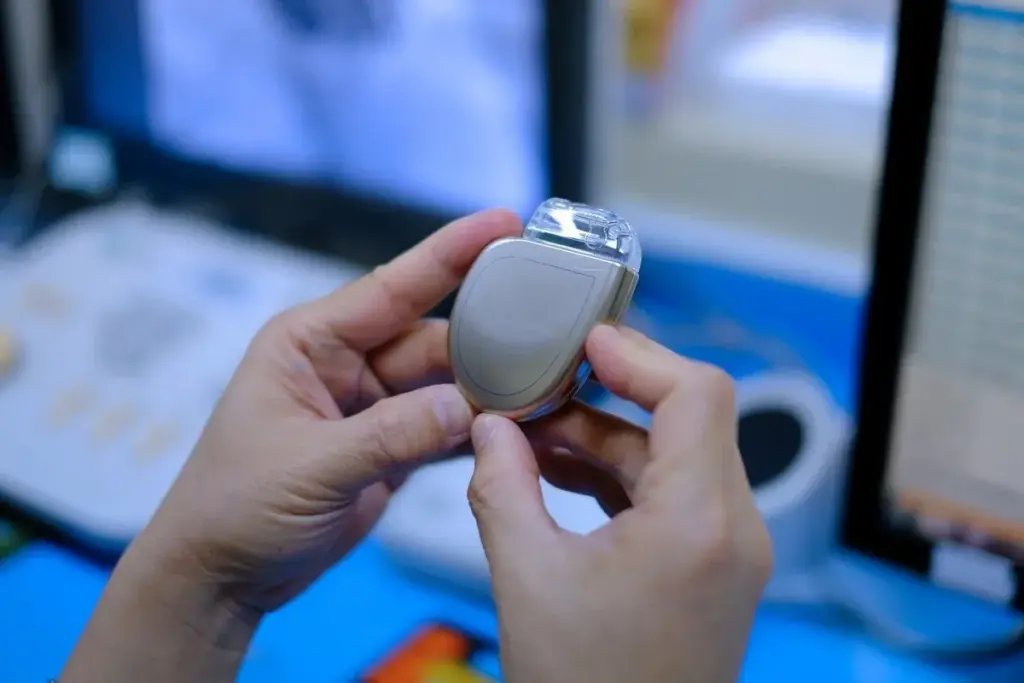
Pacemaker implants are common for treating heart rhythm problems. Thousands get them every year. But, like any medical treatment, they can have pacemaker complications that affect how well they work.Things you can’t do with a pacemaker limit problems. Get best safety info. Avoid bad interference. Proper care ensures vital device longevity.
Even though pacemakers are mostly safe, pacemaker implantation problems can happen. These can be small issues or serious heart pacemaker issues that need quick medical help. It’s important for both patients and doctors to know about these risks to get the best care.
Looking into pacemaker side effects and pacemaker risks shows how important it is to be informed. This helps patients and doctors deal with the complex treatment of pacemaker implants.
Key Takeaways
- Pacemaker implantation is a common treatment for arrhythmias.
- Potential complications can arise from pacemaker implantation.
- Understanding pacemaker risks is key for patient care.
- Pacemaker side effects can vary in severity.
- Informed decision-making is key to successful treatment.
Understanding Pacemaker Implantation

A pacemaker is a compact device designed to regulate heartbeats. It sends electrical impulses to keep the heartbeat regular. This is important for people with irregular heart rhythms, or arrhythmias.
What Is a Pacemaker and How Does It Work?
