Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir

Breast cancer is a big problem for women all over the world, and finding it early is key to treating it well. Ultrasound technology plays an important role in spotting abnormal lumps and identifying signs of a bad ultrasound that may suggest cancer. It helps doctors tell the difference between harmless and cancerous tumors.
Doctors use breast cancer ultrasound to look at lumps closely. They check the lump’s shape, size, and edges. This helps figure out if the lump is bad or not.
Key Takeaways
- Ultrasound is a key diagnostic tool for detecting breast cancer.
- Malignant lumps have distinct characteristics on ultrasound.
- Early detection improves treatment outcomes.
- Breast tumor ultrasound helps in differentiating between benign and malignant tumors.
- Regular check-ups are important for women’s health.
Understanding Breast Ultrasound Technology
It’s key for doctors and patients to know about breast ultrasound technology. This method uses sound waves to see inside the breast. It’s a non-invasive way to check for lumps and other issues.
Breast ultrasound is vital for spotting problems early. It works alongside mammograms to give a clearer picture. This helps doctors figure out if a lump is serious or not.
How Breast Ultrasound Works
Breast ultrasound sends sound waves into the breast. These waves bounce back and are caught by a transducer. The computer then makes detailed images from this info.
This method is safe and doesn’t use radiation. It’s painless. The images help doctors understand what a lump is like. This is important for deciding what to do next.
Types of Ultrasound Equipment Used

There are many ultrasound tools for checking the breast. These include:
- Handheld devices that are easy to move around.
- Automated whole breast ultrasound (AWBU) systems for a full view.
- 3D and 4D ultrasound for detailed, moving images.
Knowing the different tools is important for doctors. It helps them pick the best one for each patient. This makes care better and more accurate.
The Role of Ultrasonography of Breast in Cancer Detection
Breast ultrasound is key in finding breast cancer early, mainly for women with dense breasts. It’s a great tool that works well with mammograms. Together, they help spot cancerous lumps better.
When Ultrasound is Recommended
Ultrasound is best for women with dense breasts. It can find tumors that mammograms miss. It’s also used to check out lumps that feel different.
Using ultrasound as a second check for women with dense breasts,” they say. This shows how important it is for breast health.
Complementary Role to Mammography
Ultrasonography works with mammography to give clear images of the breast. This combo is great for spotting and figuring out breast lesions.
Using both ultrasound and mammography can make finding cancer more accurate. This is true when mammograms aren’t clear enough.
Advantages for Dense Breast Tissue
Dense breasts make mammograms less reliable because both look white. Ultrasound is better at telling apart dense tissue and cancer. It’s a big help for women with dense breasts.
Adding ultrasound to breast cancer screening can really help find cancer early. This can lead to better treatment results.
Characteristics of Malignant Breast Lumps on Ultrasound
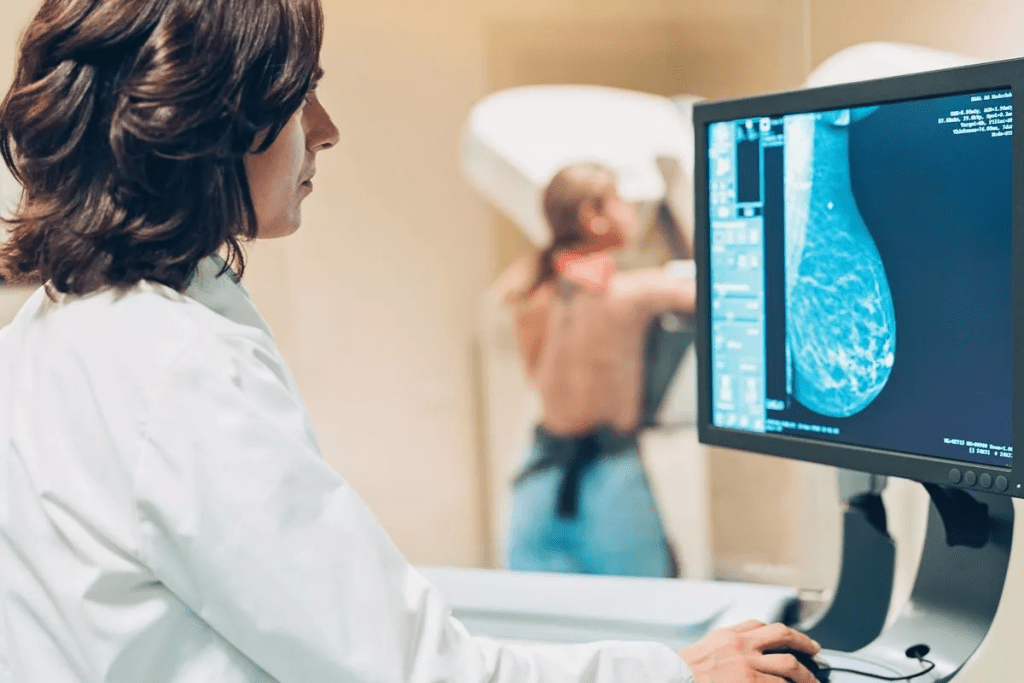
Ultrasound imaging is key in spotting the difference between benign and malignant breast tumors. It gives a clear look at the inside of the breast. This helps doctors make accurate diagnoses.
