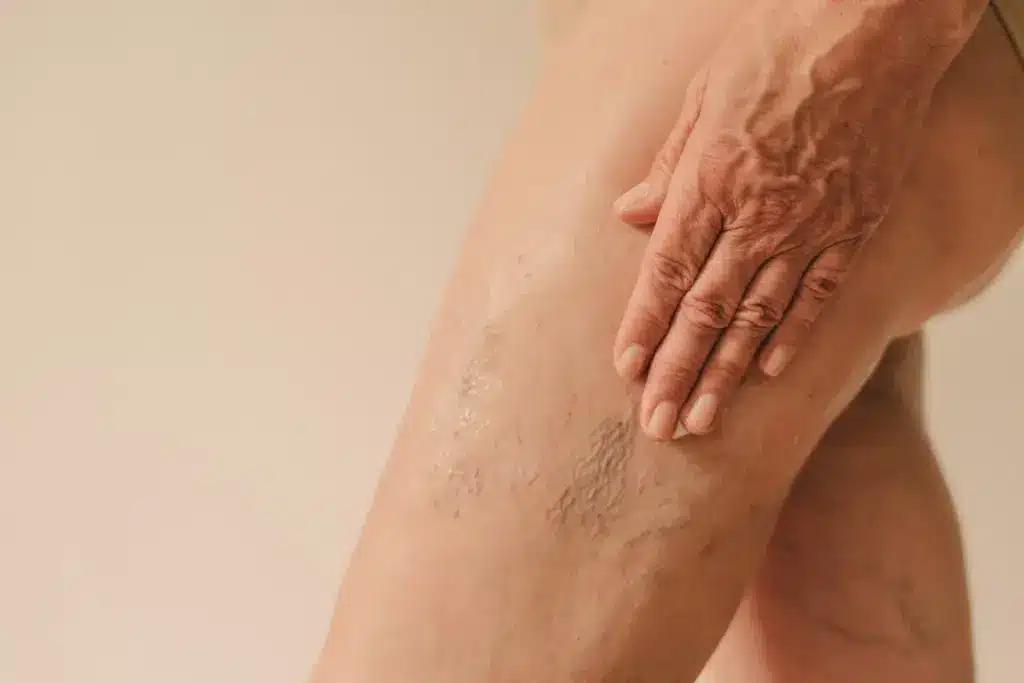

It’s important to know the signs of a blood clot after vein ablation for your health. About 3.2% of patients get Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) within 30 days. Knowing the risks of venous ablation treatments and acting fast is key.
We focus on top-notch healthcare and support for international patients. Being aware of DVT risks and signs is vital. Always follow your doctor’s advice before and after the procedure to lower DVT risk.
Key Takeaways
- About 3.2% of patients develop DVT within 30 days after vein ablation.
- Recognizing the signs of blood clots is critical for timely medical help.
- Following your doctor’s advice before and after can lower DVT risk.
- DVT is a serious issue that can block blood flow and lead to a pulmonary embolism.
- Venous ablation treatments have a DVT risk, but with proper care, it can be managed.
Understanding Vein Ablation Procedures
Vein ablation uses heat to close off bad veins. This helps blood flow to better veins. It’s a new way to treat varicose veins and other vein problems.
What is Vein Ablation?
Vein ablation treats diseased veins, like varicose veins. It uses laser or radiofrequency waves to heat the vein. This makes it close off.
Over time, blood flows through better veins. This relieves symptoms like pain, swelling, and discoloration.
Types of Vein Ablation Techniques
There are two main vein ablation methods: laser and radiofrequency ablation. Both work well, but they use different technologies.
- Laser Ablation: Laser energy heats the vein. A laser fiber is inserted through a small catheter. As it’s pulled out, it heats the vein wall, causing it to close.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: This method uses radiofrequency waves to heat the vein. A catheter is inserted into the vein. It emits radiofrequency energy to heat and close the vein.
Common Conditions Treated with Vein Ablation
Vein ablation mainly treats varicose veins and related issues, such as:
- Varicose Veins: These are enlarged, twisted veins in the legs.
