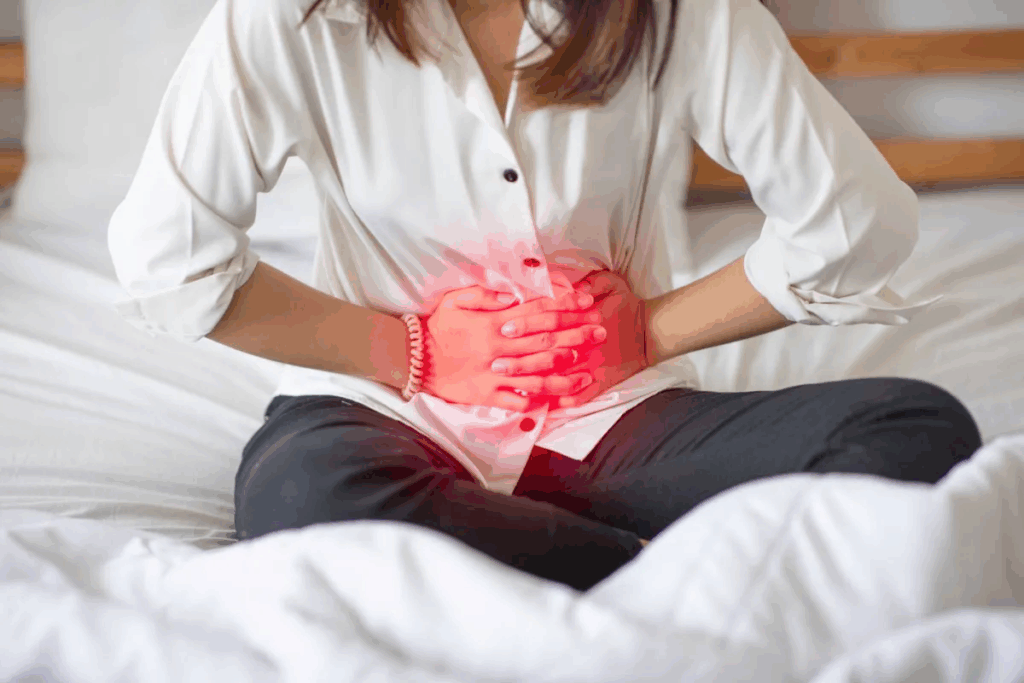
An untreated bladder infection can quietly turn into serious health issues. Many people ignore the early signs until it’s too late. We will look at the early signs and how symptoms get worse to stress the need for medical help. What are the symptoms of untreated bladder infection? Learn the signs that the infection has progressed to the kidneys (pyelonephritis).
Not treating a bladder infection can lead to serious problems like kidney infections. These can cause a lot of pain and even be life-threatening. Doctors treat 8 million to 10 million people each year for urinary tract infections. About half of all women will get at least one UTI in their lives.
Key Takeaways
- Untreated bladder infections can lead to serious medical complications.
- Early recognition of symptoms is key to avoiding problems.
- Symptoms include high fever, chills, back pain, and feeling unwell.
- Getting medical help quickly is vital for proper treatment.
- UTIs are a common health issue, affecting millions of people every year.
Understanding Bladder Infections: Causes and Risk Factors

It’s important to know why bladder infections happen to avoid them. These infections, or urinary tract infections (UTIs), start when bacteria get into the urinary tract and grow. We’ll look at what causes these infections and who is more likely to get them.
Common Causes of Bladder Infections
Most bladder infections come from bacteria getting into the urinary tract through the urethra. The main bacteria causing UTIs is Escherichia coli (E. coli), found in the gut. Other bacteria like Klebsiella and Staphylococcus saprophyticus can also cause infections. Bacteria can get in through poor hygiene, sex, and certain birth control.
Who Is Most at Risk for Developing UTIs
Some people are more likely to get UTIs because of certain factors. Women are more at risk than men because their urethra is shorter. Other risk factors include:
- Using certain types of birth control, such as diaphragms
- Being postmenopausal, as estrogen levels drop
- Having urinary tract problems or blockages
- Engaging in sexual activity, which can introduce bacteria
- Having a weakened immune system, making it hard to fight off infections
Knowing the causes and risk factors helps prevent UTIs. It’s a good idea to talk to a healthcare provider about any concerns. They can help figure out the best way to stay healthy.
Early Warning Signs of a Bladder Infection
Knowing the early signs of a bladder infection is key to better treatment. Bladder infections, or urinary tract infections (UTIs), happen when bacteria get into the urinary tract. Spotting symptoms early can stop the infection from getting worse and lower the chance of serious problems.