Shape and Margin Features
Malignant lumps in the breast are often irregular in shape and have spiculated or angular margins. This is different from benign lumps, which are usually smooth and round. The irregular shape and spiculated margins show the tumor is invasive.
The shape and margins are vital in figuring out if a lump is malignant. Lumps with irregular shapes and spiculated margins are more likely to be cancerous.
Echo Patterns in Malignant Tumors
The echo pattern of a breast lump is also important. Malignant tumors usually look hypoechoic, which means they are darker than the surrounding tissue. This is because they have a dense cellular structure.
Also, malignant tumors can have heterogeneous echo patterns. This means their cellular density varies. Such heterogeneity can indicate the tumor’s aggressiveness.
Posterior Acoustic Features
Posterior acoustic features are what appear behind a breast lump on ultrasound. Malignant tumors often cause posterior acoustic shadowing. This looks like a dark area behind the tumor. It’s because the tumor’s dense structure absorbs or scatters ultrasound waves.
In some cases, malignant tumors might also show posterior acoustic enhancement. But this is less common. The presence of these features helps doctors diagnose malignant breast lumps.
Visual Guide: Breast Cancer Ultrasound Images
Understanding breast ultrasound images is key for good treatment plans. This tool gives detailed views of the breast tissue. It helps doctors spot any issues.
Common Appearances of Malignant Tumors
Malignant tumors show certain signs on ultrasound. These signs include irregular shapes and unclear edges. They also have mixed echo patterns.
Some common signs of malignant tumors on ultrasound are:
- Hypoechoic lesions with irregular borders
- Tumors with spiculated or microlobulated margins
- Lesions that are taller than they are wide
Breast Tumor Ultrasound Pictures
Ultrasound pictures of breast tumors offer important clues. Doctors use these images to guess if a tumor is cancerous. They then decide the best treatment.
| Ultrasound Feature | Malignant Characteristics |
| Shape | Irregular, spiculated, or microlobulated |
| Margins | Poorly defined, angular, or indistinct |
| Echo Pattern | Heterogeneous, hypoechoic |
How to Interpret Dark Areas on Breast Ultrasound
Dark areas on breast ultrasound images can mean different things. They could be cysts, tumors, or other issues. It’s important to look at their size, shape, and edges.
Doctors check dark areas for:
- Size and shape: Larger or odd-shaped dark areas are more worrying.
- Margins: If the edges are unclear or odd, it might be cancer.
- Internal echo pattern: The presence or lack of echoes inside helps tell if it’s cancerous.
By studying these details, doctors can make better diagnoses. They can then plan the best treatments.
Benign vs. Malignant: Comparative Ultrasound Features
It’s important to know the difference between benign and malignant breast lumps on ultrasound. This technology helps doctors tell these lumps apart by looking at their features.
Key Differentiating Factors
There are key factors that help tell benign from malignant lumps on ultrasound. These include the shape, margin, echo pattern, and how sound waves bounce off the lump.
- Shape and Margin: Benign lumps are usually round and have clear edges. Malignant lumps are often irregular and have unclear or jagged edges.
- Echo Pattern: The echo pattern inside the lump can also tell us if it’s benign or malignant. Benign lumps have a uniform echo, while malignant lumps have a non-uniform or dark echo.
