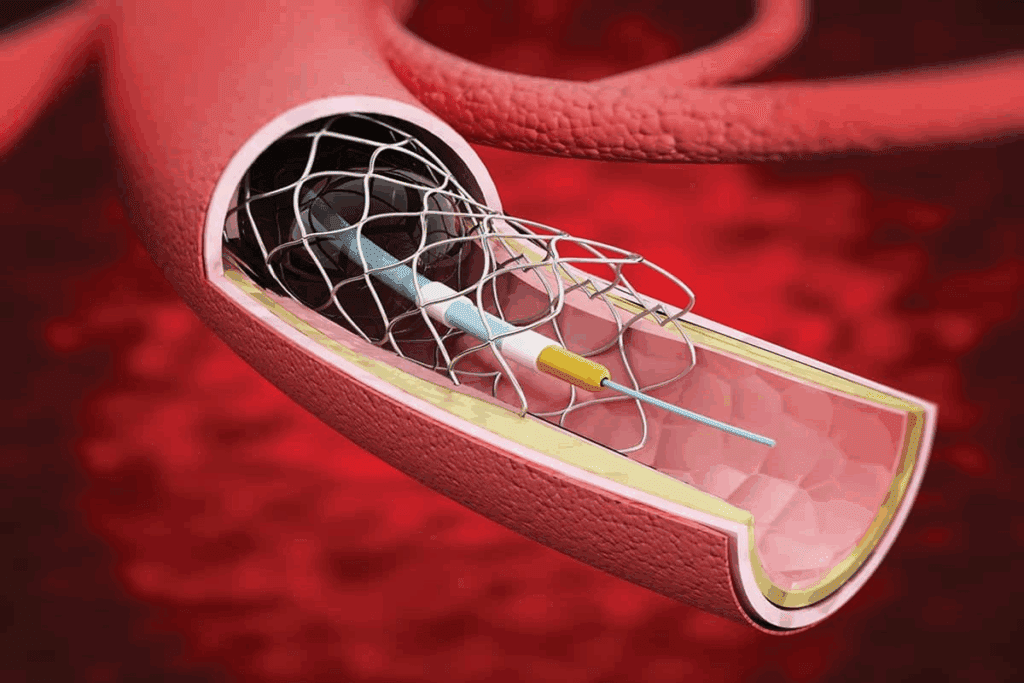
At Liv Hospital, we know how vital it is to keep arteries open. This prevents heart attacks. A stent is a tiny, metal mesh tube. It keeps an artery open, improving blood flow to the heart.
When plaque builds up in the coronary arteries, it can block blood flow. This can lead to serious problems. That’s why stents are used. They help restore blood flow, easing symptoms and lowering heart attack risk.
We use stents made from advanced materials for the best results. Knowing how stents work helps us treat coronary artery disease effectively. This way, we can help our patients get better.
Learn what is a stent used for and how heart stents work to treat blocked arteries.
Key Takeaways
- Stents are small, metal mesh tubes used to keep arteries open.
- They help restore blood flow to the heart, relieving symptoms and reducing the risk of heart attack.
- Advanced materials are used to make stents for the best possible outcomes.
- Understanding stent purpose is key for effective treatment options.
- Liv Hospital provides patient-centered care for those affected by coronary artery disease.
