Tendonitis is a common problem that affects millions of people. It causes pain and discomfort that can really get in the way of daily life. A recent study found that nearly 30% of adults experience tendonitis at some point in their lives. This makes it a condition that needs good treatment and management. Tendonitis treatment: Is ice or heat the Best choice? The Ultimate answer for Quick relief is Revealed here.
Tendonitis happens when the tendons, which connect muscles to bones, get inflamed. It can be caused by too much strain, overuse, or sudden injury. There are many tendonitis treatment options out there. But, the question of whether to use heat or ice for relief is a big debate among doctors.
This guide will look into what causes tendonitis. We’ll also explore the benefits of heat and ice therapy. Plus, we’ll share tips on how to find relief from tendonitis pain and help with tendonitis recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the causes of tendonitis is key to treating it well.
- Heat and ice therapy are two common ways to ease tendonitis pain.
- Choosing between heat and ice depends on the tendonitis’s stage and severity.
- Using therapy with other treatments can help in recovering from tendonitis.
- It’s important to talk to a healthcare professional for a treatment plan that’s right for you.
Understanding Tendonitis: Causes and Symptoms
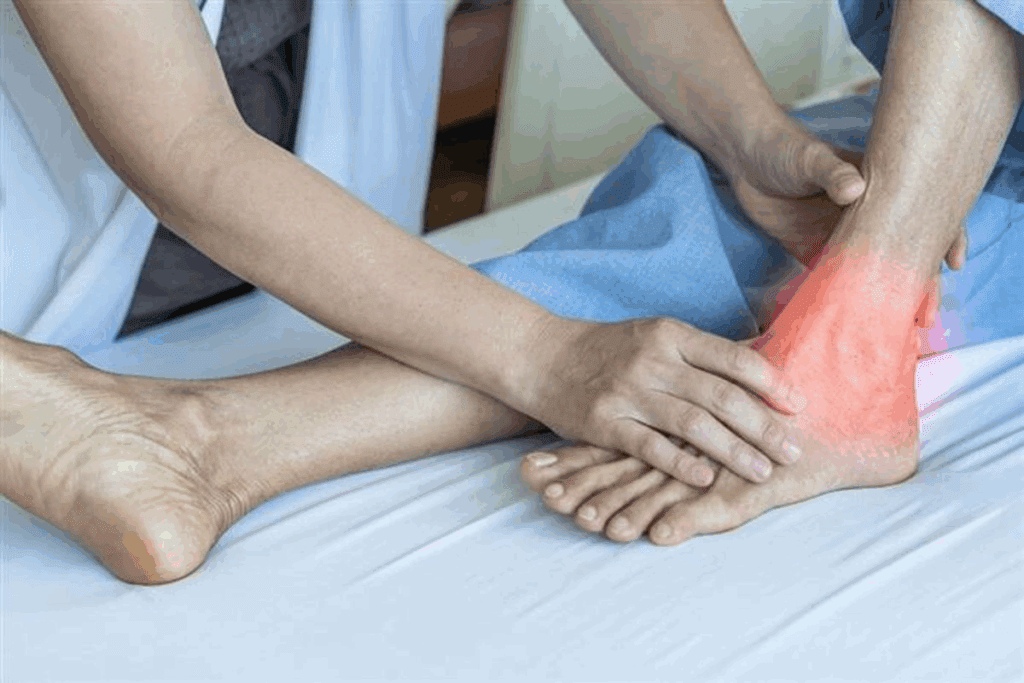
Knowing about tendonitis is key to managing and treating it. This common condition affects tendons all over the body. It’s caused by inflammation and shows different symptoms.
What Exactly Is Tendonitis?
Tendonitis is when a tendon gets inflamed or irritated. Tendons are like cords that link muscles to bones. It leads to pain, stiffness, and less mobility in the affected area. It often happens in the shoulders, elbows, wrists, knees, and heels.
Common Causes of Tendon Inflammation
There are many reasons for tendonitis, including:
- Repetitive motions or overuse
- Sudden injury or trauma
- Poor posture or biomechanics
- Age-related wear and tear
- Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or diabetes
The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons says repetitive motion is a big cause. It can cause micro-tears in the tendon, leading to inflammation.
Recognizing Tendonitis Symptoms
The signs of tendonitis vary based on where and how bad it is. Common signs include:
- Pain or tenderness near a joint
- Stiffness, mostly in the morning
- Swelling or redness
- A grating sensation when moving the tendon
- Weakness or loss of function in the affected limb
A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy says pain during movement is a key symptom of tendonitis.
