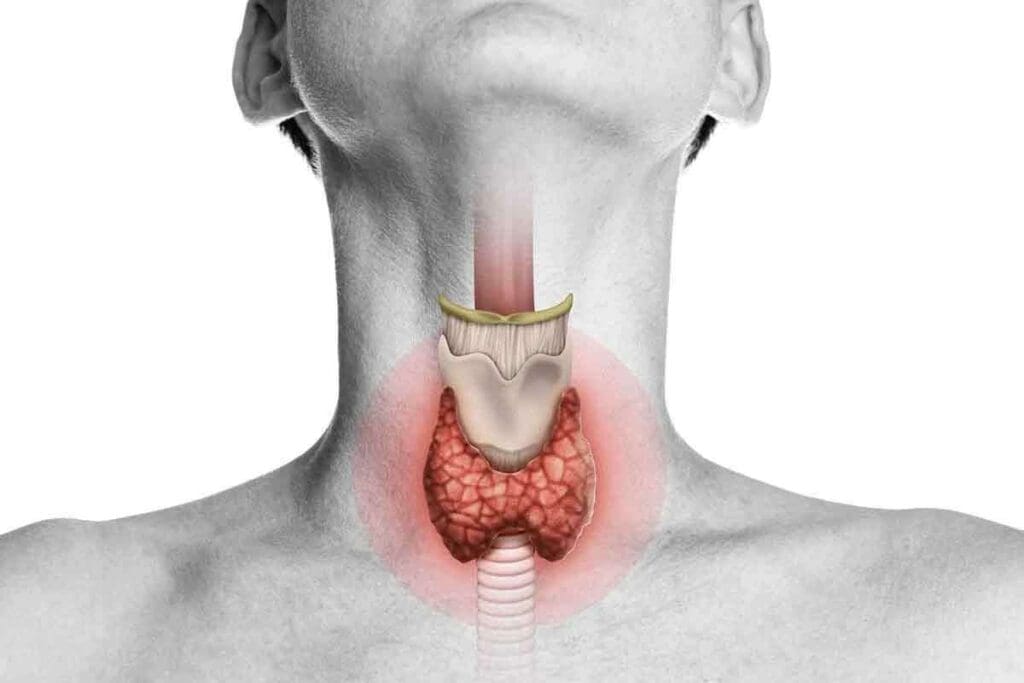
The thyroid gland is at the base of the neck. It’s key for hormone production and metabolism. But, usingX-rayss to check it is hard because it’s soft tissue.
Standard X-rays aren’t great for seeing the thyroid gland. They work better on denser things like bone. At Liv Hospital, we use advanced tests to give clear answers about the thyroid.
Thyroid cancer happens when bad cells grow in the thyroid gland. We need special imaging to find this.
Key Takeaways
- The thyroid gland is not clearly visible on standard X-rays.
- Advanced imaging techniques are necessary for thyroid evaluation.
- Thyroid cancer involves malignant cells forming in the thyroid gland.
- Liv Hospital uses patient-centered diagnostic protocols.
- Accurate diagnosis is key to good treatment.
The Thyroid Gland: Structure, Function ,and Importance
It’s key to know about the thyroid gland’s role in our health. This gland is vital for our metabolism, growth, and development. It’s an important part of our endocrine system.
Anatomy and Location at the Base of the Neck
The thyroid gland sits at the neck’s base, below the Adam’s apple. It’s shaped like a butterfly, with two lobes joined by a thin isthmus. Its position is perfect for making hormones that reach all parts of our body.
Role in Hormone Production and Metabolism
The thyroid gland makes hormones using iodine. It produces triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones control our heart rate, body temperature, and how fast we metabolize food. The gland’s work is guided by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, keeping our health in balance.
Common Thyroid Disorders and Their Prevalence
Thyroid problems are common and can really affect our lives. Some common issues include:
- Hypothyroidism: when the gland doesn’t make enough hormones.
- Hyperthyroidism: when it makes too many hormones.
- Thyroid nodules: growths on the gland.
- Thyroiditis: inflammation of the gland.
Doctors diagnose these problems with tests, exams, and imaging.
The Reality of Thyroid Gland X-ray: Capabilities and Limitations

Conventional X-rays have limits when showing the thyroid gland clearly. The thyroid gland is at the base. It’s key for metabolism through hormone production.
