Foundation of Regenerative Medicine
Stem cells are the body’s raw materials — unspecialized cells that can divide, renew, and develop into specialized cell types. These cells play a central role in tissue maintenance and repair: they can self-renew, differentiate into multiple lineages, and migrate to areas of damage where they support healing through direct replacement of cells and by releasing signaling factors that reduce inflammation and modulate immune responses.
- Self-renewal capacity — the ability to divide and create more stem cells for long-term tissue maintenance
- Differentiation potential — the ability to become specialized cells such as bone, cartilage, nerve, or insulin-producing cells
- Homing and migration to damaged tissues where repair is needed
- Anti-inflammatory effects that can reduce local tissue injury
- Immunomodulatory functions that influence immune responses in autoimmune and inflammatory conditions
Neurodegenerative Diseases and Stem Cell Therapy
- World-Class Scientific Authority
- Access to Innovative Therapies
- A Foundation of Trust & Ethics
- GMP-Certified Quality & Safety
Parkinson’s Disease
Progressive loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain leads to tremors, rigidity, and motor dysfunction. Stem cell therapy focuses on neuron replacement and neuroprotection, with promising but still experimental results in early human trials.
Alzheimer’s Disease
Ataxia
Huntington’s Disease

Get in touch
Speak to someone today, we’re ready for your enquiry. Book an appointment or ask for advice.
Important Considerations for Patients
Seeking a world-class medical standard at a reasonable cost.
Stem cells play a key role in the body’s natural repair and regeneration mechanisms. Thanks to their self-renewal and differentiation abilities, they are used in the repair of damaged tissues, improvement of organ functions, and support of the immune system. Stem cell therapies are prepared in GMP laboratory conditions with cells obtained either from the patient’s own tissue (autologous) or from a suitable donor (allogeneic), and applied with legally approved methods
Benefits:
- Aims to treat the root cause, not just manage symptoms.
- Utilizes your body's own natural healing potential.
- Minimally invasive, same-day procedure.
- Supports recovery and can improve overall quality of life.


Get in touch
Speak to someone today, we’re ready for your enquiry. Book an appointment or ask for advice.
Important Considerations for Patients

Regulatory & research guidance
Stem cell treatment rules vary by country and condition. Many options are available through approved clinical trials.
Insurance & payment considerations
Coverage depends on the treatment and insurer. Established therapies may be covered, but experimental ones usually require out of pocket payment.
Potential risks and safety
Stem cell treatments can carry risks such as infection, immune reactions, inflammation, or other procedure-related issues.

