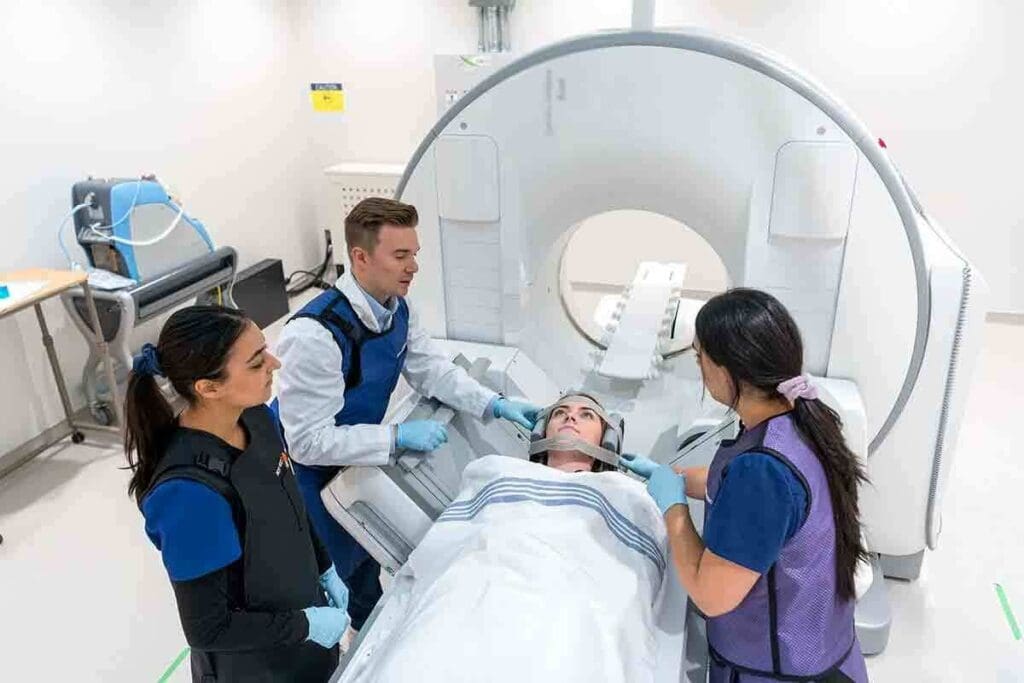
At Liv Hospital, we use top-notch diagnostic tools to check how well your kidneys work. A nuclear medicine scan for kidneys, or renal scan, is a way to see how your kidneys function. It uses tiny amounts of radioactive tracers to check blood flow and how well urine drains.
A nuclear medicine technologist will inject a small amount of radioactive material into your vein. This material is then taken up by your kidneys. A special camera then captures images of your kidneys. These images give us important details to help diagnose and treat kidney problems.
Key Takeaways
- A nuclear kidney scan assesses kidney function, blood flow, and urinary drainage.
- The scan involves injecting a small amount of radioactive material into a vein.
- A special camera takes images of the kidneys to provide valuable diagnostic information.
- The procedure helps diagnose and manage kidney disorders.
- Liv Hospital uses advanced nuclear medicine scans for accurate diagnoses.
