Gallbladder inflammation, or cholecystitis, is a serious condition. It can happen even without gallstones. We’re looking into why this happens, focusing on upper right abdominal pain. This pain is a warning sign that needs urgent attention.Learn the crucial causes of upper right abdominal pain (e.g., gallbladder inflammation without stones, hepatitis). Understand when to seek help immediately.
Acute acalculous cholecystitis is a dangerous condition. It mainly hits people who are very sick. Things like bile stasis, less blood flow, and bacteria play big roles in it. Knowing these causes helps doctors diagnose and treat it quickly.
Key Takeaways
- Acute acalculous cholecystitis is a severe inflammation of the gallbladder without gallstones.
- It mainly affects very sick, older, and frail patients.
- Bile stasis, reduced blood flow, and bacterial contamination are key causes.
- Upper right abdominal pain is a significant symptom.
- Timely diagnosis and treatment are key to avoiding serious problems.
Understanding Gallbladder Inflammation
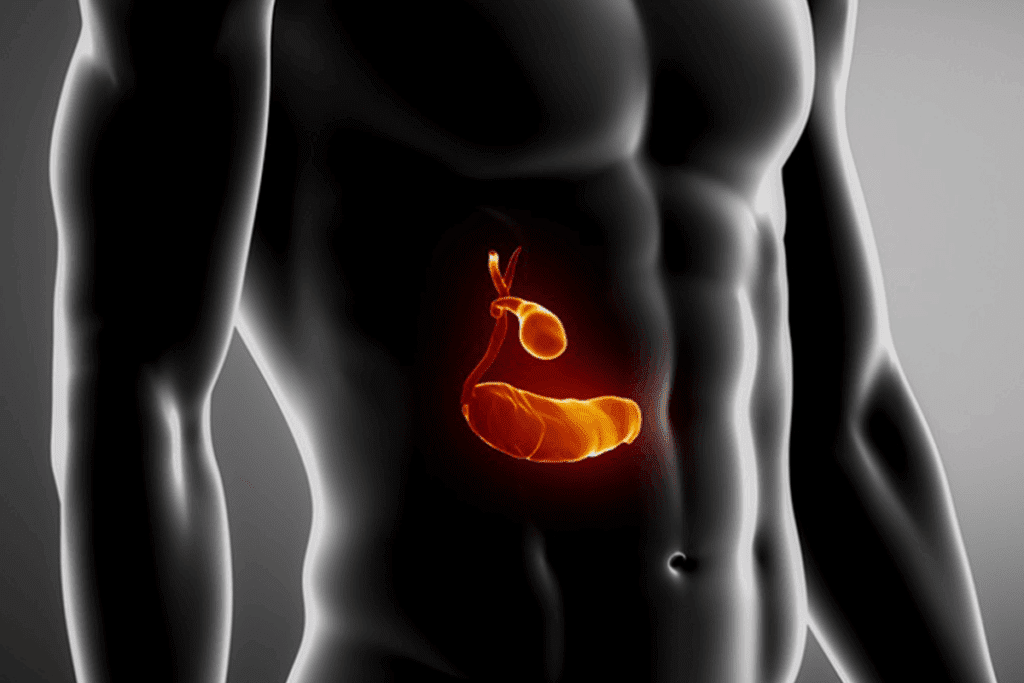
It’s important to know about gallbladder inflammation to treat it well. This condition, known as cholecystitis, can really affect someone’s life.
The Function of the Gallbladder
The gallbladder is a small sac under the liver. It stores bile, a liver-made fluid that helps digest food. When we eat, it releases bile into the small intestine.
This helps break down fats so our body can absorb them. It’s key for digesting and absorbing nutrients.
Types of Gallbladder Inflammation
Gallbladder inflammation comes in two types: calculous and acalculous cholecystitis. Calculous cholecystitis happens when gallstones block the cystic duct, causing inflammation. Acalculous cholecystitis, without gallstones, is more common in very sick patients.
