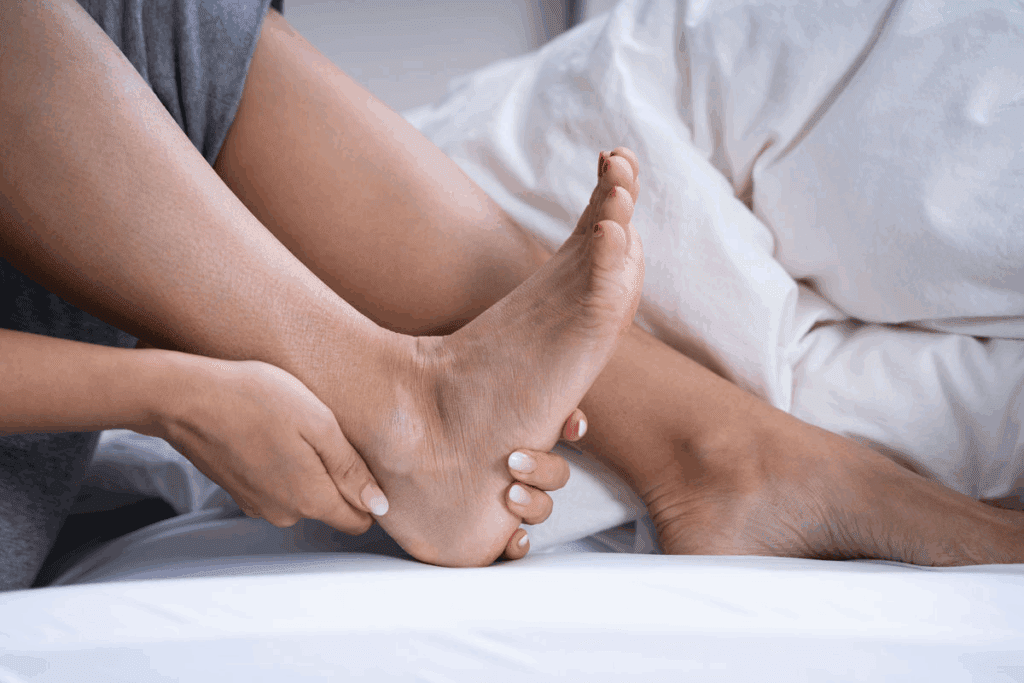
Tendonitis affects millions of people worldwide, causing significant pain and discomfort. Ignoring the pain is not a solution. It’s important to understand the causes, symptoms, and tendonitis treatment options for effective management.
Pushing through the pain can lead to further injury. This can prolong tendonitis recovery and cause chronic issues. Proper pain management for tendonitis is essential to avoid long-term damage.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding tendonitis symptoms is key for early diagnosis.
- Effective pain management is vital for recovery.
- Ignoring tendonitis can lead to chronic conditions.
- Proper treatment can significantly improve recovery time.
- A complete approach includes rehabilitation and lifestyle changes.
Understanding Tendonitis: Causes and Symptoms
Tendonitis can start suddenly or slowly. Knowing its causes and symptoms is key to managing it well. Tendonitis affects the tendons, which connect muscles to bones.
What is Tendonitis?
Tendonitis means the tendons are inflamed, causing pain and discomfort. It’s common in people who do repetitive activities or sports. It can happen in many places like elbows, shoulders, knees, and heels.
“Tendonitis is a common issue among individuals who engage in repetitive activities or sports,” says an orthopedic specialist. “Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing long-term damage.”
Common Causes of Tendon Inflammation
Tendonitis usually comes from too much strain or overuse, causing tiny tears in the tendon. Other reasons include:
- Poor training techniques
- Inadequate warm-up or cool-down exercises
- Overly tight or loose footwear
- Age-related wear and tear
Knowing these causes helps in preventing tendonitis and lowering the chance of chronic conditions.
Recognizing Tendonitis Symptoms
Symptoms of tendonitis include pain, stiffness, and swelling. The pain can be mild or severe and gets worse with activity. Other signs are:
- A sensation of grating or creaking when moving the affected tendon
- Swelling or redness around the tendon
- Pain that persists or worsens over time
Spotting these tendonitis symptoms early is vital for getting the right treatment and avoiding more damage.
The Dangers of Pushing Through Tendon Pain
Tendon pain is a warning sign that something is wrong. Ignoring it can lead to more serious injuries. These injuries might take longer to heal.
