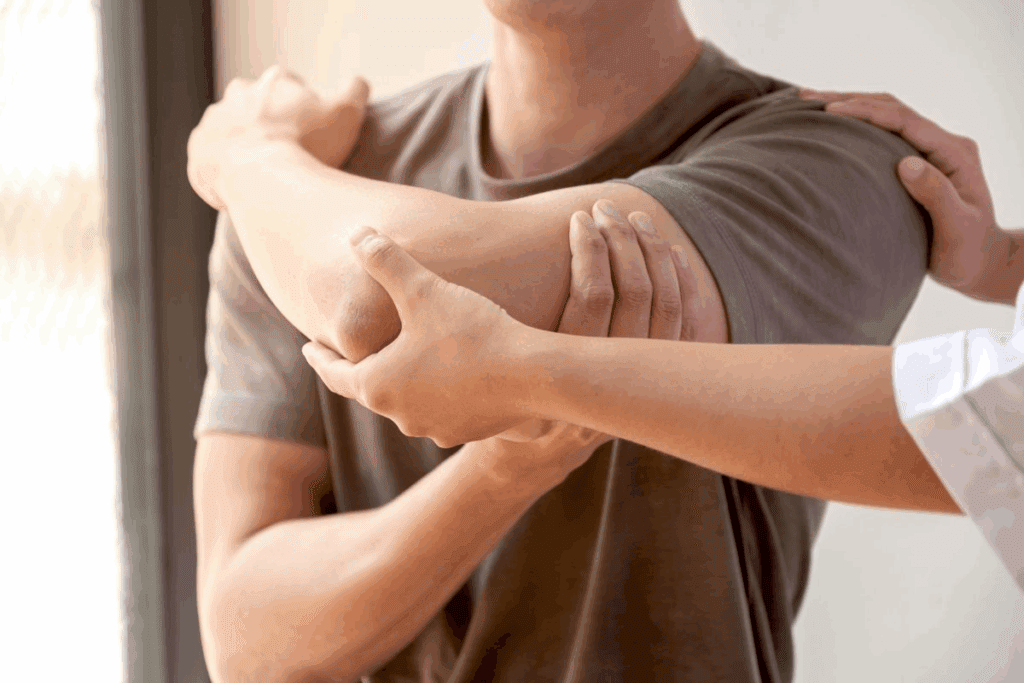
Trochanteric bursitis is a widespread condition that significantly impacts the lives of millions. It causes hip pain and discomfort that can interfere with daily activities. Knowing safe trochanteric bursitis exercises is key to managing the condition and easing pain. It’s also important to understand which exercises to avoid to prevent further irritation.
Trochanteric bursitis inflames the bursae around the hip, leading to pain on the outer side of the hip. Effective management includes proper treatment and safe trochanteric bursitis exercises to promote healing, strengthen surrounding muscles, and reduce discomfort. Knowing what to avoid and which movements to include is the first step toward recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the causes and symptoms of trochanteric bursitis is essential for effective management.
- Safe exercises play a critical role in easing hip pain and promoting healing.
- Avoiding certain exercises can prevent further irritation and discomfort.
- A complete treatment plan is necessary for the best recovery.
- Getting professional advice is recommended for a personalized exercise routine.
Understanding Trochanteric Bursitis: Causes and Symptoms
Knowing the causes and symptoms of trochanteric bursitis is key to managing this painful hip issue. This condition, also known as greater trochanteric pain syndrome, affects the bursa near the hip. It leads to discomfort and mobility problems.
What is Trochanteric Bursitis?
Trochanteric bursitis occurs when the bursa near the greater trochanter gets inflamed. The greater trochanter is the bony part on the outside of the hip. This bursa helps reduce friction between tendons and bone. When it’s inflamed, it causes pain and tenderness in the hip.
Trochanteric bursitis is a widespread condition that significantly impacts the lives of millions.
Several things can lead to trochanteric bursitis. Repetitive motion is a big one, causing irritation and inflammation. Running or cycling, which involve repetitive hip movements, can increase the risk. A direct blow to the hip from contact sports can also cause it.
Conditions like arthritis can also lead to trochanteric bursitis. Poor posture, uneven leg length, or abnormal gait can stress the hip, causing bursitis.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The symptoms of trochanteric bursitis include pain in the outer hip, which can spread down the thigh. This pain gets worse with walking, climbing stairs, or lying on the affected side. Some people may also see swelling or tenderness.
