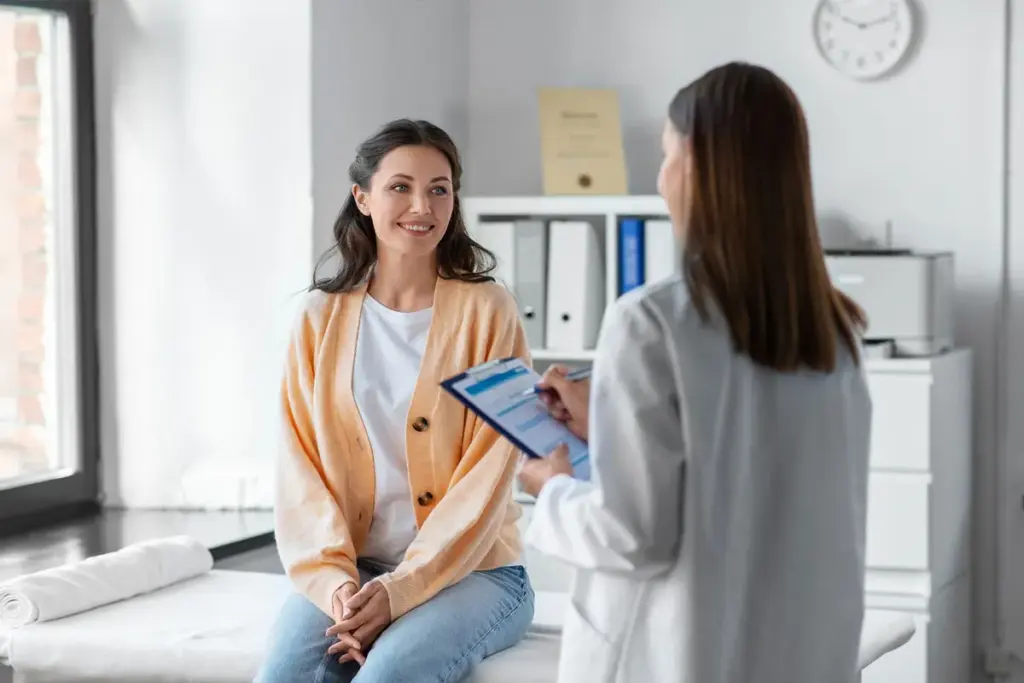
Millions of people worldwide experience urinary retention. This is when the body can’t fully empty the bladder. It causes discomfort, pain, and serious issues if not treated.
Voiding difficulties can really affect daily life. They cause anxiety and disrupt normal activities. Urinary retention can stem from many things, like neurological disorders, certain meds, and blockages.
In this article, we’ll dive into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments for urinary retention. We aim to give you a full guide on managing and possibly curing this condition.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the definition and causes of urinary retention.
- Recognizing the symptoms and when to seek medical help.
- Exploring diagnosis methods and treatment options.
- Learning about lifestyle changes that can help manage the condition.
- Discovering the potential for curing urinary retention.
Understanding Urinary Retention
It’s important to know about urinary retention if you’re experiencing symptoms. Getting a diagnosis and treatment early can really help your quality of life. This condition makes it hard to fully empty the bladder, leading to discomfort and serious issues.
What is Urinary Retention?
Urinary retention means you can’t fully urinate or empty your bladder. It can be sudden or long-term. Acutely, it’s a sudden blockage needing quick medical help. Chronic cases last longer, making it hard to fully empty the bladder over time.
The term “urinary retention” also talks about the leftover urine in the bladder. This leftover urine is called the residual volume. Doctors use ultrasound to measure it.
Common Causes of Urinary Retention
Urinary tract infections and neurological disorders often cause urinary retention. Other reasons include:
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men
- Constipation
- Certain medications
- Weak bladder muscles
- Blockages in the urinary tract
Neurological issues like multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and spinal cord injuries can also cause it. These conditions mess with the signals between the bladder and the brain.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of urinary retention include trouble starting to urinate, weak urine flow, and not being able to fully empty the bladder. Doctors use physical exams, medical history, and tests like ultrasound to diagnose it.
A medical expert says, “Urinary retention can really affect someone’s life. Knowing the causes and symptoms is key to managing it well.”
“Diagnosing urinary retention means finding the condition and its cause. This helps choose the right treatment.”
– Medical Expert, Urologist
Doctors might also do urodynamic tests to check how well the bladder and urethra work. Knowing the cause is important for the right treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Urinary Retention

There are many ways to treat urinary retention, including medicines, surgery, and other therapies. The right treatment depends on the cause, your health, and how bad your symptoms are.
Medications for Managing Symptoms
Medicines are key in treating urinary retention, often due to blockages or weak bladder muscles. Alpha-blockers help relax muscles in the prostate and bladder, making it easier to pee. Sometimes, anticholinesterase inhibitors are used to make the bladder muscles work better.
It’s important to talk to a doctor to find the best medicine and how much to take. Each person reacts differently to these treatments.