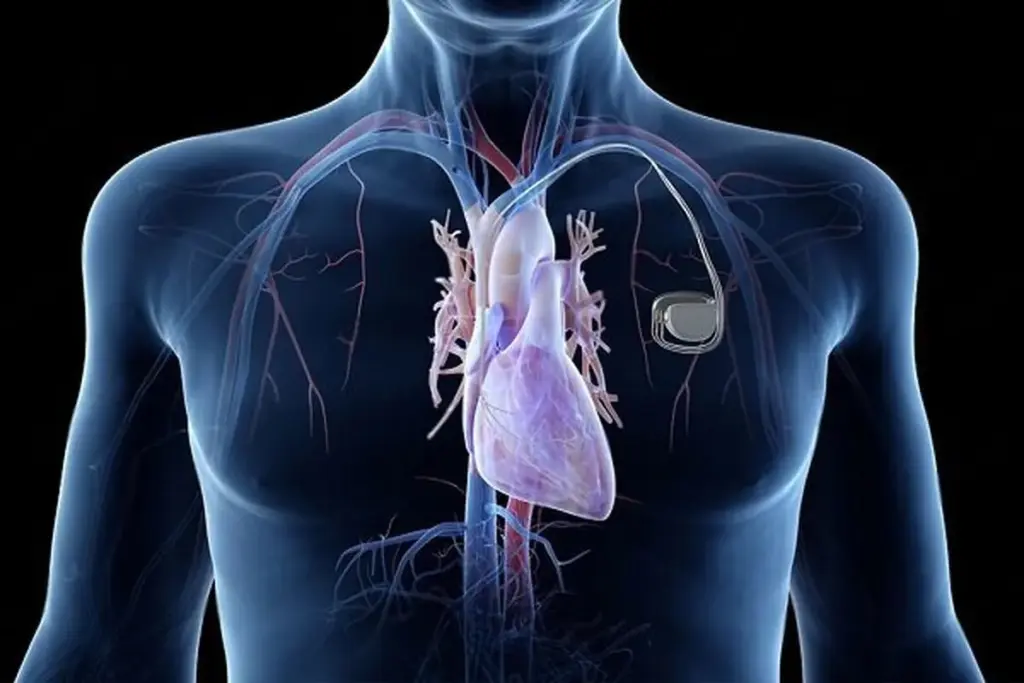
A pacemaker has two main parts: a pulse generator and leads. The pulse generator is a small metal box with a battery and a tiny computer. It’s placed under the skin, just below the collarbone.
The leads are thin wires that connect the pulse generator to the heart. They send electrical impulses to the heart, making sure it beats regularly.
The pacemaker watches the heart’s rhythm and sends impulses when needed. This helps prevent symptoms like dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
Types of Pacemakers and Their Functions
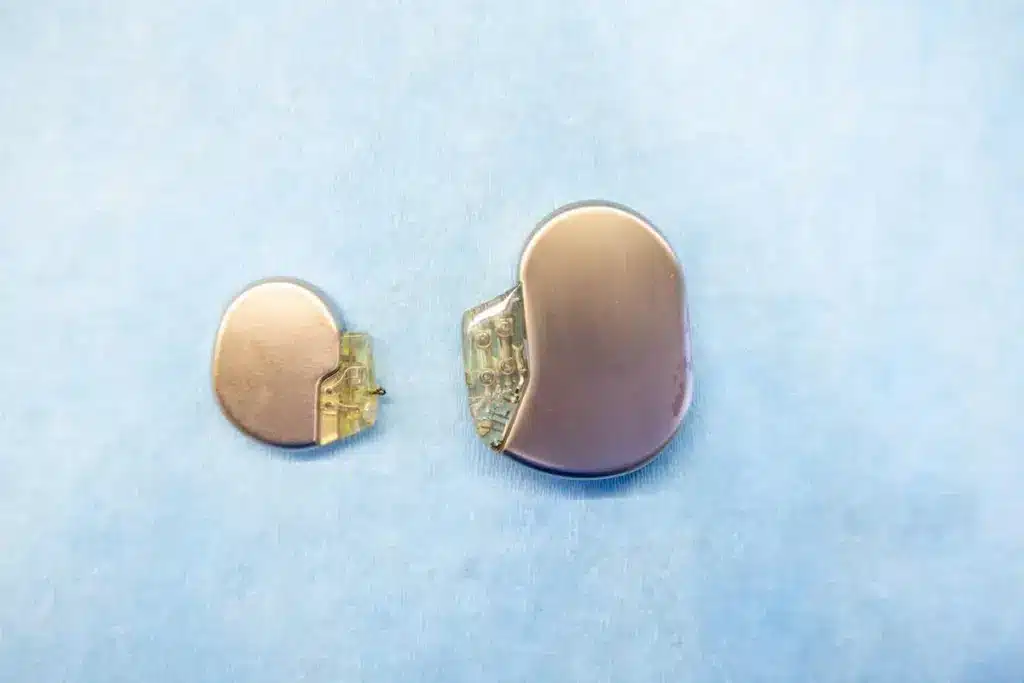
There are many types of pacemakers, each for different heart conditions. Traditional pacemakers are the most common. They have a pulse generator and leads that can be programmed for each patient.