Why Conventional X-rays Cannot Clearly Visualize the Thyroid
X-rays are not made for detailed soft tissue images like the thyroid gland. They work better for denser structures like bones.
The thyroid gland’s soft tissue is the main issue. Soft tissues don’t absorb X-rays as bones do. This makes them hard to see on X-ray images.
Soft Tissue Composition Challenges
The thyroid gland is mostly soft tissue. This makes it hard for X-rays to show its structure or any issues.
Common Misconceptions About “Thyroid X-rays”
Many think X-rays can clearly show the thyroid gland and diagnose problems like nodules or cancer.
But X-rays can only hint at thyroid issues. They’re not reliable for diagnosing thyroid problems.
| Imaging Method | Thyroid Visualization Capability | Diagnostic Accuracy for Thyroid Conditions |
| Conventional X-ray | Limited | Low |
| Ultrasound | High | High |
| CT Scan | Moderate to High | Moderate to High |
Indirect Findings on Standard X-rays
Even though X-rays can’t directly show the thyroid gland, they might hint at problems. For example, a big thyroid gland can push the trachea, seen on a chest X-ray.
These hints can lead to more detailed tests like ultrasound or CT scans. These are better for looking at the thyroid gland.
Advanced Imaging Techniques for Thyroid Evaluation
Checking the thyroid gland needs many steps. We use different imaging methods to see how it works and looks. This helps us find and treat thyroid problems.
Ultrasound: The First-Line Imaging Method
Ultrasound is the top choice for looking at the thyroid. It sends sound waves to make clear pictures of the gland. We can see its size, shape, and any nodules or issues.
Ultrasound is great because it’s safe, doesn’t use radiation, and shows things in real-time. It’s also good for taking samples from thyroid nodules.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scans for Structural Assessment
CT scans give us a closer look at the thyroid and nearby tissues. They’re good for seeing how big the thyroid is or if there are big nodules. These can press on other important areas.
CT scans help us see how the thyroid relates to other parts ,like the trachea and esophagus. This is key for planning surgery.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Applications
MRI is another tool for checking the thyroid. It makes detailed pictures without using harmful radiation. This is good for seeing the gland and soft tissues around it.
It’s best to see how far thyroid disease has spread. It’s also good for people who can’t have CT scans with contrast.
Nuclear Medicine Scans for Functional Evaluation
Nuclear medicine scans tell us how the thyroid works. They use tiny amounts of radioactive tracers. These tracers show how well the gland is working.
- Thyroid Uptake Scans: Help find hyperthyroidism and check thyroid nodules.
- Radioactive Tracers: Like I-123 and Tc-99m pertechnetate are used for thyroid images.
These imaging methods help doctors find thyroid problems more accurately. This means we can make better treatment plans for our patients.
Nuclear Medicine and Thyroid Uptake Scans
Nuclear medicine is key in checking how well the thyroid works. It uses scans to see if there are problems with the thyroid gland. This is very important when doctors think there might be an issue.
Radioactive Iodine Tracers: I-123 and I-131
Tracers like I-123 and I-131 are used in these scans. They act like regular iodine but are radioactive. This lets doctors see how the thyroid is doing. I-123 is used for tests because it’s safe and doesn’t last long. I-131 is used for treatments, like fighting thyroid cancer, because it lasts longer.
The National Center for Biotechnology Information says these tests are great for finding and managing thyroid problems.
Technetium-99m Pertechnetate Scans
Technetium-99m pertechnetate is another tool for thyroid imaging. It goes to the thyroid gland but doesn’t get used in thyroid hormones. This makes it good for looking at the gland’s shape and some of its functions. It’s also good when iodine tests don’t work well.
Procedure and Patient Experience During Scanning
To do a thyroid scan, a small amount of tracer is given, either by mouth or through an IV. Then, the patient waits a few hours before the scan. During the scan, the patient lies down while a camera takes pictures of the thyroid. It’s usually not painful, and most people can handle it.