Short-term Consequences
Ignoring tendon pain can cause immediate problems. This includes more pain and swelling. You might also see:
- Increased pain during activity and at rest
- Swelling and redness around the affected tendon
- Reduced functionality and strength in the affected limb or area
Acute inflammation is the body’s first response to injury. If not healed, it can turn chronic, causing ongoing issues.
Long-term Damage Risks
Ignoring tendon pain can lead to long-term damage. This might result in chronic tendonitis. This condition causes persistent pain and weakness. The risks include:
| Condition | Description | Potential Outcome |
| Chronic Tendonitis | Persistent inflammation and pain | Long-term disability |
| Tendon Degeneration | Wear and tear on the tendon tissue | Potential tendon rupture |
| Permanent Damage | Irreversible changes to tendon structure | Chronic pain and limited mobility |
When Tendonitis Becomes Chronic
Chronic tendonitis happens when an injury doesn’t heal right. It leads to ongoing pain and swelling. Proper tendonitis pain management is key to avoid this. Factors that can lead to chronic tendonitis include:
- Inadequate rest and recovery
- Insufficient or improper treatment
- Returning to activity too quickly
It’s important to understand the risks of ignoring tendon pain. This knowledge helps with proper tendon injury healing and tendonitis rehabilitation. By listening to your body and taking action, you can avoid chronic tendonitis.
Types of Tendonitis and Their Specific Concerns
It’s key to know the different types of tendonitis to treat them well. Tendonitis can happen in many places like the elbow, shoulder, knee, and Achilles tendon. Each has its own special issues and needs.
Tendonitis in the Elbow (Golfer’s and Tennis Elbow)
Tendonitis in the elbow is known as golfer’s or tennis elbow. It affects the tendons that link the forearm muscles to the elbow. Golfer’s elbow hits the medial epicondyle, while tennis elbow targets the lateral epicondyle. You might feel pain and tenderness on the elbow’s inner or outer side, getting worse with gripping or twisting.
Shoulder Tendonitis (Rotator Cuff)
Shoulder tendonitis, or rotator cuff tendonitis, happens when the tendons around the shoulder joint get inflamed. The rotator cuff, made of muscles and tendons, keeps the shoulder stable and lets it move freely. You might feel pain when moving your shoulder, or your arm might feel weak.
Knee Tendonitis (Jumper’s Knee)
Knee tendonitis, also called jumper’s knee or patellar tendonitis, affects the tendon between the kneecap and the shinbone. It’s common in athletes who jump a lot, putting strain on the patellar tendon. You might notice pain below the kneecap, swelling, and tenderness.
Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis is when the Achilles tendon, linking the calf muscles to the heel bone, gets inflamed. It’s often seen in runners and athletes who do lots of running or quick changes in direction. You might feel pain along the tendon, swelling, and stiffness, mainly after resting.
Every type of tendonitis needs a special treatment plan. This shows how important it is to get the right diagnosis and understand each condition’s specific needs.
The Rest vs. Activity Debate in Tendonitis Recovery
Recovering from tendonitis makes us wonder: how much rest is too much? Doctors and experts are divided on rest versus activity in healing tendonitis. Rest is key for healing, but too much can make tendons stiff and less functional.
Complete Rest: Benefits and Limitations
At first, rest is a must for tendonitis recovery. It means avoiding activities that make it worse. This helps reduce pain and swelling. The good parts of complete rest are:
- Less pain and swelling
- First steps in healing the tendon
But, too much sitting can make tendons less flexible and weak. It’s important to find a balance between rest and doing things to avoid these problems.
Active Recovery Approaches
Active recovery methods, like physical therapy for tendonitis and tendonitis exercises, are key. They help keep tendons flexible and strong while healing. These methods can:
- Improve how well you can move
- Make tendons stronger
- Help blood flow to the area
Finding the Right Balance
Finding the right mix of rest and activity is key for tendonitis rehabilitation. It’s about slowly adding exercises and activities that help heal without making it worse. A good recovery plan helps people get better faster and lowers the chance of chronic tendonitis.
Knowing the ups and downs of rest and activity helps people make better choices for their recovery. It’s smart to talk to doctors to create a recovery plan that fits you.
Comprehensive Tendonitis Treatment Options
Treating tendonitis involves many steps. It includes medical, physical, and alternative methods. Knowing these options is key to managing tendonitis well.