- Posterior Acoustic Features: The area behind the lump can also give clues. Benign lumps may show an enhancement, while malignant lumps can cause shadowing.
| Feature | Benign Characteristics | Malignant Characteristics |
| Shape | Regular, oval | Irregular, lobulated |
| Margin | Well-defined, circumscribed | Indistinct, spiculated |
| Echo Pattern | Uniform, hyperechoic or isoechoic | Non-uniform, hypoechoic |
| Posterior Acoustic Features | Enhancement | Shadowing |
Common Benign Findings
Benign breast lumps have specific features on ultrasound that help doctors tell them apart from malignant lumps. Common benign findings include:
- Cysts, which are fluid-filled and appear anechoic with posterior enhancement.
- Fibroadenomas, which are solid, hypoechoic or isoechoic lesions with well-defined margins.
Knowing these features is key for accurate diagnosis and avoiding unnecessary biopsies. By understanding the ultrasound features of benign and malignant breast lumps, healthcare professionals can make better decisions for patient care.
BI-RADS Classification System for Breast Ultrasound
Understanding the BI-RADS classification is key to accurately reading breast ultrasound results. The Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) is a widely accepted standard. It categorizes breast imaging findings, including those from ultrasound.
Understanding the Categories
The BI-RADS system has categories from 0 to 6. Each category shows a different level of suspicion for cancer.
- BI-RADS 0: Additional imaging evaluation is needed.
- BI-RADS 1: Negative, routine screening recommended.
- BI-RADS 2: Benign finding(s), non-cancerous.
- BI-RADS 3: Probably benign, short-term follow-up recommended.
- BI-RADS 4: Suspicious abnormality, biopsy should be considered.
- BI-RADS 5: Highly suggestive of malignancy, appropriate action should be taken.
- BI-RADS 6: Known biopsy-proven malignancy prior to definitive treatment.
Table: BI-RADS Categories and Management Recommendations
| BI-RADS Category | Assessment | Management Recommendation |
| 0 | Incomplete | Additional imaging |
| 1 | Negative | Routine screening |
| 2 | Benign | Routine screening |
| 3 | Probably Benign | Short-term follow-up |
| 4 | Suspicious | Biopsy |
| 5 | Highly Suggestive of Malignancy | Appropriate action |
| 6 | Known Biopsy-Proven Malignancy | Definitive treatment |
Risk Assessment and Management Recommendations
The BI-RADS category affects the recommended management. Categories 1 and 2 show a low risk of cancer. Categories 4 and 5 suggest a higher risk, needing further tests like biopsy.
Reporting Terminology
Standardized reporting is vital for clear communication. The BI-RADS lexicon helps describe breast imaging findings. It ensures consistent reporting and decision-making.
Types of Breast Cancer and Their Ultrasound Appearances
Breast cancer is not just one disease. It’s a group of different types, each with its own look on ultrasound. Knowing these differences is key for accurate diagnosis and planning treatment.
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) is the most common breast cancer. It starts in the milk ducts and spreads to the surrounding tissue. On ultrasound, IDC looks like a
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) starts in the lobules of the breast. It can be hard to spot on ultrasound because it grows in a diffuse way. ILC might look like a slight asymmetry or a vaguely defined mass. It’s common for ILC to be missed or underestimated on ultrasound.
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS)
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a non-invasive cancer where cells stay in the milk ducts. On ultrasound, DCIS might look like microcalcifications or a hypoechoic lesion with ductal extension. But, DCIS is often hard to see on ultrasound and mammography might be better for finding it.
Other Less Common Types
There are other less common types of breast cancer, like medullary carcinoma, mucinous carcinoma, and papillary carcinoma. Each type can have its own ultrasound features. For example, medullary carcinoma often looks like a well-circumscribed mass with posterior enhancement. Mucinous carcinoma might show as a hypoechoic lesion with internal heterogeneity.
It’s very important to accurately identify breast cancer types on ultrasound for the right treatment. While some features are typical of certain cancers, a biopsy is always needed for a sure diagnosis.
Stage1 Early Breast Cancer on Ultrasound
Early detection of breast cancer is key to better treatment outcomes. Ultrasound is a vital tool in spotting stage 1 breast cancer. Finding cancer early means better chances of successful treatment and survival.