Understanding What a Stent Is
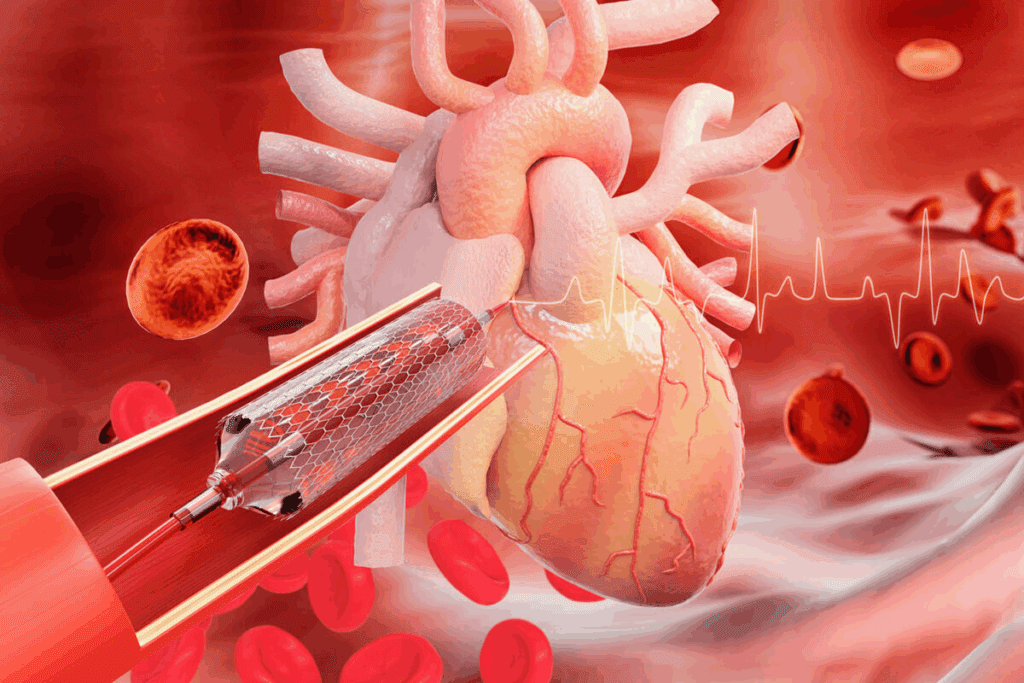
To grasp the role of stents in medicine, we must first define what a stent is. A stent is a small, expandable mesh tube. It is placed in an artery to keep it open, ensuring blood flow. We often use stents during angioplasty procedures.
Definition of Stents in Medicine
In medicine, stents are small, expandable tubes used to keep arteries open. These devices are key in treating narrowed or blocked arteries. The main job of a stent is to keep the artery open, allowing blood to flow freely.
The stent’s design is like a mesh that expands when in the artery. A balloon inflates to push the stent against the artery walls. After the balloon is deflated and removed, the stent stays in place.
Common Misconceptions: Stints vs. Stents
Many people confuse “stints” and “stents.” While they sound alike, they mean different things. Stints usually mean a short time or a limited activity period. In contrast, stents are medical devices used to keep arteries open. The confusion comes from their similar spelling and sound, but in medical terms, it’s “stents.”
- Stints are about time or limits.
- Stents are medical tools for keeping arteries open.
What Is a Stent Used For in Medical Practice

Stents are key in medical care, helping in many areas. They are mainly used to keep arteries and other passages open. This helps treat various health issues.
General Applications Across Medical Fields
Stents are not just for heart health; they help in many fields. For example, urologists use stents to prevent blockages in the urinary system. Gastroenterologists use stents to clear blockages in the digestive tract. Their wide use shows how valuable stents are in medicine.
Stents also support weak or narrowed vessels. This is important for treating many diseases. It shows how important stents are in medical care.
The Primary Purpose of Stent Placement
The main goal of stent placement is to keep passages open. This ensures blood and fluids can flow well. It’s key for organ function and health.
In the heart, stents help blood flow, reducing heart attack risks. They also ease symptoms like chest pain. The immediate and long-term benefits of stents make them a top choice for many.
Stents tackle severe blockages from plaque buildup, a big problem in heart disease. By keeping arteries open, stents greatly improve life quality for those with heart issues.
Heart Stents: Specialized Devices for Coronary Arteries
Heart stents are tiny, mesh-like devices that help restore blood flow in coronary arteries. They are key in treating coronary artery disease, affecting millions globally. We’ll look at how they work, their role in cardiology, and their importance for heart health.
What Are Stents for the Heart
Heart stents keep coronary arteries open, ensuring the heart gets the oxygen and nutrients it needs. These devices are typically made from metal mesh and are placed using a minimally invasive procedure called angioplasty. By improving blood flow, stents can greatly enhance the lives of those with coronary artery disease.
The Anatomy of Coronary Arteries
The coronary arteries are vital, supplying the heart with oxygen-rich blood. They branch from the aorta and wrap around the heart. Knowing their anatomy helps us understand how stents restore heart health.
How Plaque Buildup Affects Heart Function
Plaque buildup in coronary arteries, known as atherosclerosis, reduces blood flow to the heart. This can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. If not treated, it can lead to a heart attack, a serious condition. Stents help prevent these issues by keeping arteries open, ensuring heart function.
Heart stents are essential in managing coronary artery disease. Understanding their role highlights their importance in modern cardiology.
Types of Heart Stents and Their Materials
Heart stents are key in treating coronary artery disease. They come in different types, each made from specific materials. These materials and functions meet various patient needs.
Bare Metal Stents: Structure and Function
Bare metal stents are made from stainless steel or other metals. They work by providing a mechanical scaffold to keep the artery open. Yet, they have a higher risk of causing the artery to narrow again.
