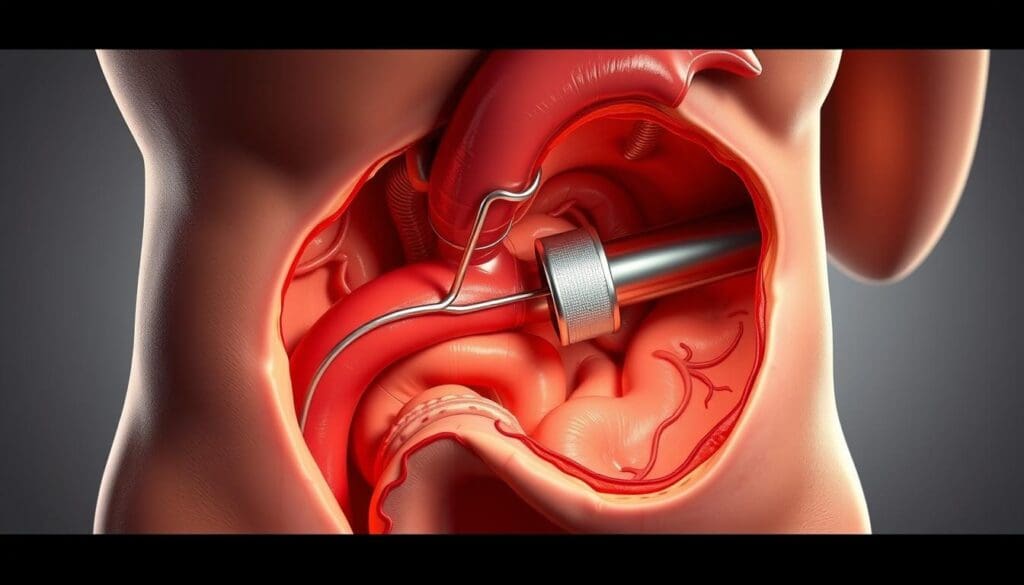
Endovascular aortic repair is changing how we treat aortic aneurysms. It’s a safer option than old-school surgery.
Aortic aneurysms are serious health threats. Thanks to new tech, treatment has gotten better. Liv Hospital leads in using endovascular stent solutions. These make recovery faster and cut down on risks.
The move to endovascular aortic repair shows a big change in vascular care. It focuses on treatments that are less invasive. This not only helps patients more but also raises the bar for treating aortic aneurysms.
Key Takeaways
- Endovascular aortic repair is a minimally invasive alternative to open surgery.
- It reduces recovery time and lowers the risk of complications.
- Liv Hospital is a leader in providing innovative endovascular stent solutions.
- The approach prioritizes patient-centered care and improves outcomes.
- Endovascular aortic repair is setting a new standard in vascular care.
Understanding Aortic Aneurysms: Why Intervention Matters
It’s important to understand aortic aneurysms to get medical help on time. Aortic aneurysms happen when the aorta gets too big. This can happen in different parts of the aorta.
Types and Locations of Aortic Aneurysms
Aortic aneurysms are mainly divided by where they happen. Abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) are in the belly area and are the most common. Thoracic aortic aneurysms (TAAs) are in the chest.
Where an aneurysm is located helps decide how to treat it. For example, aneurysms near important blood vessels might need special endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) methods.
Risk Factors and Prevalence in the United States
Things like smoking, high blood pressure, and family history can cause aortic aneurysms. In the U.S., about 5% of men between 65 and 74 have AAAs.
Knowing these risk factors helps find people who should get checked and possibly treated early.
Consequences of Untreated Aneurysms
Not treating aortic aneurysms can be very dangerous. It can cause a rupture, which is often deadly. The death rate from ruptured aneurysms is much higher than for those treated early.
So, using aneurysm stenting or aortic stent graft types early on is key to saving lives.
The Revolution of Stent Graft Surgery in Aneurysm Treatment
Stent graft surgery has changed how we treat aortic aneurysms. It’s a less invasive option compared to old-school open surgery. This new method has made recovery times much shorter and outcomes better for patients.