Let’s look at the differences in the table below:
Characteristics | Calculous Cholecystitis | Acalculous Cholecystitis |
Gallstones | Present, often blocking the cystic duct | Absent |
Patient Profile | Typically seen in patients with a history of gallstones | Often occurs in critically ill or hospitalized patients |
Cause of Inflammation | Obstruction of the cystic duct by gallstones | Various factors including bile stasis, ischemia, and infection |
Symptoms | Severe abdominal pain, fever, nausea | Abdominal pain, fever, sometimes without typical gallbladder symptoms |
Knowing these differences helps doctors diagnose and treat better. Both types cause pain, but their causes and who they affect are different.
Calculous vs. Acalculous Cholecystitis: Key Differences
It’s important to know the differences between calculous and acalculous cholecystitis. This knowledge helps in making the right diagnosis and treatment. Cholecystitis, or inflammation of the gallbladder, can lead to serious problems if not treated right.
Stone-Related Inflammation (Calculous Cholecystitis)
Calculous cholecystitis happens when a gallstone blocks the cystic duct. This causes the gallbladder to get inflamed. It’s the main cause of cholecystitis, making up about 90% of cases.
The blockage stops bile from moving, leading to inflammation. If not treated quickly, it can cause serious problems.
Inflammation Without Stones (Acalculous Cholecystitis)
Acalculous cholecystitis, on the other hand, happens without gallstones. It’s often linked to critical illness, trauma, or long periods without eating. The exact reasons are not fully understood, but bile stasis, reduced blood flow, and infection are thought to play a role.
Prevalence and Risk Comparison
Calculous cholecystitis is more common, but acalculous cholecystitis has a higher mortality rate. This is because acalculous cholecystitis is linked to severe health issues. Even though it’s less common, diagnosing it is harder because its symptoms are not as clear.
Here’s a comparison of the two:
Characteristics | Calculous Cholecystitis | Acalculous Cholecystitis |
Gallstones | Present | Absent |
Common Causes | Gallstone obstruction | Critical illness, trauma, prolonged fasting |
Prevalence | Approximately 90% | Less common |
Knowing these differences helps doctors give better care. They can treat each patient in a way that suits their needs, improving results in this tough condition.
Pathophysiology: How Inflammation Develops Without Stones
To understand acalculous cholecystitis, we must look at the underlying causes. This condition is caused by many factors working together.
Bile Stasis and Its Effects
Bile stasis is a major cause of acalculous cholecystitis. When bile doesn’t move, it can cause inflammation and infection. This can happen due to fasting, surgery, or other blockages.
- Prolonged fasting or parenteral nutrition
- Major surgery or trauma
- Critical illness
Stagnant bile allows bacteria to grow, leading to infection. The bile can also become too thick, forming sludge, which makes things worse.
Reduced Blood Flow (Ischemia)
Ischemia, or reduced blood flow, is another important factor. It can be caused by shock, heart failure, or atherosclerosis.
Ischemia makes the gallbladder less able to clear bile. This makes it more likely to get infected. The lack of oxygen can also damage tissues, making inflammation worse.
The Inflammatory Cascade
The inflammatory cascade is a series of events that can harm tissues. In acalculous cholecystitis, it starts with bile stasis and ischemia.
It leads to the release of pro-inflammatory mediators. These attract more inflammatory cells to the gallbladder. This causes more inflammation and tissue damage. The process can keep going, leading to serious problems if not treated quickly.
Primary Causes of Acalculous Cholecystitis
It’s important to know what causes acalculous cholecystitis to manage it well. We’ll look at the main factors that lead to this condition.
Critical Illness and Trauma
Critical illness and trauma are big risks for acalculous cholecystitis. Patients in ICUs are at high risk because of their serious conditions and treatments. Trauma, from injury or surgery, can also cause acalculous cholecystitis by making the gallbladder inflamed and less functional.
Research shows that acalculous cholecystitis happens more often in patients with major trauma or critical illness. The reasons are complex, involving less blood flow to the gallbladder, bile stasis, and systemic inflammation.
Prolonged Fasting and Nutritional Factors
Prolonged fasting is another key factor in acalculous cholecystitis. Not eating for a long time can cause bile stasis and less gallbladder contraction, making inflammation more likely.