Characteristic Findings
Ultrasound shows stage 1 breast cancer as a small, irregular mass. This mass’s features are important for understanding its nature. Key features include:
- A hypoechoic pattern, showing the tumor is less echogenic than the tissue around it
- Irregular margins or a spiculated appearance
- Possible presence of microcalcifications, though these are more common in mammograms
These signs help tell apart benign and malignant lesions. Yet, not all cancerous tumors show these signs, making diagnosis tricky.
Challenges in Early Detection
Ultrasound has its benefits in finding breast cancer, but there are hurdles. Dense breast tissue can make spotting issues harder. The skill of the sonographer and the quality of the equipment also play big roles in accuracy.
Survival Rates with Early Detection
Women with stage 1 breast cancer have a much better survival rate than those diagnosed later. The American Cancer Society reports a 5-year survival rate of nearly 99% for localized breast cancer (stage 1). Early detection through ultrasound and timely treatment can significantly boost patient outcomes.
In summary, ultrasound is a valuable tool for early breast cancer detection. Understanding the signs of stage 1 breast cancer on ultrasound helps healthcare providers offer timely interventions. This improves survival rates for patients.
Advanced Breast Cancer Ultrasound Findings
Advanced breast cancer shows clear signs on ultrasound. These signs are key to spotting the disease’s progress.
Local Invasion Signs
One key sign is when cancer cells spread to nearby tissues. On ultrasound, this looks like:
- Infiltration into the pectoral muscle or chest wall
- Irregular margins with spiculations extending into adjacent breast tissue
- Loss of tissue planes between the tumor and surrounding structures
Lymph Node Involvement
Lymph nodes often show signs of cancer in advanced stages. Ultrasound can spot:
- Enlarged lymph nodes with abnormal morphology
- Cortical thickening or loss of the fatty hilum
- Nodal metastasis indicated by chaotic vascularity
Metastatic Indicators
In later stages, cancer can spread to other parts of the body. Ultrasound can hint at this through:
- Suspicious axillary lymph nodes that may indicate spread
- Tumor extension into the skin or underlying muscles
Knowing these signs is vital for proper diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer.
Sonography for Breast Lumps: Process and Experience
A breast ultrasound is a non-invasive test to check breast lumps. It helps find out if a lump is benign or cancerous.
What to Expect During the Procedure
You’ll lie on your back or side on an exam table for a breast ultrasound. A gel is applied to your skin for sound wave transmission. The sonographer then uses a transducer to capture images on a monitor.
The sonographer’s skill is key for clear images. They adjust the transducer to get the best view of your breast tissue.
Preparation Guidelines
Preparation for a breast ultrasound is simple. Wear a two-piece outfit for easy access. Don’t apply lotions or powders to your breast or underarm area.
Bring any past breast imaging studies. This helps the sonographer or radiologist compare findings.
Duration and Comfort Considerations
A breast ultrasound usually takes 15 to 30 minutes. Most people find it comfortable, with slight pressure from the transducer.
If you’re in pain, tell the sonographer. They can adjust their technique to ease your discomfort.
Communicating with Your Sonographer
Talking openly with your sonographer is important. Share any breast pain, surgeries, or concerns. This helps them focus on key areas and ensure a thorough exam.
“Clear communication between the patient and sonographer is essential for a successful breast ultrasound examination.”
– Expert in Breast Imaging
Knowing what to expect and how to prepare makes your breast ultrasound experience smoother and less stressful.
Technological Advancements in Breast Ultrasound
Ultrasound technology has changed how we find breast cancer early. New tools have made breast ultrasound more accurate and reliable.
3D and 4D Ultrasound
3D and 4D ultrasound are big steps forward in breast imaging. They give a clearer view of breast tissue. This helps doctors understand breast lumps better.
A study in the Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine found 3D ultrasound helps identify breast lesions better. This is key for correct diagnosis and treatment.
Elastography
Elastography is a new tool for breast ultrasound. It checks how soft or hard breast tissue is. This helps tell if a lump is cancer or not.
Experts say elastography is a great tool for checking breast lumps. It gives more info than regular ultrasound. This can mean fewer biopsies are needed.
Automated Whole Breast Ultrasound
Automated Whole Breast Ultrasound (AWBU) makes scanning easier. AWBU scans the whole breast. It takes detailed images for doctors to review.
