Stem cells are vital for human growth and health, and researchers have identified several types, each serving unique roles.
Knowing about these different categories helps in medical research and finding new treatments. Each stem cell type is special, making it good for certain uses.
Stem cells are sorted into types based on what they can become. This sorting is key for using them in medicine and research.
In this article, we will discuss the Five types of stem cells and their significance in medical research.
Understanding the Five types of stem cells provides insight into their roles and applications in modern medicine.
Key Takeaways
- Stem cells are categorized into multiple types based on their properties and functions.
- Understanding these categories is important for medical research progress.
- The different types of stem cells have unique features.
- Each type of stem cell is useful in medicine for specific tasks.
- The way stem cells are sorted is based on their ability to change into other cells.
Understanding Stem Cells and Their Importance
Stem cells are key to regenerative medicine and developmental biology. They can grow and change into different types of cells. This makes them very important for medical uses.
What Makes Stem Cells Unique
Stem cells have special traits that set them apart. These include:
- Self-renewal: They can grow without becoming specific cells.
- Potency: They can turn into many different cell types.
- Plasticity: Some stem cells can become cells they weren’t meant to be.
These traits make stem cells very useful for research and treatments. New methods in gene editing and stem cell therapy are showing great promise. They are helping to treat genetic diseases, showing how important stem cells are.
The Role of Stem Cells in Development and Medicine
Stem cells are essential in development and medicine. In the early stages of life, they create all the cells needed for our bodies. In adults, they help fix and grow tissues.
In medicine, stem cells are being looked at for new treatments. They could help in:
- Tissue Engineering: Creating new tissues for damaged areas.
- Cell Therapy: Replacing or fixing damaged cells to treat diseases.
- Drug Discovery: Helping to find and test new medicines by modeling diseases.
Stem cells are vital in both development and medicine. Their role in research and treatments highlights their importance.
Stem Cell Potency: The Basis of Classification
Stem cell potency is key to classifying stem cells. It shows how well a stem cell can turn into different cell types. This is important for medicine and research.
The potential of the Five types of stem cells is vast, offering hope for future medical breakthroughs.
What is Cell Potency?
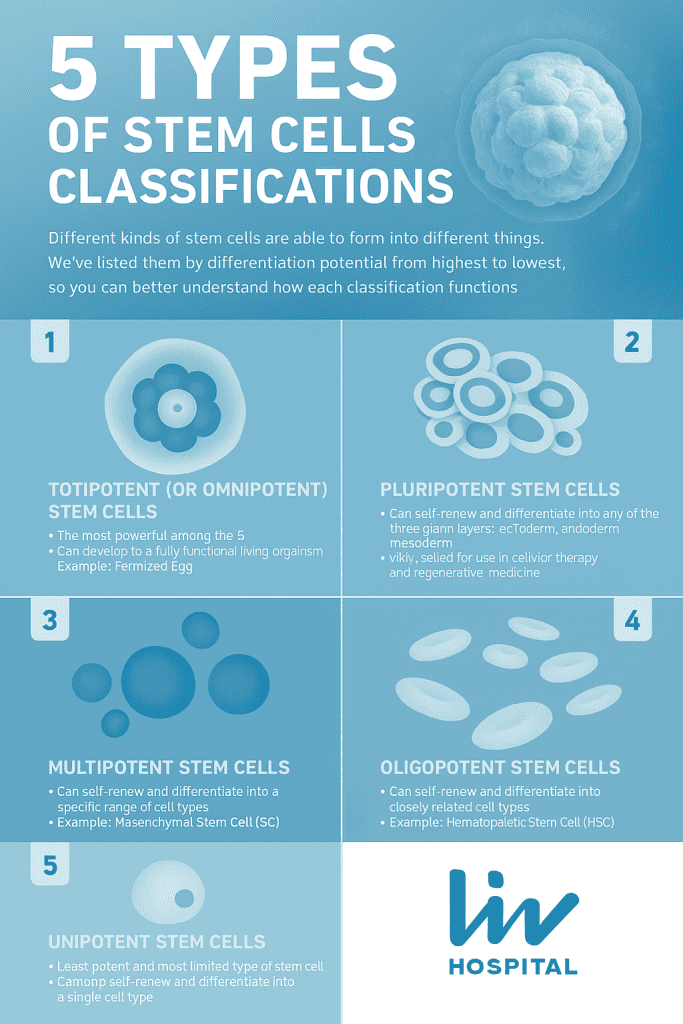
Cell potency shows how well a stem cell can become different cell types. It’s important to know what a stem cell can do. Totipotency, pluripotency, multipotency, oligopotency, and unipotency describe what types of cells a stem cell can become.