From Open Surgery to Minimally Invasive Approaches
Old methods for fixing aortic aneurysms were very invasive. They needed a big cut and a long time to heal. But endovascular stent grafting has brought a new way. It’s less invasive and might have fewer risks.
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) uses a stent graft put in through the femoral arteries. It’s guided by images to block blood from the aneurysm. Studies show it can be safer than open surgery for many people.
Key Milestones in Endovascular Technique Development
The journey of endovascular techniques has seen big steps forward. The first successful use of an endovascular stent graft was in the 1990s.
There have been many improvements. Better stent grafts, advanced imaging, and more skilled doctors have all helped. These advancements have made the procedure safer and more effective.
Current Adoption Rates and Practice Patterns
EVAR is now the top choice for treating abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs). It’s slowly taking over from open surgery. The rate of EVAR use varies worldwide. It depends on things like healthcare setup, doctor training, and who gets the treatment.
| Region | EVAR Adoption Rate (%) | Open Surgery Rate (%) |
| North America | 75 | 25 |
| Europe | 80 | 20 |
| Asia-Pacific | 60 | 40 |
The table shows how EVAR is becoming more popular than open surgery in different places. It shows the growing trend towards less invasive treatments.
How Endovascular Stent Grafts Function
Understanding endovascular stent grafts helps both patients and doctors. These devices are made to treat aortic aneurysms. They work by keeping the aneurysm out of the blood flow.
Anatomy and Components of Modern Stent Grafts
Today’s stent grafts are designed to fit each patient’s body. They have a main part and extra limbs. The main components are:
- The main body, which is usually placed in the aorta
- Iliac limbs or extensions that are used to secure the graft in place and maintain blood flow to the lower extremities
Mechanism of Aneurysm Exclusion and Remodeling
Stent grafts work by keeping the aneurysm out of the blood flow. This reduces pressure on the aneurysm wall. Over time, the aorta can change shape, possibly shrinking the aneurysm.
Materials and Engineering Considerations
Creating stent grafts requires careful material and design choices. They use strong, safe materials like polyester or polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). These are supported by a nitinol stent.
The design must be flexible, strong, and small enough for catheters. This makes the procedure minimally invasive. The modular design lets doctors tailor the graft to fit each patient perfectly.
The EVAR Surgery Process: What Patients Can Expect
Before EVAR surgery, it’s key to know what happens. The treatment stages are set up for the best results. This is for those getting endovascular aortic repair.
Pre-operative Imaging and Planning
Imaging before surgery is vital for EVAR success. High-resolution imaging like CT angiography helps. It checks the aneurysm’s size, shape, and where it is. It also looks at the blood vessels around it.
This imaging lets doctors plan the best way to fix the problem. They pick the right stent graft size and shape. This step is key to avoid problems and get good results.
| Imaging Modality | Purpose | Benefits |
| CT Angiography | Detailed assessment of aneurysm and vasculature | High-resolution images for precise planning |
| MRI | Soft tissue characterization | Useful for complex aneurysm evaluation |
| Ultrasound | Initial screening and follow-up | Non-invasive and cost-effective |
Step-by-Step Endovascular Aortic Repair Procedure
The EVAR procedure has several steps:
- Accessing the femoral arteries under local anesthesia
- Guiding catheters and wires through the arteries to the aneurysm site
- Deploying the stent graft to exclude the aneurysm from blood flow
- Confirming the stent graft’s position and exclusion of the aneurysm
- Completing the procedure with wound closure
Immediate Post-operative Care
After EVAR, patients stay in a recovery area for a few hours. Pain management is a big focus. Most patients feel little pain.
Getting up and moving is important to avoid problems. Patients usually go home in a few days. This depends on their health and if any issues arise.
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Stenting: The Triple A Stent Approach
The triple A stent approach is a big step forward in treating abdominal aortic aneurysms. It’s a less invasive option compared to traditional surgery. This method has greatly improved treatment results for patients with AAA.
Anatomical Considerations for AAA Repair
For EVAR to work well, the patient’s body shape matters a lot. The proximal and distal landing zones are key for a good seal and to stop leaks. The size, shape, and where the aneurysm is located also play a big role in choosing the right stent graft.
