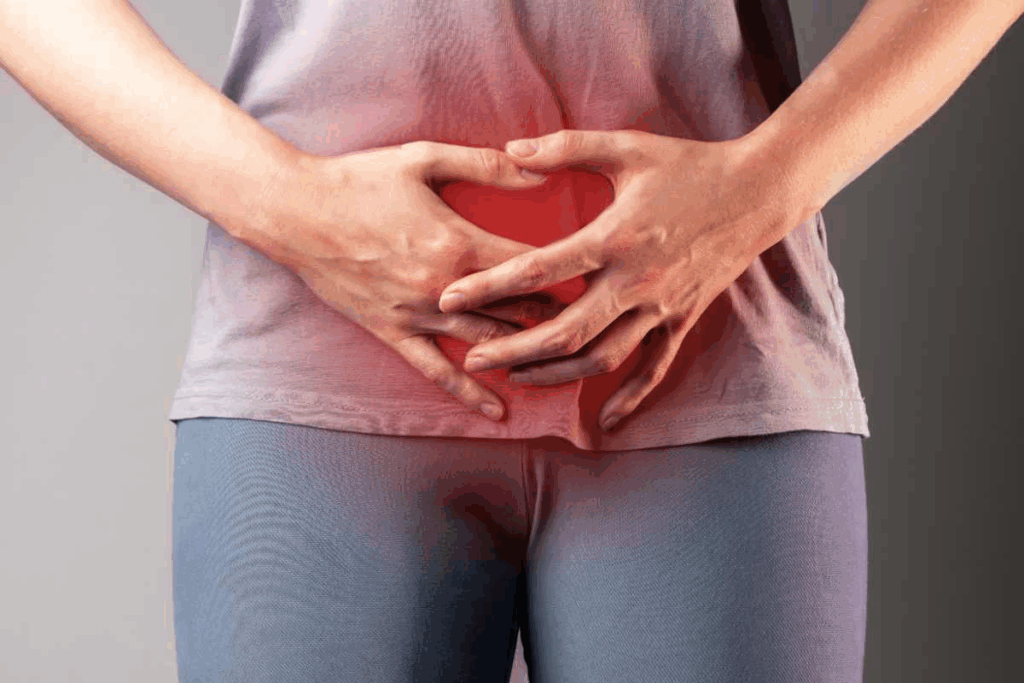

Bladder stones are small, hard mineral deposits that form inside the bladder. They can cause severe pain and make it hard to urinate. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is key to managing them well.
Learn 5 key facts about urinary bladder calculus. Understand the formation, symptoms, and medical treatment of bladder stones.
Bladder stones are hard masses of minerals that form in the bladder. Several factors can increase the risk of developing bladder stones.
Men over 50 are at a higher risk of developing bladder stones.
A diet low in fluids and high in certain minerals can increase the risk. Drinking enough water and eating a balanced diet are key to preventing bladder stones.
Certain medical conditions, such as urinary tract infections and kidney disease, can also increase the risk of developing bladder stones.

Bladder calculus, or stones in the bladder, can cause a lot of discomfort. It’s important to get medical help if you notice any symptoms. This condition can lead to serious health problems if not treated.
The symptoms of bladder calculus can vary. But they often include pain and trouble with urination. You might feel severe pain in your lower abdomen, need to urinate a lot, or find it painful to do so.
In some cases, you might see blood in your urine. These symptoms are a sign that you need to see a doctor.
To diagnose bladder calculus, doctors use a few methods. They start by asking about your medical history. This helps them understand your condition and any past health issues.
They also do a physical exam to check for tenderness in your lower abdomen. Imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans are used to see the stones. This confirms the diagnosis.
Getting diagnosed early is key to effective treatment. If your symptoms don’t go away or get worse, you should see a doctor right away.
The treatment for bladder calculus, or bladder stones, depends on several factors. These include the size of the stone, symptoms, and the patient’s health.
For small stones without symptoms, a wait-and-see approach is common. This means regular check-ups to see if the stone passes naturally.
Larger stones or those causing symptoms need surgery. This can be open surgery or minimally invasive techniques like lithotripsy.
Lithotripsy is a non-invasive method. It uses shock waves to break the stone into smaller pieces. These can then be easily passed out of the body. It’s good for those who can’t have surgery or prefer a less invasive option.
Preventing bladder stones requires a few steps. These include changing your diet, your lifestyle, and managing health issues.
Drinking lots of water is key. It helps remove minerals that can lead to stone formation.
Eating a balanced diet with calcium is also important. It helps prevent bladder stones.
By following these steps, you can lower your risk of getting bladder stones.
Living with bladder calculus means making big changes in your life. You need to change your lifestyle and learn how to handle symptoms. Making smart choices can really help your quality of life.
It’s important to know the signs of bladder stones. You might feel a lot of pain, have trouble peeing, or see blood in your urine. If you notice any of these, get help right away.
Dietary Recommendations | Benefits |
Stay hydrated | Helps flush out small stones |
Avoid oxalate-rich foods | Reduces risk of forming new stones |
Limit sodium intake | Reduces risk of stone formation |
Understanding your condition and making the right lifestyle changes can help manage bladder calculus. This can greatly improve your overall health and well-being.
Bladder calculus, or bladder stones, can cause serious health problems if not treated. Stones can lead to urinary tract infections (UTIs), blockages, and other issues.
UTIs are a big worry with bladder calculus. Bacteria can grow on the stones, causing infections. These infections can be very painful and harmful to your health.
Blockages in the urinary tract are another concern. Large stones can stop urine from flowing. This can lead to severe pain and even kidney damage if not treated quickly.
If you think you have bladder calculus, see a doctor right away. A healthcare professional can find out what’s wrong and create a treatment plan to avoid more problems.
Getting help early can make a big difference. Knowing the risks and complications helps you take care of your health better.

We know how important it is to help those with bladder calculus. We want to give patients the knowledge and support they need. This way, they can manage their condition well.
Managing bladder stones requires a mix of lifestyle changes and sometimes medical help. Knowing what causes bladder stones helps prevent them. Drinking enough water, watching your diet, and catching symptoms early are key to bladder health.
If you’re worried about your bladder health, see a doctor. They can help you get the care you need. This is the first step to feeling better and improving your health.
Bladder stones can cause severe lower abdominal pain, difficulty urinating, frequent urination, and sometimes blood in the urine. Some people may not experience noticeable symptoms at first.
Doctors diagnose bladder stones using your medical history, a physical examination, and imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasound, or CT scans.
Treatment depends on the stone’s size, location, and your overall health. Options include medications to dissolve stones, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery to remove them. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and working with a healthcare professional is also important.
Yes. Drinking plenty of water, eating a healthy diet, and managing underlying health conditions can reduce the risk of developing bladder stones.
Untreated bladder stones can lead to urinary tract infections, bladder or kidney damage, and chronic discomfort.
Bladder stones are typically removed through minimally invasive surgery. In some cases, a catheter may be used to help remove the stones.
Yes. Stones may recur if the underlying cause isn’t addressed. Following a healthy lifestyle, staying hydrated, and managing health conditions can lower the risk of recurrence.
National Center for Biotechnology Information – Facts About Urinary Bladder. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441944/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us