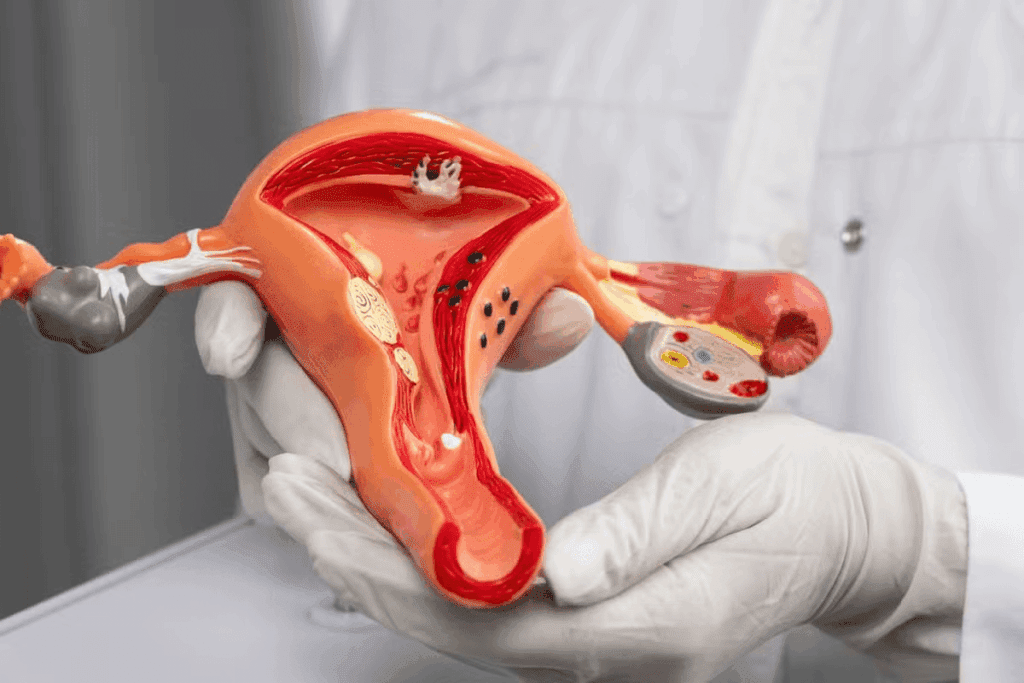
An enlarged uterus is when the uterus grows bigger than its usual size. This is usually 3 to 4 inches by 2.5 inches. Many things can make the uterus bigger, but uterine fibroids are the main reason. They affect about three-quarters of women by the time they are 50.what causes uterus to swellHernia from Coughing: Causes and What to Do
An enlarged uterus can mean different things, from harmless fibroids to serious health issues. If you’re experiencing heavy bleeding, pelvic pain, or swelling in your belly, finding out why is key. Getting a proper diagnosis is the first step to feeling better.
Key Takeaways
- An enlarged uterus is a condition where the uterus grows beyond its normal size.
- Uterine fibroids are the most common cause of an enlarged uterus.
- Symptoms can include heavy bleeding, pelvic pain, and abdominal swelling.
- Proper diagnosis is critical for effective treatment.
- Liv Hospital’s experienced gynecology team is dedicated to providing thorough care.
