Did you know that over 7 million people in the United States suffer from bone fractures every year?
A bone fracture is a serious injury that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. There are four main categories of fractures: simple, compound, comminuted, and greenstick.
Understanding the different types of fractures is key for proper diagnosis and treatment. In this article, we will explore each type’s characteristics and discuss treatment options.
Key Takeaways
- There are four main categories of bone fractures.
- Simple bone fractures are clean breaks with minimal damage.
- Compound bone fractures involve breaks in the skin.
- Comminuted bone fractures involve multiple fragments.
- Greenstick bone fractures are incomplete breaks, typically in children.
Understanding Bone Fractures
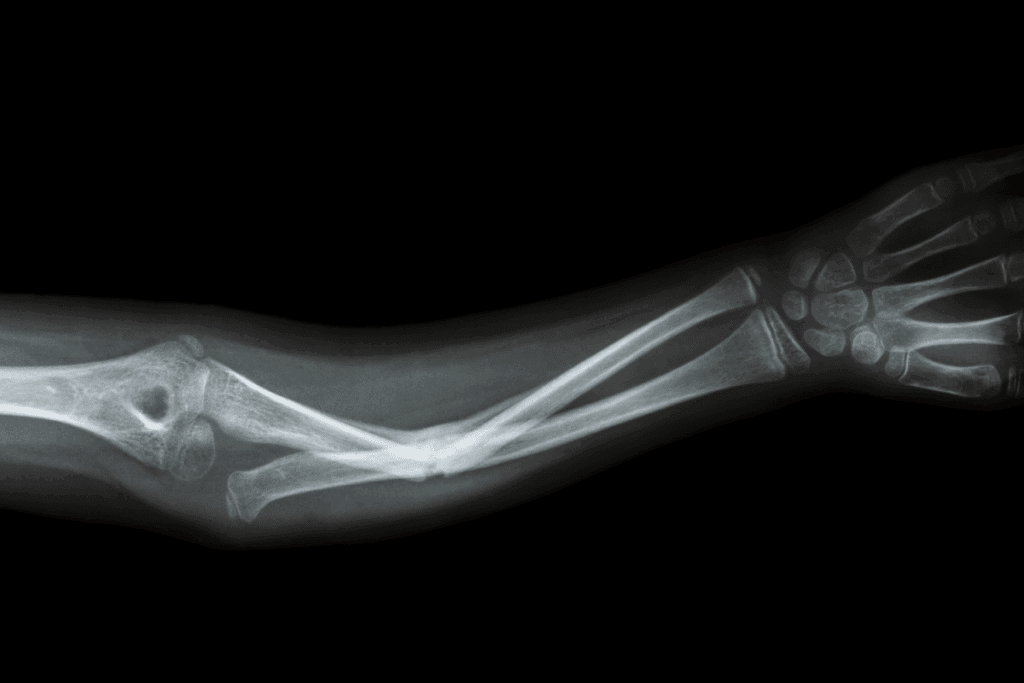
It’s key to know the basics of bone fractures for diagnosis and treatment. Bone fractures happen when a bone breaks or cracks. This is due to injury, falls, or trauma.
Definition and Basic Concepts
A bone fracture is when a bone cracks or breaks. This can be from injury, falls, or trauma. Knowing how to classify fractures is important for treatment.
Closed vs. Open Fractures: A closed fracture means the bone is broken but the skin is not. An open fracture, on the other hand, has a break in the skin. This can lead to infection risks.
How Bones Break
Bones can break in different ways. This depends on the force and direction of the impact. Common types include transverse, oblique, and spiral fractures.
| Fracture Type | Description |
| Transverse | A straight break across the bone |
| Oblique | A diagonal break across the bone |
| Spiral | A break that twists around the bone |
The 4 Main Types of Bone Fractures
There are four main types of bone fractures. Each has its own features. Knowing these helps doctors choose the right treatment and predict how well a patient will do.
Simple (Closed) Fractures
A simple fracture happens when a bone breaks but doesn’t go through the skin. This kind is usually less serious and might not need surgery.