It’s important to notice these symptoms early. This way, you can get the right medical help and avoid more problems.
What Aggravates Hip Bursitis?

Hip bursitis symptoms can get worse due to many factors. These include physical activities and health conditions. Knowing these factors helps manage the condition better.
Common Triggers for Flare-Ups
Several things can make hip bursitis symptoms worse. These include repetitive motion, direct blows to the hip, and prolonged pressure. Activities like running, cycling, or repetitive hip movements can irritate the bursae.
Everyday activities like climbing stairs or standing for long periods can also make symptoms worse. Knowing these triggers helps prevent flare-ups.
Mechanical Factors That Worsen Symptoms
Mechanical factors can also make hip bursitis worse. Poor posture, leg length discrepancies, and abnormal gait patterns can increase stress on the hip bursae. For example, a person with a leg length discrepancy may limp, putting extra pressure on the bursae in the longer leg.
Wearing the wrong shoes or having poorly fitting orthotics can also add to the mechanical stress on the hip. Fixing these issues with proper footwear, orthotics, or physical therapy can help ease symptoms.
| Mechanical Factor | Effect on Hip Bursitis |
| Poor Posture | Increases stress on the hip bursae |
| Leg Length Discrepancy | Causes abnormal gait, leading to bursae irritation |
| Inappropriate Footwear | Contributes to mechanical stress on the hip |
Inflammatory Contributors
Inflammatory conditions can also make hip bursitis worse. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or other inflammatory arthritides can increase the risk of developing bursitis or make existing symptoms worse.
Understanding the underlying inflammatory contributors is key to a good treatment plan. This may involve managing the underlying condition with medication or other treatments, along with addressing the bursitis directly.
High-Impact Activities to Avoid
Managing trochanteric bursitis means knowing which activities to stay away from. High-impact activities can make the condition worse. They put too much stress and friction on the bursa.
Running and Jogging Risks
Running and jogging can make trochanteric bursitis symptoms worse. These activities involve hip movements that can irritate the bursa. This leads to more pain and swelling. If you love running, try swimming or cycling instead. They are gentler on your joints.
Jumping Exercises (Including Jumping Jacks)
Jumping exercises, like jumping jacks, can also make trochanteric bursitis worse. The impact from landing can stress the hip joint and bursae. Try low-impact aerobics instead to reduce the risk.
Contact Sports Considerations
Contact sports, like soccer and basketball, involve a lot of impact and quick movements. These can increase the risk of making trochanteric bursitis worse. If you play sports, talk to your coach or a doctor about safer training options.
| Activity | Risk Level | Recommendation |
| Running/Jogging | High | Avoid or modify to low-impact alternatives like swimming |
| Jumping Exercises | High | Replace with low-impact aerobics |
| Contact Sports | High | Discuss alternative training with a coach or healthcare professional |
| Cycling | Low | Adjust bike settings for comfort and consider recumbent bikes |
| Swimming | Low | Recommended as a low-impact exercise option |
Trochanteric Bursitis Exercises to Avoid
Some exercises can make trochanteric bursitis worse. It’s key to know which ones to steer clear of. This helps in managing the condition effectively.
Harmful Strength Training Movements
Strength training is vital for many, but some moves can irritate the bursae. Deep squats, lunges, and leg press can stress the hip bursae, making the condition worse.
- Deep squats: Avoid deep squats as they can compress the bursae.
- Lunges: Lunges, even those that bend deeply, can irritate the trochanteric bursa.
- Leg Press: Using heavy weights on a leg press machine can also aggravate the condition.
Problematic Stretches
Stretching is good, but some stretches can make trochanteric bursitis symptoms worse. It’s important to avoid stretches that directly press on the affected area.
- IT Band Stretches: Tight IT bands can be problematic, but aggressive stretching can irritate the bursae.
- Hip Flexor Stretches: Deep hip flexor stretches can sometimes aggravate the condition.
Group Fitness Classes to Reconsider
Group fitness classes are fun and motivating. Yet, some may not be good for those with trochanteric bursitis.
- High-Impact Aerobics: Classes with high-impact movements, like jumping or running, can make the condition worse.
