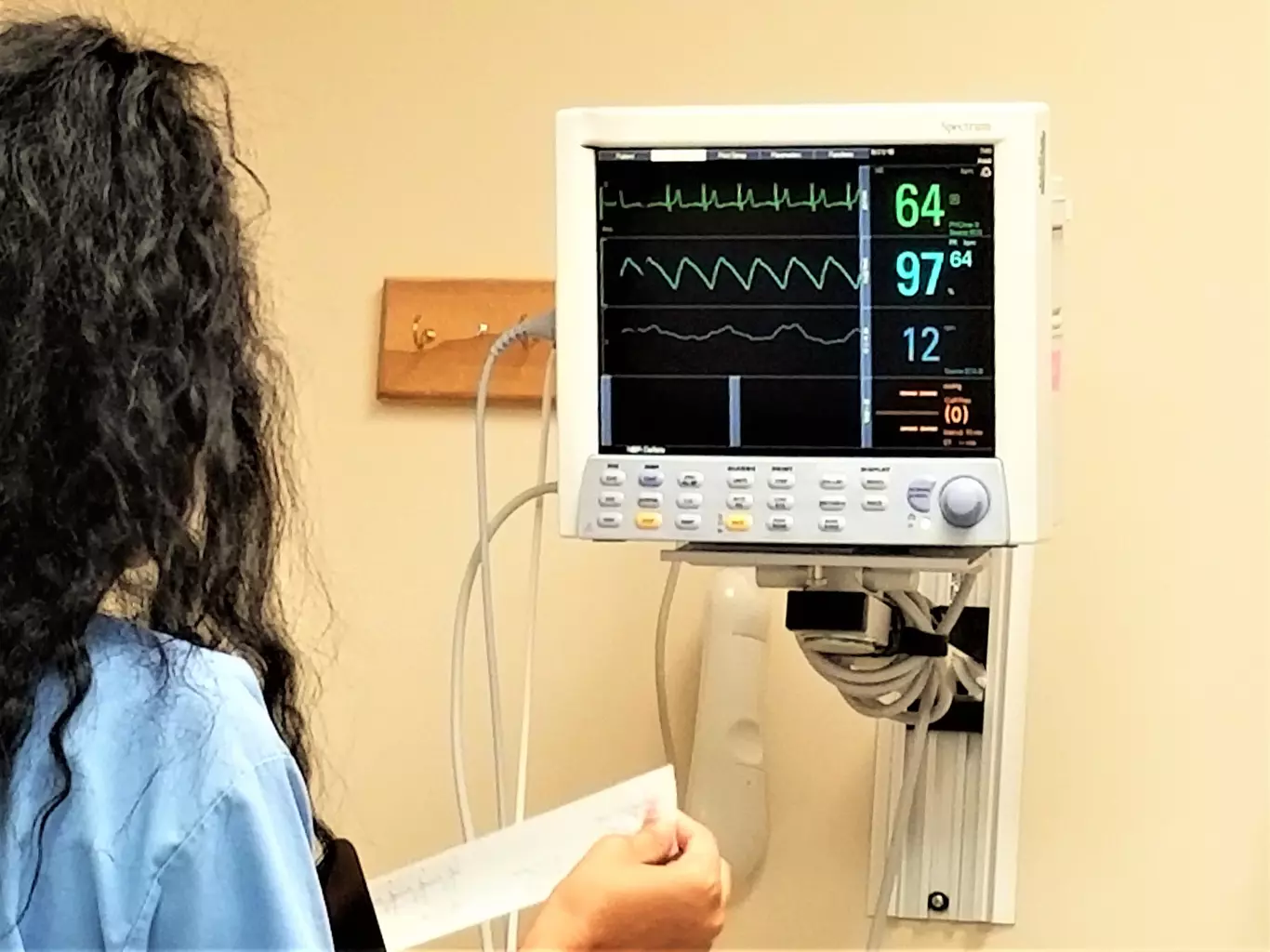
Knowing about sinus rhythm on an electrocardiogram (ECG) is key for heart health. At Liv Hospital, we aim to offer top-notch healthcare to all patients. The sinoatrial node, our heart’s natural leader, keeps our heartbeat steady.
A normal sinus rhythm shows our heart beats as it should, thanks to our natural pacemaker. We guide you to understand heart rhythms. This helps you take better care of your health.
Key Takeaways
- Sinus rhythm refers to the regular pattern of heartbeats driven by the heart’s natural pacemaker.
- A normal sinus rhythm means the heart rate is within a normal range.