Compound (Open) Fractures
A compound fracture is more serious. The bone breaks through the skin, raising the chance of infection. Quick medical care is key to avoid problems.
Comminuted Fractures
Comminuted fractures are when a bone breaks into many pieces. These often need surgery to fix the bone pieces.
Greenstick Fractures
Greenstick fractures are common in kids. The bone bends and partially breaks, like a green stick. These are usually less serious and can heal fast.
| Fracture Type | Description | Severity |
| Simple (Closed) | Bone breaks but doesn’t pierce skin | Low |
| Compound (Open) | Bone breaks through skin | High |
| Comminuted | Bone shatters into multiple pieces | High |
| Greenstick | Bone bends and partially breaks | Moderate |
It’s important for doctors to know the type of fracture to treat it right. Each fracture is different and needs a special plan for healing and to avoid complications.
Simple (Closed) Fractures in Detail
Closed fractures, also known as simple fractures, happen when a bone breaks but the skin stays whole. This is different from open fractures, where the bone goes through the skin and can get infected. Simple fractures can be divided into types based on how they break and their pattern.
Characteristics and Appearance
A simple fracture means the bone breaks but there’s no cut on the skin. It can be nondisplaced, where the bone stays in line, or displaced, needing to be fixed. Doctors use X-rays to see how bad the fracture is.
“The skin’s condition is key in telling if it’s a closed fracture,” doctors say.
Treatment Approaches
For simple fractures, doctors usually use casts or braces to help the bone heal. Sometimes, surgery is needed for more complex cases. The healing process of fractures depends on how bad the break is, the patient’s health, and following treatment.
It’s important for doctors to keep an eye on how the fracture heals. This helps avoid any problems and makes sure the bone heals right.
Knowing about simple fractures helps doctors diagnose and treat them better. By understanding these fractures and using the right treatments, patients can get better faster.
Compound (Open) Fractures in Detail
Compound fractures, also known as open fractures, are very serious. The bone breaks through the skin, making a wound. This makes it harder for the bone to heal and raises the chance of infection.
The Gustilo-Anderson classification system helps figure out how bad these fractures are. It guides doctors on how to treat them.
Severity Classifications
The Gustilo-Anderson system breaks open fractures into three levels. Each level shows how severe the injury is.
| Type | Description |
| Type I | Wound less than 1 cm, minimal soft tissue injury |
| Type II | Wound larger than 1 cm but less than 10 cm, moderate soft tissue damage |
| Type III | Extensive soft tissue damage, often with significant contamination |
Infection Risks and Management
Open fractures are at high risk for infection. Prompt treatment is key to reduce this risk. Doctors clean the wound, give antibiotics, and might need to operate to fix the bone and soft tissues.
It’s important to understand the severity and manage the risks of open fractures. This is key for effective treatment and recovery.
Comminuted Fractures in Detail
Comminuted bone fractures are tough to treat because they break into many pieces. This makes healing harder.
Challenges in Treatment
Fixing these fractures is hard because of the many bone pieces. Surgical intervention is often required to fix the bone. This helps it heal right.
The fracture’s complexity can lead to complications such as infection or malunion. So, careful management is key.
Recovery Expectations
Getting better from a comminuted fracture needs a comprehensive rehabilitation plan. This includes physical therapy to build strength and mobility. The healing process of fractures takes time.
Patient compliance with the treatment plan is essential for the best recovery. Knowing what to expect helps patients prepare for the journey ahead.
Greenstick Fractures in Detail
The greenstick fracture looks like a green branch breaking. It’s a common fracture in kids. This fracture happens when a bone bends and partially breaks, unlike a complete break.
Children’s bones are more flexible and less likely to break completely. This is why greenstick fractures are common in them.
Common in Children
Greenstick fractures are common in children because their bones are growing and flexible. When a force, like a fall, is applied, the bone bends and cracks on one side. This is unlike adult bones, which tend to break completely.
This fracture often occurs in the forearm. Kids usually use their arms to break their fall.
Healing Process
The healing process of fractures like greenstick fractures is usually straightforward. Children’s bones can grow and heal quickly. This means greenstick fractures often heal fast and without major issues.