Understanding the Uterus: Normal Size and Function
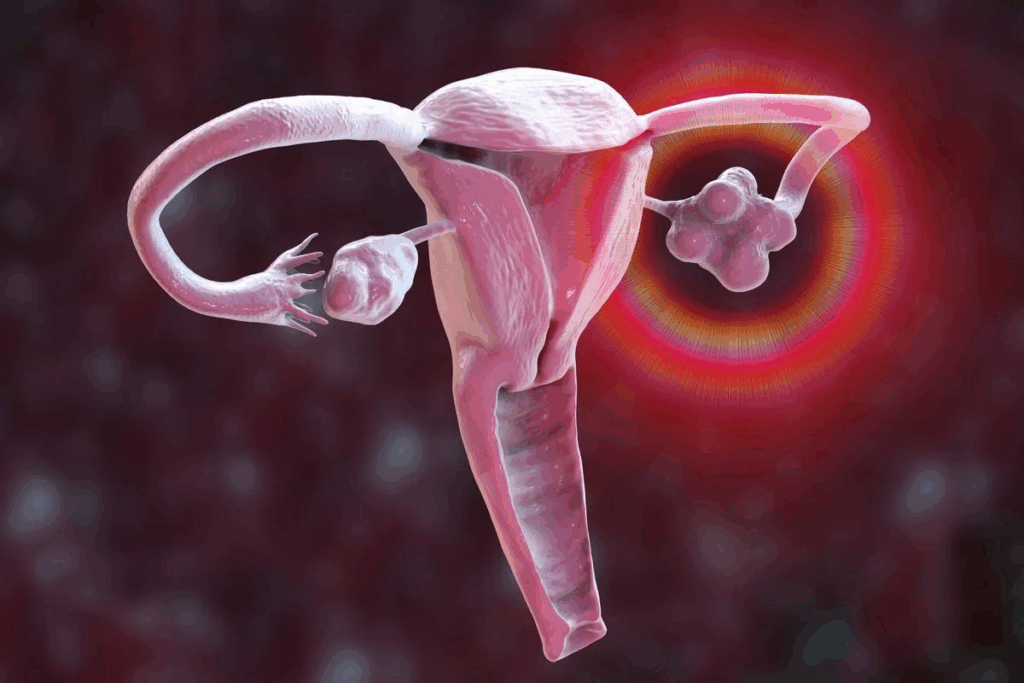
The uterus is a key part of the female body. It helps with pregnancy and menstrual cycles. Its proper work is vital for women’s health.
Normal Uterine Dimensions and Anatomy
The uterus is about 7 to 8 cm long, 5 cm wide, and 2 to 3 cm thick. Its size can change in women who have had kids. It has two main parts: the corpus (body) and the cervix.
The corpus is where a baby grows during pregnancy. The cervix is the lower part that opens into the vagina.
Key Dimensions:
Dimension | Average Measurement |
Length | 7 to 8 cm |
Width | 5 cm |
Thickness | 2 to 3 cm |
The Role of the Uterus in Female Reproductive Health
The uterus is vital for women’s health, mainly for supporting pregnancy. It’s where a fertilized egg grows. It also sheds its lining during menstruation if there’s no pregnancy.
Knowing the uterus’s normal size and function is key. It helps spot problems like an enlarged uterus. This can be due to fibroids, adenomyosis, or hormonal issues.
What Causes Uterus to Swell: Common Factors

An enlarged uterus can be caused by many things. These include hormonal changes, age-related conditions, and genetic predispositions. We will look into these factors to understand how they affect uterine size.
Hormonal Influences on Uterine Size
Hormonal changes, like changes in estrogen levels, greatly affect uterine size. Estrogen helps the uterine lining grow. An imbalance can cause endometrial hyperplasia or fibroids. These conditions can make the uterus swell, leading to symptoms.
When estrogen levels are too high compared to progesterone, the uterus grows. This imbalance can happen during perimenopause or with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Knowing how hormones affect the uterus is key to diagnosing and treating uterine enlargement.
Age-Related Changes in Uterine Structure
Age also affects uterine size. During a woman’s reproductive years, the uterus changes, mainly during pregnancy. But, even outside of pregnancy, age can cause changes. As women get closer to menopause, hormone levels drop, affecting the uterus.
The risk of getting conditions like adenomyosis or fibroids increases with age. These conditions can cause a lot of discomfort and affect daily life.
Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors
Genetic predispositions and environmental factors also contribute to uterine enlargement. Women with a family history of uterine fibroids or endometriosis are more likely to have a swollen uterus. Environmental factors, like certain chemicals or diet, can also impact uterine health.
Knowing these risk factors helps in early detection and prevention of uterine enlargement. By understanding the common causes of uterine swelling, women can get the right medical care and manage their symptoms better.
Uterine Fibroids: The Leading Cause of Enlarged Uterus
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that grow in or on the uterine wall. They are a major reason for an enlarged uterus. These growths can be different in size, number, and location, affecting the uterus in various ways.
Types and Locations of Fibroids
Fibroids can be classified based on where they grow in or around the uterus. The main types include:
- Intramural Fibroids: These are the most common type, growing within the muscular wall of the uterus.
- Submucosal Fibroids: These fibroids project into the uterine cavity, potentially causing heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Subserosal Fibroids: Growing outward from the uterus, these can sometimes be attached to other organs.
