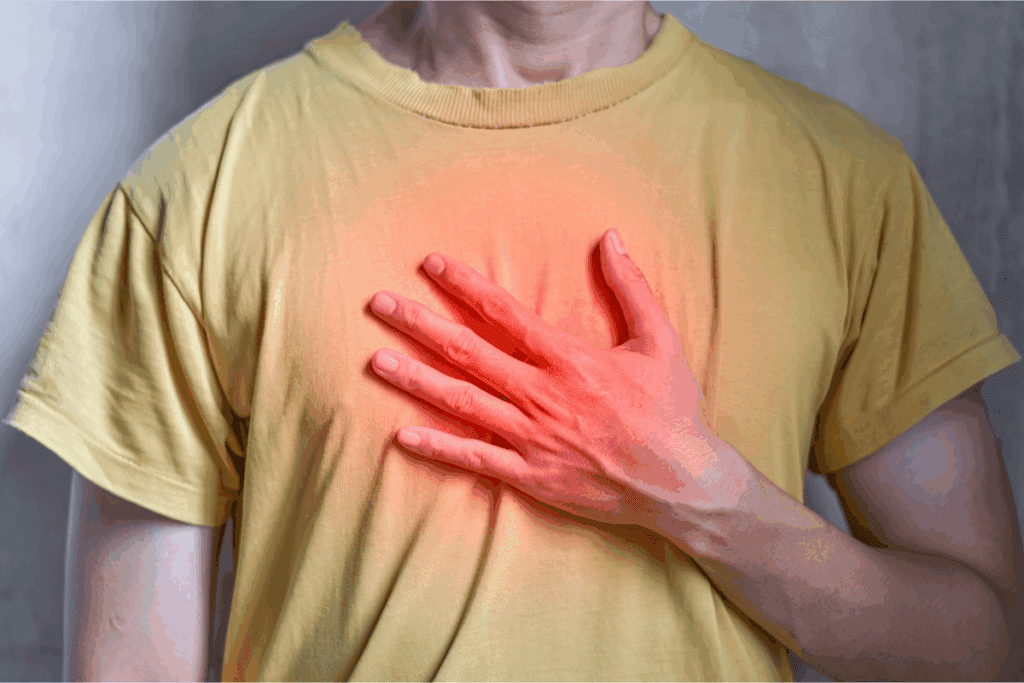
Chest pain from stress and anxiety is a common worry for many. Up to 40% of emergency visits for chest pain are due to anxiety or stress. At Liv Hospital, we help patients understand the link between stress, anxiety, and chest pain. We aim to provide the relief they need. Learn about stress causing chest pain and discover effective relief methods.
Research shows that 80% of chest pain cases aren’t heart-related. This highlights the need to find the real cause of this symptom. We offer detailed care and support to international patients. We address their unique needs with care and medical knowledge.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the link between stress, anxiety, and chest pain is key for relief.
- Chest pain from stress is common, with many cases not related to the heart.
- Liv Hospital provides patient-focused care and trusted methods for chest pain.
- There are ways to manage chest pain caused by stress.
- Our team is committed to giving full support and care to international patients.
The Alarming Connection Between Stress and Physical Symptoms
Stress affects our bodies in many ways. It triggers our “fight or flight” response, releasing hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones get our body ready to face or run from danger, leading to physical changes.
How Emotional Distress Manifests in the Body
Emotional stress shows up in our bodies in different ways. Muscle tension is common, causing pain in the neck, back, and shoulders. Stress can also harm our cardiovascular system, leading to chest pain, irregular heartbeats, or changes in heart rate.
Stress can also cause gastrointestinal issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), acid reflux, or stomach ulcers. Other symptoms include headaches, fatigue, and trouble sleeping. These symptoms show how our emotional state affects our physical health.
The Prevalence of Stress-Related Physical Complaints
Many people experience physical symptoms due to stress. Studies reveal that a large number of people face physical issues because of stress. For example, chest pain from stress is a common reason for emergency room visits, not always heart-related.
This shows how important it is to recognize and deal with stress. By understanding the link between stress and physical symptoms, we can manage our stress levels. This helps reduce its physical effects.