- Improved detection of small lesions
- Enhanced visualization of breast tissue
- Standardized imaging protocol
AI-Assisted Interpretation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing how we read ultrasound images. AI looks for patterns and oddities that humans might miss.
“AI-assisted interpretation has the power to change breast cancer diagnosis. It can find more cancers and cut down on false alarms.” – Expert Opinion
Thanks to these new technologies, doctors can diagnose and treat breast cancer more accurately.
Limitations of Breast Ultrasound in Cancer Detection
Breast ultrasound is useful but has its limits. It’s important for doctors and patients to know these to make good choices about breast health.
Technical Constraints
One big issue with breast ultrasound is its tech limitations. The quality of images depends a lot on the ultrasound machine. Older machines might not show details as well as newer ones.
Also, the sound waves used can affect image quality. Higher frequency waves give better detail but don’t go as deep. Lower frequency waves go deeper but are less clear.
Another challenge is dense breast tissue. It’s hard to see tumors clearly because dense tissue looks similar to some tumors. This makes it tough to tell if a spot is cancerous or not.
Operator Dependency
Breast ultrasound depends a lot on who is doing it. The skill of the person doing the ultrasound greatly affects how good the images are and how accurate the diagnosis is. A skilled sonographer can spot problems and take the right pictures. But someone less experienced might miss important details.
This means the results can vary a lot. To fix this, training and quality checks are key. They help make sure everyone is doing a good job.
False Positives and Negatives
Breast ultrasound can also give false results. A false positive means it says there’s cancer when there isn’t. This can cause a lot of worry and extra tests. On the other hand, a false negative means it misses cancer. This can delay treatment and affect how well it works.
How often this happens depends on the machine and who is using it. Better technology and training can help reduce these mistakes.
Complementary Imaging Methods
Complementary imaging methods are key in improving breast cancer diagnosis. They work alongside ultrasound to give a clearer picture of breast health. This helps in catching cancer early.
Mammography
Mammography uses low-dose X-rays to see the breast tissue. It’s great for finding tumors that are too small to feel. It also spots cancers before symptoms show up.
Key Benefits: Finds breast cancer early, spots tiny changes, and is easy to get.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) creates detailed images of the breast. It’s best for women with dense breasts. It can find cancers that mammograms or ultrasound miss.
Advantages: Very good at finding cancer, great for dense breasts, and checks how far cancer has spread.
Tomosynthesis
Tomosynthesis, or 3D mammography, shows the breast in 3D. It takes X-rays from many angles. This method cuts down on false alarms and boosts cancer detection.
Molecular Breast Imaging
Molecular Breast Imaging (MBI) uses a tiny bit of radioactive material. It lights up areas in the breast that might have cancer. It’s very helpful for women with dense breasts.
| Imaging Method | Key Benefits | Specific Use Cases |
| Mammography | Early detection, detects microcalcifications | General screening, detecting early-stage cancers |
| MRI | High sensitivity, assesses cancer extent | Dense breast tissue, assessing cancer spread |
| Tomosynthesis | Reduces false positives, improves detection | Women with dense breast tissue, reducing callbacks |
| Molecular Breast Imaging | Highlights metabolic activity | Dense breast tissue, detecting cancers not visible on mammogram |
Using these imaging methods together helps doctors make more accurate diagnoses. This leads to better treatment plans for each patient.
When to Seek Medical Attention for a Breast Lump
A breast lump can worry you. Knowing the warning signs helps decide when to see a doctor. Not all lumps are cancer, but some signs mean you should get checked right away.
Warning Signs
Some signs mean you should see a doctor. These include:
- A new lump or thickening in the breast or underarm area
- Change in the size or shape of the breast
- Dimpling or puckering of the skin
- Redness or scaliness of the skin
- Nipple discharge or change in nipple position
If you see any of these, go see a doctor. Early detection is key to effective treatment.
Risk Factors to Consider
Some things can make you more likely to get breast cancer. These include:
- Family history of breast cancer
- Genetic mutations (BRCA1 and BRCA2)
- Personal history of breast cancer
- Radiation exposure
- Age (risk increases after 40)
Knowing these risk factors helps you and your doctor plan the best care.