Medical Interventions
Medical treatments are important for tendonitis. They include:
- Anti-inflammatory medications: To lessen pain and swelling.
- Corticosteroid injections: For serious swelling, but used carefully due to side effects.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy: Uses the patient’s blood to help healing.
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy is vital for tendonitis. It focuses on:
- Stretching exercises to boost flexibility.
- Strengthening exercises to make tendons stronger.
- Eccentric training, which helps tendons grow under load.
These exercises are made for the specific tendon and the stage of tendonitis.
Alternative Treatments
Alternative treatments can help too. They include:
- Acupuncture: To help healing and reduce pain.
- Massage therapy: For better blood flow and relaxation.
- Low-level laser therapy (LLLT): To aid in tissue repair.
Using these treatments together helps create a full plan to fight tendonitis.
Pain Management Strategies for Tendonitis
Pain management for tendonitis needs a full plan for quick relief and long healing. It’s key for those with tendonitis to stay mobile and feel less pain.
There are many ways to ease tendonitis pain. These include medicines you can buy without a prescription, stronger medicines your doctor can give you, and non-medical methods. Knowing these options helps you create a plan that works for you.
Over-the-Counter Medications
OTC medicines are often the first choice for tendonitis pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen help by reducing swelling and pain.
A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy showed NSAIDs help with pain and function in tendonitis patients.
| Medication | Dosage | Benefits |
| Ibuprofen | 400-800 mg every 8 hours | Reduces inflammation and pain |
| Naproxen | 250-500 mg every 12 hours | Long-lasting pain relief |
Prescription Options
If OTC medicines don’t work, your doctor might prescribe stronger options. Corticosteroid injections, for example, can greatly reduce pain by lessening swelling.
“Corticosteroid injections are effective for short-term pain relief, but their long-term use can lead to tendon weakening and increased risk of tendon rupture.”
Non-Pharmaceutical Pain Relief
Non-medical methods are also vital for managing tendonitis pain. Ice therapy is a simple yet effective way to reduce swelling and pain. Just apply ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, to help symptoms.
Other non-medical strategies include resting, physical therapy, and alternative therapies like acupuncture. A good pain management plan might use a mix of these methods for the best results.
The Role of Exercise in Tendonitis Rehabilitation
Exercise plays a huge role in tendonitis recovery. It helps in restoring strength, improving flexibility, and aiding in healing. This is key to getting better and keeping tendons healthy.
Beneficial Exercises for Recovery
Some exercises are better than others for tendonitis recovery. These include:
- Eccentric exercises, which help the tendon get stronger and heal.
- Isometric exercises, which keep the tendon strong without too much strain.
- Stretching exercises, which make the tendon more flexible and less stiff.
For Achilles tendonitis, heel drops and calf stretches are very helpful.
Exercises to Avoid
It’s also important to know which exercises to stay away from. These include:
- High-impact activities like running or jumping, which can stress the tendons too much.
- Repetitive motions that make tendonitis worse, like lifting or throwing a lot.
Staying away from these activities early on helps avoid more damage and aids in healing.
Progressive Loading Techniques
Progressive loading is a method to slowly increase the tendon’s load. This builds strength and resilience. You can do this by:
- Making exercises more intense over time.
- Adding weight or resistance gradually.
- Changing exercises to make them harder.
A good progressive loading program can greatly improve tendon health and prevent injuries later on.
| Exercise Type | Benefit | Example |
| Eccentric | Promotes strength and healing | Heel drops for Achilles tendonitis |
| Isometric | Maintains strength without strain | Wall sits for knee tendonitis |
| Stretching | Improves flexibility and reduces stiffness | Calf stretches for Achilles tendonitis |
Home Remedies and Self-Care for Tendonitis
Home remedies are key in easing tendonitis symptoms and helping you heal. Simple self-care steps can make a big difference. They can also lower the chance of getting hurt again.
The RICE Method Explained
The RICE method is a well-known way to handle tendonitis. It stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Rest the area to avoid more harm, use Ice to lessen pain and swelling, apply Compression to shrink swelling, and keep the area Elevated to improve blood flow.
Using the RICE method right can really help with tendonitis. For example, ice wrapped in a cloth for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, can cut down on pain.
Effective Home Treatments
There are other home treatments that can help with tendonitis relief. Gentle stretching keeps your tendons flexible and less stiff. Over-the-counter pain meds like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can also help with pain and swelling.