- Spinning Classes: While low-impact, spinning classes with standing or aggressive pedaling can irritate the hip.
| Exercise/Activity | Potential Impact on Trochanteric Bursitis |
| Deep Squats | It can compress and irritate the bursae. |
| Lunges | It can put additional stress on the hip bursae. |
| High-Impact Aerobics | It can exacerbate the condition due to high-impact movements. |
Dangerous Stretches That Can Worsen Hip Bursitis
People with hip bursitis might stretch to feel better, but some stretches can hurt more than help. Stretching is key to staying flexible and easing pain. Yet, some movements can make hip bursitis worse if not done right.
IT Band Stretches to Reconsider
The IT band runs from the hip to the knee on the outside of the thigh. Stretching common, but it can be a problem for those with hip bursitis. Stretching the IT band while standing or lying on your side can put more pressure on the bursa, making inflammation worse.
Try gentle alternatives to avoid putting pressure on the bursa. For example, a seated IT band stretch or using a foam roller can help without direct pressure.
Hip Flexor Movements That May Aggravate Symptoms
Hip flexor stretches can also be a concern. Deep knee bends or lunges can irritate the bursa, which is bad if done wrong or too deeply. Choose gentle hip flexor stretches that don’t stretch too far.
For example, a standing hip flexor stretch with a slight tweak, like keeping the back knee slightly bent, can be safer for the bursa.
Piriformis Stretches: Proceed with Caution
The piriformis muscle goes from the lower spine to the thigh bone. Stretching it can be good, but aggressive piriformis stretches can harm. Deep stretches that cross one leg over the other and pull the knee toward the opposite shoulder can irritate the bursa.
For a safe piriformis stretch, try a gentle, seated stretch. Sit with the affected leg crossed over the other and gently pull the knee toward the opposite shoulder without forcing it.
Everyday Movements That Can Trigger Pain
Simple daily tasks can trigger or worsen pain from trochanteric bursitis. Everyday movements, if not done right, can stress the hip joint and bursae. This can lead to more discomfort. It’s key to know how to change these daily activities to manage symptoms well.
Sitting Positions to Avoid
Sitting for a long time can make trochanteric bursitis symptoms worse. Sitting with legs crossed or leaning to one side can put uneven pressure on your hips. This can irritate the bursa. To lessen discomfort, it’s best to:
- Sit with your feet flat on the floor or on a footrest, keeping your knees at or below hip level.
- Avoid crossing your legs or ankles, as this can cause uneven pressure distribution.
- Take regular breaks to stand up, stretch, and move around.
Using a chair with proper lumbar support can also help maintain a healthy posture while sitting, reducing strain on the hip area.
Sleeping Positions That Increase Pressure
Sleeping on your side, especially on the affected side, can increase pressure on the trochanteric bursa. To alleviate this:
- Consider sleeping on your back or on the unaffected side.
- Use a supportive pillow between your knees if you sleep on your side to reduce pressure on your hips.
- Ensure your mattress is supportive and not too soft or too firm.
Avoiding positions that cause your hip to rotate inward or outward can also help reduce irritation.
Standing and Walking Habits to Modify
Standing for long periods or walking improperly can also aggravate trochanteric bursitis. To modify these habits:
- Stand with your weight evenly distributed on both feet, avoiding leaning to one side.
- Wear supportive shoes with good arch support and cushioning.
- Avoid walking on uneven surfaces or stairs, which can put additional stress on your hips.
Using a walking aid, if necessary, can help reduce strain on the affected hip.
Let’s consider a summary of the modifications that can help alleviate trochanteric bursitis symptoms during daily activities:
| Activity | Modifications |
| Sitting | Keep feet flat, avoid crossing legs, and take regular breaks |
| Sleeping | Sleep on your back or unaffected side, use a pillow between your knees |
| Standing/Walking | Distribute weight evenly, wear supportive shoes, and avoid uneven surfaces |
By making these adjustments to daily activities, individuals with trochanteric bursitis can potentially reduce their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Cardio Equipment That May Worsen Symptoms
It’s important to know how different cardio machines can affect trochanteric bursitis. While cardio is good for health, some equipment can make hip bursitis worse. We need to look at how different exercises affect bursitis symptoms to help those with this condition.
Treadmill Concerns
Running or walking on a treadmill can be tough for those with trochanteric bursitis. The constant impact can make the bursa worse, leading to more pain and swelling. To lessen discomfort, try lowering the treadmill’s incline and decline. This can help reduce stress on the hip.