Understanding Nuclear Medicine Scans for Kidneys
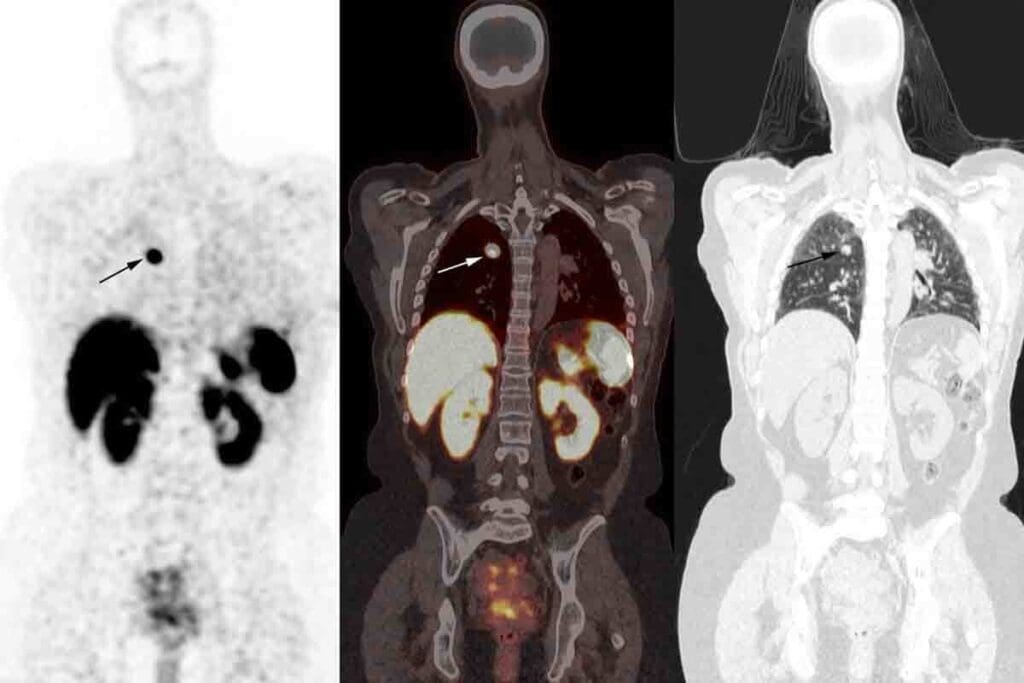
The nuclear medicine scan for the kidneys is a key test for doctors. It checks how well the kidneys work and the blood flow. These scans are vital for spotting kidney problems, blockages, and overall health.
Definition and Basic Principles
A renal scan, or renal scintigraphy, uses a tiny bit of radioactive material. It looks at kidney function and blood flow. A gamma camera takes pictures of the kidneys after the radioactive tracer is given.
This test tracks the radioactive tracer in the kidneys. It shows how well the kidneys are working. It also spots any issues.
“Nuclear medicine techniques provide a unique window into the functioning of the kidneys, allowing for the diagnosis of a wide range of renal and urinary tract disorders.” – Nuclear Medicine Expert
Types of Nuclear Kidney Scans
There are many types of nuclear kidney scans. Each one looks at different parts of kidney function and health. The right scan depends on what doctors need to know.
- Renal Flow Study: Checks blood flow to the kidneys.
- Renal Function Study: Looks at how well the kidneys work.
- Diuretic Renal Scan: Finds urinary tract blockages.
- Captopril Renal Scan: Sees how certain medicines affect the kidneys.
| Type of Scan | Purpose | Key Benefits |
| Renal Flow Study | Assess blood flow to the kidneys | Identifies issues with renal perfusion |
| Renal Function Study | Evaluate kidney function | Provides insights into renal function and possible damage |
| Diuretic Renal Scan | Diagnose urinary tract obstructions | Helps in identifying blockages in the urinary tract |
Knowing about the different kidney scans helps patients and doctors. It aids in choosing the right tests and treatments.
The Science Behind Kidney Scintigraphy
Kidney scintigraphy uses radioactive tracers and advanced imaging. It gives a detailed look at how the kidneys work and their structure.
Radioactive Tracers Used in Renal Imaging
Radioactive tracers, or radiopharmaceuticals, emit gamma rays. They are made to be taken up by the kidneys for function assessment. Technetium-99m (Tc-99m) labeled compounds like DTPA (Diethylene Triamine Pentaacetic Acid) and MAG3 (Mercaptoacetyltriglycine) are common. The right tracer depends on what info is needed about the kidneys.
- Tc-99m DTPA is mainly for checking glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
- Tc-99m MAG3 is for looking at renal tubular function, great for those with kidney issues.
How Gamma Cameras Detect Kidney Function
After the tracer is given, a gamma camera picks up the gamma rays. It takes pictures of the kidneys from different angles. This gives a full view of kidney function and shape.
The process includes injecting a tracer and then scanning with a gamma camera for 20 to 60 minutes. The tracer’s gamma rays are caught by the scanner, creating a kidney picture.
The images from kidney scintigraphy show many things about kidney function. This includes:
- Renal blood flow and perfusion.
- Glomerular filtration rate.
- Tubular function.
- Urinary tract obstruction.
Doctors can spot many kidney problems and check if treatments work by looking at these images.
When Is a Nuclear Medicine Renal Scan Necessary?
Nuclear medicine renal scans are key in diagnosing and managing kidney issues. They give vital info on kidney function and structure. This helps doctors make better decisions for patient care.