- The sinoatrial node acts as the heart’s natural pacemaker.
- Understanding sinus rhythm on an ECG is vital for heart health.
- Liv Hospital provides complete care for international patients.
Understanding the Heart’s Electrical System
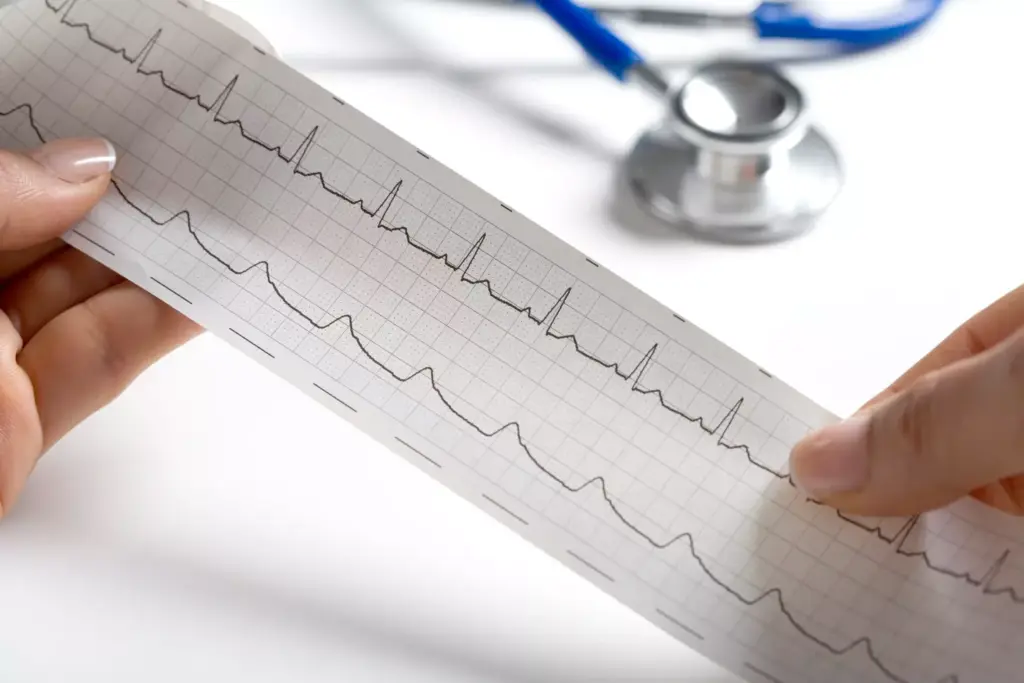
It’s important to know how the heart’s electrical system works. This system helps our heart beat in a regular rhythm. It controls when the heart’s chambers contract and relax.
The Heart’s Natural Pacemaker: The Sinoatrial Node
The sinoatrial (SA) node is in the right atrium. It’s the heart’s natural pacemaker. It sends out electrical signals that make the heart contract.
The SA node’s job is key to keeping a normal cardiac rhythm sinus. It makes sure the heart beats right for the body’s needs, whether we’re resting or active.
The Cardiac Conduction Pathway
After the SA node sends out a signal, it goes through the cardiac conduction pathway. This path includes the AV node, the bundle of His, and the Purkinje fibers. Each part is important for making sure the heart chambers contract together.
The pathway working well is key for a normal sinus rhythm. Problems here can cause arrhythmias or other heart rhythm issues.
How Electrical Signals Coordinate Heartbeats
The electrical signals from the SA node and through the pathway coordinate our heartbeat. They make the atrial and ventricular muscles contract together. This ensures blood circulates well.
Knowing how these signals work shows why a normal sinus rhythm of the heart is so important. It shows the complex ways the heart works. It also stresses the need for regular heart checks to catch any rhythm problems.
Cardiac Sinus Rhythm: The Foundation of Normal Heart Function
The cardiac sinus rhythm is key to a healthy heart. It’s the heart’s normal beat, made by the sinoatrial node. This rhythm is vital for the heart to work right.
What Constitutes a Normal Sinus Rhythm
A normal sinus rhythm has a heart rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute in adults. It shows a healthy heart. On an electrocardiogram (ECG), it looks like a steady P wave before each QRS complex. This means the heartbeat starts from the sinoatrial node.