“Tendonitis is a common condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding its causes and symptoms is key for effective management.”
Nigel Armstrong, Physical Therapist
Most Frequently Affected Areas
Tendonitis can hit different parts of the body, but some areas get it more often. The most common tendons affected include:
| Area | Common Activities Leading to Tendonitis |
| Shoulder | Throwing, lifting, overhead activities |
| Elbow | Tennis, golf, repetitive gripping |
| Wrist | Typing, assembly line work, gymnastics |
| Knee | Running, jumping, cycling |
| Heel (Achilles) | Running, dancing, jumping sports |
Knowing which areas are more likely to get tendonitis and what activities can cause it helps in prevention and early treatment.
The Science Behind Inflammation and Tendon Healing

Inflammation and tendon healing are closely linked in tendonitis. Understanding this connection is key to treating tendonitis well. Tendonitis is when tendons get inflamed, and knowing how it heals is important.
The Inflammatory Response in Tendonitis
When a tendon gets hurt, the body’s first step is to get inflamed. This process brings more blood to the area, with white blood cells to fight off infection and start repair. The inflammatory response is a double-edged sword; it helps heal but too much can cause more harm and pain.
“Inflammation is a protective response involving host cells, blood vessels, proteins, and other chemical mediators.” This quote shows how complex inflammation is. Knowing this is key to treating tendonitis well.
Acute vs. Chronic Tendonitis
Tendonitis can be either acute or chronic. Acute tendonitis is short-term inflammation from sudden injury or overuse. On the other hand, chronic tendonitis is long-term inflammation and tendon damage from repetitive strain or not recovering well.
- Acute tendonitis starts with sudden pain and inflammation.
- Chronic tendonitis has ongoing pain and stiffness, worse after rest.
The Natural Healing Process of Tendons
Tendons can only heal so much on their own. The healing process has three stages: inflammation, repair, and remodeling. Knowing these stages helps us see how treatments like heat or ice can help tendons heal.
“The healing process of tendons is a complex and highly regulated process involving various cell types and growth factors.”
Good treatment for tendonitis depends on the condition’s stage and severity. It also depends on the person’s health and how active they are.
Cold Therapy for Tendonitis: How It Works
Cold therapy treats tendonitis by shrinking blood vessels, cutting down inflammation, and numbing the area. This helps ease pain.
Physiological Effects of Ice on Inflamed Tendons
Applying ice to an inflamed tendon makes blood vessels smaller. This cuts down blood flow, reducing swelling and inflammation. The cold also numbs nerves, giving pain relief.
Cold therapy slows down tissue activity. This lowers oxygen and nutrient needs, helping to fight inflammation.
Benefits of Cold Therapy for Tendonitis
Cold therapy has many advantages for tendonitis patients, including:
- Less inflammation and swelling
- Pain relief from nerve numbing
- Lowered metabolic rate for healing
These benefits make cold therapy a good choice for tendonitis, mainly in the early stages.
Potential Drawbacks of Ice Treatment
Despite its benefits, cold therapy has some downsides:
- Long-term use can harm tissues due to low blood flow
- Some people might be cold-sensitive or allergic
- It might not work as well for long-term tendonitis, where inflammation isn’t the main issue
It’s important to think about these points when deciding on cold therapy for tendonitis.
Heat Therapy for Tendonitis: Mechanism of Action
Tendonitis treatment often includes heat therapy. It increases blood flow to the affected area, helping it heal. This method is popular for easing tendonitis symptoms.
How Heat Affects Tendon Tissue
Heat therapy works by improving blood flow to tendon tissue. Higher temperatures widen blood vessels. This increases oxygen and nutrient delivery to damaged tendons.
This process aids in healing and reduces tendon stiffness. Heat also helps lessen muscle spasms and pain. The warmth relaxes muscles around the tendon, easing discomfort.
Benefits of Heat Application for Tendonitis
Heat therapy for tendonitis has many advantages. It reduces pain by easing muscle spasms and making tendons more flexible. It also boosts blood flow, speeding up healing.
Heat therapy is easy to use with heat packs or warm baths. This makes it a handy treatment option.
A renowned orthopedic specialist, notes, “Heat therapy is great for chronic tendonitis. It keeps tendons flexible and reduces pain during daily tasks.”
Limitations and Risks of Heat Therapy
Heat therapy has its downsides and risks. One major concern is the risk of burns from too much heat or long application times. In the early stages of tendonitis, heat might make inflammation worse.