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency: This is when veins can’t return blood to the heart properly.
- Venous Ulcers: Open sores that can happen in severe venous insufficiency.
Vein ablation can greatly improve a patient’s life. It reduces discomfort and makes the affected areas look better.
Blood Clots as a Possible Complication
Vein ablation can sometimes lead to blood clots. This treatment is usually safe for varicose veins. But, knowing about clot risks is key for good care.
Normal Blood Clotting vs. Problematic Clots
Blood clots form when the body gets hurt. But, vein ablation can raise the risk of bad clots. Normal clotting helps heal, but bad clots can cause serious problems.
There are two kinds of bad clots: superficial and deep. Knowing the difference is important for spotting issues early.
Incidence Rates After Vein Ablation
Research shows DVT rates after vein ablation vary. The rate of DVT ranges from 0.4% to 2.7%. These rates depend on the procedure, patient health, and care after treatment.
|
Study |
DVT Incidence Rate |
|---|---|
|
Study A |
0.4% |
|
Study B |
1.2% |
|
Study C |
2.7% |
Difference Between Superficial and Deep Vein Thrombosis
Superficial Vein Thrombosis (SVT) happens when a clot forms near the skin. It’s uncomfortable but usually not as dangerous as DVT.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is more serious. It involves clots in deeper veins, often in the legs. DVT can cause pulmonary embolism, a serious condition if the clot goes to the lungs.
It’s important for patients and doctors to watch for clot signs after vein ablation. If symptoms show up, seek medical help right away.
Recognizing Blood Clot Symptoms After Vein Ablation
After vein ablation, knowing the signs of a blood clot is key. Vein ablation is usually safe, but there’s a chance of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). This is when a blood clot forms in the deep veins.
Common Symptoms of DVT
DVT symptoms can differ, but some signs are common. Look out for:
- Pain or tenderness in the leg, from mild to severe.
- Swelling in the leg, making it look bigger.
- Warmth or redness of the skin over the affected area.
- Cramping or soreness in the calf or thigh.
Some people might not show any symptoms. That’s why it’s important to check in with your doctor after the procedure.
Less Common but Serious Symptoms
While rare, some symptoms can be serious. They might point to a life-threatening issue like a pulmonary embolism. Watch for:
- Shortness of breath or trouble breathing.
- Chest pain or discomfort that gets worse with deep breaths.
- Coughing up blood or frothy sputum.
- Rapid heart rate or palpitations.
If you see these signs, get medical help right away.
Timeline for Symptom Development
When DVT symptoms show up can vary. Some people notice them a few days after, while others might not see anything until weeks later. Stay alert in the first few months after vein ablation.
Keep an eye on your health and tell your doctor about any odd symptoms. Catching DVT early can help a lot and lower the risk of serious problems.
Distinguishing Normal Recovery from Blood Clot Symptoms
After vein ablation, knowing the difference between normal recovery and blood clot symptoms is key. Understanding what to expect can greatly affect your recovery.
Expected Post-Procedure Sensations
Some discomfort is normal after vein ablation. You might feel bruising, swelling, or a pulling sensation in the treated area. These symptoms are usually mild and part of the healing process.
Common sensations include:
- Numbness or tingling
- Mild pain or discomfort
- Slight swelling or bruising
When Symptoms Indicate a Problem
While some discomfort is okay, certain symptoms may signal a blood clot. Watch out for:
- Severe pain not relieved by medication
- Significant swelling that worsens over time
- Redness or warmth around the treated area
If you notice these symptoms, contact your healthcare provider right away.
Tracking Your Recovery Progress
Keeping an eye on your recovery can help spot issues early. Log your symptoms, noting when and how severe they are. This info is helpful when talking to your healthcare provider.
|
Symptom |
Normal Recovery |
Potential Problem |
|---|---|---|
|
Pain |
Mild to moderate, manageable with medication |
Severe, worsening over time |
|
Swelling |
Mild, improving with elevation |
Significant, worsening despite elevation |
|
Redness/Warmth |
Minimal, localized to treatment area |
Extensive, spreading beyond treatment area |
Knowing what’s normal after vein ablation and watching for complications can make your recovery smoother and safer.