The key characteristics of a normal sinus rhythm include:
- A heart rate between 60-100 bpm
- Regular rhythm
- P wave preceding each QRS complex
- Consistent PR interval
Rate, Regularity, and Origin Characteristics
The heart rate, rhythm, and where the heartbeat starts are important. The rate should be 60-100 bpm. The rhythm should be steady. The heartbeat should start from the sinoatrial node, shown by the P wave on an ECG.
| Characteristic | Normal Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Heart Rate | 60-100 bpm |
| Rhythm | Regular |
| P Wave | Preceding each QRS complex |
| PR Interval | Consistent, 0.12-0.20 seconds |
Physiological Variations in Healthy Individuals
Healthy people can have different sinus rhythms due to age, fitness, and body position. For example, athletes might have a lower heart rate, called sinus bradycardia, which can be as low as 40 bpm. On the other hand, during exercise or stress, the heart rate can go up, leading to sinus tachycardia.
It’s important to know these variations to understand ECG readings and heart health. We’ll look at these variations and their meanings in the next sections.
Identifying Sinus Rhythm on an ECG
Understanding a normal sinus rhythm is key to checking the heart’s health. We must know the parts of an ECG and how to measure them right.
Key ECG Components: P Wave, QRS Complex, and T Wave
An ECG shows the heart’s electrical activity through different waves. The main parts are:
- The P wave, showing when the heart’s upper chambers depolarize
- The QRS complex, showing when the heart’s lower chambers depolarize
- The T wave, showing when the heart’s lower chambers repolarize
Spotting these parts is key to spotting a sinus rhythm. The P wave should be positive in lead II, showing the heart’s electrical start.
Normal ECG Parameters and Measurements
To spot a sinus rhythm, we look at ECG details closely. Normal details include:
- A heart rate of 60-100 beats per minute (bpm)
- A P wave before each QRS complex
- A normal P wave axis (upright in lead II)
- A QRS complex lasting less than 120 milliseconds
These details help us see if the heart is working right.
Step-by-Step Guide to Recognizing Sinus Rhythm
To spot sinus rhythm on an ECG, we follow these steps:
- Check the heart rate: Make sure it’s 60-100 bpm.
- Look at the P wave: It should be upright in lead II and steady before each QRS complex.
- Check the QRS complex: It should be under 120 milliseconds and follow each P wave.
- Look at the rhythm: Make sure it’s regular and steady.
By following these steps, we can accurately spot a sinus rhythm on an ECG. This is important for diagnosing and keeping an eye on heart health.
Types of Sinus Rhythms and Variations
Sinus rhythm is the heart’s natural beat. It comes in several types, each showing how well the heart is working. The sinoatrial node, or pacemaker, controls these rhythms. They can change based on our health and needs.
Normal Sinus Rhythm
A normal sinus rhythm has a heart rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute. It shows the heart is working well. It means the heart is getting the right signals from the sinoatrial node.
Sinus Bradycardia
Sinus bradycardia means the heart beats less than 60 times per minute. It’s okay for athletes or very fit people. But, it can also mean there’s a health problem, like low thyroid or certain medicines.
Sinus Tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia happens when the heart beats more than 100 times per minute. It can be from exercise, stress, or health issues like fever or anemia. If it lasts, it might mean there’s a health problem that needs help.
Sinus Arrhythmia
Sinus arrhythmia changes with breathing. It’s normal in kids and young adults. The heart rate goes up when you breathe in and down when you breathe out. This is usually not a worry.
To understand these sinus rhythms better, let’s look at a table:
| Type of Sinus Rhythm | Heart Rate (bpm) | Characteristics | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Sinus Rhythm | 60-100 | Regular rhythm, P wave precedes each QRS complex | Indicates good heart health |
| Sinus Bradycardia | <60 | Slower than normal heart rate | Can be normal in athletes; may indicate underlying issues |
| Sinus Tachycardia | >100 | Faster than normal heart rate | Response to stress, exercise, or medical conditions; may indicate underlying issues |
| Sinus Arrhythmia | Varies with breathing | Heart rate increases with inhalation, decreases with exhalation | Generally normal, specially in young individuals |
Knowing about these sinus rhythms is key to understanding heart health. Each rhythm tells us something about the heart’s function. It helps doctors make better decisions for their patients.
Common Deviations from Sinus Rhythm
It’s important to know about common heart rhythm problems. A normal heart rhythm is key to good heart health. But, many conditions can disrupt this, causing arrhythmias and other heart issues.
Atrial Arrhythmias
Atrial arrhythmias happen in the heart’s upper chambers, or atria. Atrial fibrillation is a common type, marked by uncoordinated electrical activity. It can cause symptoms like palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
It’s important to treat atrial fibrillation early because it raises the risk of stroke and heart failure. Other atrial arrhythmias include atrial flutter and supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). Atrial flutter has a rapid but regular heartbeat, while SVT is a rapid heartbeat that starts above the ventricles. These can be treated with medications, cardioversion, or catheter ablation.