Evaluating Kidney Function and Blood Flow
A nuclear medicine kidney scan is great for checking kidney function and blood flow. It uses tiny amounts of radioactive tracers. This helps see how well each kidney works and spots blood flow problems.
This scan is important for finding issues like kidney failure or renal artery stenosis.
The scan can help us understand:
- The overall function of the kidneys
- The relative function of each kidney
- Blood flow to the kidneys
Diagnosing Urinary Tract Obstructions
Nuclear medicine renal scans are also good for finding urinary tract obstructions. They track the flow of a radioactive tracer through the kidneys and urinary tract. This helps spot blockages causing pain or trouble urinating.
Key benefits of using nuclear medicine renal scans for diagnosing obstructions include:
- Accurate detection of blockages
- Assessment of the severity of the obstruction
- Guidance for possible interventions
Advantages Over Other Diagnostic Methods
Nuclear medicine kidney scans have many benefits over other tests. They don’t use harmful contrast agents, unlike some imaging methods. Also, they give functional info about the kidneys that other tests can’t.
Some of the key advantages include:
- Minimally invasive procedure
- No need for potentially nephrotoxic contrast agents
- Ability to assess both structure and function
These scans give a full view of kidney health. This helps doctors create treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs.
Preparing for Your NM Kidney Scan
A successful NM kidney scan starts with good preparation. We’ll show you how to get ready. Being well-prepared helps get accurate and useful images.
Pre-Scan Instructions
Before your NM kidney scan, you’ll get specific instructions. It’s important to follow these instructions carefully to avoid any problems or the need for a repeat scan.
One common instruction is to stay hydrated by drinking lots of water. This helps remove the radioactive tracer from your body after the scan. You might need to drink several glasses of water before the scan.
Medications and Dietary Considerations
Certain medications and diets can affect your NM kidney scan results. Inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are currently taking, as some may need to be adjusted or stopped before the scan.
Also, you might need to change your diet. For example, you might be told to avoid certain foods or drinks that could affect the scan’s results. We’ll give you specific guidance on any dietary restrictions.
| Preparation Step | Description |
| Hydration | Drink plenty of water to help remove the radioactive tracer |
| Medication Review | Inform your healthcare provider about your current medications |
| Dietary Adjustments | Avoid certain foods or drinks as advised by your healthcare provider |
What to Bring to Your Appointment
To make your appointment smooth and efficient, please bring the necessary documents and information. This includes your referral letter, insurance details, and a list of your current medications.
Comfort is also key; wear loose, comfortable clothing. Avoid jewelry or clothing with metal parts that could interfere with the scan.
The Nuclear Medicine Scan for Kidneys Procedure
Getting a nuclear medicine scan for your kidneys involves a few steps. First, you prepare, then the radiotracer is given, and lastly, images are taken with a gamma camera. This test helps check how well your kidneys are working and spot any problems.
Initial Setup and Radiotracer Administration
You’ll start by getting comfortable on an exam table. An IV line is put in your arm to give you the radiotracer. The tracer used is usually Technetium-99m DTPA or Technetium-99m MAG3. These compounds help show how your kidneys are working.
Getting the radiotracer is quick, and you might feel a tiny pinch. After it’s given, it goes through your blood to your kidneys.
Imaging Process with the Gamma Camera
Once the radiotracer is in your system, you’ll move under a gamma camera. This camera picks up the radiation from the tracer in your kidneys. It takes pictures from different angles to show how your kidneys are doing.
The camera might take static images or moving pictures over time. This helps the team see how your kidneys are working and processing the tracer.
Duration and Patient Experience
The scan usually lasts 30 minutes to 1 hour. But, you might spend more time there because of getting ready and waiting. Some scans might need more pictures a few hours later.
You’ll need to stay very quiet during the scan to get clear pictures. You might be asked to drink water to help your kidneys. Most people find the scan comfortable, with little to no pain.
| Procedure Step | Duration | Patient Experience |
| Radiotracer Administration | 1-2 minutes | Mild discomfort from IV insertion |
| Imaging with Gamma Camera | 20-30 minutes | Lying quietly on the exam table |
| Total Scan Time | 30 minutes to 1 hour | Usually comfortable, might need to drink water |
Different Protocols in Renal Scintigraphy
Renal scintigraphy offers a detailed look at kidney health and function. It’s a flexible imaging technique. It can be adjusted to check different aspects of kidney function based on the condition being studied.
