At Liv Hospital, we know that finding out about a noncancerous growth can be scary. But it’s important to understand that not all tumors are cancer. A benign neoplasm is an abnormal cell growth that doesn’t spread or invade other tissues.
Benign tumors grow slowly and have clear edges. We focus on our patients, aiming to diagnose and treat these conditions well. We offer full care and support during their treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Benign tumors are noncancerous growths that don’t invade surrounding tissues.
- They are typically slow-growing and have distinct borders.
- Unlike cancerous tumors, benign neoplasms don’t spread to other parts of the body.
- Liv Hospital offers a patient-centered approach to managing benign tumors.
- Accurate diagnosis is key for effective care and treatment.
Understanding Benign Tumors
Benign tumors are growths that don’t spread and stay in one place. They grow slowly and have clear edges. This makes them different from cancerous tumors.
Definition and Basic Characteristics
A benign tumor is not cancer and doesn’t spread. It grows slowly and has clear edges. Types include adenomas, fibromas, and hemangiomas. They can appear in the skin, organs, or bones.
Benign tumors don’t spread like cancer does. But, they can cause problems if they get too big. They can press on nearby tissues or organs.
Cellular Structure of Benign Growths
Benign tumors have cells that look like normal cells. They are organized and have the right number of chromosomes. This is different from cancer cells.
Benign tumors grow slowly and don’t invade. They might cause symptoms but are not usually deadly. Knowing how they work helps doctors treat them.
The Key Differences Between Benign Tumors and Cancer
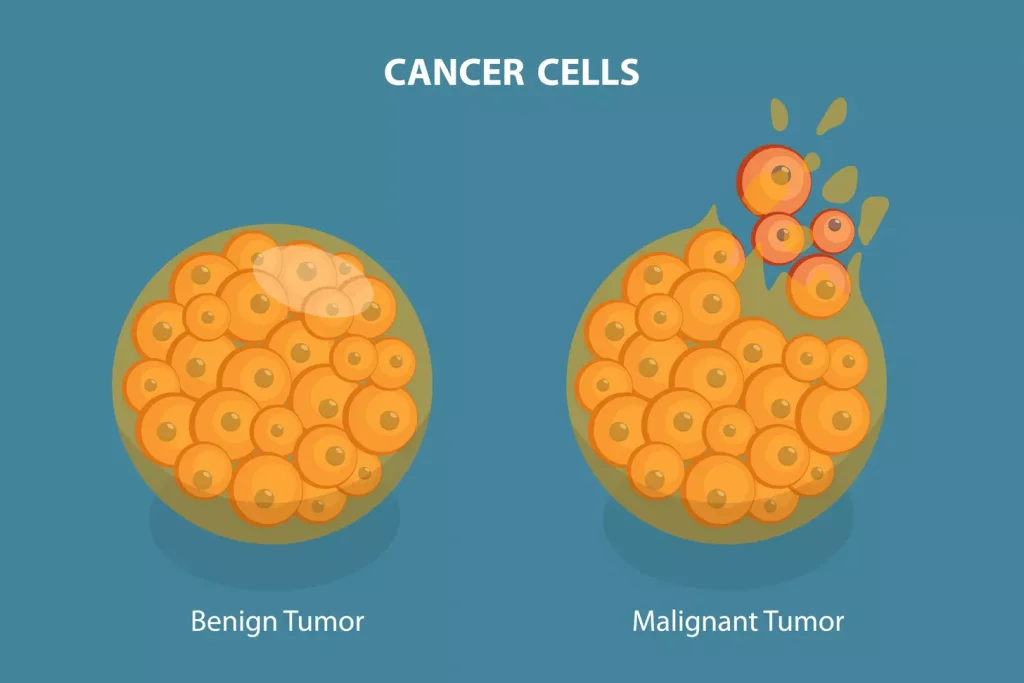
Benign tumors and cancer both involve abnormal cell growth. But they have different implications and behaviors. Knowing these differences is key to choosing the right treatment.
Growth Patterns and Invasion
Benign tumors grow slowly and stay in one place. They don’t invade nearby tissues. On the other hand, cancer grows fast and can spread to other areas. This spreading is a big sign of cancer.
Metastatic Potentia
Cancer cells can travel to other parts of the body. Benign tumors don’t spread like cancer does. This makes cancer harder to treat than benign tumors.
Cellular Appearance and Behavior
Cancer cells look and act differently than benign tumor cells. Cancer cells often look abnormal and divide quickly. Benign tumor cells look more like normal cells and divide slower. How cells behave is important in telling benign from malignant tumors.
Healthcare providers use these differences to plan treatments. For benign tumors, they might watch them or remove them surgically. Cancer, though, needs a stronger approach, like surgery, chemo, and radiation.