Ventricular Arrhythmias
Ventricular arrhythmias start in the heart’s lower chambers, or ventricles. They can range from mild to severe, like ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular tachycardia is a rapid heartbeat that can turn into ventricular fibrillation, where the heart’s ventricles quiver instead of beating.
Ventricular arrhythmias can be linked to heart disease, electrolyte imbalances, or certain medications. Treatment includes antiarrhythmic medications, implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs), and catheter ablation.
Heart Blocks and Conduction Disorders
Heart blocks and conduction disorders happen when there’s a problem with electrical signals between the heart’s chambers. First-degree heart block delays signal transmission, while second-degree heart block blocks signals sometimes. Third-degree heart block, or complete heart block, is severe and requires a pacemaker.
Other conduction disorders include bundle branch blocks, which delay or block electrical signals along the bundle branches. These can be diagnosed with an electrocardiogram (ECG) and managed based on their severity and causes.
Understanding these common heart rhythm problems helps healthcare providers treat them effectively. Early detection and proper management are vital for better outcomes in patients with arrhythmias and conduction disorders.
Clinical Significance of ECG Sinus Rhythm Assessment
ECG sinus rhythm assessment is key in modern cardiology. It shows important info about heart health. It can also spot early signs of heart disease.
Indicators of Cardiovascular Health
A normal sinus rhythm on an ECG means good heart health. It shows the heart’s electrical system works well. ECG sinus rhythm meaning is linked to heart health, showing if the heart beats right.
Early Warning Signs of Heart Disease
Any rhythm change can warn of heart disease. Issues like sinus tachycardia or bradycardia need medical check-ups. By looking at meaning sinus rhythm on an ECG, doctors can catch problems early.
Monitoring Cardiac Function Over Time
ECG sinus rhythm assessment is not just for initial checks. It also tracks heart function over time. Regular ECGs help see rhythm changes, guiding treatment plans.
Role in Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
ECG sinus rhythm findings are key for diagnosis and treatment. Knowing the sinus rhythm labeled helps doctors decide on care. This includes tests, meds, or other treatments.
| ECG Finding | Clinical Implication | Potential Action |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Sinus Rhythm | Good cardiovascular health | Continue routine care |
| Sinus Tachycardia | Possible stress, anxiety, or underlying condition | Further evaluation, possible medication change |
| Sinus Bradycardia | Possible athletic training or underlying condition | Further evaluation, possible pacemaker consideration |
In conclusion, ECG sinus rhythm assessment is vital in cardiology. It offers insights into heart health, warns of heart disease, and guides treatments. By explain sinus rhythm and its changes, doctors can give better care to patients.
Modern ECG Technology and Monitoring Options
ECG technology has changed how we check heart health. New electrocardiogram (ECG) tech has brought many monitoring choices. Each has its own benefits and uses.
Standard 12-Lead ECG
The standard 12-lead ECG is key in heart checks. It shows the heart’s electrical activity from different views. This helps doctors spot many heart problems.
Key Features of Standard 12-Lead ECG:
- Records electrical activity from 12 different leads
- Provides a detailed snapshot of heart function
- Essential for diagnosing arrhythmias, ischemia, and other cardiac conditions
Holter Monitors and Event Recorders
Holter monitors and event recorders are great for long-term watching. They let people live their daily lives while their heart is checked.
| Device | Monitoring Duration | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Holter Monitor | 24 to 48 hours | Continuous recording, detects intermittent arrhythmias |
| Event Recorder | Several days to weeks | Patient-activated, records events as they occur |
Implantable Cardiac Monitoring Devices
Implantable cardiac monitors watch the heart for a long time without needing to wear anything. These small devices are put under the skin. They catch and record heart rhythm problems for a long time.
Benefits of Implantable Cardiac Monitors:
- Long-term monitoring (up to 3 years or more)
- Continuous data collection without patient intervention
- Early detection of possible life-threatening arrhythmias
Wearable Consumer Technology for Heart Rhythm Monitoring
Wearable tech like smartwatches and fitness trackers are now used to watch heart rhythms. They’re not as exact as medical devices but are handy. They help people keep an eye on their heart health all the time.