- Totipotent stem cells can become any cell type, including those in the embryo and placenta.
- Pluripotent stem cells can become most cell types in the body, but not placenta cells.
- Multipotent stem cells can become a few cell types, but only in a specific group.
How Potency Determines Stem Cell Function
The potency of a stem cell affects its role and uses. For example, pluripotent stem cells are great for regenerative medicine because they can become any cell type. On the other hand, multipotent stem cells are good for fixing specific tissues but can’t do as much.
Stem cell potency also plays a big role in development and disease. Knowing how potency affects stem cells helps us understand how they work. This knowledge is key to understanding development and disease.
Understanding cell potency helps researchers classify stem cells better. This knowledge is important for finding new treatments. It shows what each stem cell can do and how they can be used in medicine and research.
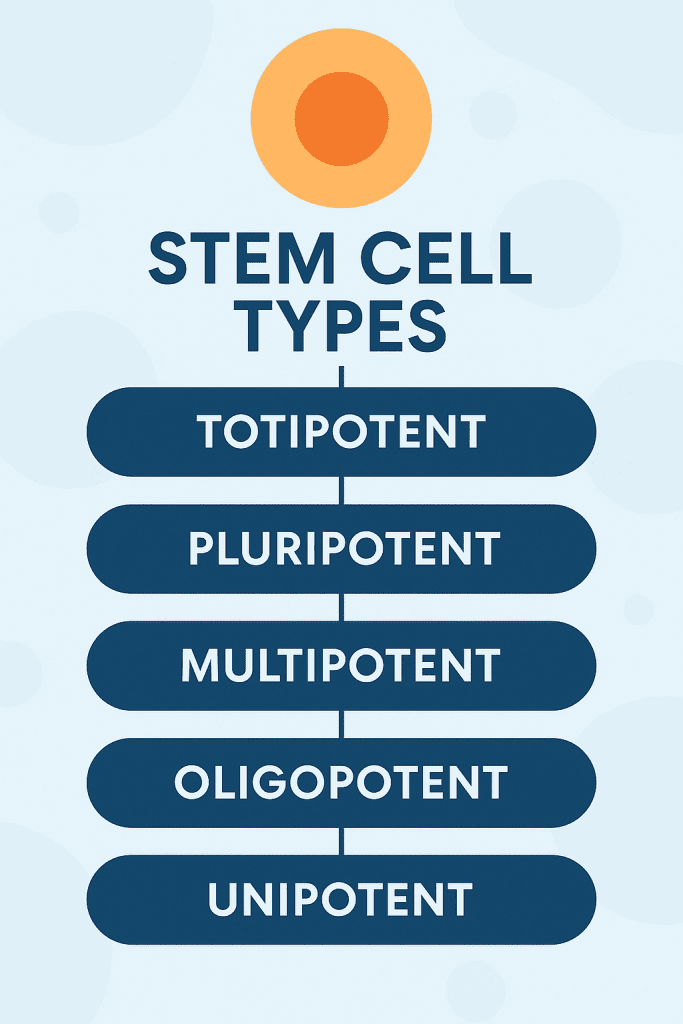
The Different Types of Stem Cells Based on Potency
Stem cells are divided into five types based on their potency. This division is key to understanding their role in medicine and research. The ability to turn into different cell types is a major factor in their use.