Common Types of Benign Tumors
Benign tumors are not cancerous but can cause health problems. Knowing the common types is key to managing them well. We’ll look at the various benign tumors found in the human body.
Adenomas
Adenomas start in gland or gland-like tissue. They can show up in places like the colon, adrenal glands, and pituitary gland. For example, adenomas in the colon might turn cancerous if not treated right.
Fibromas
Fibromas are made of fibrous or connective tissue. They can pop up in the skin, uterus, and ovaries. Usually, they’re harmless and can be removed if they bother you.
Hemangiomas
Hemangiomas are growths from too many blood vessel cells. They can be in the skin or inside organs and might be there from birth. Their size and where they are can decide if they need treatment.
Other Common Benign Neoplasms
Benign tumors also include lipomas, which are fat tissue, and leiomyomas, which are smooth muscle tumors. These can appear in different spots and might cause issues based on their size and where they are.
Benign tumors often have these traits:
- They are not cancerous and don’t spread to other areas.
- They usually don’t spread to other parts of the body.
- They can cause symptoms based on their location and size.
- They can often be treated by removing them or with other methods.
It’s important to know about the different benign tumors for the right diagnosis and treatment. Even though they’re not cancerous, they can affect your health and life quality. Getting help from doctors is key to managing benign tumors well.
Causes and Risk Factors for Benign Tumor Development
Benign tumors come from a mix of genetic, environmental, and hormonal influences. We might not always know the exact cause. But knowing these factors can help manage and maybe prevent them.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics play a big role in benign tumors. Some genetic conditions make it more likely to get these growths. For example, neurofibromatosis can cause many benign tumors. We’ll look into how genetics affect the risk of benign tumors.
- Inherited conditions that predispose to benign tumors
- Genetic mutations affecting cell growth regulation
- Family history of benign tumors or related conditions
Environmental Influences
Environmental factors also play a part in benign tumors. Things like toxins, radiation, and lifestyle can raise the risk. For example, some chemicals can increase the risk of certain benign tumors.
- Exposure to environmental toxins and chemicals
- Radiation exposure and its impact on cell growth
- Lifestyle factors, including diet and stress levels
Hormonal Factors
Hormones also have a big role in benign tumors. Hormonal changes can affect how these tumors grow. For instance, hormonal shifts during pregnancy can influence tumor growth.
Understanding hormonal effects can help manage benign tumors. This is true, even when hormonal therapies might be needed.
Signs and Symptoms of Benign Tumors
Knowing the signs of benign tumors is key for early treatment. These tumors might not show symptoms at first. But when they do, the signs can differ based on the tumor’s size and where it is.
Common Physical Manifestations
Painless lumps or masses under the skin are common signs. These can feel firm or soft and might not hurt when touched. Sometimes, these tumors can put pressure on nearby organs or nerves, causing pain or discomfort.
For example, a tumor in the thyroid gland might make swallowing hard or change your voice. This is because it’s pressing on the esophagus or nerves. A tumor in the gut can lead to changes in bowel movements or stomach pain.
When Benign Tumors Become Problematic
Even though many benign tumors are not harmful, some can be a problem. A tumor in the brain might cause headaches or vision changes because it’s pressing on the brain. Tumors in endocrine glands like the thyroid or adrenal glands can disrupt hormone levels.
- Benign tumors can cause a range of symptoms depending on their location.
- Some common symptoms include painless lumps, pressure on nearby organs, and changes in bodily functions.
- The size of the tumor can also impact the severity of symptoms.
Symptom Variations by Location
The symptoms of benign tumors can change a lot based on where they are. For example:
| Location | Possible Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Brain | Headaches, vision changes, seizures |
| Thyroid | Difficulty swallowing, voice changes, neck swelling |
| Uterus | Pelvic pain, heavy menstrual bleeding, infertility |
If you notice any unusual symptoms or body changes, see a doctor right away. Early detection and diagnosis are important for finding the right treatment for benign tumors.
Diagnostic Approaches for Benign Tumors
Diagnosing benign tumors requires imaging tests, biopsies, and lab tests. It’s key to tell benign from malignant tumors and plan treatment.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging is a big part of diagnosing benign tumors. Here are some common tests:
- X-rays: Good for finding tumors in bones and some soft tissues.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to see inside the body, great for thyroid, breast, and abdominal tumors.
- Computed Tomography (CT) scans: Gives detailed images of the body, showing tumor size and location.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Shows soft tissues clearly, useful for brain, spine, and other tumors.
Biopsy Procedures
A biopsy takes tissue from a tumor for a closer look. There are different types:
- Fine-needle aspiration biopsy: Uses a thin needle to get cells.
- Core needle biopsy: Takes a bigger piece of tissue with a larger needle.
