Seeing blood clots in urine can be scary. But knowing what they look like is key to acting right. These clots can look like strings or red, dark pieces, depending on where they come from in the urinary system what does a blood clot in urine look like.
At Liv Hospital, we stress the need to see a doctor if you find blood clots in your urine. Blood clots in urine, or hematuria with clotting, can mean different problems like injuries, infections, or stones in the kidneys or bladder.
We focus on our patients at Liv Hospital. We know that seeing clumps of blood or tiny clots in your urine is a sign of something serious. It needs the right medical care.
Key Takeaways
- Blood clots in urine can appear as stringy or chunky formations.
- The presence of blood clots may indicate urinary tract issues.
- Medical evaluation is critical when you find blood clots in urine.
- Liv Hospital offers detailed urology care with a focus on patients.
- Knowing why you have blood clots is vital for the right treatment.
Understanding Blood Clots in Urine
It’s important to know why blood clots in urine happen and what they mean. Blood clots in urine, known as hematuria with clotting, can point to several health issues.
Definition of Hematuria with Clotting
Hematuria is when blood shows up in your urine. When there are clots, it’s called hematuria with clotting. This can range from tiny blood spots to big clots. Clots usually mean there’s a big bleed somewhere in your urinary tract.
Studies show that hematuria affects up to 30% of adults at some point. But seeing clots is rare. Hematuria is important because it can show serious health problems that need doctor’s care.
Prevalence and Significance
Hematuria is common, affecting 30% of adults at some time. When you see blood in your urine, it might look pink, red, or brown. Hematuria with clotting is very serious. It can mean you have infections, kidney stones, or even cancer.
Here are some important things to know about blood clots in urine:
- It can mean you have an infection or inflammation.
- Seeing clots means there’s a big bleed in your urinary tract.
- You need a doctor to find out why you have blood clots in your urine.
Knowing about hematuria with clotting is key for both patients and doctors. It shows why getting medical help fast is so important to find and treat the cause.
What Does a Blood Clot in Urine Look Like?
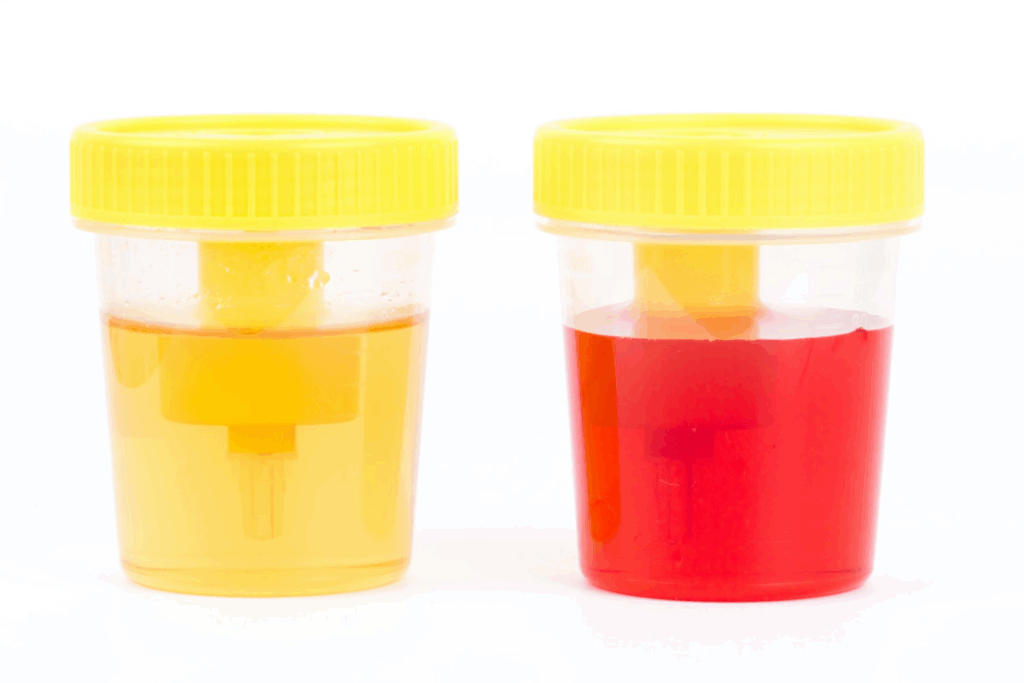
Blood clots in urine can be scary. Knowing what they look like is key to spotting health issues. It’s important to notice their shape, size, and color to understand the cause.