Risk Factors for Developing Blood Clots After Vein Ablation
Several factors can increase the risk of blood clots after vein ablation. These include pre-existing medical conditions and lifestyle choices. Knowing these risks is key to avoiding complications and ensuring a smooth recovery.
Pre-existing Medical Conditions
Certain health conditions can raise the risk of blood clots after vein ablation. These include:
- History of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) or Pulmonary Embolism (PE): Patients with a previous history of DVT or PE are at a higher risk of developing blood clots.
- Coagulopathy: Conditions that affect blood clotting, such as factor V Leiden or antiphospholipid syndrome, can increase the risk.
- Cancer: Active cancer or a history of cancer can increase the risk of blood clot formation.
- Obesity: Being significantly overweight or obese can put additional strain on the veins, increasing the risk.
Procedure-Specific Risk Factors
The specifics of the vein ablation procedure can also influence the risk of blood clot formation. These include:
- Length of the treated vein: Longer veins treated during the procedure may have a higher risk of clot formation.
- Type of ablation technique used: Different techniques, such as laser or radiofrequency ablation, may have varying risks associated with them.
- Multiple vein treatments: Treating multiple veins during a single session may increase the risk.
Lifestyle and Demographic Factors
Lifestyle and demographic factors also play a significant role in determining the risk of blood clots after vein ablation. These include:
- Age: Older patients may have a higher risk due to decreased mobility and other age-related factors.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage the vascular system and increase the risk of clot formation.
- Immobility: Prolonged periods of immobility after the procedure can increase the risk.
- Family history: A family history of blood clots can indicate a higher risk for the patient.
To better understand the interplay of these risk factors, let’s examine a summary table:
|
Risk Factor Category |
Specific Risk Factors |
Impact on Blood Clot Risk |
|---|---|---|
|
Pre-existing Medical Conditions |
History of DVT/PE, Coagulopathy, Cancer, Obesity |
High |
|
Procedure-Specific Factors |
Length of treated vein, Type of ablation, Multiple vein treatments |
Moderate to High |
|
Lifestyle and Demographic Factors |
Age, Smoking, Immobility, Family history |
Moderate |
By understanding these risk factors, patients and healthcare providers can take proactive steps to minimize the risk of blood clots after vein ablation. This ensures a safer and more effective treatment outcome.
The Science Behind Blood Clot Formation During Vein Ablation
It’s important for patients to understand how blood clots form during vein ablation. This treatment aims to close off veins with heat or laser energy. While it’s usually safe, it can sometimes cause blood clots.
How the Ablation Process Affects Blood Vessels
The ablation process damages the blood vessel lining. This damage triggers a healing response. The body starts clotting as a natural reaction to the injury.
Normal Clotting as Part of the Healing Process
Clotting is a normal healing step after vein ablation. The body forms a clot to heal the injury. This clot is later replaced by scar tissue.
Most of the time, this process works well without issues. But, it’s important to know the difference between normal clotting and dangerous clot formation. The latter can cause deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Normal clotting is usually limited to the treated area.
- The clot is gradually absorbed by the body as healing progresses.
- In some cases, the clot can extend beyond the treated segment, potentially leading to DVT.
When Normal Clotting Becomes Pathological
Clotting can sometimes turn dangerous after vein ablation. This happens due to the procedure’s extent, patient risks, and underlying venous disease. When clotting spreads or forms in deep veins, it can cause serious issues like DVT or pulmonary embolism.
It’s key to know the signs of dangerous clotting. Patients should watch for these signs closely after vein ablation.
Diagnostic Methods for Blood Clots After Vein Ablation
Diagnosing blood clots after vein ablation needs a mix of clinical checks and tests. We use different methods to find blood clots. This ensures we treat them quickly and well.