Treatment usually involves a cast to help the bone heal. Sometimes, the bone needs to be gently moved back into place. It’s important for a healthcare provider to monitor the healing process to avoid long-term problems.
Comprehensive Types of Bone Fractures Classification
Beyond the main four types, bone fractures are further categorized into several other classifications. These classifications are based on the fracture pattern, location, and other factors. This detailed classification helps us understand the complexity of bone fractures and find the best treatment.
Transverse, Oblique, and Spiral Fractures
Transverse, oblique, and spiral fractures are classified by the direction and pattern of the fracture line. A transverse bone fracture happens straight across the bone, often from a direct blow. An oblique bone fracture has an angled or diagonal line, caused by bending and twisting forces. A spiral bone fracture, or torsion fracture, occurs when a bone twists, leading to a spiral fracture line. These fractures are common in sports injuries and accidents.
To diagnose these fractures, doctors use imaging like X-rays or CT scans. Treatment depends on the fracture’s severity and location. It can range from a cast to surgery with plates and screws.
Stress, Avulsion, and Pathological Fractures
Stress bone fractures, or fatigue fractures, happen from repeated stress or strain. They are common in athletes in high-impact sports. Avulsion bone fractures occur when a tendon or ligament pulls off a bone piece, often from sudden contraction or trauma. Pathological bone fractures happen in weakened bones due to diseases like osteoporosis or cancer.
| Fracture Type | Cause | Common Locations |
| Stress Fracture | Repeated stress or strain | Lower limbs, specially the tibia and metatarsals |
| Avulsion Fracture | Tendon or ligament pull-off | Various, depending on the tendon or ligament involved |
| Pathological Fracture | Underlying bone disease | Any bone weakened by disease |
Knowing these classifications is key for healthcare providers to diagnose and treat bone fractures well. The treatment plan is customized based on the fracture type, the patient’s health, and the fracture’s severity.
Impacted and Hairline Fractures
Bone fractures come in different forms, with impacted and hairline fractures being quite subtle yet important. They need careful diagnosis and treatment to avoid further issues.
Identifying Subtle Fractures
Finding subtle fractures like hairline fractures is hard because they show little sign of damage. A hairline fracture happens when a bone gets stressed or forced too much. To spot these, doctors use X-rays or MRI scans.
Treatment Considerations
Treatment considerations for these fractures include rest, managing pain, and sometimes surgery. For impacted fractures, making sure the bone pieces fit right is key to avoid problems. The aim is to fix the bone and help you get back to your usual activities.
Displaced vs. Nondisplaced Fractures
It’s important to know the difference between displaced and nondisplaced fractures for good treatment. Fractures are sorted by how much the bone moves. This affects how we treat them.
A displaced fracture happens when a bone breaks into pieces that move apart. This usually needs surgery to fix. A nondisplaced fracture is when a bone cracks but doesn’t move much. It’s often treated without surgery.
Diagnostic Differences
Doctors use physical checks and images to tell if a fracture is displaced or not. X-rays are key for seeing how much the bone has moved. Sometimes, CT scans or MRIs are needed to see the full picture.
For displaced fractures, images help figure out how much the bone has moved. This is key for planning surgery.
Treatment Approaches
Displaced fractures usually need surgery to fix the bone. This can involve using plates, screws, or rods to hold the bone in place.
Nondisplaced fractures are treated with casts or splints. We also use pain meds and watch the healing to avoid problems.
Intraarticular and Burst Fractures
Understanding intraarticular and burst fractures is key for managing these complex bone injuries. Intraarticular fractures happen inside the joint. They can lead to arthritis and limited mobility if not treated right. Burst fractures are tough, with a bone fragment displaced into the surrounding tissue. They are even harder when they happen in the spine.
Joint Involvement Complications
Intraarticular fractures affect the joint surface. Accurate reduction and stable fixation are vital to avoid long-term joint problems. Complications include post-traumatic osteoarthritis, joint stiffness, and instability. The severity of these issues depends on the fracture’s complexity and the treatment’s quality and timing.