Leadless pacemakers, like the Micra, are newer and smaller. They’re placed directly in the heart, without leads. This reduces the risk of complications.
Other pacemakers include biventricular pacemakers for CRT and MRI-compatible pacemakers for MRI scans. Each pacemaker has its own functions and benefits. The right one depends on the patient’s condition and needs.
Immediate Complications After Pacemaker Surgery
Pacemaker implantation is usually safe but can lead to some immediate issues. It’s important for patients to know about these problems. This way, they can get help quickly if needed.
Infection at the Implant Site
One common problem right after surgery is infection at the implant site. Look out for redness, swelling, or more pain at the pacemaker spot. Signs of infection can also be fever, chills, or discharge from the wound. If you notice these, call your doctor right away.
- Monitor the wound for signs of infection
- Keep the area clean and dry
- Follow post-operative care instructions
Bleeding and Bruising
Bleeding and bruising are common right after pacemaker surgery. Some bruising is okay, but big bleeding or growing bruises need a doctor’s call. Applying gentle pressure and elevating the area can help with bruising.
Pain and Discomfort
Pain and discomfort at the implant site are normal after surgery. But, severe or worsening pain needs to be talked about with your doctor. Your doctor might suggest pain meds, rest, and avoiding hard activities.
- Take pain medication as directed by your healthcare provider
- Avoid heavy lifting or bending
- Rest adequately to allow healing
Knowing about these immediate issues and acting fast can make recovery better. Always follow your doctor’s advice and report any worries.
Pacemaker Pocket Complications
The pacemaker pocket is a space made by surgery. It can cause problems. These issues come from how the body reacts to the device and the surgery.
Hematoma Formation
A hematoma is blood outside of blood vessels. It can happen at the pacemaker pocket site. Hematoma formation causes swelling, pain, and can lead to infection. We watch for signs of hematoma closely.
If it happens, we might need to drain it or treat it further.
Pocket Erosion
Pocket erosion is when the tissue over the pacemaker gets thin or wears away. This can expose the device. It’s a big problem because it can cause infection or need more surgery.
Pocket Infection and Treatment
Pocket infection is a serious issue that needs quick action. Signs of infection include redness, swelling, warmth, and pain. We treat it with antibiotics.
In some cases, we might have to remove and reimplant the pacemaker.
It’s key for patients and doctors to know about these complications. Spotting them early helps us manage them well.
After the pacemaker is put in, we stress the need for follow-up care. Regular visits help us catch any problems early. This ensures the best results for patients.
Lead-Related Complications
The leads of a pacemaker are key to its work. But, they can sometimes cause problems like dislodgement or fracture. These issues are big worries for those with pacemakers.
Lead Dislodgement and Migration
Lead dislodgement happens when the pacemaker lead moves from its spot. This can happen right after it’s put in or later. If the lead moves, the pacemaker might not work right, leading to heart rate problems.
Symptoms of lead dislodgement may include:
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeats
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
If you notice these signs, get medical help fast.
