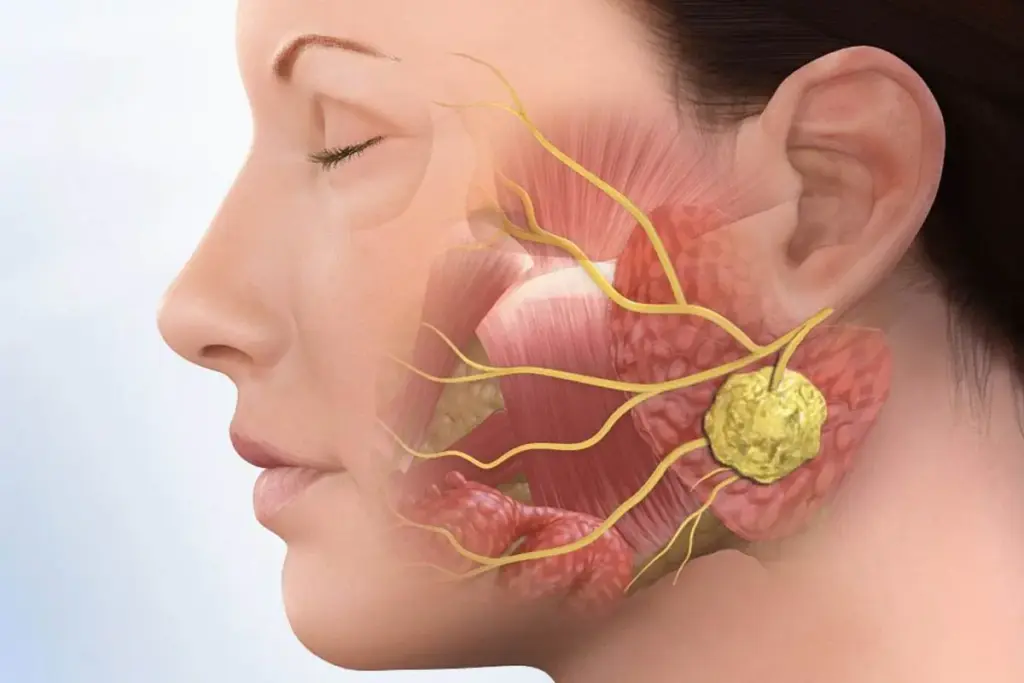
Submandibular gland cancer is a rare disease, found in about 0.17 per 100,000 people yearly in developed countries. It’s a type of salivary gland cancer that affects the submandibular gland. This gland makes saliva.
Knowing the symptoms, how to diagnose it, and treatment options is key. At Liv Hospital, we focus on the patient and use the latest in salivary gland carcinoma care.
Key Takeaways
- Submandibular gland cancer is a rare type of salivary gland cancer.
- Early recognition of symptoms is key for good treatment.
- Diagnosis uses imaging tests and biopsy.
- Treatment includes surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
- A team of experts is vital for the best care plan.
Understanding Submandibular Gland Cancer: Epidemiology and Types
It’s important to know about the types and how common submandibular gland cancer is. This cancer is rare and makes up a small part of all salivary gland cancers.
Compared to other salivary gland cancers, submandibular gland cancer is less common. Most salivary gland cancers start in the parotid gland. But, submandibular gland cancer is special because of its unique challenges in diagnosis and treatment.
Rarity and Prevalence
The submandibular gland is a major salivary gland, and cancer here is rare. Studies show that salivary gland cancers, including submandibular gland cancer, make up less than 1% of all cancers.
The National Cancer Institute’s data shows that salivary gland cancers, including submandibular gland cancer, are not very common. We will look at how rare this is and what it means for salivary gland cancer overall.
| Type of Salivary Gland Cancer | Prevalence |
| Parotid Gland Cancer | Most common |
| Submandibular Gland Cancer | Less common |
| Sublingual Gland Cancer | Rare |
Common Histologic Subtypes
The main types of submandibular gland cancer are adenoid cystic carcinoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. Adenoid cystic carcinoma is the most common, making up 36-50% of cases. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is next, at 16-22%, and squamous cell carcinoma makes up about 18%.