Stress Causing Chest Pain: Understanding the Phenomenon

It’s important to understand how stress and chest pain are connected. This connection can be scary and disrupt our daily lives. We’ll look into the facts and how our bodies react to stress.
Statistics: 40% of Emergency Visits for Chest Pain Linked to Stress
Studies show that about 40% of chest pain visits to the emergency room are due to stress or anxiety. This shows how big a role emotional stress plays in physical symptoms. It’s clear we need care that looks at both the body and mind.
The Physiological Pathway from Stress to Pain
Stress can lead to chest pain through a complex process. When we’re stressed, our body’s “fight or flight” response kicks in. This releases hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones can make our heart beat faster and blood pressure go up, causing chest pain.
Stress hormones can also make our muscles tense, adding to the pain. Knowing how our body reacts to stress helps doctors find better ways to help us feel better.
How Stress Hormones Affect Your Cardiovascular System
Stress affects our heart health through special hormones. These hormones help us react to danger. When we’re stressed, our body’s ‘fight or flight’ response kicks in. This releases hormones that change how our heart works.
The Adrenaline and Cortisol Response
When we face stress, our adrenal glands send out adrenaline (also known as epinephrine) and cortisol. Adrenaline makes our heart beat faster and blood pressure go up. Cortisol keeps us alert for longer.
These hormones quickly change our heart and blood system:
- Increased heart rate: Adrenaline makes our heart pump more blood to our muscles.
- Elevated blood pressure: Adrenaline and cortisol make our blood vessels narrow, raising blood pressure.
- Cardiac output increase: Our heart pumps more blood to meet the demand for oxygen and nutrients.
Elevated Heart Rate and Blood Pressure During Stress
Our heart rate and blood pressure go up when we’re stressed. This is a natural way to deal with danger. But, too much stress can harm our heart over time.
High heart rate and blood pressure can lead to:
- More strain on the heart muscle.
- Potential damage to blood vessels from high pressure.
- Risks of long-term high blood pressure, like heart disease and stroke.
Knowing how stress hormones affect our heart is key. It helps us manage stress-related chest pain and keep our heart healthy.
Recognizing Chest Pain Related to Stress
It’s important to know the signs of stress-related chest pain. This helps us tell it apart from serious health issues. Stress makes our body’s “fight or flight” response kick in, causing physical symptoms like chest pain. Knowing what this pain feels like can help us handle it better.
Common Sensations: Tightness, Pressure, and Discomfort
Stress can make your chest feel tight or pressured. Some people say it feels like a discomfort that scares them. Doctors say this pain is often sharp and short-lived or feels like a sudden “catch” that stops your breath. This feeling can be scary, but knowing why it happens can help you feel better.
One person said, “When I’m really stressed, I feel a tight band around my chest, making it hard to breathe deeply.” This shows how important it is to recognize the signs of stress-related chest pain.
Location and Radiation Patterns
Stress-induced chest pain can happen anywhere in the chest. It might also spread to your arms, back, or jaw. The way it spreads can sometimes be mistaken for heart pain, so it’s key to know the difference.
- Central chest pain
- Radiation to the arms or back
- Occasional jaw pain
Knowing these patterns helps us figure out what’s causing the pain.
Duration and Intensity Variations
The length and how bad the pain feels can change a lot. It might last from seconds to hours or even days. The pain can be mild or very severe. Watching how it changes helps us know if it’s stress or something else.
“The pain was so intense that it felt like my heart was being squeezed,” said a patient describing their experience with stress-induced chest pain. Such descriptions underscore the need to differentiate between stress-related and other forms of chest pain.
By recognizing these signs, we can better deal with stress-related chest pain. This improves our overall health and well-being.
Anxiety and Persistent Chest Pain: Why It Can Last for Days
Anxiety can cause persistent chest pain, leaving people wondering why it doesn’t go away. When we feel anxious, our body’s stress response kicks in. This can lead to physical symptoms like chest pain.
The Cycle of Symptom Monitoring and Increased Anxiety
One reason anxiety-related chest pain lasts is the cycle of monitoring symptoms and feeling more anxious. When chest pain happens, people start to watch their symptoms closely. This makes them even more anxious, starting a cycle.