Specialized Techniques for Complex Anatomies
Dealing with tricky body shapes, like short or bent necks, is hard for EVAR. Specialized techniques and custom stent grafts help solve these problems. With fenestrated and branched EVAR, doctors can now treat aneurysms that were once too hard to fix.
Outcomes and Success Rates
EVAR’s success is shown by its ability to stop aneurysms from bursting and lower death rates. EVAR is safer than traditional surgery, with lower risks of complications and death right after surgery. But, how long the stent graft lasts and if there are leaks are key to long-term success.
| Outcome Measure | EVAR | Open Repair |
| 30-Day Mortality | 1.2% | 4.5% |
| Major Complications | 10.5% | 25.8% |
| Reintervention Rate | 15.2% | 5.5% |
The table shows how EVAR compares to traditional surgery for treating abdominal aortic aneurysms. EVAR is better in the short term for survival and fewer complications. But, it might need more follow-up surgeries because of possible leaks.
Thoracic Aorta Stent Surgery: Addressing the Challenges
Thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR) has greatly improved for patients with thoracic aortic issues. Thoracic aorta stent surgery is now a key treatment, being less invasive than traditional surgery.
Unique Aspects of Thoracic Endovascular Repair
TEVAR faces unique challenges compared to abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repair. The thoracic aorta is more complex, with a higher risk of neurological issues. TEVAR has been shown to significantly reduce the risks associated with open surgery, such as the need for large incisions and cardiopulmonary bypass.
Managing Branch Vessels and Arch Anatomy
Managing branch vessels and complex arch anatomy is a big challenge in TEVAR. The thoracic aorta has critical branches for the head and upper limbs. Techniques like chimney grafts and fenestrated stent grafts help preserve blood flow to vital organs.
The success of TEVAR relies on accurate preoperative planning and imaging. Advanced imaging, including 3D reconstructions, is key in assessing the aortic anatomy and its branches.
Recovery Timeline and Expectations
The recovery time for TEVAR is generally shorter than open surgery. Most patients are discharged within a few days. But, recovery time can vary based on individual factors and procedure complexity.
Patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities for weeks after the procedure. Regular follow-up appointments are important to check the stent graft’s position and ensure the aneurysm is excluded.
Advanced Aortic Stent Graft Types Expanding Treatment Options
New stent graft technologies have opened up more treatment options for complex aortic aneurysms. These advanced grafts have greatly improved the safety and success of endovascular aortic repair (EVAR).
Fenestrated Endovascular Grafts for Complex Anatomies
Fenestrated endovascular grafts are made for aneurysms near vital blood vessels. They have special holes that match up with these vessels. This allows for better blood flow to important organs.
Key benefits of fenestrated grafts include:
- Expanded treatment eligibility for patients with complex aortic aneurysms
- Preservation of blood flow to critical branch vessels
- Potential for improved outcomes due to more precise graft placement
Branched Stent Systems for Thoracoabdominal Aneurysms
Branched stent systems are a big step forward in treating thoracoabdominal aneurysms. These systems have special branches for the complex aorta area. They are designed to fit the unique shape of these aneurysms.
Advantages of branched stent systems:
- Ability to treat complex thoracoabdominal aneurysms with a minimally invasive approach
- Customization options to fit individual patient anatomies
- Potential for reduced morbidity compared to open surgical repair
Physician-Modified and Custom-Made Solutions
Physician-modified and custom-made solutions are also being developed. These are tailored to meet the unique needs of each patient. They offer more flexibility in treating complex aortic conditions.
The future of aortic aneurysm treatment lies in the continued innovation of stent graft technology, enabling more patients to benefit from minimally invasive procedures.
Comparing Endovascular Aneurysm Repair to Open Surgery
EVAR surgery is a less invasive option compared to open surgery for aortic aneurysms. It has become popular for its benefits in recovery and outcomes.