Key Features of Bare Metal Stents:
- Made from stainless steel or other metals
- Provide a mechanical scaffold to keep the artery open
- Higher risk of restenosis
Drug-Eluting Stents: Advanced Protection
Drug-eluting stents are coated with medication. This medication is slowly released into the artery wall. It significantly reduces the risk of restenosis, making them a popular choice.
Advantages of Drug-Eluting Stents:
- Reduced risk of restenosis due to medication release
- Effective for patients at higher risk of artery narrowing
Bioresorbable Stents: Temporary Support Solutions
Bioresorbable stents are made from materials that dissolve in the body over time. They offer temporary support to the artery and then disappear. This could potentially reduce long-term complications.
Features of Bioresorbable Stents:
- Made from dissolvable materials
- Provide temporary support to the artery
- May reduce long-term complications
Here’s a comparison of the different types of heart stents:
| Type of Stent | Material | Key Feature | Restenosis Risk |
| Bare Metal Stent | Stainless Steel | Mechanical Scaffold | Higher |
| Drug-Eluting Stent | Metal with Drug Coating | Medication Release | Lower |
| Bioresorbable Stent | Dissolvable Material | Temporary Support | Varies |
How Do Stents Work in the Heart?
Stents are tiny, mesh-like tubes that help keep arteries open. This ensures the heart gets the blood it needs. When a coronary artery is narrowed or blocked, a stent can restore blood flow.
The Mechanism of Blood Flow Restoration
Restoring blood flow involves several steps. First, an angioplasty compresses the plaque against the artery walls. Then, a stent is placed to keep the artery open.
- The stent expands against the artery walls, improving blood flow.
- It provides structural support to prevent the artery from collapsing.
- By keeping the artery open, stents help to reduce symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath.
How Stents Maintain Artery Patency
Stents are designed to keep arteries open by providing a scaffold. Over time, the stent becomes embedded in the artery wall. Drug-eluting stents release medication to prevent tissue growth that could cause re-narrowing.
Key benefits of stents in maintaining artery patency include:
- Prevention of re-narrowing through the release of medication.
- Structural support to the artery walls.
- Improved long-term blood flow to the heart muscle.
Immediate and Long-term Effects on Cardiac Function
The immediate effect of stent placement is restoring blood flow to the heart muscle. This can reduce symptoms like angina. In the long term, stents can prevent heart attacks by keeping arteries open.
Long-term benefits may include:
- Reduced risk of heart attacks.
- Improved quality of life due to reduced symptoms.
- Enhanced cardiac function due to improved blood flow.
The Heart Stent Procedure Explained
The heart stent procedure, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a minimally invasive treatment. It opens narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. This helps restore blood flow to the heart and relieves symptoms of coronary artery disease.
Pre-Procedure Preparation and Evaluation
Before the heart stent procedure, patients go through a detailed evaluation. They review their medical history, current medications, and diagnostic tests like angiograms or stress tests. Preparation is key to ensure the procedure’s success and reduce risks.
- Patients are advised on necessary dietary restrictions and medication adjustments.
- A pre-procedure consultation is conducted to discuss the procedure’s details and address any patient concerns.
Angioplasty and Stent Placement Process
A catheter is inserted into an artery in the leg or arm during the procedure. Angioplasty is done by inflating a balloon to widen the artery. Then, a stent is placed to keep the artery open.
The entire process is monitored using advanced imaging techniques. This ensures the stent is placed precisely at the blockage site.
Is a Stent Considered Major Surgery?
While the heart stent procedure is a significant medical intervention, it is not considered major surgery. It is performed under local anesthesia, and most patients can resume normal activities within a few days. The minimally invasive nature of the procedure reduces recovery time and lowers the risk of complications.
In conclusion, the heart stent procedure is a safe and effective treatment for coronary artery disease. By understanding the steps involved, from preparation to the actual stent placement, patients can better navigate their treatment options.
Benefits of Heart Stent Placement
Stent placement can greatly improve a patient’s health and function. Heart stents keep coronary arteries open, ensuring blood flows to the heart muscle. This is a big step forward in treating coronary artery disease.
Heart stent placement offers many benefits for heart health and overall well-being. We’ll look at these advantages in detail. This will show how stents help improve health outcomes.
Relief from Angina Symptoms
One key benefit of heart stent placement is relief from angina symptoms. Angina is chest pain or discomfort due to lack of oxygen-rich blood. Stents keep arteries open, restoring blood flow and reducing or eliminating angina symptoms.