Overview of the Five Classifications
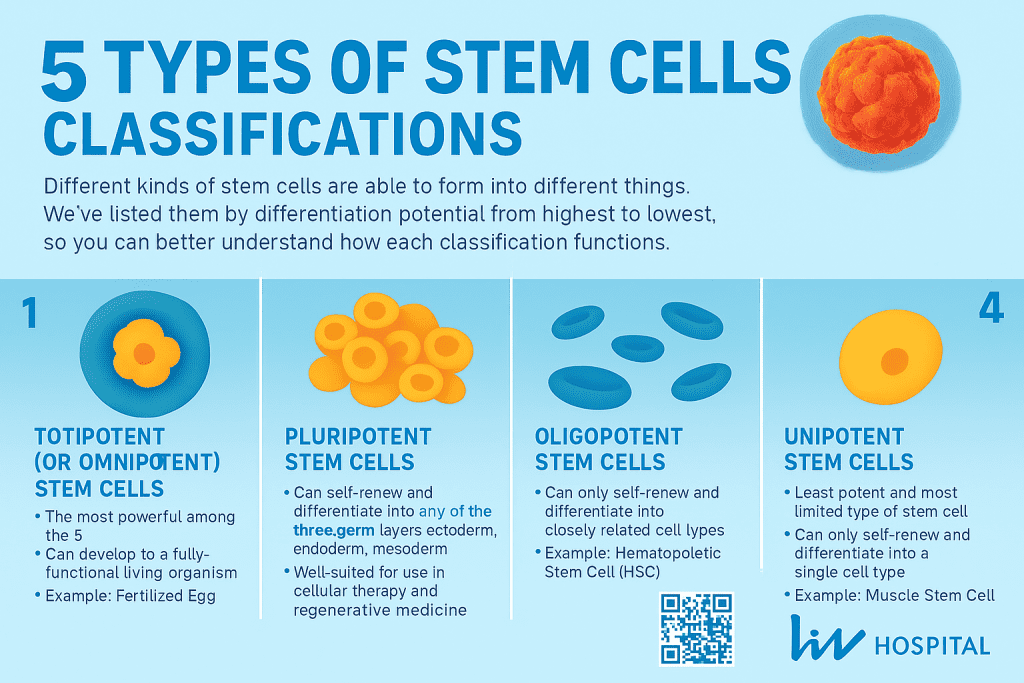
There are five main types of stem cells: totipotent, pluripotent, multipotent, oligopotent, and unipotent. Each type has a different ability to become various cell types.
- Totipotent stem cells can become all cell types, including placental cells.
- Pluripotent stem cells can become every somatic cell type but not placental cells.
- Multipotent stem cells can turn into several cell types but are limited to a specific lineage.
- Oligopotent stem cells can only turn into a few cell types, less than multipotent cells.
- Unipotent stem cells can only turn into one cell type, acting as a specific lineage’s progenitor.
The Hierarchy of Stem Cell Potency
The hierarchy of stem cell potency goes from totipotent at the top to unipotent at the bottom. Knowing this hierarchy helps us understand the strengths and limits of each stem cell type.
| Potency Level | Differentiation Ability | Examples |
| Totipotent | All cell types, including placental cells | Fertilized egg cells |
| Pluripotent | All somatic cell types | Embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells |
| Multipotent | Multiple cell types within a specific lineage | Hematopoietic stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells |
| Oligopotent | A few cell types within a specific lineage | Lymphoid progenitor cells |
| Unipotent | One cell type | Progenitor cells for a specific lineage |
Understanding the Five types of stem cells helps clarify their roles in treatment development.
Understanding stem cell types based on potency helps us see their capabilities and uses. As research grows, so does the promise of these stem cells in medicine.
Totipotent Stem Cells: The Most Versatile
Totipotent stem cells can turn into any cell type in an organism. This makes them very important in developmental biology and regenerative medicine.
To summarize, the Five types of stem cells are essential for advancements in medical research and therapy.
Characteristics of Totipotent Stem Cells
Totipotent stem cells can become every cell type in the body. This includes both embryonic and extraembryonic tissues. They are different from other stem cells because of this wide range of possibilities.
We will delve into the Five types of stem cells to understand their unique properties and potential.
In the discussion of the Five types of stem cells, we explore their significance in regenerative medicine.
The Five types of stem cells are crucial for understanding the potential of stem cell therapy in various diseases.
Key Features of Totipotent Stem Cells:
Each of the Five types of stem cells has distinct characteristics that contribute to their unique applications.
- Ability to form a complete organism
- Capacity to differentiate into all cell types
- Involvement in early developmental stages
Sources and Examples of Totipotent Cells
Totipotent stem cells are found in the early stages of embryonic development. The zygote, formed by sperm and egg, is a main source of these cells.
A leading researcher says, “The zygote represents the ultimate totipotent state, capable of giving rise to a fully formed organism” (
“The Biology of Totipotency,” Developmental Cell, 2018
).
| Source | Description |
| Zygote | The initial cell formed during fertilization, considered totipotent. |
| Early Embryonic Cells | Cells in the early stages of embryonic development that retain totipotency. |
Research Applications and Limitations
Totipotent stem cells are key in research, helping us understand early development and regenerative medicine. But, there are ethical and technical hurdles to overcome.