As we worry more about our chest pain, our anxiety grows. This can make the pain worse. It’s hard to stop this cycle because watching our symptoms makes us more anxious, which makes the pain worse.
Breaking this cycle is key to easing persistent chest pain.
Muscle Tension and Prolonged Discomfort
Muscle tension also plays a part in persistent chest pain. Anxiety makes our muscles tight, including in the chest. This tightness can cause long-lasting discomfort because the muscles stay contracted.
To show how muscle tension affects chest pain, look at this table:
| Muscle Tension Level | Chest Pain Severity | Duration of Discomfort |
| Mild | Minimal | Short-term |
| Moderate | Noticeable | Several hours |
| Severe | Significant | Prolonged, potentially days |
The table shows that more muscle tension means more severe chest pain and longer discomfort.
In summary, anxiety-related chest pain can last because of monitoring symptoms and muscle tension. Knowing these reasons helps us manage and reduce persistent chest pain.
Chest Pressure During High-Stress Periods: Mechanisms Explained
When we’re under a lot of stress, many feel chest pressure. This feeling can be scary and really bothers us. It’s not just a physical feeling; it’s also linked to how our body reacts to stress.
“Stress can show up in many ways, and chest pressure is a big worry for many,” says a medical expert. Knowing why this happens is key to feeling better.
Hyperventilation and Its Effects on Chest Muscles
Hyperventilation is a big reason for chest pressure when we’re stressed. When we’re stressed, we breathe fast and shallow. This can upset the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in our blood. It can make us feel dizzy, lightheaded, and our chest can feel tight or pressured.
The muscles between our ribs can get strained from breathing too fast. This strain can make our chest feel tight or uncomfortable.
Esophageal Spasms and Acid Reflux Under Stress
Stress can also mess with our digestive system. It can cause esophageal spasms and acid reflux. The esophagus is a muscular tube that carries food to our stomach. Stress can make the muscles in the esophagus spasm, causing pain or pressure in the chest. Stress can also make acid reflux worse, which can make our chest hurt.
These problems can be really upsetting because they can feel like a heart attack. This can make us even more stressed and anxious.
Cardiovascular Responses to Prolonged Stress
Long-term stress can make our heart rate and blood pressure go up. Our body’s ‘fight or flight’ response, triggered by stress hormones, gets ready to face danger. But if this response goes on too long, it can strain our heart, leading to chest pressure or discomfort.
Our heart pumps more blood when we’re stressed, which can make our heart beat irregularly. This can lead to heart disease if not managed well.
Knowing how stress affects our body is the first step to dealing with chest pressure. By understanding how stress, breathing, digestion, and heart function are connected, we can start to manage our symptoms and feel better overall.
When Chest Pain and Stress Trigger Panic Attacks
Stress and chest pain together can start a panic attack. This creates a cycle of fear and physical symptoms. It’s hard to deal with because the symptoms feel like a heart attack.
Escalation to Panic
Chest pain and stress can quickly turn into panic attacks. The body’s stress response, or “fight or flight,” gets ready to face danger. This can cause a fast heartbeat, sweating, and other scary symptoms.
As these symptoms get worse, people might think they’re having a heart attack. This fear makes the symptoms even worse, starting a cycle that’s hard to stop.
Panic Attacks and Heart Attack Symptoms
Panic attacks and heart attacks share similar symptoms like chest pain and rapid heartbeat. But, panic attacks are a response to stress, not a heart problem. Heart attacks are caused by blocked arteries.
It’s hard to tell the difference between the two, which can make people even more scared. But, panic attacks are not as dangerous as heart attacks.
The Cycle of Fear and Physical Symptoms
The fear and physical symptoms of a panic attack go hand in hand. The symptoms can make people more afraid, which makes the symptoms worse. It’s a cycle that’s hard to break.
Deep breathing, muscle relaxation, and therapy can help manage panic attacks. By tackling both the physical and emotional sides, people can reduce how often and how bad panic attacks are.
Differentiating Between Cardiac and Stress-Induced Chest Pain
It’s important to know the difference between cardiac and stress-induced chest pain. Both can be scary, but they have different causes and health effects.
Key Distinguishing Features
There are key differences between cardiac and stress-induced chest pain. Cardiac chest pain is linked to heart issues. It often shows up with:
- It gets worse with physical activity.