Heat therapy’s effectiveness can differ for everyone. Some see big improvements, while others don’t notice much. It’s important to watch how you react to heat therapy and adjust your treatment as needed.
Ice vs. Heat: Which Is More Effective for Tendonitis Treatment?
When dealing with tendonitis, many wonder if ice or heat is better. Both methods are used to ease symptoms, but which one works best?
Comparative Research Findings
Studies have looked into ice vs. heat for tendonitis. They found ice is better in the early stages. It helps reduce swelling and pain.
A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy showed cold therapy cuts down pain and swelling in acute tendonitis. Heat, on the other hand, is better for long-term use. It makes tendons more flexible and less stiff.
| Therapy Type | Acute Phase Benefits | Chronic Phase Benefits |
| Cold Therapy | Reduces inflammation and pain | Limited long-term benefits |
| Heat Therapy | Limited immediate benefits | Improves flexibility, reduces stiffness |
Effectiveness for Different Types of Tendonitis
The right choice between ice and heat depends on the tendonitis type. For example, acute calcific tendinitis might do better with cold. This is because cold fights inflammation. On the other hand, chronic Achilles tendinopathy could benefit from heat. Heat helps with blood flow and stiffness.
Many experts agree that using both ice and heat at different times can be effective. This approach can help manage tendonitis better.
“The choice between ice and heat for tendonitis treatment should be based on the stage and severity of the condition. Cold therapy is generally recommended for acute injuries, while heat is more suitable for chronic conditions.”
An Orthopedic Specialist
Expert Opinions on the Ice vs. Heat Debate
Experts in sports medicine and orthopedics share their views on ice vs. heat. They suggest starting with cold for acute injuries. Then, switch to heat for chronic conditions.
A survey among physical therapists shows a preference for cold therapy first. This is to reduce swelling. Then, they use heat to aid in healing and relaxation.
In summary, both ice and heat have their roles in treating tendonitis. The best approach often combines both, based on the condition’s stage and type.
When to Use Ice for Tendonitis
Knowing when to use ice is key for managing tendonitis. Ice therapy, or cryotherapy, is a common treatment for tendonitis. It’s most helpful in the early stages or during flare-ups.
Acute Injuries and Initial Inflammation
For acute tendonitis, ice is often the first treatment. When a tendon gets hurt, the body naturally gets inflamed. Ice helps by shrinking blood vessels, lowering metabolic rates, and reducing swelling.
In the first 48 to 72 hours after an injury, ice is very effective. It’s important to ice correctly: 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
Post-Activity Pain Management
Ice is also good for pain after activities that make tendonitis worse. If you feel more pain or stiffness after exercising or doing repetitive motions, ice can help.
Post-activity icing is common among athletes to lessen muscle soreness and tendon inflammation. It’s important to watch how your body reacts and adjust the icing time as needed.
Specific Tendonitis Conditions That Respond Well to Ice
Some tendonitis types do better with ice therapy. For example, Achilles tendonitis and patellar tendonitis often get better with ice, during acute phases or after activities that make it worse.
Remember, ice can work best when used with other treatments like compression and elevation.
When to Use Heat for Tendonitis
Heat therapy is a good choice for tendonitis, even the chronic kind. It helps with relief and function in many tendonitis cases.
Chronic Tendonitis Management
Heat therapy is often suggested for chronic tendonitis. It boosts blood flow and eases stiffness in tendons. This can make moving easier and hurt less.
Heat is very helpful for long-term issues like patellar tendonitis or Achilles tendonitis. These conditions often have ongoing inflammation and pain.
| Condition | Benefits of Heat Therapy |
| Patellar Tendonitis | Increased blood flow, reduced stiffness |
| Achilles Tendonitis | Pain relief, improved mobility |
Pre-Activity Warm-Up
Heat before activities is a great warm-up. It gets the tendons ready for exercise or sports. This makes them more flexible and less likely to get hurt.
Just using a heat wrap or a warm bath can be enough for a warm-up.
Tendonitis Conditions That Benefit from Heat
Many tendonitis conditions do well with heat therapy. These include:
- Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis)
- Golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis)
- Rotator cuff tendonitis
Proper Application Methods for Cold Therapy
Using cold therapy right can really help with tendonitis pain. Cold therapy, or cryotherapy, uses cold to lessen pain and swelling. It’s a common treatment for tendonitis.
Ice Pack Techniques and Duration
Ice packs are a top choice for cold therapy. Here’s how to use them:
- Wrap the ice pack in a towel or cloth to avoid direct contact with the skin.
- Apply the ice pack to the affected area for 15-20 minutes.