- Pedunculated Fibroids: These are attached to the uterus by a stalk-like structure, and can be either subserosal or submucosal.
How Fibroids Cause Uterine Enlargement
Fibroids can cause the uterus to grow by increasing its size. As fibroids grow, they stretch the uterus, sometimes a lot. This stretching can cause discomfort, pain, and other issues.
The fibroids push against the uterine walls, making it stretch and grow. This growth can lead to discomfort, pain, and other complications.
Risk Factors for Developing Fibroids
Several factors increase the risk of developing uterine fibroids, including:
- Genetic Predisposition: Women with a family history of fibroids are more likely to develop them.
- Hormonal Influences: Estrogen and progesterone promote the growth of fibroids.
- Age: Fibroids are more common in women of reproductive age.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese may increase the risk.
Knowing these risk factors can help in early detection and management of uterine fibroids.
Adenomyosis: Endometrial Tissue in the Uterine Wall
Adenomyosis happens when tissue like the uterus lining grows in the uterine walls. This can cause a lot of discomfort and change a woman’s life.
Mechanism of Uterine Enlargement
Adenomyosis makes the uterus swell because of inflammation and swelling. This swelling can lead to heavy bleeding and pelvic pain.
We don’t know exactly why adenomyosis happens. But it might be because of hormones and genetics. It can make the uterus feel hard or look bigger, which doctors can see during an exam.
Differentiating Adenomyosis from Endometriosis
Adenomyosis and endometriosis both involve endometrial tissue in the wrong place. But they are different. Endometriosis grows outside the uterus, often on ovaries or tubes.
Adenomyosis, on the other hand, has endometrial tissue inside the uterine wall. This difference changes how symptoms and treatments work for each condition.
- Adenomyosis: Endometrial tissue within the uterine wall.
- Endometriosis: Endometrial tissue outside the uterus, often on other pelvic structures.
Impact on Menstrual Cycles and Fertility
Adenomyosis can make menstrual cycles heavy or long. It also causes pelvic pain and discomfort during periods.
It can also hurt fertility. The inflammation and scarring might stop an embryo from implanting or change the uterine environment.
- Heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Pelvic pain and discomfort.
- Potential impact on fertility.
Knowing about adenomyosis is key to managing its symptoms and its effects on fertility. Women with symptoms should see a doctor for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Endometrial Hyperplasia and Hormonal Imbalances
Understanding endometrial hyperplasia means looking at hormonal imbalances in uterine health. This condition makes the endometrium thicker, often because of hormones.
Unopposed Estrogen Exposure and Uterine Growth
When estrogen isn’t balanced by progesterone, it can cause endometrial hyperplasia. This imbalance makes the endometrium grow too much.
Estrogen is key in the female reproductive system. It helps the endometrium grow. But without progesterone, estrogen can make it too thick, leading to hyperplasia.
Connection to Endometrial Cancer Risk
Endometrial cancer risk is high with endometrial hyperplasia, mainly with cellular atypia. The move from hyperplasia to cancer involves many molecular changes. Hormonal and genetic factors play a big role.
It’s important to find risk factors and understand endometrial hyperplasia. This helps in early treatment and preventing serious issues like endometrial cancer.
Identifying Abnormal Endometrial Thickening
Diagnosing endometrial hyperplasia checks the endometrium’s thickness, usually with ultrasound. A thickness that’s too high for a woman’s age or menopausal status might show hyperplasia.
Diagnosing endometrial hyperplasia needs a full approach. This includes clinical checks, imaging, and sometimes a biopsy. It helps find out if the condition is there and how severe it is.
Pregnancy and Natural Uterine Enlargement
During pregnancy, the uterus grows, a natural step for the baby’s development. As the baby grows, the uterus gets bigger to hold it. This change happens throughout the pregnancy.
Normal Uterine Growth Timeline During Pregnancy
The uterus starts to grow early in pregnancy. By the 12th week, it’s as big as an orange. By the 20th week, it’s at the navel level. By the end of the third trimester, it’s just below the rib cage. This growth is a gradual process that supports the baby.
Gestational Age | Uterine Size Comparison |
12 weeks | Orange size |
20 weeks | Navel level |
36-40 weeks | Just below rib cage |
Postpartum Uterine Involution Process
After giving birth, the uterus goes back to its original size. This takes about 6-8 weeks. Women may experience postpartum bleeding as the uterus sheds its lining.