Lead Fracture and Insulation Failure
Lead fracture is when the lead wire breaks, breaking the connection to the heart. Insulation failure is when the lead’s protective layer gets damaged, causing electrical problems.
|
Complication |
Description |
Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|
|
Lead Fracture |
Break in the lead wire |
Loss of pacing, inappropriate sensing |
|
Insulation Failure |
Damage to the lead’s insulation |
Electrical shorts, oversensing |
Both can make the pacemaker not work right, needing more medical help.
Cardiac Perforation and Tamponade
Cardiac perforation is when the lead goes through the heart wall. This can cause tamponade, a serious condition where fluid builds up around the heart, squeezing it and stopping it from working.
“Cardiac perforation is a medical emergency requiring immediate attention. Symptoms can include chest pain, shortness of breath, and hypotension.”
Quick diagnosis and treatment are key to dealing with these problems well.
Pacemaker Malfunction Issues
Pacemakers are lifesavers, but they can malfunction. This can happen for many reasons. It’s important to watch them closely and act fast if there’s a problem.
Battery Depletion and Replacement Timing
Battery problems are a common issue. Pacemaker batteries last 5 to 15 years, depending on the model and settings. Regular check-ups are essential to monitor battery life and know when to replace it. If the battery runs out, the device might fail.
Programming Errors and Sensing Problems
Programming mistakes can cause pacemakers to work wrong. Sensing problems can make the pacemaker think the heart is beating wrong. This can lead to too much pacing or not enough. Changing the settings can fix these issues.
Complete Device Failure
Device failure is rare but serious. It can happen due to defects, damage, or wear and tear. Immediate medical attention is required to replace the device and fix the heart’s rhythm.
Pacemaker malfunctions can be serious, but they can be managed. Regular check-ups and quick action can prevent or fix many problems. Patients with pacemakers should follow their doctor’s advice and report any issues.
Things You Can’t Do With a Pacemaker
If you have a pacemaker, you need to know what activities and medical procedures could harm it. A pacemaker is a lifesaver, but you must take some precautions. This ensures it works right.
Electromagnetic Interference Concerns
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is a big worry for pacemaker users. EMI can mess with how your pacemaker works. Stay away from strong magnetic fields and some electronic devices that might cause trouble.
- Avoid standing near large magnets or magnetic fields, such as those found in MRI machines (unless it’s an MRI-conditional pacemaker) or certain industrial equipment.
- Be cautious with devices that have strong magnetic fields, like some welding equipment or large motors.
Prohibited Medical Procedures
Some medical procedures are risky for people with pacemakers. Always tell your doctor about your pacemaker before any treatment.
- MRI scans: Unless you have an MRI-conditional pacemaker, MRI scans are generally contraindicated.
- Electrocautery: This surgical technique can interfere with pacemaker function. Special precautions or alternative methods may be used.
- Radiation therapy: While not typically a problem, high doses of radiation therapy can potentially damage the pacemaker.
Sports and Activities to Avoid
Many physical activities are safe for pacemaker users, but some should be avoided or done with care.
- Contact sports: Activities like football, rugby, or hockey can pose a risk of damaging the pacemaker or causing lead displacement.
- High-impact activities: Exercises or sports that involve significant jarring or repetitive stress on the chest area should be done cautiously.
Knowing and avoiding these risks helps pacemaker users live active and happy lives. Always talk to your doctor for advice on living with a pacemaker.
Electromagnetic Interference and Your Pacemaker
Electromagnetic interference can disrupt pacemaker operation. It’s key to know its sources and how to lessen risks. Today’s world is full of devices that can cause EMI.
We’ll look at EMI sources and their impact on pacemakers. This will help you manage your device well.
Household Appliances and Consumer Electronics
Most household items are safe if used right. But, some devices can create strong electromagnetic fields. These fields might affect pacemaker work.
- Microwaves: Modern microwaves are designed to minimize EMI, but it’s wise to keep a safe distance.
- Cell Phones: Keep cell phones at least 6 inches away from your pacemaker to avoid interference.
- Headphones and Earpieces: Avoid placing headphones or earpieces directly over your pacemaker site.