Urinary Symptoms to Watch For
Changes in how we urinate can signal a bladder infection. Look out for:
- A burning feeling when we pee, called dysuria
- A strong need to pee often, even when there’s not much urine
- Small amounts of urine
- Urine that looks cloudy, dark, or smells strongly
- Blood in the urine, making it red, bright pink, or cola-colored
These urinary symptoms can be uncomfortable and disrupt our daily life. If you notice any, watch them closely and see a doctor if they don’t get better or get worse.
Discomfort and Pain Indicators
Discomfort and pain are also signs of a bladder infection. We might feel:
- Pelvic pain or pressure, mainly in women
- Lower belly discomfort or cramping
- Pain or discomfort during sex
Bladder infection pain can be different for everyone. It might be constant or come and go. Pain or discomfort, along with urinary symptoms, often means a UTI.
By recognizing these early signs, we can act fast to get medical help. This might stop the infection from getting worse. If you’re showing any symptoms, it’s best to talk to a healthcare professional for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of an Untreated Bladder Infection
Not treating a bladder infection can make symptoms worse. We’ll explain how symptoms get more serious and how long it takes.
How Symptoms Progress When Left Untreated
At first, a bladder infection might just make you pee a lot and feel some pain while doing it. But if you don’t treat it, things can get much worse. The infection could move up to your kidneys, causing fever, chills, and pain in your side.
As the infection gets worse, you might feel more pain in your lower belly and pelvis. Your pee might look cloudy, be bloody, or smell really bad. In some cases, not treating a UTI can lead to sepsis, a serious condition that needs quick medical help.
Timeline of Symptom Development
How fast symptoms get worse can depend on the infection’s severity and your health. Usually, symptoms can get worse in a few days to a week if not treated.
Timeline | Potential Symptoms |
0-3 days | Mild symptoms such as frequent urination and slight discomfort |
3-7 days | Increased severity of symptoms, including pain and possible fever |
Beyond 7 days | Risk of complications such as kidney infection or sepsis |
It’s very important to see a doctor if your symptoms don’t get better or get worse. Getting treatment early can stop serious problems and prevent long-term damage.
Fever and Chills: Signs the Infection Is Spreading
Fever and chills are signs that a UTI might be getting worse. They can mean the infection has moved up to the kidneys. It’s important to know these symptoms to get help quickly.
Understanding the Significance of Fever with UTIs
A fever with a UTI means your body is fighting hard. It usually means the infection has reached the kidneys. It’s key to watch your temperature and get help if it’s high or doesn’t go away.
Fever and UTIs are closely linked. Lower UTIs might not cause fever, but upper UTIs can make your body temperature rise a lot. Knowing this helps figure out how serious the infection is.
Symptom | Lower UTI | Upper UTI |
Fever | Rarely present | Often present |
Chills | Uncommon | Common |
Pain Location | Bladder and urethra | Flank and back |
When Chills Indicate a Serious Problem
Chills with a UTI are a big worry. They often mean the infection has reached the kidneys. Quick treatment is needed to avoid bigger problems.
Chills with fever, flank pain, or nausea mean it’s a serious case. Doctors can find out how bad the infection is with tests and exams.
In short, fever and chills are big warning signs. They mean a UTI has moved up to the kidneys. Spotting these signs early and getting medical help fast can stop serious issues and help patients get better.
Pain Patterns in Advanced Bladder Infections
Advanced bladder infections show different pain patterns. These patterns help figure out how serious the infection is. The type and where the pain is can tell us a lot about the infection’s spread and possible problems.
Lower Abdominal and Pelvic Pain
Lower abdominal and pelvic pain are common signs of bladder infections. This pain feels like a dull ache or discomfort in the lower belly or pelvic area. It can be mild or severe and may come and go.
In some cases, you might feel a pressure or heaviness in the pelvic area too.
Some key signs of lower abdominal and pelvic pain in advanced bladder infections include:
- Persistent or recurring pain
- Pain that gets worse during urination
- Discomfort that spreads to the lower back or groin
Back and Flank Pain: Warning Signs of Kidney Involvement
Back and flank pain can mean the infection has moved to the kidneys. This pain feels sharp and stabbing in the flank area or lower back.
If you have back and flank pain, fever, and chills, you need to see a doctor right away. This could be a sign of pyelonephritis, a serious condition.
Some signs that back and flank pain might mean kidney involvement include:
- Severe pain that gets worse over time
- Pain with fever, chills, or nausea
- Hard time urinating or blood in the urine
Knowing these pain patterns is key to understanding how serious a bladder infection is. If you have these symptoms, you should get medical help fast.
Systemic Symptoms: Body Aches, Fatigue, and Malaise
As a UTI gets worse, it can cause body aches and fatigue. This happens because the infection can make the whole body inflamed.