Visual Characteristics of Blood Clots
Blood clots in urine look different. They are usually red or brown and can be stringy or worm-like. The shape can change because of the urethra’s shape.
In some cases, they look like jelly or chunks of blood. This shows bleeding in the urinary tract. It could be due to infections, kidney stones, or injuries.
The size of these clots varies too. They can be tiny or quite big. Seeing them means there’s bleeding in the urinary tract.
Changes in Urine Color and Appearance
Blood clots change urine’s color and look. Normally, urine is pale yellow. But with blood clots, it turns pink, red, or brown. This depends on the blood amount and how long it’s been there.
Urine might also look cloudy or hazy. This is because of blood or other substances. It could mean an infection or inflammation.
To understand urine color changes, let’s look at possible reasons:
| Urine Color | Possible Cause |
| Pink or Light Red | Small amount of blood, possibly due to minor infection or irritation |
| Deep Red or Brown | Significant bleeding, potentially caused by kidney stones, injury, or severe infection |
| Cloudy or Hazy | Presence of blood, pus, or other substances, possibly indicating infection or inflammation |
Knowing these signs can help spot health problems early. If your urine looks different, see a doctor. They can check and diagnose the issue.
Types of Blood Clots in Urine
It’s key to know the different types of blood clots in urine to find the cause of hematuria. Each clot looks different, which can help figure out the problem.
Stringy or Worm-like Clots
Stringy or worm-like clots are found in urine. They form in the urinary tract and can be linked to infections or kidney stones. These clots suggest the bleeding might be from the kidneys or ureters.
Doctors say the shape and size of these clots are clues. For example, worm-like clots often mean the bleeding is in the upper urinary tract. This is because they form as they move through narrow passages.
Chunky or Amorphous Clots
Chunky or amorphous clots are another type of blood clot in urine. They look like red or darkened chunks and usually mean bleeding from the bladder or urethra. Chunky clots are often linked to bladder infections or stones.
- Chunky clots may suggest a more localized source of bleeding.
- The presence of amorphous clots could indicate a more severe infection or inflammation.
- In some cases, these clots may be accompanied by other symptoms such as pain or difficulty urinating.
As Verywell Health points out, “Blood clots can be stringy or worm-like, or they can appear as chunky or amorphous clots.” This shows why it’s vital to see a doctor to find out why you have hematuria with clotting.
Common Causes of Blood Clots in Urine
It’s important to know why blood clots might show up in your urine. These clots can signal serious health issues that need quick attention. We’ll look at the main reasons, like infections, structural problems, and side effects from medicines.
Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a top reason for blood clots in urine. When bacteria infect the urinary tract, it can cause inflammation and bleeding. This might make your urine look cloudy or bloody, and sometimes, blood clots will form.
Symptoms of UTIs include:
- Burning sensation while urinating
- Frequent urination
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain in women
- Rectal pain in men
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are another common reason for blood clots in urine. These stones are hard deposits made of minerals and salts in the kidneys. When a stone moves through the urinary tract, it can irritate, bleed, and lead to blood clots.
| Size of Kidney Stone | Likelihood of Causing Blood Clots |
| Less than 5 mm | Less likely |
| 5 mm to 1 cm | Moderately likely |
| Greater than 1 cm | More likely |
Injuries to the Urinary Tract
Injuries to the urinary tract can cause bleeding and blood clots in urine. The severity of the injury often affects how likely it is to see blood clots.
“Trauma to the urinary tract can cause significant bleeding, leading to the presence of blood clots in the urine. Prompt medical evaluation is essential in such cases.”
Medication Side Effects
Some medicines, like blood thinners, can increase the risk of bleeding and blood clots in urine. Aspirin and other NSAIDs can also affect blood clotting, leading to this condition.
In summary, blood clots in urine can stem from infections, kidney stones, injuries, or medicine side effects. Knowing these causes is key to getting the right diagnosis and treatment.
Serious Medical Conditions Associated with Urinary Blood Clots
Blood clots in the urine can signal serious health issues. These problems can include infections or even cancers. It’s important to find out what’s causing them to get the right treatment.