Workplace and Industrial Equipment Hazards
Some workplace and industrial equipment can be risky for pacemakers. It’s important to find EMI sources in your work area.
|
Equipment Type |
Potential Risk |
Precaution |
|---|---|---|
|
Welding Equipment |
High |
Avoid direct exposure |
|
Large Motors |
Moderate |
Maintain distance |
|
Industrial Magnets |
High |
Use protective measures |
Security Systems and Metal Detectors
Security systems, like metal detectors and EAS systems, can interfere with pacemakers. When going through security, do the following:
- Inform security about your pacemaker.
- Ask for a manual search if you can.
- Walk through scanners at a normal pace to lessen exposure.
Knowing about EMI sources and taking steps to avoid them can lower pacemaker malfunction risks. This ensures your heart stays healthy.
Medical Procedures to Avoid With a Pacemaker
People with pacemakers should know about medical procedures that might harm their device. Pacemakers are safe and work well, but some treatments can be risky. It’s important to be careful.
MRI Restrictions and MRI-Conditional Pacemakers
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves. These can mess with pacemakers. But, new MRI-conditional pacemakers are safe under certain conditions.
Before an MRI, tell your doctor about your pacemaker. The MRI place will check your pacemaker type and follow safety rules. Not all pacemakers can go through MRI, and even MRI-conditional ones have rules to follow.
Radiation Therapy Considerations
Radiation therapy kills cancer cells with high-energy waves. It’s key to think about how radiation might affect your pacemaker. Radiation might not hurt the pacemaker itself but can mess with its electrical signals.
Tell your radiation doctor about your pacemaker. They might change your treatment to avoid problems. It’s also good to keep an eye on your pacemaker during and after treatment.
Electrocautery and Other Surgical Concerns
Electrocautery uses electrical current to cut or coagulate tissue. This can confuse your pacemaker. Doctors should know about your pacemaker and take extra steps, like using different techniques or adjusting your pacemaker.
Other surgeries might also need careful planning. Procedures with strong magnetic fields or electrical currents should be done with caution. Always tell your doctors about your pacemaker before surgery to make sure they’re ready.
Physical Activity Restrictions After Pacemaker Implantation
Knowing what activities to avoid after getting a pacemaker is key to a smooth recovery. It’s important to let your body heal well to avoid any problems.
Immediate Post-Surgery Limitations
Right after surgery, you should avoid certain activities to avoid pain and ensure healing. Here are some things to avoid:
- Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or stretching for at least a week.
- Refrain from raising the arm on the side of the implant above shoulder level for 2-3 weeks.
- Limit strenuous activities, including housework or gardening, for a few weeks.
These steps help prevent issues like lead displacement or other problems at the pacemaker site.
Long-Term Exercise Guidelines and Recommendations
After the healing phase, you can start doing normal activities again, including exercise. But, it’s important to follow some guidelines:
- Start with low-intensity exercises such as walking or light stretching.
- Gradually increase the intensity and duration based on comfort and tolerance.
- Avoid contact sports or activities that could result in a direct blow to the pacemaker site.
Regular exercise is good for your heart, but you need to be careful to protect your pacemaker.
Contact Sports and High-Impact Activities
Playing contact sports or doing high-impact activities is risky for pacemaker users. These activities can harm the device or cause lead displacement. We recommend avoiding:
- Contact sports like football, rugby, or hockey.
- High-impact aerobics or gymnastics.
- Activities that involve significant jarring or collision.
Always talk to your doctor before starting any intense activities. They can give you advice tailored to your situation and pacemaker type.
Traveling With a Pacemaker
Pacemaker patients can travel safely with a few precautions. Whether it’s a short trip or a long journey abroad, knowing how to manage your pacemaker is key.
Airport Security and Flying Considerations
When flying, being ready for security checks is important. Tell security you have a pacemaker and show your ID card. Most airport scanners are safe for pacemaker users. But, ask for a manual pat-down or a handheld scanner instead of metal detectors or full-body scanners.