Tips for Treadmill Use:
- Reduce the incline to minimize stress on the hip.
- Use a softer walking or running surface if available.
- Consider holding onto the handrails to reduce strain on the hips.
Elliptical Trainer Considerations
The elliptical trainer is seen as a lower-impact option than the treadmill. But the motion can irritate if not set right. Make sure the elliptical is set to a stride length that feels natural to avoid hip strain.
Adjusting the Elliptical Trainer:
- Adjust the stride length to fit your natural gait.
- Avoid overreaching, which can strain the hip.
- Keep your posture upright to distribute the impact evenly.
Cycling Modifications for Hip Pain
Cycling is usually low-impact, but it can be uncomfortable for those with trochanteric bursitis. This is often due to a bike that’s not adjusted correctly.. Adjust the saddle height and position to avoid over-extending the leg, which can irritate the bursa.
| Cardio Equipment | Potential Risks | Modifications |
| Treadmill | High impact, repetitive stress | Reduce incline, softer surface |
| Elliptical Trainer | Incorrect stride length, overreaching | Adjust stride length, maintain posture |
| Cycling | Poor bike fit, over-extension | Adjust saddle height, position |
Knowing the risks of different cardio equipment and making adjustments can help those with trochanteric bursitis. They can keep enjoying cardio while reducing discomfort.
Safe and Effective Trochanteric Bursitis Exercises
Exercises that are gentle and focused can help manage trochanteric bursitis. It’s key to pick exercises that strengthen the hip without irritating it further. We’ll look at safe and effective options, like gentle strengthening, water-based activities, and yoga poses. We’ll also focus on exercises good for seniors.
Gentle Strengthening Options
Exercises that are gentle but effective are important for hip stability and pain relief. Start with low-impact, non-weight-bearing exercises. Then, as you get better, move to more challenging ones.
- Clamshell exercise: This targets the gluteal muscles and improves hip stability.
- Bridging: Strengthens the glutes and hamstrings, helping with better hip alignment.
- Leg raises: Lying on your side or back, lifting your leg strengthens the hip muscles without too much strain.
Water-Based Exercises
Water-based exercises, or aquatic therapy, are great for strengthening hip muscles without too much strain.
- Water walking: It’s good for your heart while being easy on your joints.
- Leg swings: Done in the water, these loosen the hip joint.
- Aquatic cycling: It’s a low-impact way to boost your heart health and strengthen your legs.
Modified Yoga Poses
Yoga can help with trochanteric bursitis if you modify it to avoid making it worse. Some poses can improve flexibility and strength.
- Modified Warrior Pose: It avoids deep hip flexion that could irritate the bursae.
- Gentle Tree Pose: It improves balance and stability.
- Supported Pigeon Pose: It stretches the glutes without putting pressure on the bursae.
Hip Bursitis Exercises for Seniors
Seniors with trochanteric bursitis need exercises that are easy on the joints. They should also improve balance and strength to prevent falls.
| Exercise | Benefit | Precaution |
| Seated leg lifts | Strengthens hip muscles | Avoid lifting too high |
| Chair squats | Improves leg strength | Use a sturdy chair, avoid deep squats |
| Wall stands | Enhances balance and leg strength | Stand near a wall for support |
Heat vs. Ice: Proper Application for Bursitis Relief
Knowing when to use heat or ice is key to treating trochanteric bursitis. Both methods help with bursitis pain, but they’re used differently based on the condition’s stage and severity.
When to Use Ice for Bursitis
Ice therapy is best in the early stages of bursitis, within the first 48 hours. It reduces inflammation and numbs the pain. Here’s how to use ice effectively:
- Apply ice packs for 15-20 minutes at a time
- Use a barrier between the ice and skin to avoid ice burns
- Repeat every 2-3 hours as needed
When Heat Therapy is Beneficial
Heat therapy is more helpful once the initial inflammation has gone down. It relaxes muscles and boosts blood flow, aiding in healing. Use heat therapy:
- After the acute phase (usually after 48-72 hours)
- For chronic bursitis pain
- Before activities to increase flexibility
It’s important to listen to your body and adjust your treatment as needed. If you feel more pain or discomfort with either heat or ice, stop and talk to your healthcare provider.