Surgical Interventions for Obstruction
If urinary retention is caused by a blockage, like a big prostate or a bladder stone, surgery might be needed. Cystolitholapaxy can break down bladder stones. Other surgeries might include cutting the prostate or the bladder neck.
Surgery aims to remove the blockage and help urine flow normally. The type of surgery depends on the blockage and your health.
Exploring Alternative Therapies
Some people find relief with alternative therapies for urinary retention. Acupuncture and physical therapy can help improve bladder function and overall health.
While these therapies can be helpful, it’s important to talk to a doctor. They can make sure these treatments work well with your main treatment plan.
Lifestyle Changes to Alleviate Symptoms
Making some simple changes in your lifestyle can make voiding easier. These changes can also reduce symptoms of urinary retention. By adjusting a few habits, you can greatly improve your urinary health and life quality.
Dietary Adjustments for Better Urinary Health
Your diet is key in managing urinary retention. Some foods can irritate your bladder, while others can soothe it. It’s best to avoid caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods as they can worsen symptoms.
Instead, eat foods high in fiber like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These can help regulate bowel movements and ease bladder pressure.
Also, keeping a healthy weight through a balanced diet can help. Excess weight can put extra pressure on your bladder and pelvic muscles, making it harder to empty your bladder.
Foods to Avoid | Beneficial Foods |
|---|---|
Caffeine | Fruits (e.g., berries, citrus fruits) |
Alcohol | Vegetables (e.g., leafy greens, bell peppers) |
Spicy foods | Whole grains (e.g., brown rice, quinoa) |
Exercises to Strengthen the Bladder
Pelvic floor exercises, or Kegel exercises, can strengthen the bladder muscles. To do Kegels, squeeze the muscles that stop urine flow, hold for a few seconds, then release. Doing this several times a day can boost bladder muscle strength.
- Identify the correct muscles by stopping the flow of urine mid-stream.
- Squeeze and hold the muscles for 5-10 seconds.
- Release and rest for 5-10 seconds.
- Repeat the exercise 10-15 times, several times a day.
Importance of Hydration
Staying hydrated is vital for urinary health. Drinking enough water helps flush out bacteria and toxins from the urinary tract. This reduces the risk of infections that can worsen urinary retention. Aim to drink 8-10 glasses of water a day, unless your healthcare provider advises differently.
While staying hydrated is important, listen to your body. If urinating becomes painful or difficult, seek advice from a healthcare professional.
By making these lifestyle changes, you can better manage urinary retention symptoms and improve your urinary health. It’s about making choices that support your health and well-being.
The Role of Medical Professionals
Medical professionals are key in diagnosing and treating urinary retention. They help find the cause and suggest the best treatments. If you have trouble starting to pee or have a weak flow, seeing a doctor is a must.
When to Consult a Specialist
If you’re having trouble peeing, it’s time to see a specialist. A urologist is a doctor who knows a lot about the urinary tract. They can figure out why you’re having trouble and create a treatment plan just for you.
Some people might feel like they’re having female trouble because of urinary retention. This shows how important it is to get medical help.
Urinary retention can be caused by conditions like diabetes or multiple sclerosis. In these cases, a neurologist or a specialist in the condition might also be needed.
Common Tests and Procedures
To find out why you’re having trouble peeing, doctors might do several tests. These include:
- Urinalysis: A test to check for infections or other problems in your urine.
- Urodynamic tests: These tests check how well your bladder and urethra work.
- Imaging tests: Like ultrasound or MRI, to see the urinary tract and find any issues.
- Cystoscopy: A procedure where a small camera is put into the bladder to look inside.
These tests help doctors understand what’s going on and plan the best treatment. By seeing the right doctors and getting the right tests, you can get the care you need.
Complications Associated with Urinary Retention
Urinary retention, or not being able to empty the bladder, is a serious health issue. It can cause mild discomfort or severe health problems if not treated quickly.
Urinary retention can lead to many health complications. It’s important for patients to know these risks and seek medical help fast.
Potential Health Risks
One big risk is getting urinary tract infections (UTIs). When the bladder stays full, bacteria can grow, causing infections.
Other risks include bladder damage and bladder stones. The bladder can get damaged if it stays stretched out for too long.
- Urinary tract infections due to bacterial multiplication
- Bladder damage from prolonged distension
- Formation of bladder stones
- Increased risk of kidney damage
Long-term Effects on the Kidneys
Long-term urinary retention can harm the kidneys. The urine backup can damage the kidneys or make existing problems worse.
Potential Complication | Description | Impact on Health |
|---|---|---|
Kidney Damage | Backup of urine can cause damage | Long-term kidney function impairment |
Bladder Damage | Prolonged distension affects bladder muscles | Loss of bladder function |
Urinary Tract Infections | Bacterial multiplication in retained urine | Recurring infections, possible sepsis |
Knowing the risks of urinary retention shows why medical care is key. Treating urinary retention can prevent serious health problems and keep you healthy.
Mental and Emotional Impact
The emotional side of urinary retention is often ignored, but it greatly affects life quality. People with this condition may feel embarrassed, anxious, and depressed. These feelings can make everyday life harder and affect overall happiness.