Seeking a world-class medical standard at a reasonable cost.
Stem cells play a key role in the body’s natural repair and regeneration mechanisms. Thanks to their self-renewal and differentiation abilities, they are used in the repair of damaged tissues, improvement of organ functions, and support of the immune system. Stem cell therapies are prepared in GMP laboratory conditions with cells obtained either from the patient’s own tissue (autologous) or from a suitable donor (allogeneic), and applied with legally approved methods
Benefits:
- Aims to treat the root cause, not just manage symptoms.
- Utilizes your body's own natural healing potential.
- Minimally invasive, same-day procedure.
- Supports recovery and can improve overall quality of life.
Current Status of Diabetes Stem Cell Research
The research landscape is evolving quickly; key themes include:
- Numerous Phase 1 and Phase 2 clinical trials testing cell implants, encapsulation devices, and immunomodulatory combinations
- Successful laboratory production of insulin‑producing cells from stem cell lines—translation to widely available treatments remains in progress
- Development of implantable devices and matrix systems to protect and support transplanted cells
- Combination approaches that pair cell replacement with immune‑modulating therapies to improve durability
- International research collaborations and stem cell institutes contributing to protocol development and multi‑center trials
- Potential for reduced insulin dependence in responsive patients, pending longer‑term data
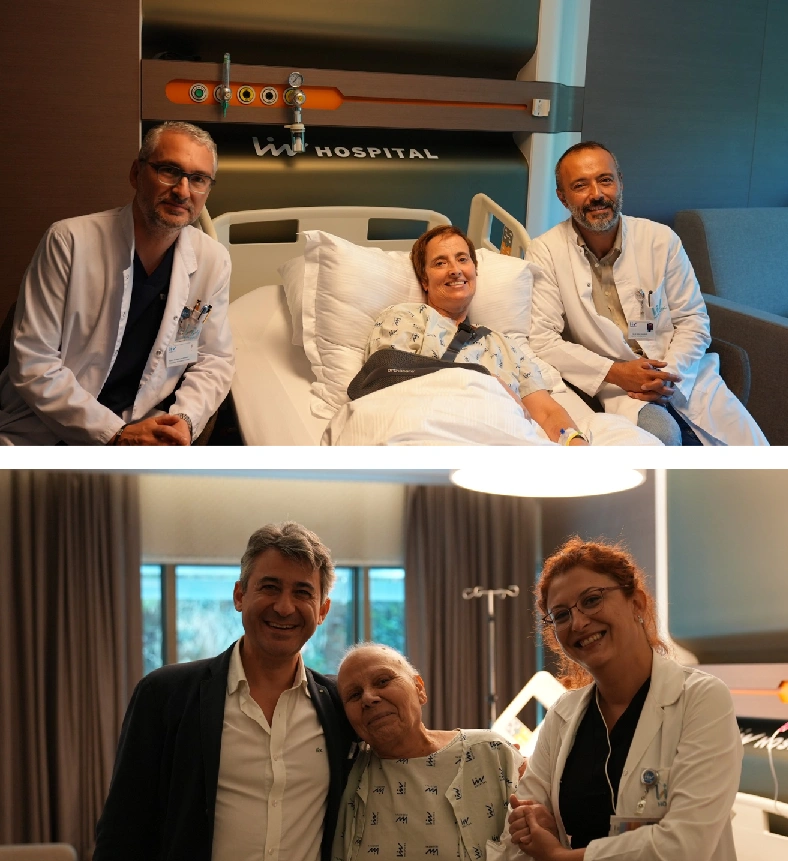
Seeking a world-class medical standard at a reasonable cost.
Stem cells, as one of modern medicine’s most important discoveries, are at the center of our body’s natural repair and regeneration mechanisms. These extraordinary cells possess two fundamental properties: self-renewal and differentiation capacity. Through their self-renewal ability, stem cells can divide to create copies of themselves, while their differentiation capacity allows them to transform into any specialized cell type in the body.
Types and Classification of Stem Cells
1. Classification by Potency:
Totipotent Stem Cells: These are the most powerful stem cells, found in the first few divisions after fertilization, capable of forming a complete organism.
Pluripotent Stem Cells: These can differentiate into almost all cell types in the body, including embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs).
Multipotent Stem Cells: These can develop into multiple cell types within a specific tissue or organ system. Examples include hematopoietic stem cells that produce all blood cell types, and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) found in bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord.
Oligopotent Stem Cells: These have a more limited differentiation capacity, able to become only a few cell types within their lineage.
Unipotent Stem Cells: These can only produce one cell type but maintain self-renewal capacity.
2. Classification by Source:
Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs): Derived from the inner cell mass of blastocysts, these pluripotent cells can differentiate into any cell type but raise ethical concerns.
Adult Stem Cells (Somatic Stem Cells): Found in various tissues throughout the body, these multipotent cells maintain and repair the tissue in which they reside.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): Adult cells reprogrammed to an embryonic-like pluripotent state through genetic manipulation, offering ethical advantages.
Perinatal Stem Cells: Obtained from umbilical cord blood, umbilical cord tissue (Wharton’s jelly), placenta, and amniotic fluid.
Why Turkey for Regenerative Medicine?
A Leading European Destination for Medical Innovation
Exceptional Value
Get high-quality, JCI-accredited regenerative care at prices more accessible than many private clinics.
A Hub for European Patients
Istanbul is a medical hub, easy to reach from many places. Liv Hospital is trusted by thousands seeking advanced care.
Top Doctors & Technology
Our specialists use the latest regenerative techniques and protocols for the best outcomes.
Seamless Patient Experience
Multilingual coordinators handle all details from transfers to accommodation for a stress free journey.

● Contact Us
Get in Touch

- +90 (530) 174 28 49
- info@livhospital.com.tr
- Ahmet Adnan Saygun Cad. Canan Sok. No:5 34340 Beşiktaş İstanbul