Nutrition also matters. Patients on total parenteral nutrition (TPN) are at higher risk because of the lack of food, which affects gallbladder movement. It’s important to provide the right nutrition to avoid this problem.
Vascular Insufficiency
Vascular insufficiency, or less blood flow to the gallbladder, is a big factor in acalculous cholecystitis. This reduced blood flow can cause ischemia and inflammation of the gallbladder wall.
Conditions that reduce blood flow, like shock, sepsis, or atherosclerosis, raise the risk of acalculous cholecystitis. Knowing about these vascular issues is key to diagnosing and treating the condition well.
Infectious Triggers of Gallbladder Inflammation
Gallbladder inflammation can come from many sources, like bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Knowing these causes helps doctors find and treat acalculous cholecystitis better.
Bacterial Infections
Bacteria often cause gallbladder inflammation. Pathogens such as E. coli, Klebsiella, and Streptococcus are common culprits. They can get into the gallbladder through the blood or by spreading from nearby tissues.
This can lead to serious inflammation and even life-threatening issues if not treated right away.
Viral Infections
Viruses can also cause gallbladder problems. Hepatitis A and Cytomegalovirus are viruses that can lead to inflammation. These viruses can harm the gallbladder directly or cause inflammation throughout the body.
In people with weakened immune systems, viral infections can be very severe. They might need special antiviral treatments.
Parasitic Causes
Parasites can also cause gallbladder inflammation, more so in certain areas. These parasites can infect the gallbladder and the biliary tract, causing inflammation and other issues.
It’s key to understand the parasitic causes of gallbladder inflammation. This knowledge helps in creating effective treatments, mainly in areas where parasites are common.
Medical Conditions Associated with Acalculous Cholecystitis
Some medical conditions can raise the risk of gallbladder inflammation without stones. Acalculous cholecystitis is often tied to various health issues. These issues can make the condition more complex.
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune disorders are a big risk for acalculous cholecystitis. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and scleroderma can cause inflammation in the gallbladder. The immune system’s wrong response can damage the gallbladder, raising the risk of inflammation.
Key autoimmune disorders associated with acalculous cholecystitis include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (lupus)
- Scleroderma
Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders
Diabetes and metabolic disorders also increase the risk of acalculous cholecystitis. Diabetes can harm the gallbladder’s function, leading to bile stasis and inflammation risk. Metabolic syndrome, with obesity, high blood pressure, and abnormal lipids, can also harm gallbladder health.
The mechanisms behind this association include:
- Impaired gallbladder motility
- Increased bile concentration
- Systemic inflammation
Post-Surgical Complications
Post-surgical complications are another big risk for acalculous cholecystitis. Patients who have had major surgery, or those with long hospital stays or total parenteral nutrition, are at higher risk. Surgery stress, fasting, and reduced gallbladder contraction can lead to acalculous cholecystitis.
Knowing these medical conditions is key for early diagnosis and treatment of acalculous cholecystitis. Healthcare providers can prevent and treat this condition by recognizing risk factors.
Upper Right Abdominal Pain: The Primary Symptom of Gallbladder Inflammation
Upper right abdominal pain is a key sign of gallbladder inflammation. This pain can be quite severe. It often makes people worry and seek medical help.
Characteristic Pain Patterns and Location
The pain from gallbladder inflammation usually happens in the upper right abdomen. It can feel sharp or dull. The pain may also spread to the right shoulder or back, making it hard to bear.
Pain When Breathing and Other Triggers
Deep breathing can make the pain worse. This is because the diaphragm’s movement adds pressure on the inflamed gallbladder. Eating fatty meals can also trigger the pain. Knowing what triggers the pain helps manage it better.
Differentiating from Stone-Related Pain
Pain from gallbladder inflammation and gallstones can seem similar. But, there are key differences. Gallstone pain usually happens after eating and goes away by itself. Inflammation pain, without stones, can be more constant and unpredictable.