Interpretation of Uptake Results
The scan results show how much tracer the thyroid takes in. If it takes in a lot, it might mean Graves’ disease. If it takes in little, it could be thyroiditis or thyroid hormone resistance. The scan can also spot nodules or areas that aren’t working right.
| Condition | Uptake Pattern | Clinical Implication |
| Graves’ Disease | Diffuse High Uptake | Hyperthyroidism |
| Thyroiditis | Low Uptake | Inflammation of the Thyroid |
| Toxic Nodule | Focal High Uptake | Hyperfunctioning Nodule |
Can Thyroid Cancer Be Detected From X-rays?
X-rays have limits in finding thyroid cancer. They are used for many test,s but can’t see thyroid cancer well. This is because of how thyroid tissue works and how X-rays work.
Limitations of X-ray in Cancer Detection
The thyroid gland is soft tissue, hard to see on X-rays. Other imaging, like ultrasound, CT scans, or MR,I works better for it.
- X-rays are better for bones and calcifications.
- Thyroid cancer’s soft tissue changes are hard to spot on X-ray.
Indirect Signs of Large Thyroid Masses
Big thyroid masses can show signs on X-rays. For example, they can push the trachea, seen on chest X-rays.
Bt, these signs don’t just mean thyroid cancer. They can also mean other thyroid issues.
Why Advanced Imaging is Necessary for Cancer Diagnosis
For an accurate thyroid cancer diagnosis, advanced imaging is key. Ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration biopsy give detailed information on thyroid nodules.
- Ultrasound is great for checking thyroid nodules and guiding biopsies.
- CT and MRI scans show the thyroid gland and nearby areas in detail.
The Diagnostic Accuracy Gap
Using only X-rays for thyroid cancer detection has a big accuracy gap. X-rays can’t see the soft tissue changes of thyroid cancer. So, other tests are needed for accurate detection.
Using clinical checks, lab tests, and advanced imaging is key toacan curate thyroid cancer diagnosis.
Thyroid Nodule Evaluation and Classification
Checking thyroid nodules is key to finding thyroid problems, like cancer. Many people have thyroid nodules.
Types and Characteristics of Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules can be solid, cystic, or both. Most are not cancer, but some might be.
Solid Nodules: These are solid and can be checked for details on ultrasound.
Cystic Nodules: These have fluid and might have a solid part too.
Role of Imaging in Nodule Assessment
Imaging is very important for checking thyroid nodules. Ultrasound is the main tool because it shows details well.
- Ultrasound can spot signs of cancer, like dark spots and irregular shapes.
- CT and MRI might be used for bigger goiters or to check for invasion.
Risk Stratification Systems
There are systems to help manage thyroid nodules based on ultrasound. They aim to find nodules at risk for cancer.
When Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy is Recommended
Fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) is used to take samples from nodules. It’s suggested for nodules that look suspicious or are big.
Choosing to do FNAB depends on ultrasound results, size, and sometimes molecular tests.
Understanding Thyroid Measurement and Dimensional Analysis
Getting the right thyroid measurement is key to diagnosing and treating thyroid issues. Knowing the size of the thyroid gland helps doctors understand its health and how well it’s working.
Interpreting Measurement Formats
Thyroid measurements are often given as “6.7 x 5.2 x 12.3.” This shows the gland’s size in three different ways. It’s usually from ultrasound or imaging tests to figure out the gland’s volume.
Understanding these measurements is essential for:
- Assessing thyroid size and volume
- Monitoring changes over time
- Diagnosing thyroid disorders
Volumetric Assessment Methods on Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a main way to measure thyroid volume. It uses the formula: length x width x height x 0.52 for each lobe. Then, it adds the volumes of both lobes together.
The advantages of ultrasound for thyroid measurement include:
- Non-invasive and safe
- High accuracy for volume assessment
- Ability to detect nodules and other abnormalities
Normal vs. Abnormal Thyroid Size Parameters
Normal thyroid size can vary, but there are signs of abnormal size. For adults, a total thyroid volume of up to 18-20 mL is usually normal.
| Parameter | Normal Range |
| Total Thyroid Volume | Up to 18-20 mL |
| Right Lobe Volume | Typically smaller than lthe eft |
| Left Lobe Volume | Variable, often larger than the right |
Clinical Significance of Thyroid Dimensions
Thyroid dimensions are very important for health. A bigger thyroid gland (goiter) might mean iodine deficiency, autoimmune thyroiditis, or Graves’ disease.