Uterine involution happens due to hormonal changes and uterine contractions. Breastfeeding can also help by making the uterus contract more.
Distinguishing Normal from Abnormal Enlargement
Uterine growth during pregnancy is normal. But, it’s important to know when it’s not. Abnormal growth can be caused by fibroids, adenomyosis, or other issues.
Healthcare providers use ultrasound and check-ups to see if the uterus is growing as it should. Women should watch their body changes and tell their doctor if anything seems off.
Other Medical Causes of Enlarged Uterus
Many medical conditions can make the uterus bigger, not just the usual ones. We’ll look at these conditions to understand how they affect the uterus and health.
Endometrial and Uterine Cancer
Uterine cancers, like endometrial cancer, can make the uterus grow. Endometrial cancer starts in the uterus lining. It’s linked to obesity, hormonal issues, and some genetic syndromes. Catching it early is key to treating it well.
“Cancer can make the uterus bigger, causing bleeding and pain,” says a top doctor. Knowing these risks helps find and treat it early.
Uterine Polyps and Their Effects
Uterine polyps grow on the uterus wall and can make it bigger. They’re usually not cancerous but can cause irregular bleeding. Hormones and inflammation might make them grow.
Even though uterine polyps are often not cancerous, they can affect fertility and cause pain. Removing them might help symptoms and reproductive health.
Ovarian Cysts and Their Impact on Uterine Position
Big ovarian cysts can push on the uterus, changing its shape or causing pain. These cysts are fluid-filled and can be benign or cancerous. Symptoms include pelvic pain and swelling.
Ovarian cysts can make reproductive health tricky, needing careful management to avoid problems.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Complications
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the reproductive organs, often from STIs. It can cause the uterus to grow, chronic pain, and infertility if not treated quickly.
Quick diagnosis and antibiotics are vital to avoid lasting harm. Spotting PID symptoms like pain and unusual discharge is important for early action.
Recognizing Symptoms of an Enlarged Uterus
It’s important for women to know about uterine enlargement symptoms. An enlarged uterus can cause various symptoms that affect a woman’s life quality.
Abdominal Heaviness and Protrusion
Abdominal heaviness or pressure in the lower abdomen is a common sign. Sometimes, the abdomen may also swell or protrude.
- Feeling of fullness: Women might feel constantly full or bloated.
- Visible enlargement: The abdomen might look bigger.
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Patterns
Abnormal bleeding is a key symptom. This includes:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding: Too much blood during periods.
- Irregular periods: Changes in menstrual cycle length or frequency.
- Intermenstrual bleeding: Bleeding between periods.
Pelvic Pain and Pressure Symptoms
Pelvic pain or discomfort is common in women with an enlarged uterus. This pain can be mild or severe and may come and go.
- Dysmenorrhea: Painful menstruation.
- Pelvic pressure: Feeling of pressure or heaviness in the pelvic area.
Urinary and Bowel Complications
An enlarged uterus can also cause urinary and bowel issues. This is due to the pressure on nearby organs.
- Frequent urination: Need to urinate often due to bladder pressure.
- Constipation: Difficulty in bowel movements or constipation due to bowel pressure.
It’s vital to recognize these symptoms and seek medical help. If you notice any of these signs, see a healthcare provider for a diagnosis and treatment plan.
Diagnosis and Medical Assessment Methods
Figuring out why a uterus is enlarged takes a mix of physical checks and high-tech scans. When signs point to a big uterus, doctors use many tools to get a clear picture.
Physical Examination Techniques
A detailed physical check is often the first step. Doctors feel the belly to see how big and shaped the uterus is. They also do a pelvic exam to look for any oddities in the reproductive area.
Imaging Methods for Uterine Evaluation
Scans are key in checking if the uterus is too big. Ultrasound is a top choice because it shows the uterus and nearby areas clearly. An enlarged uterus ultrasound can spot fibroids, adenomyosis, or other reasons for the size increase.
Laboratory Tests and Biopsy Procedures
Sometimes, laboratory tests are needed to find the real reason for a big uterus. These tests might include blood work to check hormone levels or other issues. A biopsy might also be done, where a piece of uterine tissue is looked at for abnormal cells or other problems.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Get help right away if you have bad symptoms like a lot of bleeding, sharp pelvic pain, or trouble peeing. These signs could mean a serious problem that needs quick action.