It’s important to know these differences for the right diagnosis and treatment. We’ll look at how to diagnose and treat it in the next parts.
Additional Symptoms and Warning Signs
Other symptoms can show gallbladder inflammation, aside from upper right abdominal pain. It’s key to spot these signs early for timely medical help.
Systemic Symptoms (Fever, Nausea, Vomiting)
Gallbladder inflammation can cause body-wide symptoms. Fever shows the body’s fight against infection or inflammation. Nausea and vomiting can cause dehydration and imbalance of electrolytes if not handled right.
In severe cases of acalculous cholecystitis, these symptoms can be serious. Fever, in particular, is a red flag for a severe infection and needs quick medical care.
Physical Examination Findings
Healthcare providers look for specific signs during a physical exam. Tenderness in the right upper abdomen is a key indicator. This tenderness might also cause guarding, where muscles tighten in response to pressure, showing irritation.
Progression of Symptoms
Symptoms of gallbladder inflammation can change based on the cause and severity. Symptoms might come on fast or slowly over days.
It’s vital for patients to watch their symptoms closely. If pain gets worse, fever goes up, or other signs worry you, get medical help. Early treatment can greatly improve outcomes.
Diagnostic Approaches for Gallbladder Inflammation Without Stones
Diagnosing acalculous cholecystitis requires a detailed approach. It includes advanced imaging and lab tests. Finding gallbladder inflammation without stones is tricky but key for treatment.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging is essential for diagnosing gallbladder issues without stones. The main tools are:
- Ultrasound: It’s often first because it’s non-invasive and easy to get. It shows gallbladder swelling, wall thickening, and fluid around it.
- CT Scan: Gives detailed views of the gallbladder and nearby areas. It spots inflammation, swelling, and possible problems.
- HIDA Scan (Hepatobiliary Iminodiacetic Acid Scan): A nuclear test that checks the gallbladder’s function. It’s great for finding acalculous cholecystitis by seeing if the gallbladder shows up.
Laboratory Tests
Labs play a big part in diagnosing gallbladder issues without stones. Important tests are:
Test | Significance |
White Blood Cell Count | High levels mean infection or inflammation |
Liver Function Tests | Abnormal results suggest bile duct blockage or liver issues |
Bilirubin Levels | High bilirubin means bile duct blockage |
Differential Diagnosis
It’s important to rule out other conditions when diagnosing acalculous cholecystitis. Doctors must think of other possible causes of symptoms, like:
“The clinical presentation of acalculous cholecystitis can mimic other acute abdominal conditions, making differential diagnosis a critical step in patient management.” –
Medical Expert
- Hepatitis
- Peptic Ulcer Disease
- Pancreatitis
- Gastroenteritis
By using imaging, lab tests, and a detailed clinical check, doctors can accurately diagnose and treat gallbladder inflammation without stones.
Treatment Options for Acalculous Cholecystitis
Treating acalculous cholecystitis requires a mix of antibiotics, supportive care, and sometimes surgery. We will look at the different ways to manage this condition effectively.
Medical Management
Medical management is often the first step. It includes using antibiotics to fight off infections. These infections are a common cause of the condition.
Supportive care is also key. It includes giving fluids, nutrients, and managing pain. Patients with severe symptoms or those who are very sick may need to be in the ICU for close care.
Aspect of Care | Description | Benefits |
Antibiotics | Targeted against bacterial infections | Reduces infection severity |
Fluid Resuscitation | Restores fluid balance | Improves circulation and organ function |
Nutritional Support | Ensures adequate nutrition | Supports healing and recovery |
Surgical Interventions
When medical treatment doesn’t work or the condition is severe, surgical interventions may be needed. The most common surgery is cholecystectomy, which removes the gallbladder.
Cholecystectomy can be done in two ways: open or laparoscopic. The laparoscopic method is less invasive and usually leads to quicker recovery and fewer complications.
Alternative Drainage Procedures
For those at high risk for surgery, alternative drainage procedures are options. One such procedure is percutaneous cholecystostomy. It involves placing a tube into the gallbladder to drain inflammation and infection.