Physical Examination Techniques
A detailed physical check is the first step to find blood clots after vein ablation. We look for swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected limb. Palpation and checking for tenderness along the vein are also key. Healthcare providers might use the Homans’ sign test, but its reliability is questioned.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies are vital to confirm blood clots. The most common method is duplex ultrasound. It combines Doppler and conventional ultrasound to see blood flow and find clots. Sometimes, venography is used. It involves injecting contrast material into the veins to see the clot.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests help check for blood clot risk and presence. D-dimer tests are often used to find blood clots. High D-dimer levels suggest clotting, but this test alone is not enough. Other tests may be done to check blood clotting function and rule out other issues.
By using these diagnostic methods together, we can accurately spot blood clots after vein ablation. This allows us to give the right treatment. It’s also important to keep up with regular follow-ups and monitoring for patients who have had vein ablation.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Knowing when to get urgent medical help is key to recovering from vein ablation. The procedure is usually safe, but knowing about possible complications is important. This way, you can act quickly if needed.
Emergency Warning Signs
After vein ablation, watch your body closely for signs of trouble. Look out for:
- Leg pain or swelling that doesn’t get better with rest or gets worse
- Redness or warmth in the leg
- Shortness of breath or trouble breathing
- Chest pain or discomfort that spreads to the arm, back, or other areas
If you see any of these emergency signs of DVT, get medical help right away.
Pulmonary Embolism Symptoms
A pulmonary embolism is a serious condition where a blood clot goes to the lungs. It can be deadly. Look out for:
|
Symptom |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Shortness of breath |
Sudden trouble breathing or feeling out of breath even when sitting |
|
Chest pain |
Pain or discomfort that gets worse with deep breathing or coughing |
|
Rapid heart rate |
A sudden jump in heart rate or palpitations |
Spotting these pulmonary embolism symptoms early can save your life.
Contacting Your Healthcare Provider vs. Emergency Services
If you’re showing emergency signs or symptoms of pulmonary embolism, know when to seek medical attention. For serious symptoms like trouble breathing, chest pain, or severe leg pain, call emergency services right away.
If symptoms are less severe but concerning, reach out to your healthcare provider. They can check your condition and tell you what to do next.
Treatment Options for Blood Clots Following Vein Ablation
Knowing the treatment options for blood clots after vein ablation is key for patient care. When a blood clot forms after this procedure, quick and effective treatment is needed to avoid complications.
Anticoagulation Therapy
Anticoagulation therapy is a main treatment for blood clots after vein ablation. This method uses medicines to stop the clot from growing and new ones from forming. Anticoagulants are given orally or through injection. The length of treatment depends on the patient’s risk factors and the clot’s severity.
“Anticoagulation therapy is a cornerstone in the management of deep vein thrombosis,” as noted by vascular specialists. “It significantly reduces the risk of clot progression and recurrence.”
Compression Therapy
Compression therapy is also a vital treatment. It uses compression stockings to improve blood flow and reduce swelling. This therapy helps ease symptoms and prevent post-thrombotic syndrome, a condition with chronic pain and swelling.
Advanced Treatment Options for Severe Cases
In severe cases of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), more advanced treatments may be needed. These include:
- Thrombolysis: A procedure to dissolve the clot using medicines.
- Catheter-directed thrombolysis: A targeted method where the medicine is directly delivered to the clot.
- Mechanical thrombectomy: A surgical procedure to remove the clot.
These advanced treatments are usually for patients with severe symptoms or high risk of complications.
Recovery Timeline with Treatment
The recovery time for patients treated for blood clots after vein ablation varies. Most patients see symptom improvement in a few weeks with anticoagulation and compression therapy. Advanced treatments can lead to quicker relief but come with higher risks and are used carefully.
It’s important for patients to follow their healthcare provider’s instructions and attend follow-up appointments. This helps monitor progress and reduces the risk of complications, leading to the best outcomes.
Preventing Blood Clots Before and After Vein Ablation
There are ways to lower the chance of blood clots after vein ablation. Knowing and using these steps can make patients safer and help them recover better.
Pre-procedure Preparations
Before vein ablation, you can take steps to lower blood clot risk. These include:
- Telling your doctor about any medicines you take, like blood thinners.
- Talking about your health history, like if you’ve had DVT or clotting problems before.