Standard Renal Scans for Function Assessment
Standard renal scans are key for checking kidney function. They use a radioactive tracer that the kidneys absorb and then release. This shows how well the kidneys work.
Key features of standard renal scans include:
- Assessment of renal function and perfusion
- Evaluation of the kidneys’ ability to uptake and excrete the tracer
- Measurement of split renal function, which compares the function of the two kidneys
NM Kidney Flow/Function with Diuretic
The NM kidney flow/function with the diuretic protocol is great for finding urinary tract blockages. A diuretic is given during the scan. This helps see how the kidneys handle the extra urine, spotting any blockages.
The use of diuretics in renal scintigraphy enhances the diagnostic capability by:
- Increasing urine flow, which helps in identifying obstructions
- Assessing the kidney’s ability to respond to diuretic stress
- Providing dynamic information about kidney function
Captopril-Enhanced Renal Scans
Captopril-enhanced renal scans help with renovascular hypertension. Captopril, an ACE inhibitor, is given before the scan. It shows changes in kidney function, helping spot renal artery stenosis.
The captopril-enhanced renal scan is great for:
- Diagnosing renovascular hypertension
- Assessing the functional significance of renal artery stenosis
- Guiding treatment decisions for patients with suspected renovascular disease
Specialized Protocols for Specific Conditions
There are special renal scintigraphy protocols for certain conditions. These include checking kidney transplant function, complex urinary tract issues, or specific kidney injuries.
Examples of specialized protocols include:
| Protocol | Clinical Use |
| Transplant kidney function assessment | Evaluating the function of transplanted kidneys |
| Complex urinary tract evaluation | Assessing complex abnormalities of the urinary tract |
| Kidney injury assessment | Investigating acute or chronic kidney injuries |
Interpreting Nuclear Renal Scan Results
Understanding renal scan results is key to knowing how well our kidneys are working. These scans show us split renal function measurements and kidney perfusion. This helps us spot any problems early on.
Understanding Split Renal Function Measurements
Split renal function measurements tell us how each kidney is doing. This is important for people with kidney disease or blockages. It helps us see if one kidney is working better than the other.
For more info on how kidneys work, check out NCBI’s guide on renal scintigraphy.
Evaluating Kidney Perfusion and Filtration
Kidney perfusion and filtration are signs of good kidney health. Nuclear scans let us check these areas well. They show us how blood flows to the kidneys and how they filter waste.
Common Findings and Their Clinical Significance
Nuclear scans often show differences in kidney size, function, and blood flow. These differences can mean serious issues like blockages or narrowed arteries. Knowing this helps us create better treatment plans.
In short, reading nuclear renal scan results needs a deep understanding of kidney function and health. By doing this, we can help patients get the right care for their kidneys.
Safety and Radiation Exposure Concerns
The safety of nuclear medicine kidney scans is a big deal for everyone involved. It’s important to know the risks and benefits of these tests. This helps patients and doctors make the right choices.
Radiation Levels in Nuclear Medicine Kidney Scans
Nuclear medicine kidney scans use tiny amounts of radioactive tracers. These tracers help doctors see how well the kidneys are working. The amount of radiation from these tracers is very small.
The risk from the radioactive tracer is very low, and most of the radiation is gone from the body in 24 hours. This is similar to the radiation from many other medical tests.
| Procedure | Effective Dose (mSv) |
| Nuclear Medicine Kidney Scan | 1-5 |
| Abdominal CT Scan | 10-20 |
| Chest X-ray | 0.1 |
Special Considerations for Pregnant Women and Children
Pregnant women and kids need extra care when it comes to radiation. Pregnant women should tell their doctor about their pregnancy before the scan. This helps weigh the risks and benefits.
For kids, the doctor adjusts the dose of the tracer. This is based on their size and age. It helps keep their radiation exposure low.
Risk vs. Benefit Analysis
It’s key to look at the risks and benefits of nuclear medicine kidney scans. In most cases, the scan’s benefits outweigh the small risk of radiation. But, this decision depends on the patient’s health and history.
Knowing about the safety and radiation of these scans helps everyone make better choices. This is true for both patients and doctors.