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is the most common salivary gland cancer in both kids and adults. Knowing these types is key to figuring out the prognosis and treatment plan.
Diagnosing and treating submandibular gland cancer depends on knowing the exact type. Each type has its own traits and affects treatment differently.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Submandibular Gland Cancer
Spotting early signs of salivary gland cancer can greatly help treatment. Submandibular gland cancer, a salivary gland cancer type, is tricky to diagnose. This is because of its location and the many symptoms it can cause.
Recognizing Warning Signs
People with submandibular gland cancer may notice several symptoms. A common sign is a persistent lump or swelling in the neck or jaw. Facial numbness, weakness, or palsy can also indicate nerve problems, a serious issue.
Other signs include trouble swallowing or pain in the mouth, face, or neck. These symptoms can be like those of other conditions. So, it’s very important to see a doctor for a correct diagnosis.
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing submandibular gland cancer involves several steps. Imaging tests like MRI and CT scans are used to see how big the tumor is and its effect on nearby tissues.
A fine-needle aspiration biopsy is often done to check for cancer cells. This method uses a thin needle to take a sample from the tumor.
| Diagnostic Method | Description | Use in Submandibular Gland Cancer |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging provides detailed images of soft tissues. | Assesses tumor extent and involvement of surrounding structures. |
| CT Scan | Computed Tomography Scan offers detailed cross-sectional images. | Evaluates tumor size, location, and possible spread to lymph nodes. |
| Fine-needle Aspiration Biopsy | A procedure to collect cell samples from the tumor. | Confirms the presence of cancerous tumor of glandular tissue. |
Treatment Options and Survival Outlook
Submandibular gland cancer treatment includes surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. The choice depends on the cancer stage, cell type, and patient health. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma, a common salivary gland cancer, needs a detailed treatment plan.
The parotid gland is the biggest salivary gland, but submandibular gland cancer is serious. It needs quick action. Gland cancer treatment has improved, helping patients more.
The 5-year survival rate for submandibular gland cancer is 59.7% to 64%. Disease-specific survival is about 74%. A gland cancer diagnosis is tough. Our team offers full care and support during treatment.
FAQ:
What is submandibular gland cancer?
Submandibular gland cancer is a rare malignancy that forms in the salivary glands located just under the jawline. These tumours can be slow-growing or aggressive and usually appear as a firm, painless lump in the upper neck.
What are the common symptoms of submandibular gland cancer?
The most frequent symptom is a persistent, painless swelling under the chin or jaw. Other signs include facial numbness, difficulty swallowing, or weakness in facial muscles if the tumor presses against nearby nerves.
How is submandibular gland cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis begins with a physical exam and imaging like an MRI or CT scan to see the tumor’s size. A fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy is then performed to collect tissue and determine if cells are cancerous.
What are the treatment options for submandibular gland cancer?
Primary treatment involves surgical removal of the gland, often with a neck dissection to check for spreading. Depending on the stage, radiation or chemotherapy may follow to target remaining malignant cells.
What is mucoepidermoid carcinoma, and how is it related to submandibular gland cancer?
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is the most common type of malignant salivary gland tumor. It can originate in the submandibular gland and is classified by grades that determine how aggressively it might grow.
What is the survival outlook for submandibular gland cancer?
The outlook depends on the tumor’s stage and grade at diagnosis. Generally, low-grade tumors caught early have a high survival rate, while high-grade tumors require more intensive treatment and long-term monitoring.
Which of the major salivary glands is the largest?
The parotid gland, located in front of the ears, is the largest. While the submandibular gland is smaller, it produces the majority of your mouth’s resting saliva flow.
Can submandibular gland cancer be treated with surgery alone?
Surgery alone may work for small, low-grade tumors that haven’t spread. However, doctors often add radiation if the tumor is high-grade, has invaded local nerves, or shows signs of spreading to lymph nodes.
References:
JAMA Network. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaotolaryngology/fullarticle/2442631