- Following any instructions from your healthcare team, like not eating or avoiding certain medicines.
Post-procedure Care Guidelines
After the procedure, it’s important to follow care guidelines. This means:
- Moving gently as your doctor suggests to help blood flow.
- Wearing compression stockings as advised to stop clots.
- Watching for any unusual symptoms and telling your doctor right away.
Also, drink plenty of water and don’t sit for too long.
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Risk
Changing your lifestyle can also help prevent blood clots. These changes include:
|
Lifestyle Change |
Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Regular Exercise |
Improves circulation and heart health |
|
Maintaining a Healthy Weight |
Less pressure on veins and better health |
|
Avoiding Smoking |
Less damage to blood vessels and better flow |
By making these lifestyle changes and following pre- and post-procedure advice, patients can lower their risk of blood clots after vein ablation.
Long-term Monitoring After Vein Ablation
Monitoring over time is key after vein ablation. It helps ensure the best results. Patients must follow up to catch any issues early.
Follow-up Appointment Schedule
Stick to your follow-up plan after vein ablation. You’ll need to see your doctor within a week, then at 1-3 months, and again at 6-12 months. These visits help your doctor check on you and make sure everything is healing right.
|
Follow-up Timeframe |
Purpose of Visit |
|---|---|
|
1-7 days post-procedure |
Initial assessment of treated area, checking for immediate complications |
|
1-3 months post-procedure |
Evaluation of recovery progress, checking for signs of DVT |
|
6-12 months post-procedure |
Long-term assessment of treated vein, overall vascular health evaluation |
Self-monitoring Practices
Keep an eye on yourself too. Watch for signs of DVT like leg pain or swelling. Also, track how you’re feeling and any changes to share with your doctor.
Key self-monitoring practices include:
- Regularly checking for signs of swelling or pain in the treated leg
- Monitoring for any unusual symptoms or changes
- Maintaining a recovery journal to track progress and note any concerns
When Additional Imaging May Be Necessary
Sometimes, more tests are needed. This could be an ultrasound to check the treated vein or for DVT. Your doctor will let you know if you need these tests.
Following your follow-up plan and watching yourself can lower risks after vein ablation. Always talk to your doctor to get the best care.
Comparing Blood Clot Risk: Laser vs. Radiofrequency Vein Ablation
Vein ablation is a common treatment for varicose veins. It comes in two main forms: laser and radiofrequency ablation. Each has its own risk for blood clots. It’s important for patients and healthcare providers to understand these differences.
Statistical Differences in DVT Rates
Studies have shown different results on deep vein thrombosis (DVT) rates for laser and radiofrequency ablation. A meta-analysis in a Journal found laser ablation has a slightly higher DVT rate than radiofrequency. But, the risk is low for both methods.
|
Ablation Technique |
DVT Incidence Rate |
Study Sample Size |
|---|---|---|
|
Laser Ablation |
2.5% |
1,200 patients |
|
Radiofrequency Ablation |
1.8% |
1,500 patients |
The table shows radiofrequency ablation has a slightly lower DVT rate. But, it’s important to remember that results can vary. This depends on patient demographics, procedural techniques, and follow-up protocols.
Factors Influencing Technique Selection
The choice between laser and radiofrequency ablation depends on several factors. These include the size and location of the varicose veins, patient anatomy, and the operator’s preference. Radiofrequency ablation is often chosen for its lower risk of complications and controlled heating of the vein wall.
“The selection of ablation technique should be tailored to the individual patient’s condition and the physician’s expertise, considering the risk-benefit analysis of each method.” – Vascular Surgeon
Latest Research Findings
Recent studies have improved our understanding of vein ablation risks. A 2023 study in a European Journal found laser technology advancements have reduced DVT risk. Now, laser ablation is as safe as radiofrequency ablation.
In conclusion, both laser and radiofrequency vein ablation are effective for treating varicose veins. But, they have slightly different risks for blood clot formation. Keeping up with the latest research and considering individual patient factors are key to minimizing risks.