- Repeat every 2-3 hours as needed.
Duration Guidelines:
| Condition | Application Time | Frequency |
| Acute Tendonitis | 15-20 minutes | Every 2 hours |
| Chronic Tendonitis | 10-15 minutes | Every 3-4 hours |
Ice Massage for Tendonitis
Ice massage is another good method. It involves rubbing ice on the affected area. Here’s how to do it:
- Freeze water in a paper cup.
- Peel back the top edge of the cup to expose the ice.
- Massage the affected area in a circular motion for 5-10 minutes.
Benefits of Ice Massage: It cuts down pain and swelling by improving blood flow after the cold effect wears off.
Cold Compression Wraps and Devices
Cold compression wraps and devices mix cold therapy with compression. They’re great for:
- Reducing swelling.
- Keeping cold therapy going.
- Adjusting compression levels.
When using cold compression wraps, always follow the maker’s guide. This is for both the cold and compression parts.
Effective Heat Application Techniques
Heat therapy is a common way to ease tendonitis pain. But, it only works well if done right. When used correctly, heat can relax muscles, boost blood flow, and lessen stiffness from tendonitis.
Moist vs. Dry Heat: Which Is Better?
The debate on moist versus dry heat for tendonitis treatment is ongoing. Moist heat, like warm towels or special wraps, is often seen as more effective. It goes deeper into the tissue. Dry heat, from electric pads or lamps, is another option.
Moist heat has several advantages:
- It penetrates deeper into tissues
- It offers better pain relief
- It improves flexibility
For more details on heat therapy for tendonitis.
Heat Wraps and Pads for Tendonitis
Heat wraps and pads are popular for heat therapy. They come in many types, like electric pads, microwaveable wraps, and thermally activated ones. When picking a heat wrap or pad, think about:
- How easy it is to use
- How well it controls temperature
- Its flexibility and comfort
Warm Water Therapies
Warm water therapies are another good way to apply heat. Soaking in a warm bath or using a whirlpool can relax muscles and lessen tendonitis symptoms. Warm water therapy has several benefits:
- It relaxes many muscle groups at once
- It improves blood flow
- It reduces muscle spasms
By learning and using these heat application techniques, people with tendonitis can manage their symptoms better. This can greatly improve their quality of life.
Combining Heat and Ice: Alternating Therapy Approaches
Contrast therapy uses heat and ice together to treat tendonitis. It combines the good points of both to make a strong treatment plan.
The Science Behind Contrast Therapy
Contrast therapy switches between cold and heat to help blood vessels. The blood vessels expand and shrink to fight inflammation and aid healing by boosting blood flow.
“Using contrast therapy can greatly help healing,” say sports medicine experts. “It boosts blood flow and lessens muscle tightness.”
Step-by-Step Guide to Alternating Heat and Ice
To use contrast therapy right, follow these steps:
- Begin with heat for 3-4 minutes to get blood flowing.
- Then, use ice for 1-2 minutes to cut down inflammation.
- Keep switching 3-4 times, ending with ice.
When Contrast Therapy Works Best
Contrast therapy is great for long-term tendonitis. It helps manage pain and boosts function. It’s also good for athletes who need fast recovery after hard workouts.
Knowing and using contrast therapy well can really help those with tendonitis. It can bring a lot of relief and better healing.
Complementary Tendonitis Treatment Options
Heat and ice therapy are just the start for tendonitis recovery. Other treatments help reduce inflammation and promote healing. They also help restore normal function to the affected tendons.
Rest and Activity Modification
Rest is key in treating tendonitis. It means avoiding activities that make the condition worse. Adequate rest helps the tendon repair and rebuild.
- Avoid repetitive motions that exacerbate the condition
- Modify daily activities to reduce strain on affected tendons
- Use ergonomic equipment to minimize stress on tendons
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Stretching and strengthening exercises are essential for recovery. They improve flexibility, reduce stiffness, and strengthen muscles around the tendon.
- Start with gentle stretching to improve flexibility
- Gradually introduce strengthening exercises
- Move to more intense exercises as symptoms improve
Anti-inflammatory Medications
Anti-inflammatory medications help manage pain and reduce inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often used.
- Over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen can be effective
- Prescription NSAIDs may be recommended for more severe cases
- Always follow the recommended dosage to minimize side effects
Physical Therapy Interventions
Physical therapy is a valuable part of tendonitis treatment. A physical therapist can create a personalized exercise program. They also provide manual therapy and teach proper movement techniques.