Tips for Flying:
- Notify the airline about your pacemaker when booking your ticket or checking in.
- Carry your pacemaker identification card with you at all times.
- Be prepared for security checks by wearing loose clothing and being ready to explain your pacemaker.
International Travel Preparations
Before going abroad, prepare well. Research the healthcare system of your destination and get travel insurance that covers medical costs. Also, carry a doctor’s letter about your pacemaker and any other health issues.
Additional Preparations:
- Check if your destination has any specific medical facilities or specialists you might need.
- Make photocopies of important documents, such as your pacemaker ID and insurance cards, and leave a copy with a trusted friend or family member back home.
- Pack any necessary medications and keep them in your carry-on luggage.
Finding Medical Care While Away from Home
If you need medical help while traveling, there are ways to find it. Contact your pacemaker manufacturer for help finding local healthcare. Many countries also have international hospitals or clinics for travelers.
Steps to Take:
- Research local hospitals and clinics before you travel.
- Keep a list of emergency contact numbers, including your doctor and pacemaker manufacturer.
- Consider registering with your country’s embassy or consulate if you’re traveling abroad.
Psychological and Emotional Challenges
After getting a pacemaker, patients often face many psychological and emotional challenges. Adjusting to life with a pacemaker can change many parts of their life.
Anxiety and Depression After Implantation
Many patients feel anxious or depressed after getting a pacemaker. Having a device inside can make them worry about its work. Anxiety might come from fears about the pacemaker’s performance or how it affects daily life. Depression can happen as they adjust, feel overwhelmed, or worry about the future.
We know these feelings are real and need to be addressed. It’s important for patients to talk to their doctors. Support and advice can really help.
Body Image Concerns and Coping Strategies
Body image issues can also be a problem after getting a pacemaker. Even small changes can make people feel self-conscious. They might worry about the pacemaker being seen or feel it changes how they see themselves.
To deal with these issues, patients can try different things. Counseling or support groups can offer a place to share and learn. Focusing on the benefits of the pacemaker, like better health and longer life, can also help.
It’s key to tackle these challenges in a complete way. By recognizing them and using good coping strategies, patients can live better lives.
Long-Term Complications of Pacemakers
Pacemakers save lives but can cause long-term problems. It’s important for patients to know about these issues. This knowledge helps in managing their care better.
Venous Thrombosis and Occlusion
Venous thrombosis and occlusion can happen after a pacemaker is put in. The leads in the veins can irritate the blood, causing clots. Symptoms include swelling, pain, or discoloration in the affected limb.
In some cases, doctors might use anticoagulation therapy. This is to prevent or treat venous thrombosis.
- Factors like lead placement and the number of leads used increase the risk.
- Regular checks are key to catch problems early.
Tricuspid Valve Regurgitation
Tricuspid valve regurgitation can also occur. It happens when the pacemaker lead affects the tricuspid valve’s function. This can cause right-sided heart failure if not treated.
Treatment might include adjusting the lead or, in severe cases, surgery.
- Those with pre-existing tricuspid valve disease are at higher risk.
- Regular echocardiograms help monitor the valve’s function.
Pacemaker Syndrome and Pacemaker-Mediated Tachycardia
Pacemaker syndrome and pacemaker-mediated tachycardia are related to how the pacemaker works. Pacemaker syndrome happens when the pacemaker’s timing doesn’t match the heart’s natural rhythm. This can cause dizziness and shortness of breath.
Pacemaker-mediated tachycardia is a fast heart rate caused by the pacemaker tracking atrial arrhythmias. Changing the pacemaker’s settings can often fix these problems.
- Pacemaker syndrome can be managed by adjusting the device settings.
- Pacemaker-mediated tachycardia can be prevented with the right device programming and follow-up.
Warning Signs: When to Seek Medical Help
After getting a pacemaker, knowing the warning signs is key. Pacemakers help the heart work better, but problems can happen. Knowing these signs helps you get help fast.