- The pain feels like pressure or heaviness in the chest.
- It can spread to arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
- The pain doesn’t change with breathing or movement.
Stress-induced chest pain has its own signs:
- It’s often caused by emotional stress or anxiety.
- The pain can be sharp or a dull ache.
- It might come with anxiety symptoms like fast breathing or heart racing.
- The pain can get worse with deep breathing or moving.
When Symptoms Overlap: The Diagnostic Challenge
But sometimes, symptoms can look the same, making it hard to tell what’s causing the pain. Stress can make heart problems worse, leading to pain that’s both stress and heart-related. On the other hand, fear of heart problems can cause anxiety, making symptoms look like heart pain.
To figure out the cause of chest pain, doctors use:
- A detailed medical history.
- A physical check-up.
- Tests like ECGs and blood work.
Knowing the difference between cardiac and stress-induced chest pain is key. It helps get the right treatment. Whether it’s for heart health or stress and anxiety, finding the cause is important.
Immediate Relief Strategies for Stress Chest Pain
When stress shows up as chest pain, it’s key to have quick fixes. Stress chest pain can be scary, but there are ways to feel better right away.
Breathing Techniques to Calm Your Nervous System
One top way to ease stress chest pain is through deep breathing. Diaphragmatic breathing can slow your heart and ease chest tightness. To do it, sit up straight, put one hand on your belly and the other on your chest. Breathe in deeply through your nose, letting your belly rise while your chest stays steady.
Benefits of Diaphragmatic Breathing:
- Reduces stress and anxiety
- Lowers blood pressure
- Promotes relaxation
Progressive Muscle Relaxation for Chest Tightness
Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) is great for easing chest tightness from stress. PMR involves tensing and relaxing muscles all over your body. Start with your toes and move up to your head, including your chest and shoulders.
“By systematically tensing and relaxing muscle groups, you can release physical tension and reduce the sensation of chest pain.”
| Muscle Group | Tense for (seconds) | Release |
| Toes | 5 | Relax |
| Calves | 5 | Relax |
| Chest & Shoulders | 5 | Relax |
Cognitive Approaches to Break the Stress Response
Cognitive methods are also key in handling stress chest pain. Changing how you see the pain and cutting down on negative thoughts can help. Mindfulness meditation and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) are very helpful.
“Mindfulness is the practice of being present in the moment, observing your thoughts and feelings without judgment. Regular mindfulness practice can reduce stress and anxiety, which helps lower stress chest pain.”
By using these quick relief strategies every day, you can manage stress chest pain better and feel better overall.
Long-Term Management to Prevent Stress and Chest Tightness
Managing stress and chest tightness over time requires lifestyle changes and stress management. These steps help reduce stress-induced chest pain. They also improve overall well-being.
Lifestyle Modifications That Reduce Stress Responses
Changing your lifestyle can lessen stress and chest tightness. Here are some key changes:
- Regular Exercise: Exercise lowers stress and boosts heart health.
- Dietary Changes: Eating well, with lots of fruits and whole grains, helps manage stress.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough sleep is key to stress control and less chest tightness.
- Relaxation Techniques: Daily activities like deep breathing or meditation can reduce stress.
| Lifestyle Modification | Benefits |
| Regular Exercise | Reduces stress, improves cardiovascular health |
| Dietary Changes | Manages stress, supports overall health |
| Adequate Sleep | Essential for stress management, overall well-being |
Mind-Body Practices for Stress Resilience
Mind-body practices are vital for stress resilience. They include:
- Meditation: Regular meditation lowers stress and anxiety.
- Yoga: Yoga combines physical postures, breathing, and meditation to build resilience.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps change negative thought patterns, managing stress and anxiety.
These practices not only manage stress but also improve overall health.
Addressing Underlying Anxiety Disorders
For those with stress-induced chest pain, tackling anxiety disorders is key. This may involve:
- Professional Help: Mental health professionals offer tools and strategies for anxiety management.
- Therapy: Therapies like CBT are effective in managing anxiety disorders.
- Medication: Sometimes, medication is needed to control severe anxiety.
By tackling anxiety, individuals can better manage stress and reduce chest tightness.