Kidney Infections and Disease
Kidney infections, or pyelonephritis, happen when bacteria move up to the kidneys. They can cause a lot of pain, fever, and blood in the urine. If not treated, they can harm the kidneys permanently.
Key symptoms of kidney infections include:
- Pain in the back or side
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Blood or clots in the urine
| Condition | Symptoms | Potential Complications |
| Kidney Infection | Pain, fever, nausea, blood in urine | Permanent kidney damage, sepsis |
| Bladder Cancer | Blood in urine, pain during urination | Metastasis, urinary tract obstruction |
| Kidney Cancer | Blood in urine, flank pain, weight loss | Metastasis, kidney failure |
Bladder or Kidney Cancer
Blood clots in the urine can also mean bladder or kidney cancer. These cancers can cause bleeding, leading to clots. Finding them early is key to treating them well.
Prostate Conditions
In men, prostate issues like prostatitis or BPH can cause blood clots in urine. Prostatitis is an infection, while BPH is an enlargement. Both can lead to blood in the urine.
Prostate conditions can be managed with the right medical care. The treatment depends on the condition and how severe it is.
Gender-Specific Causes of Blood Clots in Urine
Blood clots in urine have different causes for men and women. Knowing these causes helps doctors diagnose and treat better.
Causes Specific to Women
Women might get blood clots in urine from endometriosis. This is when tissue like the uterus lining grows outside the uterus. It can harm the urinary tract. Other reasons include menstrual issues, pregnancy problems, and some cancers.
Endometriosis is a big problem that can cause bleeding in the urine. Verywell Health says it can make lesions on the bladder or ureters, leading to bleeding.
Causes Specific to Men
Men often get blood clots in urine because of an enlarged prostate or prostate cancer. An enlarged prostate can block urine flow and cause bleeding. This is because the prostate puts too much pressure on the urethra.
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center says an enlarged prostate is common in older men. It can cause bleeding in the urine.
| Gender | Common Causes | Associated Conditions |
| Women | Endometriosis, Menstrual Contamination | Gynecological Cancers, Pregnancy Complications |
| Men | Enlarged Prostate, Prostate Cancer | Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), Prostatitis |
Understanding these differences helps doctors give better care for blood clots in urine.
Diagnostic Process for Blood Clots in Urine
Diagnosing blood clots in urine is a detailed process. It starts with reviewing your medical history and includes several tests. When you show signs of blood in your urine, doctors start a thorough check to find the cause.
Initial Evaluation and Medical History
The first step is a detailed look at your medical history. Your healthcare provider will check your history and risk factors for blood in your urine. They look for past issues like urinary tract infections or kidney stones.
- Review of symptoms and medical history
- Assessment of risk factors for urinary tract issues
- Physical examination
Laboratory Tests and Urinalysis
Laboratory tests are key to finding the cause of blood clots in urine. The main test is urinalysis, which checks a urine sample for different things.
Urinalysis can show:
- Presence of blood or clots
- Infection or inflammation
- Abnormal cells or other substances
Also, a urine culture might be done to look for infections.
Advanced Imaging and Specialized Tests
At times, more advanced tests are needed to understand blood clots in urine. These include:
- Imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI to see the urinary tract
- Cystoscopy to look inside the bladder
- Blood tests to check kidney function or other conditions
By using the results from these steps, doctors can find the cause of blood clots in urine. Then, they can plan the right treatment.
Treatment Approaches for Blood Clots in Urine
The treatment for blood clots in urine depends on the cause. Doctors need to find the root cause to choose the best treatment.
Treating Infections and Inflammatory Causes
For infections or inflammation, the main treatment is antibiotic therapy or anti-inflammatory drugs. Antibiotics are key for urinary tract infections (UTIs) to kill the bacteria. It’s important to finish all antibiotics as told by the doctor.
For inflammation, treatments aim to manage the condition. This might include drugs to reduce swelling and ease symptoms.
Managing Kidney Stones and Structural Issues
Kidney stones often cause blood clots in urine. Treatment varies by stone size and location. Small stones might pass with more water and pain relief. But, bigger stones might need extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) or surgery.
Structural problems need surgical fixes or other procedures to correct them.