Mortality and Morbidity Differences
EVAR has lower risks of complications and death compared to open surgery, mainly for older or high-risk patients. This is because EVAR is less invasive, reducing risks from large cuts and long surgeries.
A meta-analysis showed EVAR patients had much lower 30-day death rates. EVAR’s benefits include fewer heart and lung problems and less stress from surgery.
| Outcome Measure | EVAR | Open Surgery |
| 30-day Mortality Rate | 1.2% | 3.5% |
| Major Complications | 10% | 25% |
| Median Hospital Stay | 3 days | 8 days |
Recovery Time and Hospital Stay Advantages
EVAR offers quicker recovery and shorter hospital stays compared to open surgery. Patients often have less pain and can get back to normal faster.
A study showed EVAR patients stayed in the hospital for 3 days, while open surgery patients stayed for 8. This not only makes patients happier but also saves money on hospital costs.
Long-term Durability Considerations
EVAR has many short-term benefits, but its long-term success is a concern. Open surgery, on the other hand, offers a more lasting fix with fewer long-term issues.
Long-term studies indicate EVAR is good at preventing aneurysm rupture but may need more follow-up surgeries. This is mainly due to issues like endoleaks and graft migration.
In conclusion, choosing between EVAR and open surgery depends on the patient’s specific needs and risks. Knowing the differences between these options is key to making the right choice.
Potential Complications After Aortic Stent Placement
Even though aortic stent placement is minimally invasive, it can lead to complications. It’s important to know about these issues to manage patient care effectively.
Endoleaks: Classification and Management
Endoleaks are a big problem after aortic stent placement. They happen when blood leaks into the aneurysm sac around the stent. There are five types, each needing different treatments.
- Type I: Leak at the attachment site, often requiring additional stenting or open surgery.
- Type II: Retrograde flow from branches, sometimes resolving spontaneously but may need embolization.
- Type III: Graft failure, necessitating further intervention.
- Type IV: Graft porosity, typically managed conservatively.
- Type V: Endotension, where the sac expands without visible leak, requiring close surveillance.
It’s key to accurately classify and manage endoleaks. This helps prevent aneurysm rupture and ensures the stent graft works well long-term.
Device-Related Complications
Complications can happen due to stent graft migration, fracture, or kinking. These issues can make the repair less effective and might need more procedures.
Key device-related complications include:
- Stent graft migration or movement from the intended position.
- Material fatigue leading to fracture or component separation.
- Kinking or twisting of the stent graft, potentially causing flow limitation.
Regular checks are vital to catch these problems early. This way, we can act before things get worse.
Surveillance Protocols and Reintervention Rates
After aortic stent placement, lifelong checks are recommended. These checks involve imaging studies to watch the stent graft and aneurysm sac.
How often you need more procedures depends on the complication and your health. Studies show that the need for more procedures varies a lot. This highlights the need for a plan tailored to each patient.
| Surveillance Interval | Imaging Modality | Purpose |
| 1-3 months post-procedure | CT Angiography | Assess stent graft position and exclude endoleak |
| 6-12 months post-procedure | CT Angiography or Duplex Ultrasound | Monitor aneurysm sac size and detect possible complications |
Good surveillance and quick action are key. They help manage complications and ensure the stent placement works well in the long run.
Patient Selection for Endovascular Aortic Repair
The success of endovascular aortic repair (EVAR) depends a lot on choosing the right patients. Doctors carefully check each patient to see if they’re a good fit for the treatment.
Anatomical Eligibility Criteria
When picking patients for EVAR, the shape and size of the aorta matter a lot. Doctors look at the aneurysm’s size, where it can be fixed, and the health of the blood vessels. Patients with the right anatomy tend to do better with EVAR.
Medical Risk Assessment
A detailed medical risk assessment is key to find out who might face big risks during or after EVAR. Doctors check the patient’s health, heart condition, and any other health issues that could affect the outcome.
Age and Life Expectancy Considerations
Age and life expectancy play a big role in deciding if EVAR is right for someone. The treatment is best for those who have a good chance of living a long life. Doctors weigh the risks and benefits, considering the patient’s age and health.