This method is great for critically ill patients. It helps manage the condition until they are well enough for surgery.
The right treatment depends on the patient’s health, how severe their condition is, and other factors.
Complications of Untreated Acalculous Cholecystitis
If acalculous cholecystitis is not treated, it can cause serious problems. These issues can be life-threatening. It’s vital to get medical help quickly.
Gallbladder Perforation
Gallbladder perforation is a serious issue. It happens when the gallbladder wall gets weak and bursts. This lets bile and possibly infected material spill into the belly.
Gallbladder perforation can cause peritonitis. This is a severe infection of the belly lining. It needs surgery right away.
Sepsis and Systemic Inflammatory Response
Untreated acalculous cholecystitis can cause sepsis. Sepsis is a dangerous condition where the body’s infection response gets out of control. It can harm organs and even cause them to fail if not treated fast.
The body’s inflammatory response to sepsis makes things harder to manage. It’s key to treat acalculous cholecystitis early to avoid these problems.
Long-term Gallbladder Dysfunction
Not treating acalculous cholecystitis can also lead to long-term gallbladder dysfunction. Chronic inflammation can damage the gallbladder. This can make it hard for the gallbladder to work right and cause ongoing symptoms.
In some cases, surgery to remove the gallbladder might be needed. This can help solve symptoms and prevent more issues.
Knowing about these risks shows why it’s important to see a doctor if you have symptoms. If you have ongoing pain in the upper right belly, fever, or other symptoms, get help right away.
Conclusion: When to Seek Medical Attention and Prognosis
Knowing the causes and signs of gallbladder inflammation without stones is key. We’ve talked about why it happens, like being very sick or hurt, and the signs like pain in the upper right side of your belly.
It’s important to get medical help fast. If you have ongoing or bad pain, fever, or can’t keep food down, go to the doctor right away. Quick action can make a big difference in how well you get better.
The outcome for gallbladder problems without stones can vary. It depends on the cause and how quickly you get treated. With the right care, many people get better. But, waiting too long can cause serious problems like a hole in the gallbladder or infection. Knowing the risks and signs helps you stay healthy.
FAQ
What causes gallbladder inflammation without stones?
Gallbladder inflammation without stones, or acalculous cholecystitis, can happen for many reasons. These include bile stasis, reduced blood flow, and bacterial contamination. It can also be caused by critical illness, trauma, and certain nutritional factors.
What is the difference between calculous and acalculous cholecystitis?
Calculous cholecystitis is caused by gallstones. Acalculous cholecystitis, on the other hand, happens without gallstones. The causes and risk factors for these conditions differ.
What are the symptoms of gallbladder inflammation?
The main symptom is upper right abdominal pain. This pain can be very severe and last a long time. Other signs include fever, nausea, vomiting, and a systemic inflammatory response.
How is acalculous cholecystitis diagnosed?
Doctors use imaging like ultrasound, CT, and HIDA scans to diagnose acalculous cholecystitis. They also check liver function and inflammation through lab tests.
What are the treatment options for acalculous cholecystitis?
Treatment includes antibiotics and supportive care. Surgery, like cholecystectomy, and alternative drainage procedures are also options.
What are the complications of untreated acalculous cholecystitis?
Untreated acalculous cholecystitis can cause serious problems. These include gallbladder perforation, sepsis, and long-term dysfunction of the gallbladder.
Can acalculous cholecystitis occur in people with underlying medical conditions?
Yes, it can happen in people with certain conditions. These include autoimmune disorders, diabetes, and post-surgical complications.
How can I differentiate gallbladder pain from other types of abdominal pain?
Gallbladder pain is usually in the upper right abdomen. It can be triggered by fatty meals. It’s important to see a doctor to find out the cause of your pain.
What is the prognosis for patients with acalculous cholecystitis?
The outcome depends on the cause, severity, and how quickly treatment is given. Many patients can recover with the right treatment.
When should I seek medical attention for gallbladder symptoms?
Seek medical help right away if you have severe abdominal pain, fever, or other signs of gallbladder inflammation.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459182/