Coping with Urinary Retention
Urinary retention can deeply affect mental health. The ongoing battle to manage symptoms can raise stress levels and anxiety about future episodes. The loss of control over one’s body can be very upsetting.
Dealing with urinary retention requires a broad approach. It’s key to recognize the emotional impact and seek help. This might include counseling or therapy to handle feelings of shame or worry.
Support groups also offer a place to share and learn from others facing similar issues.
Seeking Support from Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers are vital in helping those with urinary retention. They can give guidance on managing symptoms and refer patients to resources for emotional support. It’s important for patients to talk openly with their healthcare team.
By understanding and addressing urinement comprehensively, healthcare providers can greatly enhance the lives of those with urinary retention.
Preventive Measures
Preventing urinary retention needs a mix of lifestyle changes and regular health checks. By making some simple changes, you can lower your risk of urinary retention. We’ll look at how to avoid it and why regular doctor visits are key.
Strategies to Avoid Urinary Retention
To keep your urine flowing, try a few things. Drink more water and eat foods that are easy on your bladder. Doing Kegel exercises can also help your muscles work better.
Understanding what urinary retention means can motivate you to stay healthy. It’s all about taking care of your body.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular health visits are vital for catching problems early. Doctors can spot issues like bladder stones during these visits. They might suggest treatments like cystolitholapaxy.
By fixing these problems quickly, you can stop urinary retention from happening. It’s all about staying proactive with your health.
Patient Experiences and Stories
Every person’s journey with urinary retention is unique. It’s filled with personal struggles and victories. We’ve collected stories from those who’ve faced this condition. Their experiences offer valuable insights and hope to others facing similar challenges.
Real-life Testimonials
Many people have shared their stories of living with urinary retention. For example, a man in his late 50s felt like an “empty man” due to constant discomfort and anxiety. He found solace in support groups and learned to manage his symptoms well.
Women have also shared their experiences, calling it “female trouble.” It’s not just physical discomfort but also emotional distress. One woman said she coped by making big lifestyle changes, like changing her diet and doing pelvic floor exercises.
Lessons Learned from Others
These personal stories teach us important lessons. First, getting support from healthcare providers and support groups is key. Second, making smart lifestyle choices can help ease symptoms. Lastly, staying positive and proactive in managing the condition is essential.
“I learned that I am not alone in this journey. Connecting with others who understand what I’m going through has been incredibly empowering.”
A patient sharing their experience
Future Research and Developments
Understanding urinary retention is key to finding new treatments. The International Classification of Diseases (ICD10) code shows its importance. Research is vital for better patient care.
Advancements in Treatment Options
New treatments are on the horizon. These include new medicines and less invasive surgeries. They aim to lessen symptoms and improve life quality for those with urinary retention.
Ongoing Research and Its Importance
More research is needed to tackle urinary retention’s challenges. By looking into new treatments and improving old ones, we can help patients more. Studies will help us understand and manage the condition better.
FAQ
What is urinary retention?
Urinary retention is when you can’t fully empty your bladder. This can happen for many reasons, like blockages or nerve issues. It’s also caused by some medicines.
What are the symptoms of urinary retention?
Signs include trouble starting to pee, weak or broken urine flow, and needing to pee a lot. You might also feel like your bladder isn’t empty. If it gets worse, it could cause infections or harm your kidneys.
How is urinary retention diagnosed?
Doctors check you physically and ask about your health history. They might use tests like uroflowmetry and ultrasound. These help find out why you have urinary retention.
What are the treatment options for urinary retention?
Treatment varies based on the cause. It might include medicines to relax the bladder or surgery to remove blockages. You might also need catheterization or bladder training.
Can lifestyle changes help alleviate urinary retention symptoms?
Yes, changing your lifestyle can help. Eating right, doing pelvic floor exercises, and drinking plenty of water can help. These steps can prevent constipation and infections.
What are the possible complications of urinary retention?
Untreated urinary retention can cause infections, bladder damage, and even kidney damage. It’s important to see a doctor if you can’t pee normally.
When should I seek medical attention for urinary retention?
See a doctor if you can’t pee, it hurts when you try, or you can’t pee at all. A urologist can find out why and how to fix it.
How can I prevent urinary retention?
To prevent it, live a healthy lifestyle, manage health conditions like diabetes, and avoid medicines that can cause it. Also, don’t delay going to the bathroom.
What is the role of catheterization in managing urinary retention?
Catheterization is when a tube is put into your bladder to drain urine. It’s often used when other treatments don’t work.
Are there any new treatments being developed for urinary retention?
Yes, new treatments are being researched. This includes things like neuromodulation and advanced surgery. They aim to help people with urinary retention more effectively.
What does retained urine mean?
Retained urine is when you can’t pee all the urine out. It might mean you have urinary retention and need to see a doctor.
How does urinary retention affect mental health?
It can make you feel embarrassed, anxious, and depressed. It disrupts your life. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider about both the physical and emotional effects.
References
National Institutes of Health. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/urinary-retention/symptoms-causes[2


