- Surgical biopsy: Removes part or all of the tumor for study.
Biopsy results tell if a tumor is benign or cancerous and guide treatment.
Laboratory Tests and Markers
Lab tests are key for analyzing tumor samples and finding markers. These include:
- Histopathological examination: Looks at tissue structure under a microscope.
- Immunohistochemistry: Uses antibodies to find specific proteins in samples.
- Molecular tests: Checks genetic material for mutations or expressions.
These tests give vital info about the tumor, helping doctors plan treatment.
Treatment Options for Benign Tumors
Dealing with benign tumors involves several steps. It depends on the tumor’s type and the patient’s health. Treatments range from watching the tumor to surgery or medication.
Watchful Waiting Approach
For small, symptom-free tumors, watching them closely is often the best plan. This means regular checks with imaging and doctor visits. It’s good for tumors that don’t cause problems and won’t turn cancerous.
Benefits of Watchful Waiting:
- Avoids unnecessary surgical risks
- Reduces healthcare costs
- Minimizes the risk of complications from treatment
Surgical Interventions
If a tumor is causing trouble, is big, or growing fast, surgery might be needed. Surgery is key for tumors that bother you or could turn cancerous. The aim is to take out the tumor completely to stop it from coming back.
Types of Surgical Interventions:
| Surgical Method | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Excisional Biopsy | Removal of the entire tumor for examination | Diagnostic and therapeutic |
| Minimally Invasive Surgery | Surgery through small incisions using specialized tools | Less recovery time, fewer complications |
| Open Surgery | Traditional surgery with a larger incision | Direct access to the tumor, effective for large tumors |
Medication and Therapy Options
Medicine or therapy might help with some benign tumors. For example, hormone treatments work on hormone-sensitive tumors like some uterine fibroids. Medications can also shrink tumors or ease symptoms.
Medication Options:
- Hormonal therapies for hormone-sensitive tumors
- Medications to reduce symptoms or tumor size
Knowing the different treatments helps patients and doctors choose the best way to handle benign tumors.
The Malignant Potentail of Benign Tumors
It’s important to know that some benign tumors can turn into cancer. While most benign tumors are not cancerous, some can become cancerous under certain conditions.
Understanding Premalignant Conditions
Premalignant conditions are not cancer but can turn into it. For example, adenomatous polyps in the colon are considered premalignant. They can become cancerous if not treated.
Key characteristics of premalignant conditions include:
- Abnormal cellular growth patterns
- Increased cellular proliferation rates
- Genetic mutations that predispose to malignancy
Monitoring for Changes
It’s vital to keep an eye on benign tumors with cancer risk. This means regular check-ups, imaging tests, and sometimes biopsies. These steps help spot any signs of cancer growth.
Effective monitoring strategies include:
- Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers
- Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI
- Endoscopic examinations for tumors in accessible locations
Risk Assessment and Management
Assessing the risk of benign tumors involves looking at several factors. These include the tumor’s type, the patient’s medical history, and genetic factors. Based on this, a management plan is created.
Risk management may involve:
- Surgical removal of the tumor, if it’s premalignant
- Regular surveillance to monitor for changes
- Lifestyle modifications to reduce overall cancer risk
By understanding the cancer risk of benign tumors and using the right monitoring and management, we can better care for patients. This approach helps prevent cancer and improves patient outcomes.
Living with a Benign Tumor Diagnosis
Getting a diagnosis of a benign tumor can be tough. It brings up a lot of feelings and things to think about. Even though it’s not cancer, it can really change your life.
Managing Anxiety and Uncertainty
Getting a diagnosis can be scary. It’s important to manage your anxiety. Getting help from doctors, family, and friends can make you feel better. Also, seeing a counselor or therapist can help with the emotional side of things.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Living with a benign tumor might mean changing your lifestyle. This could be about what you eat, how you exercise, and how you handle stress. It’s best to talk to your doctor about what’s right for you.
- Eating a diet full of good nutrients
- Staying active with exercise
- Trying stress-reducing activities like meditation or yoga
Follow-up Care Requirements
It’s key to keep up with follow-up care. This helps keep an eye on the tumor and any changes. Following the recommended schedule is important for your health.
- Make sure to see your doctor regularly
- Do any tests or scans your doctor suggests
- Tell your doctor right away if you notice anything new or different
Understanding your diagnosis, making lifestyle changes, and sticking to follow-up care can help you manage your condition. This way, you can live a better life.
Prevention and Risk Reduction Strategies
While we can’t prevent all benign tumors, making lifestyle changes and getting regular screenings can help. These steps can lead to early detection and better management. Let’s look at how to lower the risk of benign tumors.