Symptoms of Pacemaker Malfunction
Pacemaker problems can show up in different ways. Look out for:
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- irregular heartbeats or palpitations
- fatigue or weakness
- shortness of breath
If you see these signs, call your doctor right away.
Signs of Infection or Rejection
Signs of infection or pacemaker rejection are serious. Watch for:
- redness, swelling, or warmth around the pacemaker site
- pus or discharge from the incision
- increasing pain or tenderness
- fever or chills
Seeing these signs means you need to see a doctor fast.
Cardiac Symptoms That Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Some heart symptoms are serious and need quick help. These include:
- chest pain or discomfort
- severe shortness of breath
- rapid or irregular heartbeat
- dizziness or fainting
Don’t ignore these signs. Get medical help right away.
Staying alert to your health is hard, but it’s important. If you’re unsure about your symptoms, call your doctor.
Conclusion
It’s important to know about the possible problems with pacemaker implants. We’ve looked at different issues, from right after surgery to long-term problems. Taking care of your health with a pacemaker means watching for signs that you need to see a doctor.
Looking after your pacemaker means more than just knowing about the device. It’s about making smart choices about your daily life, travel, and medical tests. By working with your doctors and staying up-to-date, you can live a full and happy life with a pacemaker. A summary of pacemaker complications shows how key it is to be careful and proactive.
The best way to manage a pacemaker is through teamwork. Patients, caregivers, and doctors all play a role. By focusing on education, staying alert, and regular check-ups, we can make pacemaker therapy work well for everyone.
FAQ
What is a pacemaker and how does it work?
A pacemaker is a device that helps control the heartbeat. It sends electrical impulses to the heart. It has a generator and leads implanted under the skin, usually in the chest.
What are the immediate complications after pacemaker surgery?
Right after surgery, you might face infection, bleeding, or pain. It’s important to watch for these signs closely.
What are pacemaker pocket complications?
Complications can happen in the pocket where the pacemaker is placed. These include hematoma, pocket erosion, and infection. They might need medical treatment.
What are lead-related complications associated with pacemaker implantation?
Complications can happen with the leads, which connect the pacemaker to the heart. Issues include dislodgment, fracture, or cardiac perforation.
What are the things you can’t do with a pacemaker?
With a pacemaker, you should avoid MRI scans without special precautions. Also, be careful with activities that could harm the device or cause interference.
How can electromagnetic interference impact pacemaker function?
Electromagnetic interference can affect pacemakers. This includes interference from household items, work equipment, and security systems. It’s important to take precautions.
What medical procedures should be avoided with a pacemaker?
Stay away from MRI scans, radiation therapy, and electrocautery. Knowing these precautions can help prevent problems.
What are the physical activity restrictions after pacemaker implantation?
Follow the doctor’s advice on exercise and physical activity right after surgery. Avoid contact sports and high-impact activities.
How should I prepare for traveling with a pacemaker?
When traveling, know about airport security and flying with a pacemaker. Also, research medical care options abroad.
What are the psychological and emotional challenges after pacemaker implantation?
After surgery, you might feel anxious, depressed, or concerned about your body image. There are ways to cope with these feelings.
What are the long-term complications associated with pacemakers?
Long-term issues can include blood clots, valve problems, and pacemaker-related syndromes. Understanding these risks helps in managing care.
What are the warning signs that indicate when to seek medical help?
If you notice pacemaker malfunction, infection signs, or cardiac symptoms, seek help right away.
Can I undergo an MRI with a pacemaker?
There are MRI restrictions for pacemaker users. But, MRI-conditional pacemakers are available. Always check with your doctor before an MRI.
How long does a pacemaker last?
The pacemaker’s lifespan varies. Battery depletion is common. Replacement timing depends on the device and patient factors.
Can I exercise with a pacemaker?
Yes, you can exercise with a pacemaker. Just follow your doctor’s guidelines to avoid complications.
Reference
JAMA Network. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2781927




