As tech gets better, we’ll see even more advanced ECG monitoring tools. These new tools will help doctors diagnose and treat heart issues better. This will lead to better health outcomes for patients.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Heart Rhythm Concerns
Knowing the warning signs of heart rhythm problems is key. It can mean the difference between quick medical help and serious issues. Heart rhythm problems can show up in many ways. It’s important to know these signs to keep your heart healthy.
Warning Signs and Symptoms
There are several symptoms that might mean you have heart rhythm issues. These include:
- Palpitations: A feeling of skipped beats or irregular heart rhythms.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Feeling like you might pass out.
- Shortness of Breath: Trouble breathing or feeling like you’re not getting enough air.
- Chest Pain or Discomfort: Pain or pressure in the chest that might spread to the arms, back, or jaw.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or weak.
If you’re feeling any of these symptoms, check how bad they are and how long they last. Severe or lasting symptoms need quick medical help.
Emergency Situations vs. Non-Urgent Concerns
It’s important to know when to call for emergency help versus when to see a doctor. Emergency situations include:
- Severe chest pain or pressure
- Severe trouble breathing
- Loss of consciousness or fainting
- Severe palpitations or irregular heartbeats
In emergencies, call emergency services or get to the hospital fast. For less urgent issues, make an appointment with your doctor. Talk about your symptoms and figure out what to do next.
Preparing for Your Cardiology Appointment
Before your doctor’s visit, do a few things to help:
- Document your symptoms: Write down how often, how long, and what makes them better or worse.
- Gather relevant medical records: Bring any ECGs, test results, and a list of your medicines.
- Prepare questions: Write down any questions or worries you have for your cardiologist.
Being ready can make your visit more useful. It helps your doctor diagnose and treat your heart rhythm problems better.
Conclusion: The Importance of Regular Cardiac Monitoring
Regular cardiac monitoring is key to keeping your heart healthy and catching problems early. Knowing about sinus rhythm is important because it shows how well your heart is working. At Liv Hospital, we stress how vital monitoring is for heart health.
By watching your heart’s rhythm, you can spot any unusual patterns. This lets doctors act fast to help you. We offer top-notch heart care, including for international patients, with detailed monitoring and treatment plans.
Looking after your heart health is a smart move for a better life. We urge you to be proactive about your heart health. Stay informed and seek professional help when you need it.
What is sinus rhythm of the heart?
Sinus rhythm is the normal heartbeat rhythm. It’s controlled by the sinoatrial node, the heart’s natural pacemaker. A normal sinus rhythm is between 60 to 100 beats per minute and is usually regular.
What does sinus rhythm mean on an ECG?
On an electrocardiogram (ECG), sinus rhythm shows a P wave before each QRS complex. This means the heartbeat starts from the sinoatrial node. We look for consistent P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves to confirm it.
What is the difference between sinus bradycardia and sinus tachycardia?
Sinus bradycardia is when the heart rate is slower than 60 beats per minute. Sinus tachycardia is when it’s faster than 100 beats per minute. Both are types of sinus rhythms but show different conditions.
How is sinus arrhythmia different from other sinus rhythms?
Sinus arrhythmia changes with breathing. The heart rate goes up during inhalation and down during exhalation. It’s a normal variation, mostly seen in young people.
What are the clinical implications of an abnormal sinus rhythm?
Abnormal sinus rhythms can signal health issues like cardiac disease or metabolic disorders. They can also be caused by medication side effects. We use ECGs to monitor heart function and plan treatments.
How do modern ECG technologies enhance heart rhythm monitoring?
Modern ECG technologies, like Holter monitors and wearable tech, allow for long-term heart rhythm monitoring. These tools help us detect arrhythmias and keep track of heart health better.
When should I seek medical attention for heart rhythm concerns?
Seek immediate medical help for severe chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or palpitations. For less urgent issues, schedule a cardiology appointment for a detailed check-up.
How can I prepare for a cardiology appointment regarding heart rhythm?
To get ready for your appointment, bring any past ECGs, list your symptoms and meds, and share your medical history. We’ll use this info to check your heart health and create a care plan just for you.
References
- (n.d.). aHEW_0056i [Video]. Medmovie. Retrieved from https://www.medmovie.com/topicahew_0056i
- Wikipedia. (n.d.). Sinus rhythm. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sinus_rhythm Wikipedia
- LITFL. (n.d.). Normal sinus rhythm – ECG library. Retrieved from https://litfl.com/normal-sinus-rhythm-ecg-library/
- Healthline. (n.d.). Sinus rhythm: What it is and how it differs from arrhythmia. Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/health/sinus-rhythm




