Lifestyle Modifications
Healthy choices are key to reducing benign tumor risk. Eating a diet full of fruits, veggies, and whole grains is important. Not drinking too much alcohol and not smoking also helps, as these habits are linked to lower tumor risks.
Regular exercise is another must. Doing moderate exercise helps control hormones and boosts the immune system. This can lower the chance of benign growths. Keeping a healthy weight is also vital, as extra fat increases tumor risk.
- Eating a balanced diet
- Avoiding harmful substances like tobacco and excessive alcohol
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Maintaining a healthy weight
Regular Screening
Screening is key for catching benign tumors early. Screening tests can spot tumors when they’re easier to treat. It’s important to follow the screening advice from your doctor, as it’s based on your risk and age.
For some benign tumors, like breast or colon polyps, there are specific tests. Sticking to these screening schedules boosts early detection chances.
- Mammograms for breast tumor detection
- Colonoscopy for colon polyps
- Regular check-ups for other types of benign tumors
Early Intervention Approaches
Acting fast is key when a benign tumor is found. Watching the tumor for changes and noticing new symptoms is important. Sometimes, removing the tumor is needed, like if it’s causing pain or could turn cancerous.
We also look at other treatments, like medicine or watching it closely, based on the tumor’s type and where it is. Working with your doctor to create a treatment plan is essential.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Suspected Benign Tumors
Knowing when to see a doctor for a suspected benign tumor is key. It’s important to watch for warning signs and emergency situations. Being aware of body changes that might need a doctor’s check-up is vital.
Warning Signs That Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Some symptoms suggest a benign tumor might be present or causing problems. Look for medical help if you notice:
- Persistent pain or discomfort that doesn’t improve with time
- Changes in bowel or bladder habits
- Unusual bleeding or discharge
- A noticeable lump or swelling that is growing or changing
It’s important to watch these symptoms closely. If you’re unsure, talk to a healthcare professional. Early check-ups can help figure out the cause and how to manage it.
Emergency Situations
At times, a benign tumor can cause emergencies needing quick medical help. Here are some emergency signs:
- Severe pain that is sudden in onset
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Heavy bleeding
- Sudden changes in vision or other neurological symptoms
If you or someone you know has these symptoms, get emergency care right away. Waiting too long can lead to serious issues.
Finding Specialized Care
Getting the right doctor is important if you have a benign tumor. Look for specialists who know how to handle these tumors. This might include:
- Oncologists with a focus on benign neoplasms
- Surgeons experienced in removing benign tumors
- Other specialists depending on the tumor’s location and type
Choosing experienced professionals can greatly improve your treatment. Don’t be shy to ask about their experience and treatment plans.
Conclusion
It’s important to know about benign tumors to manage them well. These growths are not cancer but can cause problems if they press on other parts. We’ve talked about what they are, how they differ from cancer, and how to treat them.
Benign tumors need careful attention to avoid serious issues. At Liv Hospital, we offer top-notch care and support for international patients. Our team is ready to help those dealing with benign tumors with personalized care.
Understanding benign tumors and getting help early is key to good health. If you have a benign tumor, don’t hesitate to contact our skilled healthcare team. We’re here to support and treat you.
What is a benign tumor?
A benign tumor is a non-cancerous growth. It doesn’t invade nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body. These tumors grow slowly and don’t spread.
What are the common types of benign tumors?
Common types include adenomas, fibromas, hemangiomas, and lipomas. They can appear in the skin, organs, and soft tissues.
How are benign tumors diagnosed?
Doctors use X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans to diagnose them. They also do biopsies and lab tests.
What are the treatment options for benign tumors?
Treatment options are watchful waiting, surgery, and medication. The choice depends on the tumor’s type, size, and location, and the person’s health.
Can benign tumors become cancerous?
While benign, some tumors can turn malignant over time. Regular check-ups are key to catch any changes.
What are the risk factors for developing benign tumors?
Risk factors include genetics, environment, and hormones. Making lifestyle changes and getting regular screenings can help.
How can I manage anxiety and uncertainty related to a benign tumor diagnosis?
Understanding your condition and making lifestyle changes can help. Getting support from loved ones and support groups is also important.
When should I seek medical attention for a suspected benign tumor?
Seek medical help for unusual growths, pain, bleeding, or changes in bowel or bladder habits. Don’t ignore rapid growth, swallowing trouble, or shortness of breath.
What is the prognosis for individuals with benign tumors?
The outlook is good, as these tumors are non-cancerous. They usually don’t affect life expectancy. But, regular check-ups are needed to prevent complications.
How can I find specialized care for a benign tumor?
Talk to your primary care doctor or get a referral to a specialist. Contact a reputable hospital like Liv Hospital for international patient support.




