“Thyroid size and volume are critical indicators of thyroid health, and accurate measurement is essential for diagnosis and treatment planning.” – Thyroid Expert
Thyroid measurements help doctors make the right decisions for patient care. This includes deciding on more tests or treatment.
Chest X-rays and Indirect Thyroid Findings
Chest X-rays are not made to see the thyroid gland directly. Yet, they can show signs of thyroid problems. These X-rays are mainly used to check the lungs. But they can also show information about the thyroid gland.
Tracheal Deviation as an Indicator of Thyroid Pathology
Tracheal deviation is a key sign of thyroid issues on a chest X-ray. The trachea should be in the middle. If it’s not, it might mean there’s a thyroid problem. This usually happens when a thyroid goiter or nodule presses on the trachea.
The direction of the tracheal deviation can hint at the thyroid problem’s location and size. For example, if the trachea leans to one side, it might mean there’s a big thyroid mass on the other side.
Detecting Enlarged Thyroid Through Secondary Signs
Other signs on a chest X-ray can also suggest thyroid enlargement. These include:
- Superior mediastinal widening: An enlarged thyroid can spread into the superior mediastinum, making this area wider on the X-ray.
- Tracheal compression or narrowing: Large thyroid masses can squeeze the trachea, making it narrower.
- Soft tissue density: Sometimes, a big thyroid goiter or mass can show up as soft tissue in the neck or superior mediastinum.
Limitations of This Approach for Diagnosis
Chest X-rays can hint at thyroid problems, but they’re not reliable for diagnosing them. They’re not made to see the thyroid gland directly. This means they’re not very good at finding thyroid issues.
Many thyroid problems might not change the anatomy enough to be seen on a chest X-ray. So, even if the X-ray looks normal, thyroid issues could be present.
When Further Investigation is Warranted
If a chest X-ray suggests thyroid problems, more tests are needed. These tests usually include ultrasound or CT ,,or MRI scans. These methods can give a detailed look at the thyroid gland. They help doctors accurately diagnose and understand thyroid issues.
In summary, chest X-rays are not the first choice for finding thyroid problems. Bu, they can sometimes give clues. These clues can lead to more tests, helping to diagnose and treat thyroid conditions.
Comprehensive Diagnostic Pathway for Suspected Thyroid Disorders
Diagnosing thyroid disorders requires a mix of clinical checks, lab tests, and imaging. This approach helps patients get the right diagnosis and treatment.
Initial Clinical Evaluation and Physical Examination
The first step is a detailed clinical check and physical exam. Doctors look at symptoms, medical history, and perform physical checks. They look for signs like changes in heart rate, skin, and thyroid size.
Key components of the initial evaluation include:
- Patient history and symptom assessment
- Physical examination of the thyroid gland
- Evaluation of overall health and thyroid-related complications
Laboratory Testing for Thyroid Function
Lab tests are key to checking thyroid function. They measure TSH and thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) in blood. Abnormal levels can show hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, or other issues.
Common thyroid function tests include:
- TSH test
- Free T4 (FT4) test
- Free T3 (FT3) test
- Thyroid antibody tests (e.g., anti-TPO, anti-TG)
Appropriate Imaging Selection Strategy
Imaging is vital for diagnosing and managing thyroid issues. The right imaging depends on the case and suspected problem.
Common imaging techniques for thyroid evaluation include:
- Ultrasound: Useful for assessing thyroid gland morphology, detecting nodules, and guiding fine-needle aspiration biopsies.
- CT and MRI: Provide detailed images of the thyroid gland and surrounding structures, useful for evaluating large goiters or suspected thyroid cancers.
- Nuclear medicine scans: Assess thyroid function and detect abnormalities in thyroid hormone production.
Follow-up Procedures and Monitoring Protocols
After diagnosis, ongoing care and monitoring are key. This includes regular lab tests, adjusting medication, and imaging to check thyroid changes.
“Regular follow-up is vital for managing thyroid disorders well and avoiding complications.”
Using a detailed diagnostic process, doctors can ensure patients get the right diagnosis and care. This leads to better health outcomes.
Modern Approaches to Thyroid Cancer Detection at Liv Hospital
Liv Hospital leads in thyroid cancer detection, using the latest technology. Their radiology department has top-notch imaging tools. This helps in accurate diagnosis and planning for treatment.