By looking at these factors closely, doctors can make sure EVAR is offered to those who will get the most benefit from it.
The Future of Aneurysm Stenting: Innovations on the Horizon
The world of aneurysm stenting is about to change a lot. New endovascular technology is coming. This will make treatments better and give more options to patients.
Advancements in Endovascular Devices
New endovascular devices are being made. They will fix old problems and make treatments work better. These new devices will:
- Be more flexible and fit complex aortas better.
- Last longer and not wear out as fast. This lowers the chance of future problems.
- Have better delivery systems. This means they can be placed more accurately and quickly.
Expanding Indications for EVAR and TEVAR
More people can get treated with EVAR and TEVAR now. This is because of new technology. It includes:
- Treating harder-to-reach aneurysms.
- Helping younger patients, maybe avoiding more surgeries later.
- Being used in emergencies, like when an aneurysm bursts.
Personalized Treatment Algorithms
Personalized treatments are coming for aneurysm stenting. New imaging and computer models will help doctors. They can:
- Guess how well a treatment will work for each patient.
- Choose the best device for each patient’s body.
- Make follow-up plans that fit each patient’s needs.
These new ideas will change aneurysm stenting for the better. Patients will get better care and more options. As research and tech keep improving, we’ll see even more changes soon.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Aortic Aneurysm Treatment
Aortic aneurysm treatment has changed a lot with the introduction of endovascular aortic repair (EVAR). This method is less invasive than traditional surgery. It’s important to know about EVAR and other treatments to make good choices about your care.
If you have an aortic aneurysm, you should learn about the different treatments. Each has its own benefits and risks. By thinking about your health and what you prefer, you can choose the best treatment with your doctor’s help.
Understanding your aortic aneurysm and the treatments available is key. Being well-informed and talking openly with your doctor helps you make the right choices. This way, you can get the best care for your condition.
FAQ
What is endovascular aortic repair (EVAR)?
EVAR is a minimally invasive surgery for aortic aneurysms. It uses a stent graft inserted through small groin incisions. Imaging guides it to the aneurysm, reinforcing the aorta.
How does an endovascular stent graft work?
The stent graft is placed in the aorta at the aneurysm site. It lines the aorta, creating a new blood flow path. This bypasses the aneurysm, reducing pressure and rupture risk.
What are the benefits of EVAR compared to open surgery?
EVAR has smaller incisions, less pain, and quicker recovery. It also has lower complication risks. This makes it a better option for many patients.
What is the difference between EVAR and TEVAR?
EVAR treats abdominal aortic aneurysms. TEVAR is for thoracic aortic aneurysms. Both use stent grafts but in different aorta sections.
What are fenestrated and branched stent grafts?
These grafts treat complex aortic aneurysms near major branches. Fenestrated grafts have holes for branch alignment. Branched grafts have limbs for more complex cases.
What are the possible complications of aortic stent placement?
Complications include endoleaks, stent migration, and vessel injury. Regular checks are key to early detection and management.
How are endoleaks classified and managed?
Endoleaks are categorized by cause. Management varies by type and severity. It may include observation, additional procedures, or open repair.
What factors are considered in selecting patients for EVAR?
Patient selection looks at anatomy, medical risks, age, and life expectancy. A detailed evaluation is needed to determine suitability for EVAR.
What advancements are on the horizon for aneurysm stenting?
Future advancements include better devices and expanded indications. Personalized treatment plans based on anatomy and risk factors are also expected.
How does the recovery process differ between EVAR and open surgery?
EVAR recovery is faster and less painful. Open surgery recovery is longer due to larger incisions and more tissue disruption.
What is the role of surveillance after EVAR?
Surveillance monitors the stent graft and detects complications like endoleaks. Regular imaging studies are vital for long-term success.
References
- Fernandes, J. F. E. (2020). Abdominal aortic aneurysms – how to treat in today’s practice. European Society of Cardiology Journal of Cardiology Practice. https://www.escardio.org/Journals/E-Journal-of-Cardiology-Practice/Volume-18/abdominal-aortic-aneurysms-how-to-treat-in-today-s-practice