Combination Approaches for Pain Management
Some people find relief by switching between heat and ice. This method, called contrast therapy, works well for long-term bursitis symptoms. But it’s important to stick to a routine and watch how your body reacts.
In summary, both heat and ice have their roles in managing trochanteric bursitis pain. By knowing when to use each, you can better manage your pain and improve youe quality.
The Role of Massage and Manual Therapy
Massage therapy is gaining attention for helping with trochanteric bursitis symptoms. It’s key to know both the good and bad sides of massage and manual therapy for this condition.
Massage can ease muscle tension, boost blood flow, and aid in healing. But not every massage method is right for trochanteric bursitis.
Can Massage Help Bursitis?
Yes, massage can help with bursitis if done right. Soft massage can cut down inflammation and ease pain from trochanteric bursitis. Always talk to a healthcare expert to find the best massage for your needs.
Types of Massage to Avoid
While massage is good, some methods are not safe, like deep pressure or friction on the bursa. Deep tissue massage or trigger point therapy might make things worse if not done carefully.
The table below lists massage methods to use with caution:
| Massage Technique | Considerations |
| Deep Tissue Massage | MIt maybe too intense for acute bursitis |
| Trigger Point Therapy | Can be beneficial if applied gently, but may irritate if too intense |
| Swedish Massage | Gentle techniques can be soothing |
Professional vs. Self-Massage Techniques
Professional massage is best for the best results, but self-massage can work too if done right. It’s vital to learn the right techniques from a pro to avoid making things worse.
We stress the need for a custom massage plan for trochanteric bursitis. This should include professional help and self-care as needed.
Physical Therapy Approaches for Trochanteric Bursitis
Physical therapy is key in treating trochanteric bursitis. It helps reduce symptoms and improves function. We’ll look at the different physical therapy methods used for this condition.
Therapeutic Exercises
Therapeutic exercises are vital in treating trochanteric bursitis. They strengthen the hip muscles, improve flexibility, and lessen pain. Strengthening the gluteal muscles is important for hip stability. Examples of exercises include:
- Clamshell exercise
- Side-lying leg lifts
- Glute bridges
It’s important to do these exercises with a physical therapist. They ensure the right technique and avoid making the condition worse.
Kinesio Taping Methods
Kinesio taping is another physical therapy technique for trochanteric bursitis. It involves applying special tape to the affected area. This tape reduces pain and inflammation by reducing pressure on the bursa. A physical therapist can show you how to apply the tape correctly.
Trochanteric Bursitis Special Tests
Special tests are used to diagnose and monitor trochanteric bursitis. The Fabere test and the Ober test check hip function and identify bursitis causes. These tests help physical therapists create the right treatment plan.
Measuring Progress in Therapy
Tracking progress is critical in physical therapy for trochanteric bursitis. We use patient reports and objective measures to see how well you’re doing. This includes pain scales, functional assessments, and strength tests. Regular checks help us adjust the treatment plan for the best results.
A leading physical therapy expert says, “A well-structured physical therapy program can significantly reduce trochanteric bursitis symptoms and improve quality of life.” We focus on a complete approach tailored to your needs and goals.
“Physical therapy is not just about exercises; it’s about educating the patient on how to manage their condition and prevent future flare-ups.”
– Physical Therapy Professional
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Flare-Ups
Making simple lifestyle changes can help reduce trochanteric bursitis flare-ups. These changes can improve your daily life and manage your condition better.
Weight Management Strategies
Keeping a healthy weight is key to reducing hip joint pressure. Extra weight can make trochanteric bursitis symptoms worse. A balanced diet and gentle exercise are essential for maintaining a healthy weight.
- Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Try low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling.
- Stay away from high-calorie foods and drinks.
Ergonomic Adjustments at Home and Work
Making ergonomic changes can reduce hip strain. Small changes in your environment can make a big difference. Here are some tips:
- Use a chair with good lumbar support when sitting.
- Adjust your workstation to avoid bending or stretching.
- Stand and stretch regularly when working at a desk.
Supportive Devices and Cushions
Using supportive devices and cushions can ease hip pressure. Supportive cushions are great for sitting or sleeping. Look into these options:
- Hip support cushions for chairs.
- Orthotic pillows for better sleeping posture.
Trochanteric Precautions in Daily Activities
Being careful with daily activities can prevent flare-ups. Being mindful and making small changes can help manage symptoms. Here are some tips:
- Avoid crossing your legs or ankles when sitting.