Addressing Serious Underlying Conditions
Blood clots in urine can signal serious issues like bladder or kidney cancer. Treatment depends on the cancer stage and the patient’s health. It might include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
It’s vital for patients to team up with their doctors to find the right treatment for their case.
| Cause | Treatment Approach | Examples of Treatment |
| Infections | Antibiotic therapy | Ciprofloxacin, Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole |
| Kidney Stones | Hydration, pain management, or surgical intervention | ESWL, surgical removal |
| Cancer | Surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy | Tumor resection, chemotherapy regimens, radiation therapy protocols |
When to Seek Emergency Medical Care
It’s important to know when to get emergency help for blood clots in urine. These clots can be a sign of a serious problem that needs quick attention.
Warning Signs Requiring Immediate Attention
Some symptoms with blood clots in urine mean you need to go to the emergency room. These include:
- Numerous or large clots: Seeing many or big clots could mean a serious issue.
- Obstruction of urinary flow: Clots that block urine flow can cause serious problems, like kidney damage.
- Severe pain: Pain in the lower abdomen, back, or flank area could be a sign of something serious, like kidney stones or a urinary tract infection.
- Hematuria with clots and fever: Having fever with blood clots in urine might mean you have an infection that needs quick treatment.
If you see any of these signs, get medical help fast. Waiting too long can make things worse and could even be life-threatening.
What to Expect During Emergency Evaluation
When you go to the emergency room for blood clots in urine, you’ll get a detailed check-up. This includes:
- Initial assessment: Doctors will check your overall health, ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any medicines you’re taking.
- Laboratory tests: They might do urinalysis and blood tests to look for infection signs, kidney function, and other problems.
- Imaging studies: They might use ultrasound, CT scans, or X-rays to see the urinary tract and find any problems.
It’s key to share as much as you can about your symptoms and medical history during the emergency check-up. This helps doctors figure out and treat your problem well.
Conclusion
Understanding blood clots in urine is key for getting the right medical care. This article covered many important points about hematuria with clotting. We talked about what it is, how common it is, and why it matters.
We looked at the main signs of blood clots in urine. We also talked about what might cause them and serious health issues they can lead to. It’s very important to see a doctor if you keep getting these symptoms.
We want to help people understand their health better. Doctors from Verywell Health and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center say it’s vital to get checked out fast. This helps find out why you have blood clots in your urine.
Our summary covers the main points. It shows how important it is to know the risks of ignoring blood clots in urine. We urge everyone to see a doctor if they notice anything strange.
FAQ
What does a blood clot in urine look like?
Blood clots in urine can look like stringy or worm-like shapes. They can also appear as red or darkened chunks. This can change the urine’s color to pink, red, or brown.
Should I go to the emergency room if I see blood clots in my urine?
Yes, if you see many or large clots, or if it’s hard to pee, go to the emergency room right away.
What are the common causes of blood clots in urine?
Blood clots in urine can be caused by urinary tract infections, kidney stones, injuries, or medication side effects.
Can blood clots in urine be a sign of a serious medical condition?
Yes, they can be signs of serious issues like kidney infections, bladder or kidney cancer, or prostate problems.
Are there different types of blood clots that can be found in urine?
Yes, there are stringy or worm-like clots and chunky or amorphous clots. Each type might mean a different cause.
How are blood clots in urine diagnosed?
Doctors first check your medical history and symptoms. Then, they do lab tests and urinalysis. Sometimes, they use advanced imaging and tests.
What are the treatment approaches for blood clots in urine?
Treatment depends on the cause. It might include treating infections, managing kidney stones, or addressing serious conditions.
Are there gender-specific causes of blood clots in urine?
Yes, women might get blood clots from endometriosis, while men might get them from an enlarged prostate.
What should I expect during an emergency evaluation for blood clots in urine?
Doctors will check your symptoms and do tests. They’ll then treat the cause of the clots.
Can medication side effects cause blood clots in urine?
Yes, some medications can cause blood clots in urine. It’s important to talk to your doctor about your meds.
How do blood clots in urine affect urine color and appearance?
Blood clots can change urine color to pink, red, or brown. They can also change how urine looks.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). What Does a Blood Clot in Urine Look. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534213/