- Ultrasound therapy to promote healing
- Manual therapy to improve tendon mobility
- Customized exercise programs to strengthen surrounding muscles
When to Seek Medical Help for Tendonitis
Knowing when to see a doctor for tendonitis is important. It depends on how bad the condition is and if it could get worse. Tendonitis can usually be treated at home, but sometimes you need a doctor to avoid serious problems.
Warning Signs That Require Professional Attention
Some signs mean you should see a doctor for tendonitis. These include:
- Persistent or severe pain that interferes with daily activities
- Swelling or redness around the affected tendon
- A sensation of grinding or crunching when moving the affected limb
- A sudden, sharp pain that may indicate a tendon rupture
The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons says seeing a doctor is a good idea if you have these symptoms.
“Tendonitis can be a challenging condition to manage, even if it’s not chronic. Getting help early is important to avoid long-term damage and get better.”
Advanced Treatment Options
If regular treatments don’t work, there are more options:
| Treatment | Description | Benefits |
| Corticosteroid Injections | Injecting corticosteroids into the affected tendon to reduce inflammation | Quick reduction in inflammation and pain |
| Platelet-rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy | Injecting PRP derived from the patient’s own blood to stimulate healing | Promotes tendon healing and regeneration |
| Tendon Debridement | A surgical procedure to remove damaged tendon tissue | Removes degenerative tissue, promoting healthier tendon |
These treatments are for when regular care doesn’t work. They aim to reduce pain, help healing, and improve function.
Recovery Expectations and Timelines
How long it takes to get better from tendonitis depends on a few things. These include how bad it is, the treatment, and your health. Mild cases might get better in a few weeks. But, more serious or long-term cases could take months.
A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy shows the importance of a good rehab plan. It helps tendonitis patients get better faster.
Knowing what to expect during recovery is key. Recognizing when you need a doctor and knowing about treatment options helps you recover better.
Conclusion: Creating an Effective Tendonitis Treatment Plan
Creating a good plan for tendonitis means knowing what causes it and its symptoms. It also means knowing the different ways to treat it. By mixing the right treatments, people can handle tendonitis well and feel better.
For tendonitis relief, using cold for new injuries and heat for long-term ones is key. Switching between cold and heat can also help. Adding rest, stretching, and strengthening exercises can make healing faster.
Finding the best treatment for your tendonitis is critical. This helps reduce swelling, aids in healing, and gets you moving better. Following this guide is a great start to managing tendonitis and finding relief.
FAQ
What is the best treatment for tendonitis?
The best treatment for tendonitis includes rest, physical therapy, and pain management. This can include ice or heat therapy. Sometimes, doctors may suggest anti-inflammatory medications or corticosteroid injections.
Is heat or ice better for tendonitis pain relief?
Both heat and ice can help with tendonitis pain. Ice is best for new injuries and inflammation. Heat is better for long-term pain and stiffness.
How do I apply ice for tendonitis?
To use ice for tendonitis, wrap an ice pack or frozen peas in a towel. Apply it to the affected area for 15-20 minutes, several times a day. You can also try ice massage or cold compression wraps.
Can I use heat and ice together for tendonitis?
Yes, some people find alternating between heat and ice helpful. This method, called contrast therapy, can manage tendonitis pain and inflammation.
What are some natural remedies for tendonitis?
Natural remedies for tendonitis include turmeric, ginger, and omega-3 fatty acids. These have anti-inflammatory properties. Topical creams with arnica or capsaicin can also provide relief.
How long does it take to recover from tendonitis?
Recovery time for tendonitis varies. Mild cases may heal in a few weeks. More severe cases can take months.
Can stretching and strengthening exercises help with tendonitis?
Yes, stretching and strengthening exercises are part of treatment for tendonitis. They improve flexibility, reduce stiffness, and promote healing.
When should I seek medical help for tendonitis?
Seek medical help for tendonitis if you have severe pain, swelling, or limited mobility. Also, if symptoms persist or worsen, or if you have a fever or signs of infection.
Can I prevent tendonitis injuries?
While some injuries are unavoidable, you can reduce your risk. Warm up before exercise, use proper technique, and include strengthening exercises in your routine.
What is contrast therapy, and how does it work?
Contrast therapy alternates between heat and ice to promote healing. It’s thought to improve circulation and reduce muscle spasms. The exact mechanism is not fully understood.
References
- (2013). Contrast Water Therapy and exercise‑induced muscle damage: a systematic review and meta‑analysis. PubMed. PubMed



