Treatment Options for Enlarged Uterus
The treatment for an enlarged uterus varies based on the cause. We’ll look at different options, like medicines, surgery, and lifestyle changes.
Medication-Based Approaches
For some, medicine is the first step to treat symptoms of an enlarged uterus. These drugs can lessen heavy bleeding, pain, and other issues.
- Hormonal therapies can reduce bleeding and shrink the uterus.
- Pain relief medications help manage pain from an enlarged uterus.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists can shrink fibroids and cut down on bleeding.
Surgical Interventions
If medicine doesn’t work or the condition is serious, surgery might be needed. There are various surgical options, from small procedures to bigger surgeries.
Surgical Option | Description | Benefits |
Myomectomy | Surgical removal of fibroids | Preserves the uterus, relieves symptoms |
Hysterectomy | Removal of the uterus | Definitive treatment for severe cases |
Uterine artery embolization | Cutting off blood supply to fibroids | Minimally invasive, reduces symptoms |
Lifestyle Modifications and Self-Care
Along with medical treatments, lifestyle changes can help manage an enlarged uterus. These changes can boost well-being and lessen discomfort.
- Dietary changes can help manage symptoms; a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is recommended.
- Regular exercise can help reduce pain and improve overall health.
- Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help alleviate stress and discomfort.
By exploring these treatment options and making informed choices, women can manage an enlarged uterus and enhance their life quality.
Conclusion
Knowing what makes a womb enlarge is key for women’s health. An enlarged uterus can come from many things like uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, and hormonal imbalances. When the uterus grows too big, it can cause discomfort and serious health issues.
We’ve looked at why the uterus might get bigger, its symptoms, how doctors diagnose it, and treatment options. It’s important to notice the signs and get medical help early. This helps manage uterine health better. By knowing the causes and acting early, people can lower their risk of problems and feel better overall.
In short, an enlarged uterus needs care and attention from doctors. If you’re worried about your uterine health or notice symptoms, see a healthcare professional. They can offer advice and support tailored to you.
FAQ
What is considered an enlarged uterus?
An enlarged uterus is when the uterus is bigger than usual. This is often due to conditions like fibroids, adenomyosis, or hormonal issues.
What are the common causes of an enlarged uterus?
Causes include uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, and endometrial hyperplasia. Pregnancy and other conditions like cancer can also cause it.
What are the symptoms of an enlarged uterus?
Symptoms include feeling heavy in the abdomen and abnormal bleeding. You might also feel pelvic pain and have trouble with urination or bowel movements.
How is an enlarged uterus diagnosed?
Doctors use physical exams, ultrasound, and lab tests to diagnose it. They might also do a biopsy to find the cause.
What are the treatment options for an enlarged uterus?
Treatment includes medicines for symptoms and surgery for the cause. Changing your lifestyle can also help.
Can an enlarged uterus be a sign of cancer?
Yes, it can be a sign of endometrial or uterine cancer. It’s important to get checked by a doctor.
How does pregnancy affect uterine size?
Pregnancy makes the uterus grow to fit the baby. After giving birth, it goes back to normal size through a process called postpartum involution.
What is adenomyosis and how does it cause uterine enlargement?
Adenomyosis is when endometrial tissue grows into the uterine wall. It causes the uterus to grow, heavy bleeding, and pelvic pain.
Can lifestyle changes help manage symptoms of an enlarged uterus?
Yes, staying healthy, eating right, and managing stress can help with symptoms.
When should I seek medical attention for an enlarged uterus?
See a doctor if you have severe pain, heavy bleeding, or trouble with urination or bowel movements. These could be signs of a serious problem.
What is the normal size of the uterus?
The normal uterus is about 7 to 8 centimeters long, 5 centimeters wide, and 2 to 3 centimeters thick. Sizes can vary slightly.
Can fibroids cause the uterus to become enlarged?
Yes, fibroids can make the uterus bigger. They grow inside or on the uterine walls.
How do hormonal influences affect uterine size?
Hormonal imbalances, like too much estrogen, can cause the uterus to grow. This is seen in conditions like endometrial hyperplasia.
References
Government Health Resource. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra1401429