Research on totipotent stem cells is growing. It helps us understand their role in development and their possible uses. As scientists face and solve these challenges, new treatments could emerge.
Pluripotent Stem Cells: Almost Unlimited Potencial
Pluripotent stem cells can turn into almost any cell type. This makes them very promising for medical research and treatments. They can become many different cell types, which is very useful.
Defining Features
These cells can keep growing and changing into different cell types. They can become ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm. This is why they are so valuable for research and treatments.
The key feature of pluripotency is different from totipotency. Pluripotent cells can’t make a whole organism by themselves. But they can make most cell types in an organism.
Embryonic vs. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
There are two main types of pluripotent stem cells. Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) come from early-stage embryos. They can naturally turn into many cell types.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are made from adult cells that are changed to be pluripotent. This makes them a big deal for research and treatments. They don’t have the same ethical issues as ESCs.
- Embryonic stem cells are from embryos and can naturally change into different cells.
- Induced pluripotent stem cells are made from adult cells that are changed to be pluripotent.
Current Research and Therapeutic Applications
Pluripotent stem cells are key in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. Scientists are working hard to understand how to make them into specific cells for treatments. For example, iPSCs can be used to study diseases in a lab dish.
This helps us understand diseases better and develop personalized treatments. The possibilities for using these cells are huge. They could help with heart disease, neurological disorders, and diabetes, among others.
Multipotent Stem Cells: Tissue-Specific Differentiation
Multipotent stem cells can turn into many cell types within a certain group. They are very useful in regenerative medicine. But, they can only become specific cell types, not all types.
Key Characteristics of Multipotent Stem Cells
Multipotent stem cells can grow and change into different cell types in a specific area. This ability is key for fixing and growing tissues. They can’t turn into all cell types like some other stem cells can.
Hematopoietic stem cells, for example, can become all blood cells. This shows how multipotent stem cells work.
Examples Including Hematopoietic and Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are examples of multipotent stem cells. HSCs make all blood cells and help with blood diseases. MSCs can become bone, cartilage, and fat cells.
MSCs are great for fixing tissues and helping the immune system. They could help with many health problems, from bone issues to skin treatments.
Clinical Applications and Treatments
Multipotent stem cells are used in many treatments. HSCs help with blood cancers through bone marrow transplants. MSCs might help with arthritis, heart disease, and more.
“The use of multipotent stem cells in regenerative medicine holds great promise for the treatment of various diseases and injuries, and offers new hope for patients with limited treatment options.”
There’s a lot of hope for using multipotent stem cells to make people healthier. Scientists are working hard to make this happen.
Oligopotent and Unipotent Stem Cells: Limited but Specialized
Oligopotent and unipotent stem cells have a special role in fixing and keeping tissues healthy. They are key to learning how to grow new tissues and keep them balanced.
Oligopotent Stem Cells: Definition and Examples
Oligopotent stem cells can turn into a few different cell types. This is less than what multipotent stem cells can do. For example, they can become different immune cells.
These stem cells are special because they can become many cell types in one family. For example, lymphoid stem cells can turn into T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells. These cells are vital for our immune system.
Unipotent Stem Cells: The Most Specialized Type
Unipotent stem cells can only turn into one cell type. They are very specialized. Muscle stem cells are a good example. They help grow new muscle tissue.
These stem cells are very important for keeping tissues healthy, like the skin and gut. They can quickly fix damaged tissues.
Roles in Tissue Maintenance and Repair
Oligopotent and unipotent stem cells are both important for fixing and keeping tissues healthy. They can target specific tissues for repair. This ensures that tissues are fixed and maintained as needed.
- Oligopotent stem cells help develop many cell types in a specific family.
- Unipotent stem cells are key for growing specific tissues, like muscle and skin layers.
- Both types are vital for keeping tissues balanced and fixing injuries.
Studying oligopotent and unipotent stem cells helps us understand how to grow new tissues and fix them. This knowledge can help create new treatments for many diseases and injuries.
Comparing the Different Types of Stem Cells: Clinical Applications
Stem cells have many uses in medicine, based on their type and strength. As we learn more, knowing the differences between stem cells is key to using them to help people.
The therapeutic applications of the Five types of stem cells are evolving as new techniques are developed.
Therapeutic Potentials of Each Stem Cell Type
Each stem cell type can do different things to help us. Totipotent stem cells can grow into a whole organism. This makes them very useful for studying how we develop early in life.
Pluripotent stem cells, like those from embryos, can turn into almost any cell. This makes them very promising for fixing damaged tissues.