Other tendonitis remedies include using creams or ointments with anti-inflammatory stuff. These can be put right on the sore spot to ease the pain.
Lifestyle Modifications During Recovery
Changing your lifestyle can also help with tendonitis recovery. Keeping a healthy weight eases the load on your tendons, like in your knees and ankles. Also, avoid doing the same thing over and over and take breaks to stop making it worse.
Adding lifestyle modifications like better ergonomics at work or home can also help. Make sure your workspace supports good posture and doesn’t strain your tendons too much.
When to Seek Professional Medical Help
If you’re dealing with tendonitis symptoms, knowing when to get medical help is key. Tendonitis can really impact your daily life and quality of life.
Some tendonitis cases might get better with rest and self-care. But, other times, you need a doctor’s help. It’s important to know when to seek medical attention.
Warning Signs That Require Medical Attention
Here are signs that mean you should see a doctor:
- Severe pain that makes it hard to do daily tasks or sleep
- Swelling or redness around the tendon
- Instability or feeling like the tendon might break
- Numbness or tingling in the affected limb
- Recent injury or trauma to the tendon area
What to Expect at Your Doctor’s Appointment
When you decide to see a doctor, they’ll start with a detailed check-up and talk about your health history. Be ready to share your symptoms, when they started, and what makes them better or worse.
Here’s what you can expect at the appointment:
- A physical check to see how strong, flexible, and painful the tendon is
- Questions about your health history, including past injuries or conditions
- Possible tests like X-rays or an MRI to confirm the diagnosis and check for other issues
- Talk about treatment options that fit your specific situation and needs
By knowing when to get medical help and what to expect at the doctor’s, you can manage your tendonitis better. This can help you recover more successfully.
Managing Chronic Tendonitis
Living with chronic tendonitis means you need a long-term plan. This plan should cover both physical and mental health. It’s a condition that needs ongoing care to prevent flare-ups and improve overall well-being.
Long-term Treatment Approaches
Managing chronic tendonitis involves medical treatments and self-care. Physical therapy is key to keeping tendons healthy and improving function.
- Regular exercises to strengthen the muscles around the affected tendon
- Manual therapy techniques to improve tendon mobility
- Modalities such as ultrasound or laser therapy to promote healing
Lifestyle Adaptations
Making lifestyle adaptations is vital for managing chronic tendonitis. This means changing daily activities to avoid making the condition worse.
| Activity | Modification |
| Exercise Routine | Avoid high-impact activities; opt for low-impact alternatives like swimming or cycling |
| Workplace Ergonomics | Ensure proper desk setup and take regular breaks to stretch |
| Daily Tasks | Use assistive devices or tools to reduce strain on tendons |
Mental Health Considerations
Chronic tendonitis can affect mental health a lot. It’s important to deal with the emotional side of having a chronic condition.
Stress management, like meditation or deep breathing, can help. Also, talking to healthcare professionals or joining support groups can offer emotional support.
Tendonitis Prevention Strategies
Preventing tendonitis requires several strategies. By understanding and using these methods, you can lower your risk of getting tendonitis.
Proper Warm-up and Cool-down Techniques
Proper warm-up and cool-down are key to preventing tendonitis. A good warm-up gets your tendons ready for activity by increasing blood flow and temperature. This makes them more flexible and less likely to get hurt. You can do light cardio, dynamic stretching, and mobility drills for this.
Effective Warm-up Strategies:
- Light cardio to increase heart rate and blood flow
- Dynamic stretching to improve flexibility
- Mobility drills to enhance range of motion
Cooling down after exercise is just as important. It helps your heart rate and blood pressure return to normal. It also reduces muscle soreness and improves flexibility. You can use static stretching and foam rolling for this.
Equipment and Ergonomic Considerations
Choosing the right equipment and ensuring proper ergonomics are vital. Wear the right shoes, use the correct sports equipment, and set up your workspace for good posture.
| Equipment | Ergonomic Consideration | Benefit |
| Footwear | Proper fit and support | Reduces strain on foot and ankle tendons |
| Sports Equipment | Correct size and type for the activity | Minimizes unnecessary stress on tendons |
| Workstation Setup | Promotes good posture | Decreases risk of tendonitis in the upper body |
For more detailed information on preventing tendonitis, visit URMC Encyclopedia.
Training Modifications to Prevent Recurrence
Changing your training routine is key to avoiding tendonitis. Increase exercise intensity slowly, take rest days, and try different activities to avoid repetitive strain.