When to Seek Medical Help for Chest Discomfort
If you’re feeling chest discomfort, it’s key to know when to get medical help. Stress can cause chest pain, but serious conditions need attention too. It’s important to tell the difference.
Red Flags That Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Some symptoms with chest pain mean you need to see a doctor right away. These include:
- Severe pain or pressure in the chest that doesn’t go away
- Pain that radiates to the arm, neck, or jaw
- Shortness of breath or trouble breathing
- Dizziness or fainting
- A rapid or irregular heartbeat
If you have any of these symptoms, go to a doctor or the emergency room fast.
What Tests Might Be Performed
When you see a doctor, they might run tests to find out why you’re feeling chest pain. These tests include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to check the heart
- Blood tests to look for heart damage or other issues
- Chest X-ray to see the heart and lungs
- Stress test to see how the heart works under stress
- Echocardiogram to see the heart’s structure and function
These tests help doctors find out what’s causing your chest pain and what treatment you need.
Communicating Effectively With Healthcare Providers
Talking clearly with your doctor is very important. Be ready to share:
- The kind and how bad your chest pain is
- What makes your symptoms better or worse
- Your medical history and family health
- Any medicines or supplements you’re taking
Good communication helps doctors make the right diagnosis and treatment plan for you.
Conclusion: Living Confidently Despite Stress-Related Chest Symptoms
Stress-related chest pain is common and can really affect our daily lives. It’s important to understand how stress can cause physical symptoms. By knowing the signs and using stress management techniques, we can feel more confident.
We talked about ways to feel better right away, like breathing exercises and muscle relaxation. We also looked at long-term strategies, like changing our lifestyle and practicing mind-body techniques. Using these methods can help reduce stress and chest tightness.
Managing stress-related chest symptoms needs a full approach that covers both body and mind. By controlling stress, we can feel more confident in handling symptoms. We urge readers to actively manage their stress, seek help when needed, and build resilience. This way, we can face life’s challenges with confidence.
FAQ
Can stress cause chest pain?
Yes, stress can lead to chest pain. Stress triggers our body’s “fight or flight” response. This releases hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones can make our heart rate and blood pressure go up, causing chest discomfort or pain.
How can I tell if my chest pain is related to stress or a heart condition?
It’s hard to tell if chest pain is from stress or a heart issue. Stress-related chest pain often comes with anxiety, panic, or a fast heart rate. If you’re not sure, it’s best to see a doctor for a check-up.
What are some common sensations associated with stress-related chest pain?
Stress can cause tightness, pressure, or discomfort in the chest. Some people feel sharp pains or a dull ache. This pain can spread to the arms, back, or shoulders.
Can anxiety cause persistent chest pain for days?
Yes, anxiety can lead to chest pain that lasts for days. The worry about symptoms can make the pain worse. Muscle tension and long-term stress can also cause ongoing pain.
What are some immediate relief strategies for stress chest pain?
Techniques like breathing, muscle relaxation, and thinking positively can help. Relaxation methods, such as deep breathing or meditation, can calm your nervous system. This can reduce stress symptoms.
How can I prevent stress and chest tightness in the long term?
Making lifestyle changes can help. Regular exercise, healthy eating, and managing stress are key. Practices like yoga, tai chi, or mindfulness meditation can also help you handle stress better. Getting help for anxiety can also be beneficial.
When should I seek medical help for chest discomfort?
Seek help right away for severe chest pain, trouble breathing, or other serious symptoms. If you have heart problems or are unsure about your pain, see a doctor for advice and care.
Can chest tightness be caused by stress?
Yes, stress can cause chest tightness. Things like hyperventilation, esophageal spasms, acid reflux, and stress responses can lead to discomfort or tightness in the chest.
How can I communicate effectively with my healthcare provider about my chest pain?
Share all the details about your symptoms with your doctor. Tell them when and how long the pain lasts, and what might make it better or worse. Giving them all the information helps them figure out what’s going on and how to help you.
References:
- Krantz, D. S., & McCeney, M. K. (2001). Effects of psychological and social factors on the risk of cardiovascular disease. The American Journal of Cardiology, 88(16A), 1207–1211.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11734684/




