- Multipotent stem cells, like those in blood and bone, are already helping in treatments. They fix blood problems and help repair tissues.
- Oligopotent and unipotent stem cells can fix specific tissues. They are useful for repairing certain parts of the body.
Ethical Considerations and Regulatory Challenges
Using stem cells in medicine is a topic of debate. People worry about where stem cells come from, like from embryos. There are also rules to follow as this field grows fast.
“The debate on stem cell research is complex. It involves where stem cells come from, the chance of cloning, and balancing science with respect for life.”
Future Directions in Stem Cell Research and Therapy
The future of stem cell research looks bright. We’ll work on making treatments safer and more effective. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are a big hope. They could lead to treatments made just for each patient, without the ethics worries of embryonic stem cells.
- Gene editing tools like CRISPR/Cas9 will help stem cells do more for us.
- Learning more about stem cells will help us make treatments that work better.
Conclusion
Knowing about the different stem cells is key for moving forward in research and treatments. The way we sort stem cells by their power helps us see what they can do and what they can’t.
Looking at stem cells, we see a range from the most powerful to the least. Each type has its own special traits and uses. This research could change medicine a lot, leading to new ways to treat diseases.
As scientists learn more about stem cells, we get closer to using them to help people. Understanding each type of stem cell is essential. It helps us see how they work in our bodies and how they can help with health problems.
FAQ
What are the different types of stem cells?
There are five main types of stem cells. These include totipotent, pluripotent, multipotent, oligopotent, and unipotent”collectively known as the Five types of stem cells. Each type has different abilities to become various cell types.
What is the difference between totipotent, pluripotent, and multipotent stem cells?
Future research will further illuminate the functions of the Five types of stem cells in health and disease.
Totipotent stem cells can turn into any cell type, including placental cells. Pluripotent stem cells can turn into almost any cell type, except placental cells. Multipotent stem cells can turn into several cell types, but only within a specific lineage or tissue.
In conclusion, recognizing the Five types of stem cells is vital for the future of regenerative medicine.
What are pluripotent stem cells?
Pluripotent stem cells can turn into almost any cell type in the body, except placental cells. They come from embryonic stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells.
What is the role of multipotent stem cells in the body?
Multipotent stem cells are key in keeping and fixing tissues. They can turn into several cell types in a specific lineage or tissue. For example, hematopoietic stem cells can turn into blood cells.
What are oligopotent and unipotent stem cells?
Oligopotent stem cells can turn into a few cell types, usually in a specific lineage. Unipotent stem cells can only turn into one cell type, but they can grow and keep tissue balance.
In the context of regenerative medicine, the Five types of stem cells offer significant insights into healing processes.
Ethical discussions surrounding the Five types of stem cells are essential for responsible research practices.
What are the clinical applications of different types of stem cells?
Different stem cells have different uses in medicine. Totipotent and pluripotent stem cells are promising for regenerative medicine. Multipotent stem cells are used in treatments like bone marrow transplants. Oligopotent and unipotent stem cells help in maintaining and repairing tissues.
What is the potency of embryonic stem cells?
Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent. This means they can turn into almost any cell type in the body.
What are the ethical considerations in stem cell research?
Ethical issues in stem cell research include the source of stem cells, like embryonic stem cells. There’s also worry about uncontrolled cell growth or tumors.
What is the future of stem cell research and therapy?
Stem cell research and therapy have a bright future. They could lead to new treatments for many diseases and injuries. Understanding stem cell biology and improving cell culture techniques are key to unlocking their full therapeutic power.
The Five types of stem cells represent a frontier in understanding cellular biology and their applications in health.
What are induced pluripotent stem cells?
Induced pluripotent stem cells are made from adult cells, like skin or blood cells. They are reprogrammed to have similar properties to embryonic stem cells. They are used for research and could be used for treatments in the future.
The Five types of stem cells will play a key role in future innovations in biomedical research.
Exploring the Five types of stem cells allows us to harness their potential for therapeutic use.
By studying the Five types of stem cells, we can uncover new treatment strategies for various conditions.
In summary, the Five types of stem cells provide a foundation for advancing our understanding of cellular differentiation.
The implications of the Five types of stem cells extend across many fields in science and medicine.
The study of the Five types of stem cells reveals their critical importance in advancing medical science.
The future of the Five types of stem cells in therapy is an exciting area of ongoing research and development.