Why UTIs Can Cause Whole-Body Symptoms
UTIs can make you feel sick all over because of how your body reacts. When bacteria get into your urinary tract, it sets off an immune response. This can lead to inflammation and the release of chemicals that make you feel tired, achy, and generally unwell.
In severe cases, the infection can reach your kidneys. This can make the symptoms even worse. The body’s fight against the infection can make it hard to do everyday things and affect your quality of life.
Symptom | Description | Severity |
Fatigue | Persistent feeling of tiredness | Mild to Severe |
Body Aches | Pain or discomfort in muscles and joints | Moderate to Severe |
Malaise | General feeling of being unwell | Mild to Severe |
Distinguishing UTI Fatigue from Other Conditions
Telling if your fatigue is from a UTI or something else can be hard. UTI fatigue often comes with other symptoms like dysuria, frequency, and urgency. If you’re tired and have these urinary symptoms, it’s probably a UTI.
But fatigue from other issues like anemia or thyroid problems might not have these symptoms. Knowing the symptoms together helps figure out why you’re tired.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Nausea, Vomiting, and Appetite Changes
UTIs can sometimes cause stomach problems like nausea, vomiting, and changes in appetite. These symptoms are not as common with UTIs as urinary ones. But they can happen, mainly in more serious infections.
The Link Between UTIs and Digestive Issues
The relationship between UTIs and stomach issues is complex. When a UTI happens, the body might react with nausea and vomiting. This is more likely if the infection reaches the kidneys, leading to pyelonephritis.
Key factors that contribute to GI symptoms in UTIs:
- The body’s systemic response to the infection
- The spread of the infection to the kidneys
- The release of toxins and inflammatory mediators
When to Be Concerned About GI Symptoms
If you have nausea, vomiting, or big appetite changes with UTI symptoms, get medical help. These stomach symptoms can mean a serious infection that needs quick treatment.
Watch for these warning signs:
- Persistent or severe vomiting
- Significant loss of appetite or dehydration
- Fever accompanied by chills or flank pain
Knowing how UTIs and stomach symptoms are linked helps people spot when their condition is getting worse. This way, they can get the right medical care.
Kidney Infection: A Serious Complication of Untreated UTIs
Untreated UTIs can lead to a serious kidney infection called pyelonephritis. This happens when bacteria from the bladder move up to the kidneys. We’ll look at how this occurs and the signs of a kidney infection.
Bacterial Ascension to the Kidneys
Pyelonephritis happens when bacteria from a bladder infection reach the kidneys. This can be due to delayed treatment, antibiotic resistance, or urinary tract issues.
The bacteria travel from the bladder to the kidneys through the ureters. This can cause inflammation and infection in the kidney. If not treated quickly, it can lead to permanent damage.
Recognizing Pyelonephritis Symptoms
Symptoms of pyelonephritis include high fever, flank pain, and nausea. Some people may also feel vomiting, chills, and unwell.
It’s important to notice these symptoms early. Quick treatment can prevent serious problems. The symptoms can be worse than a typical UTI and can get worse fast.
Common Symptoms of Pyelonephritis:
- High fever
- Flank pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Chills
- General malaise
Knowing these symptoms helps people get medical help fast. This can lower the risk of serious issues.
Symptom | Description | Severity |
High Fever | Elevated body temperature, often above 101°F | Severe |
Flank Pain | Pain on one side of the back, below the ribs | Moderate to Severe |
Nausea and Vomiting | Feeling queasy or vomiting | Moderate |
Blood in Urine: Causes and Significance
Blood in urine, or hematuria, is a worrying sign for those with urinary tract infections (UTIs). It can show up in various ways. Knowing its causes and what it means is key for the right treatment.
Visible vs. Microscopic Hematuria
Hematuria comes in two forms: visible and microscopic. Visible hematuria means you can see the blood in your urine, making it look pink, red, or cola-like. Microscopic hematuria is when you can only spot the blood with a microscope.
Both types can be linked to UTIs. Visible blood is usually more alarming. But, the amount of blood doesn’t always show how serious the infection is.
When Blood in Urine Requires Immediate Attention
While hematuria can signal a UTI, some cases need quick medical help. Look for urgent care if you see:
- Heavy bleeding that doesn’t stop
- Severe pain in the abdomen or back
- Fever or chills
- Difficulty urinating
- Blood clots in the urine
In some cases, hematuria might point to kidney damage or a UTI complication. So, it’s important to talk to a doctor to figure out the cause and get the right treatment.
Understanding hematuria’s role in UTIs helps patients get medical help on time. This can prevent serious issues and improve health outcomes.
Diagnostic Procedures for Suspected UTI Complications
When a urinary tract infection (UTI) might have caused complications, doctors use several tests to check how bad it is. These tests help figure out how serious the infection is and spot any complications early.