Effective management might need surgery to fix the joint surface and ensure stability. This helps in early mobilization and lowers the risk of long-term problems.
Spinal Considerations
Burst fractures of the spine are unstable and can cause serious neurological problems. The treatment usually involves surgery to fix the spine and prevent further injury. Factors to consider include the fracture’s location, how much of the vertebral body is involved, and any neurological deficits.
Advanced imaging like MRI and CT scans are vital for assessing the injury and planning surgery.
Common Causes of Bone Fractures
Bone fractures can happen for many reasons. Each reason has its own risk factors and effects on bone health. Knowing these causes helps us prevent and treat fractures better.
Traumatic Injuries
Traumatic injuries often lead to bone fractures. These injuries can come from falls, car accidents, or direct hits to the bone. The force from these incidents can break or fracture the bone.
Sports-Related Fractures
Sports injuries are common in athletes, mainly in high-impact sports. Football, basketball, and gymnastics can lead to fractures from falls, collisions, or overuse. Using proper training, equipment, and safety can lower this risk.
Age-Related Vulnerability
As people get older, their bones weaken. This makes them more likely to get fractures. Osteoporosis, a condition of weak bones, is common in the elderly. It raises the risk of fractures even more.
| Cause | Description | Risk Factors |
| Traumatic Injuries | Fractures due to falls, accidents, or direct blows | High-impact activities, poor safety measures |
| Sports-Related Fractures | Fractures occurring during sports activities | Participation in high-impact sports, inadequate training |
| Age-Related Vulnerability | Increased fracture risk due to aging | Osteoporosis, decreased bone density |
Recognizing Fracture Symptoms
It’s important to know the signs of a fracture to get help quickly. Fractures happen from falls, accidents, or sports injuries. Spotting these signs can lead to the right care.
Obvious Signs
Some fracture symptoms are clear right away. Look for severe pain at the injury site, deformity or odd limb position, and swelling or bruises. If the bone looks out of place or the skin is broken, it’s a serious injury.
Subtle Indicators
Not all fractures show obvious signs. Some have subtle indicators like mild pain that gets worse or pain when you move the bone. Knowing these signs is key, as they might mean you need to see a doctor.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to get medical help is vital. If you have severe pain, deformity, or trouble moving the limb, get help right away. If you think you might have a fracture, don’t wait. Quick treatment can avoid serious problems and help you heal better.
| Symptom | Description | Action |
| Severe Pain | Pain that is intense and unrelenting | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Deformity | Visible deformity or unnatural positioning | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Mild Pain | Pain that worsens over time | Schedule a medical appointment |
Diagnosis of Bone Fractures
Diagnosing bone fractures needs a mix of clinical checks and new tech. Getting the diagnosis right is key for good treatment and recovery. So, the first check is very important for patient care.
Physical Examination
The first step is a physical check. It looks at the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and does a clinical check. This is to find signs of a fracture, like deformity, swelling, or tenderness.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging is key to confirm a bone fracture. X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans are used. Each has its own benefits and is picked based on the fracture’s type and where it is.
| Imaging Modality | Advantages | Common Uses |
| X-ray | Quick, widely available | Initial assessment of fractures |
| CT Scan | High detail, useful for complex fractures | Detailed assessment of fracture patterns |
| MRI | Excellent soft tissue detail | Assessing soft tissue injuries associated with fractures |
Advanced Diagnostic Methods
For some fractures, more advanced tests are used. These include 3D CT scans and bone scans. They help see how bad the fracture is or how it’s healing.
Treatment Options for Different Types of Bone Fractures
Different bone fractures need different treatments to heal right. The right treatment depends on the fracture type, how bad it is, the patient’s health, and if there are any complications.
Conservative Management
For simple or nondisplaced fractures, conservative management is often the best choice. This method uses a cast or splint to let the bone heal on its own. Patients are told not to put weight on the affected area and to watch their condition closely.
Benefits of conservative management include avoiding surgery risks and sometimes shorter recovery times. But, it’s key to follow a healthcare provider’s advice for proper healing.
Surgical Interventions
For complex fractures like compound or comminuted ones, surgery is needed. Surgery realigns and stabilizes the bone fragments using plates, screws, or rods. This helps the bone heal properly.