Patient Experiences: Recognizing and Managing Blood Clots After Vein Ablation
Learning from patients who had vein ablation helps us understand blood clots better. Real-life stories show the ups and downs of this procedure. They give us a closer look at the challenges and victories.
Case Studies and Patient Stories
A 45-year-old woman got leg pain and swelling a week after her vein ablation. She was found to have a DVT. Quick treatment with anticoagulation therapy fixed the clot without issues.
A 60-year-old man noticed DVT symptoms a few days after his procedure. He followed care instructions closely, including walking and wearing compression stockings. Yet, he got a clot, showing the need for constant watchfulness and doctor visits.
Lessons Learned from Real-World Experiences
These stories teach us a lot. Knowing DVT symptoms is vital. Patients should learn to spot signs like leg pain, swelling, and warmth. Following care instructions closely also helps avoid problems.
“Being alert and well-informed is key to avoiding blood clots after vein ablation,” a vascular specialist says. This advice stresses the importance of active recovery and detailed guidance from doctors.
Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider
It’s important to talk to your doctor about your recovery. Discuss these topics:
- What are the specific risks of DVT associated with my procedure?
- How can I minimize my risk of developing blood clots?
- What symptoms should I be monitoring for, and what should I do if I experience them?
- Are there any additional precautions or treatments that can be taken to reduce the risk of blood clots?
By asking these questions, patients can be more involved in their recovery. This helps reduce the chance of complications after vein ablation.
Conclusion: Staying Vigilant While Recovering from Vein Ablation
As we wrap up our talk on blood clots after vein ablation, it’s clear that knowing what to do is key. We’ve looked at the risks and signs of blood clots, like deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Recovering from vein ablation means being careful and knowing the signs of DVT. Understanding the risks, spotting symptoms early, and following care instructions can help a lot. It’s important to watch for DVT signs closely, as quick medical help can avoid serious problems.
Patients can feel more confident in their recovery by being proactive and informed. If they have any worries or symptoms, they should reach out to their doctor right away. Our aim is to help patients get the knowledge and support they need to recover safely from vein ablation.
FAQ
What is vein ablation, and how is it used to treat varicose veins?
Vein ablation is a procedure to treat varicose veins. It uses heat from lasers or radiofrequency to close off the vein. This redirects blood to healthier veins.
What are the different techniques used in vein ablation?
There are two main techniques: endovenous laser ablation and radiofrequency ablation. Both use heat to seal off the vein.
What are the common symptoms of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) after vein ablation?
Symptoms of DVT include leg swelling and pain. You might also notice warmth or redness in the leg. Severe cases can make walking hard or cause a lot of pain.
How soon after vein ablation can symptoms of DVT appear?
DVT symptoms can start within a few weeks, often in the first week. But the risk stays for several weeks after the procedure.
What are the risk factors for developing blood clots after vein ablation?
Risk factors include medical conditions like clotting disorders. The length of the vein treated also matters. Lifestyle factors like age, obesity, and not moving much also play a role.
How is DVT diagnosed after vein ablation?
Doctors use physical exams, ultrasound, and lab tests to diagnose DVT. These tests check for clots and rule out other conditions.
What are the treatment options for DVT after vein ablation?
Treatment for DVT includes medicines to stop clot growth. Compression therapy helps reduce swelling. In severe cases, more advanced treatments like thrombolysis or thrombectomy might be needed.
How can I reduce the risk of developing blood clots after vein ablation?
To lower the risk, follow pre-procedure and post-procedure care. Stay hydrated, move often, and wear compression stockings as advised.
Is there a difference in DVT risk between laser and radiofrequency vein ablation?
Both methods have a low DVT risk. But laser ablation might have a slightly higher risk, according to some studies.
How often should I have follow-up appointments after vein ablation?
You’ll need follow-up appointments within the first week. Then, check-ups will be spaced out over weeks to months to monitor healing and watch for complications.
When should I seek immediate medical attention after vein ablation?
If you have severe symptoms like trouble breathing, chest pain, or severe leg pain, seek help right away. These could be signs of a serious problem like a pulmonary embolism or severe DVT.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from