Laboratory Tests and Urinalysis
Laboratory tests are key in finding UTI complications. Urinalysis is the first test, looking for signs of infection in urine. It checks for bacteria, blood, or pus.
A urine culture is also important. It finds the bacteria causing the UTI. This helps doctors pick the right antibiotic. Sometimes, blood tests are done to see if the infection has spread to the blood.
Imaging Studies for Advanced Infections
For UTI complications, imaging studies are needed to see the urinary tract. Ultrasound is often used to find problems like kidney stones or blockages.
In serious cases, a CT scan might be needed. CT scans give detailed pictures of the urinary tract. They help find issues like kidney infections or abscesses that need to be drained.
Doctors stress that catching UTI complications early is very important. It helps avoid lasting damage to the urinary tract and kidneys. Knowing about these tests helps both doctors and patients manage UTI complications well.
When to Seek Medical Attention for UTI Symptoms
It’s key to know when to see a doctor for UTI symptoms. UTIs can get worse fast if not treated. This can lead to serious health problems.
We’ll show you the important signs that mean you need to see a doctor right away. This way, you’ll know when to act.
Emergency Warning Signs
Some symptoms mean you need to go to the hospital fast. These include:
- High Fever: A fever over 101.5°F (38.6°C) might mean the infection has reached your kidneys or blood.
- Severe Pain: Pain in your lower belly, back, or side could mean a serious UTI.
- Vomiting: Vomiting a lot can cause dehydration, making treatment harder.
- Blood in Urine: Seeing blood in your pee, even if it’s just a little, is a bad sign.
Symptoms That Shouldn’t Wait for Treatment
Even mild UTI symptoms can get worse quickly. You should see a doctor right away if you have:
Symptom | Description | Potential Complication |
Frequent Urination | Needing to pee more than usual | Kidney damage if infection spreads |
Burning Sensation | Pain or burning while peeing | Increased risk of sepsis |
Cloudy or Strong-smelling Urine | Urine that’s cloudy, dark, or smells bad | Sign of bacterial infection |
Knowing these symptoms and their risks helps you take care of your health. If you have any of these, see a doctor for the right treatment.
Getting medical help for UTI symptoms fast is very important. It helps avoid long-term damage and ensures you get the right treatment.
Conclusion: Preventing Complications Through Early Treatment
Early treatment of UTIs can stop serious problems like kidney damage and sepsis. It’s key to know the signs of untreated bladder infections to get help fast.
Quick action in treating UTIs lowers the chance of worse conditions. It’s vital to prevent UTIs and treat them early to manage them well.
To avoid UTI complications, be aware of symptoms and risk factors. If you think you have a UTI, see a doctor right away.
Acting quickly can greatly help those with UTIs. By focusing on preventing UTIs and treating them early, we can keep health better.
FAQ
Can a urinary tract infection cause chills and fever?
Yes, a urinary tract infection (UTI) can cause chills and fever. This is more likely if the infection reaches the kidneys. These symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away.
What are the symptoms of an untreated bladder infection?
Untreated bladder infections can cause pain when you pee, needing to pee a lot, and feeling uncomfortable in your pelvis. If it spreads to the kidneys, you might also feel fever, chills, and pain in your side.
Can a UTI cause body aches and fatigue?
Yes, UTIs can make you feel tired and have body aches. This is because your body is fighting the infection. It’s important to know these symptoms can also mean other things, so getting checked is key.
Is nausea and vomiting a symptom of a UTI?
Yes, UTIs can make you feel sick to your stomach and even throw up. If this happens, it’s a sign you need to see a doctor fast.
What is the significance of fever in UTIs?
Fever with a UTI means the infection might have moved up to your kidneys. This is a serious sign that needs quick medical help.
Can a bladder infection cause blood in the urine?
Yes, a bladder infection can make your pee turn red or brown. Knowing if this is just a sign of infection or something more serious is important.
How are UTI complications diagnosed?
Doctors use tests like urinalysis and urine cultures to find UTI complications. They might also use imaging to check your urinary tract.
When should I seek medical attention for UTI symptoms?
You should see a doctor right away if you have fever, severe pain, or signs of dehydration. If you often get UTIs, you should also get checked.
Can UTIs be treated without complications?
Yes, UTIs can be treated with antibiotics. Getting treatment quickly can stop complications. Knowing the symptoms and getting help fast is important.
What are the risk factors for developing UTIs?
Women, certain birth control, and menopause increase UTI risk. These factors make it easier for bacteria to get into your urinary tract.
References
- Madersbacher, S., Alivizatos, G., Nordling, J., Bouffioux, C., de la Rosette, J., & Wood, S. (2004). EAU 2004 Guidelines on assessment, therapy and follow-up of men with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic obstruction (BPH guidelines). European Urology, 46(5), 547–554. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15533355/