Advances in surgical techniques have made treating complex fractures better. But, surgery comes with risks, so patients need close monitoring during recovery.
Rehabilitation Strategies
Rehabilitation is key for bone fracture healing. It includes exercises and physical therapy to regain strength, flexibility, and function. The plan is made based on the patient’s needs and the fracture type.
A good rehabilitation program can greatly improve recovery, lower complication risks, and help patients get back to their usual activities.
Prevention Strategies and Risk Reduction
Bone fracture prevention is possible with lifestyle modifications and health care. Knowing the risks and using prevention methods can lower fracture chances.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle adjustments is key to avoiding bone fractures. Regular exercise, like weight-bearing activities, strengthens bones and improves balance. Also, eating a diet full of calcium and vitamin D is important for bone health.
Bone Health Maintenance
Bone health maintenance means regular health checks and screenings. It’s important to get enough calcium and vitamin D, either from food or supplements. Also, not smoking and drinking less alcohol helps keep bones strong.
Special Considerations for Athletes and Elderly
Athletes and the elderly need special considerations to avoid fractures. Athletes should wear the right gear and join injury prevention programs. The elderly can benefit from home safety changes and exercises to boost balance and strength.
Conclusion
Bone fractures are a common injury that can really affect someone’s life. We’ve looked at the different types of bone fractures in this article. This includes simple, compound, comminuted, and greenstick fractures, along with their causes.
Managing bone fractures well starts with a correct diagnosis and the right treatment. Knowing what each fracture type is helps decide the best treatment. This could be non-surgical or surgery.
Fracture prevention is key to keeping bones healthy. Making lifestyle changes, keeping bones dense, and being careful, can lower fracture risk. This is true for athletes and the elderly too.
In conclusion, knowing about fractures and getting the right care is vital. Understanding fracture types and treatments helps achieve the best treatment outcomes. It also reduces the chance of long-term problems.
FAQ
What are the main differences between simple and compound fractures?
Simple fractures happen when a bone breaks but the skin stays intact. Compound fractures, on the other hand, occur when the bone breaks through the skin. This makes compound fractures more likely to get infected.
How are comminuted fractures treated?
Comminuted fractures, where bones break into pieces, usually need surgery. The goal is to put the bone pieces back together and stabilize them. After surgery, a rehabilitation program helps the bone heal.
What is a greenstick fracture, and who is it most common in?
A greenstick fracture is when a bone bends but doesn’t fully break. It’s common in kids because their bones are softer and more flexible.
What are the characteristics of a stress fracture?
Stress fractures are tiny cracks in bones caused by repeated stress. They often happen in athletes or anyone who is very active.
How do doctors diagnose bone fractures?
Doctors first do a physical check-up. Then, they use X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to see if there’s a fracture and how bad it is.
What are the treatment options for displaced fractures?
For displaced fractures, where the bone is out of place, surgery might be needed. After that, the bone is immobilized and the patient goes through a rehabilitation program to heal properly.
Can fractures be prevented?
Some fractures can’t be avoided, but a healthy lifestyle can help. Eating right, exercising regularly, and not putting too much stress on bones can lower the risk of fractures.
What are the risks associated with intraarticular fractures?
Intraarticular fractures can cause arthritis, limited mobility, and chronic pain if not treated right. This is because they involve the joint.
How do age-related changes affect bone health?
As we get older, our bones get weaker and more likely to break. This is because of conditions like osteoporosis.
What are the symptoms of a fracture?
Fracture symptoms include a lot of pain, swelling, bruising, and the bone looking different. It’s also hard to move the affected area.
What is the healing process for fractures?
Healing a fracture goes through stages like inflammation and bone resorption. It ends with the bone getting strong again and working properly.
Are there any special considerations for athletes with fractures?
Athletes need careful management to heal properly and avoid getting hurt again. This includes a slow return to activity and specific rehabilitation plans.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024). Older adult falls and fracture prevention. CDC. Retrieved October 2025, from https://www.cdc.gov/falls/prevention/index.html