Multi-modality Imaging Techniques
Liv Hospital uses a multi-modality approach for detecting thyroid cancer. They use ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI. This gives a full view of the thyroid gland.
Benefits of Multi-modality Imaging:
- Enhanced diagnostic accuracy
- Comprehensive assessment of thyroid pathology
- Guiding fine-needle aspiration biopsies
PET/CT Scans for Advanced Cases
For complex thyroid cancer cases, Liv Hospital uses PET/CT scans. This combines PET’s functional info with CT’s anatomical details. It offers insights into cancer spread and metabolism.
Emerging Technologies in Thyroid Imaging
Liv Hospital keeps up with new thyroid imaging tech. They use contrast-enhanced ultrasound and elastography. These help improve detection accuracy.
Liv Hospital’s Specialized Thyroid Evaluation Protocols
Liv Hospital has special thyroid evaluation protocols. They ensure patients get thorough care. A team of radiologists, endocrinologists, and surgeons works together. They create personalized treatment plans.
| Imaging Technique | Application | Benefits |
| Ultrasound | Initial assessment of thyroid nodules | Non-invasive, high-resolution images |
| PET/CT | Advanced thyroid cancer staging | Functional and anatomical information |
| CT/MRI | Detailed structural assessment | High sensitivity for soft tissue abnormalities |
Conclusion
It’s very important to check the thyroid gland well to find thyroid disorders, like cancer. Old X-rays can’t show the thyroid gland very well. But new imaging methods have changed this.
Tools like ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, and nuclear medicine scans help a lot. They let doctors see how the thyroid works and what’s wrong. This helps find thyroid cancer early, when it’s easier to treat.
Finding and treating thyroid cancer early makes a big difference. Using these new imaging methods is now the main way doctors diagnose and treat thyroid problems. This makes sure patients get the right care.
Thanks to these advanced imaging tools, doctors can give better care to people with thyroid issues. This leads to better health for their patients.
FAQ
Can the thyroid gland be seen on a standard X-ray?
No, the thyroid gland can’t be seen directly on a standard X-ray. This is because it’s made of soft tissue. But, signs like tracheal deviation might hint at thyroid issues.
What are the limitations of using x-rays to evaluate the thyroid gland?
X-rays struggle to show the thyroid gland because it’s soft tissue. For a clear view, we need more advanced imaging methods.
How is thyroid cancer detected?
Finding thyroid cancer involves several steps. First, doctors do a physical check and lab tests. Then, they use ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, and nuclear scans. X-rays alone aren’t enough.
What is the role of nuclear medicine scans in thyroid evaluation?
Nuclear medicine scans use radioactive iodine and technetium-99m pertechnetate. They check thyroid function and find nodules. These scans are key for diagnosing thyroid issues.
How are thyroid nodules evaluated and classified?
Doctors use ultrasound to check thyroid nodules. They look at the nodule’s features to see if it might be cancerous. If it looks suspicious, they do a fine-needle aspiration biopsy.
What is the significance of thyroid measurements, such as 6.7 x 5.2 x 12.3?
Thyroid measurements, like those from ultrasound, tell us about the gland’s size and volume. These details help doctors understand thyroid problems and track changes.
Can chest x-rays indicate thyroid pathology?
Chest x-rays might hint at thyroid issues with signs like tracheal deviation. But, more tests are needed to confirm the problem.
What is the diagnostic pathway for suspected thyroid disorders?
First, doctors do a physical check and lab tests for thyroid function. Then, they choose the right imaging tests. After that, they follow up and monitor the patient’s condition.
What modern approaches are used at Liv Hospital for thyroid cancer detection?
Liv Hospital uses many imaging methods, including PET/CT scans for tough cases. They also use new technologies in thyroid imaging to find cancer accurately.
Why are advanced imaging techniques necessary for thyroid evaluation?
Advanced imaging is key for precise thyroid evaluation and cancer detection. This is because regular x-rays can’t show the thyroid gland well.
References:
- StatPearls. (2022). Thyroid uptake and scan. National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555978/




