- Use canes or walkers to reduce hip strain.
- Be careful when getting in and out of cars or beds.
By making these lifestyle changes, you can reduce flare-ups and improve your life with trochanteric bursitis.
Walking with Bursitis: Do’s and Don’ts
Trochanteric bursitis can make walking hard. It’s important to know how to walk with it. Walking is basic but can be tough with trochanteric bursitis. Knowing how to manage it helps keep you moving and lessens pain.
Is Walking Good for Bursitis of the Hip?
Walking can help hip bursitis by keeping the joint moving and building muscle. But it’s important to walk carefully so as not to make it worse. “Walking with trochanteric bursitis should be done in moderation,” as too much can cause more pain and swelling.
Proper Walking Technique
Walking right is key to not putting too much stress on your hip. Keep your back straight, don’t take big steps, and wear the right shoes. Good walking technique can help avoid flare-ups by spreading out the impact.
Footwear Considerations
The right shoes are important for walking with trochanteric bursitis. Look for shoes with good arch support and cushioning. Shoes made for walking or running are best because they support and absorb shock better.
When to Limit Walking
Sometimes, you need to cut back on walking to manage trochanteric bursitis. If walking hurts a lot, you might need to walk less or for shorter times.
“Rest and recovery are key to managing trochanteric bursitis,” and knowing when to stop is part of that.
Conclusion: Living Well with Trochanteric Bursitis
Managing trochanteric bursitis well means using medical treatments, changing your lifestyle, and doing the right exercises. Knowing what makes hip bursitis worse and staying away from hard activities can help a lot.
We’ve looked at ways to handle hip bursitis, like doing gentle exercises, swimming, and doing yoga safely. Also, making your home and work places better for your hips, using aids, and keeping a healthy weight can help a lot.
Dealing with trochanteric bursitis needs a big plan. By using treatment tips every day, you can cut down on bad days and feel better. We suggest you get involved in your care. Work with doctors to make a plan that’s just right for you.
FAQ
What is trochanteric bursitis, and how does it occur?
Trochanteric bursitis occurs when the bursa near the hip joint becomes inflamed. It’s often caused by doing the same thing over and over, getting hurt, or having other health issues. This leads to pain on the outside of the hip.
What activities aggravate hip bursitis?
Running, jumping, and playing contact sports can make hip bursitis worse. Some strength training and stretches can also irritate the hip.
Are there specific exercises to avoid with trochanteric bursitis?
Yes, people with trochanteric bursitis should stay away from high-impact activities. Avoid deep squats and stretches that bother the hip, like some IT band stretches.
Can daily activities trigger or exacerbate pain in trochanteric bursitis?
Yes, sitting, sleeping, standing, and walking can make pain worse if not done right. Changing how you do these activities can help ease the pain.
Is cycling good for hip pain caused by bursitis?
Cycling can be good or bad, depending on your condition and bike setup. Adjusting the saddle height can help make it more comfortable.
How can I manage trochanteric bursitis pain with heat or ice?
Use ice for sudden inflammation and heat for long-term pain. Switching between them or using them at different times can help.
Can massage help alleviate bursitis symptoms?
Massage can ease bursitis symptoms by relaxing muscles and improving blood flow. But, avoid certain massages and use professional techniques.
What role does physical therapy play in managing trochanteric bursitis?
Physical therapy includes exercises, kinesio taping, and tests to diagnose and treat trochanteric bursitis. It helps track progress and customize treatment.
Are there lifestyle changes that can reduce bursitis flare-ups?
Yes, staying at a healthy weight, making ergonomic changes, using supportive devices, and being careful with daily activities can help prevent flare-ups.
Is walking beneficial or harmful for hip bursitis?
Walking can be good for hip bursitis if done correctly, with the right technique and shoes. But it might need to be limited during bad flare-ups.
What are some safe exercises for trochanteric bursitis?
Gentle strengthening, water-based exercises, and modified yoga are safe. It’s important to choose exercises that are good for seniors, too.
References
- Reid, D. (2016). The management of greater trochanteric pain syndrome: A systematic literature review. Journal of Orthopaedics, *13*(1), 15–28. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4761624/




