Scheduling Your First Appointment
If you’re worried about a breast lump, make an appointment. At your visit, you’ll get:
- A thorough medical history
- Clinical breast examination
- Discussion of risk factors and symptoms
- Recommendations for further testing (e.g., ultrasound, mammogram)
Don’t hesitate to seek medical attention if you’re unsure about a breast lump. Your health is important, and early checks can save lives.
Follow-up Procedures After Suspicious Ultrasound Findings
When ultrasound results show something suspicious, figuring out what it is is key. This step is important to tell if the growth is harmless or could be cancerous.
Biopsy Types and Procedures
A biopsy is usually the next step for suspicious ultrasound results. There are different types of biopsies, each with its own use and benefits.
- Fine-needle aspiration biopsy: This is a small, non-invasive way to get cell samples with a thin needle.
- Core needle biopsy: It uses a bigger needle to take tissue samples, giving more detailed info about the lump.
- Surgical biopsy: Sometimes, removing the whole lump or a bigger tissue sample is needed for a closer look.
Monitoring Recommendations
Not every suspicious finding needs a biopsy right away. Sometimes, monitoring is suggested, mainly if the lump is likely to be harmless or if it’s needed to watch for changes over time.
Regular follow-up ultrasounds or other imaging tests might be advised to keep an eye on the lump’s size and shape. This helps spot any changes that could mean it’s turning into cancer.
Whether to do a biopsy or just monitor depends on several things. These include the lump’s characteristics, the patient’s medical history, and other important factors.
Conclusion
Ultrasonography of the breast is now a key tool in finding and managing breast cancer. It helps spot cancerous lumps, which is very important in dense breast tissue.
Ultrasound can tell the difference between cancerous and non-cancerous lumps by looking at their shape and sound patterns. The BI-RADS system helps doctors understand the risk and plan the next steps.
New technologies like 3D and 4D ultrasound, elastography, and AI help make breast cancer detection more accurate. Even though there are challenges, using ultrasound with mammograms and MRI makes diagnosis better.
In short, breast cancer ultrasound is a vital tool. It helps find cancer early, which can save lives. It’s important for women to get regular check-ups and stay informed about their breast health.
FAQ
What does breast cancer look like on an ultrasound?
Breast cancer on ultrasound looks like a hypoechoic mass. It has irregular margins and a non-uniform shape. Sometimes, it shows posterior acoustic shadowing or enhancement.
Can ultrasound detect breast cancer?
Yes, ultrasound is great for finding breast cancer. It works well in dense breast tissue, where mammograms might not be as good.
How does breast ultrasound work?
Breast ultrasound uses sound waves to make images of the breast. It helps see lumps, tumors, and other issues.
What is the BI-RADS classification system for breast ultrasound?
The BI-RADS system is used to report breast imaging findings. It includes ultrasound and helps decide what to do next.
What are the characteristics of a malignant breast lump on ultrasound?
Malignant lumps have irregular shapes and non-circumscribed margins. They also show hypoechoic echo patterns.
Can benign breast lumps be mistaken for cancer on ultrasound?
Yes, some benign lumps can look like cancer on ultrasound. This is why biopsies and more tests are needed.
What is the role of elastography in breast ultrasound?
Elastography checks tissue stiffness. It helps tell if a lesion is benign or malignant.
How do I prepare for a breast ultrasound?
No special prep is needed for a breast ultrasound. Wear something comfy and avoid lotions or deodorants on the day.
What are the limitations of breast ultrasound in cancer detection?
Ultrasound has its limits. It depends on the operator, can have false positives and negatives, and has technical issues.
What are the next steps after a suspicious ultrasound finding?
After a suspicious finding, you might need a biopsy, more imaging, or monitoring. This depends on the BI-RADS category and your situation.
Can ultrasound detect early-stage breast cancer?
Yes, ultrasound can find early-stage breast cancer. It’s very useful in dense breast tissue.
How does 3D/4D ultrasound contribute to breast cancer diagnosis?
3D/4D ultrasound gives detailed images of the breast. This can help better detect and understand breast lesions.
References
- Ovarian Cancer Guidelines. (2025). Medscape.
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/255771-guidelines
- European Society for Medical Oncology. (2025). ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines: Gynaecological Cancers.
https://www.esmo.org/guidelines/esmo-clinical-practice-guidelines-gynaecological-cancers
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. (2023). Ovarian cancer: recognition and initial management (NG122).