Limitations and Alternatives to Kidney Nuclear Medicine Scans
It’s important to know the limits of nuclear scans for kidney checks. These scans give valuable info on kidney function and structure. But, sometimes other tests are better or used with nuclear scans.
When Nuclear Scans May Not Be Appropriate
Nuclear scans might not fit all patients or situations. Pregnant women and kids are more sensitive to radiation. So, safer tests are often chosen for them. Also, people with certain health issues or allergies to the scan’s materials might need other tests.
We look at many things before deciding on a nuclear scan. We consider the patient’s health history, the condition being checked, and other test options.
Other Diagnostic Options for Kidney Assessment
There are many tests to check kidney function and structure. The right one depends on the condition being looked at. Here are a few:
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to show kidney images without harm.
- CT Scans: Give detailed kidney images and can spot problems.
- MRI: Shows kidney details without radiation.
| Diagnostic Method | Advantages | Limitations |
| Nuclear Medicine Scan | Shows how kidneys work | Uses radiation |
| Ultrasound | Safe, no radiation | May not show all details |
| CT Scan | Clear images, fast | Uses radiation, might need contrast |
| MRI | No radiation, detailed images | Not for everyone with implants |
Complementary Diagnostic Approaches
Using different tests together can give a full picture of kidney health. For example, a nuclear scan with ultrasound or CT scans can show both how the kidneys work and their structure.
Knowing what each test does helps us choose the best one for each patient. This way, we get the most accurate and helpful diagnosis.
Conclusion
Renal imaging with nuclear medicine is key in modern kidney and bladder care. It gives us important information about kidney function and health. A nuclear scan for kidneys, or renal scintigraphy, is vital for spotting and treating kidney problems.
Renal scintigraphy is a trusted way to find kidney diseases. It’s as good as ultrasound in spotting issues. Plus, it uses less radiation and might catch health problems better.
Knowing the good and bad of renal scintigraphy helps doctors make better choices for patients. This leads to better kidney health. As medical tech gets better, nuclear medicine will play an even bigger role in kidney care.
FAQ
What is a nuclear medicine scan for the kidneys?
A nuclear medicine scan for the kidneys is a test that uses tiny amounts of radioactive tracers. It checks how well the kidneys work, blood flow, and how urine drains.
How does a nuclear medicine kidney scan work?
The scan starts with a radioactive tracer injected into a vein. The kidneys absorb it. A gamma camera then picks up the gamma rays, showing detailed images of the kidneys.
What are the different types of nuclear kidney scans?
There are many types of scans, like standard renal scans and NM kidney flow/function with diuretic. Each type gives different information about kidney health.
Why is a nuclear medicine renal scan necessary?
This scan is key for checking kidney function and blood flow. It helps find urinary tract blockages and manage kidney issues. It’s also for those who can’t do other tests due to allergies or kidney problems.
How do I prepare for a nuclear medicine kidney scan?
To get ready, follow your doctor’s pre-scan instructions. Tell them about your meds and diet. Bring what you need to your appointment for the best images.
What happens during a nuclear medicine scan for the kidneys?
During the scan, a tracer is given, and images are taken. It’s usually comfortable, with little to no discomfort.
How long does a renal scan take?
The scan’s length varies by the type and the needed info. But it usually takes 1-3 hours.
Is a nuclear medicine kidney scan safe?
Yes, it’s safe, with low radiation levels. The scan’s benefits usually outweigh the risks. But pregnant women and kids need special care.
What are the limitations of kidney nuclear medicine scans?
Not all patients can have this scan. There are other tests and ways to diagnose kidney issues.
How are nuclear renal scan results interpreted?
Results show kidney function, blood flow, and more. This info helps diagnose and manage kidney problems.
What is the difference between a renal scan and other kidney imaging tests?
A renal scan focuses on function and blood flow. Other tests, like ultrasound or CT scans, look at structure and anatomy.
Can I undergo a nuclear medicine kidney scan if I have kidney disease?
Yes, scans can help manage kidney disease. But tell your doctor about your condition and any concerns.
References
- Einstein, A. J. et al. (2018). SNMMI Procedure Standard/EANM Practice Guideline for Renal Scintigraphy. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 59(5), 756-762. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6020824/
- RadiologyInfo.org. (2023). Renal (Kidney) Scintigraphy. https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/renal