Key Training Modifications:
- Gradually increase exercise intensity and volume
- Include rest days to allow tendon recovery
- Cross-train to vary the stress on different tendons
Returning to Activities After Tendonitis
Getting back to activities after tendonitis takes time, patience, and a good plan. It’s a key part of getting better, but it must be done right to avoid injury or longer healing times.
Gradual Return Protocols
Starting slow is key to avoiding injury. Begin with easy exercises and slowly add more intensity and time. For example, if you have Achilles tendonitis, start with short walks and then move to longer ones or jogging.
It’s important to listen to your body during this time. If you feel pain or discomfort, it means you’re doing too much too soon.
Monitoring Symptoms During Return
Watching your symptoms closely is essential. Keep an eye on any pain, stiffness, or swelling. If these signs don’t go away or get worse, slow down or talk to a doctor.
- Pay attention to pain levels
- Monitor for swelling or inflammation
- Assess your overall comfort during activities
Adjusting Expectations and Goals
Changing your expectations and goals is important. Recovery takes time, and you can’t go back to your old self right away.
Setting realistic goals and celebrating small wins can keep you motivated. Being flexible and adjusting your goals as you progress is also key.
By starting slow, watching your symptoms, and adjusting your goals, you can safely get back to your activities after tendonitis. Remember, being patient and persistent is the way to a successful recovery.
Conclusion: Finding the Balance Between Recovery and Activity
Managing tendonitis well means finding the right mix of rest and activity. Studies show that many athletes, even top ones, deal with Achilles tendinopathy. This shows how common tendonitis is in sports.
Rest, rehab, and slowly getting back into activities are key. Research backs up the idea that exercises that load the Achilles tendon are the best treatment. This is shown in a study on the National Center for Biotechnology Information website.
Knowing what causes tendonitis, its signs, and how to treat it helps a lot. People can then make a good plan. This includes changing how they do activities, doing exercises that strengthen the tendon, and slowly getting back into things. This way, they can find a good balance between resting and staying active, which is key to managing tendonitis well.
FAQ
What is tendonitis and how does it occur?
Tendonitis is when the tendons, which connect muscles to bones, get inflamed. It usually happens from too much strain or overuse. This leads to pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Is it okay to push through tendonitis pain?
No, it’s not good to ignore tendonitis pain. Doing so can cause more harm and make recovery longer. Ignoring the pain can turn it into a long-term problem.
What are the common symptoms of tendonitis?
Symptoms of tendonitis include pain, stiffness, and swelling. The pain can be mild or very severe.
How is tendonitis treated?
Treating tendonitis involves several steps. This includes medical treatments, physical therapy, and other methods. Treatment plans might include medicines, injections, exercises, and changes in lifestyle.
What is the role of rest and activity in tendonitis recovery?
Rest and activity are both important for healing. Too much rest can make the tendon stiff. But, too much activity can hurt it more. Physical therapy and exercises help keep it flexible and strong.
Can tendonitis be prevented?
Yes, you can prevent tendonitis by being proactive. Use proper warm-up and cool-down, consider your equipment and work area, and make training adjustments.
How can I manage chronic tendonitis?
Managing chronic tendonitis needs a detailed plan. This includes long-term treatments, lifestyle changes, and taking care of your mental health.
What are some effective home remedies for tendonitis?
The RICE method is often suggested. It stands for rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Other home treatments and lifestyle changes, like staying healthy and avoiding strain, can also help.
When should I seek professional medical help for tendonitis?
See a doctor if you have severe pain or swelling, or if your symptoms get worse. Knowing what to expect at the doctor’s can help you prepare and make good choices for your care.
How can I return to activities after tendonitis?
Going back to activities after tendonitis needs a slow and careful approach. Watch your symptoms closely and adjust your goals to avoid getting hurt again.
What exercises are beneficial for tendonitis recovery?
Exercises that improve flexibility and strength are good for tendonitis recovery. Techniques that gradually increase load can also help keep the tendons healthy.
What are some pain management strategies for tendonitis?
There are many ways to manage pain from tendonitis. This includes over-the-counter and prescription medicines, as well as non-medical methods like ice therapy and rest.
References
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). (2022). Tendon overuse injuries (tendinopathy).




