Effective angina relief greatly improves a patient’s life. They can do daily activities without chest pain. Studies show stent placement significantly reduces angina episodes.
Prevention of Heart Attacks
Heart stents also prevent heart attacks by keeping arteries open. A blocked artery can lead to a heart attack, which can be deadly. Stents ensure the heart muscle gets the oxygen and nutrients it needs.
The prevention of heart attacks is vital. It saves lives and reduces the need for more serious medical treatments after a heart attack.
Improved Quality of Life and Functionality
Heart stent placement also improves quality of life and functionality. Patients can do daily tasks and physical activities more easily and confidently after the procedure.
| Benefits | Description | Impact on Patient |
| Relief from Angina | Reduction or elimination of chest pain | Increased ability to engage in daily activities |
| Prevention of Heart Attacks | Maintenance of coronary artery patency | Reduced risk of serious cardiac events |
| Improved Quality of Life | Enhanced overall well-being and functionality | Greater ease in performing daily tasks and physical activities |
The table shows the many benefits of heart stent placement. It covers heart health and patient well-being. Understanding these benefits helps patients make informed treatment choices.
Potential Risks and Complications
Heart stent placement is a serious medical procedure. It comes with risks that patients need to know about. Knowing these risks helps patients make better health choices.
Short-term Complications After Stent Placement
Right after the procedure, patients face some risks. These include:
- Bleeding at the catheter site
- Blood clots forming on the stent
- Allergic reactions to the stent material or medications used during the procedure
- Damage to the blood vessels or heart
Doctors closely watch patients to reduce these risks. They often give medicines to stop blood clots from forming on the stent.
Long-term Considerations and Monitoring
After recovery, patients with heart stents face ongoing issues. These include:
- Restenosis, or the re-narrowing of the arteries
- The need for more procedures or stent replacement
- Managing risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol
Regular check-ups with doctors are key. They help keep an eye on the stent and manage any problems early.
Risk Factors That May Affect Outcomes
Some factors can change how well a heart stent works. These include:
| Risk Factor | Potential Impact |
| Smoking | Increased risk of restenosis and further cardiovascular events |
| Diabetes | Higher risk of complications and restenosis |
| High Blood Pressure | Increased strain on the heart and possible damage |
By managing these risk factors, patients can better their outcomes. This helps lower the chance of complications.
Recovery and Life After a Heart Stent
Recovering from a heart stent is a journey. It starts with immediate care, medication, and changes in your daily life. We know this time is key for your heart’s health and the success of the procedure.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
Right after the stent is placed, we watch you closely for a few hours. Sometimes, you’ll need to stay in the hospital overnight. It’s important to follow our advice on rest, medication, and follow-up visits for a smooth recovery.
Key aspects of immediate care include:
- Resting the catheter insertion site to prevent bleeding
- Taking prescribed medications as directed
- Attending follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider
Long-term Medication Requirements
To keep the stent open, you’ll need to take antiplatelet meds for a while. Your doctor will tell you how long. This is a big part of your care plan to keep the stent working right.
| Medication Type | Purpose | Duration |
| Aspirin | Prevent blood clots | Indefinitely |
| P2Y12 Inhibitors (e.g., clopidogrel) | Prevent platelet aggregation | 6-12 months or more |
Lifestyle Modifications for Stent Longevity
Living a healthier lifestyle is key for your stent’s life and heart health. This means eating right, exercising, quitting smoking, and managing stress.
Recommended lifestyle changes:
- Eating a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or other aerobic exercises
- Avoiding tobacco products
- Managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga
By sticking to these tips and working with your healthcare team, you can live better after a heart stent. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
When Is a Heart Stent Necessary?
Doctors use tests and patient factors to decide if a heart stent is needed. This helps find the best treatment for coronary artery disease.
Diagnostic Criteria for Stent Candidacy
Tests are used to check artery blockage and heart health. These include:
- Stress tests to see how the heart works under stress
- Coronary angiography to see the arteries
- Cardiac catheterization to measure heart pressure and flow
- Fractional flow reserve (FFR) to check stenosis severity
Doctors use these test results to see if a stent is needed to improve heart blood flow.
Alternative Treatments to Consider
Stents are a common treatment, but other options exist. These include:
| Treatment | Description | Benefits |
| Medication Therapy | Medicines to manage symptoms and slow disease | Non-invasive, can manage symptoms well |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Changes in diet, exercise, and smoking | Improves heart health, reduces risk factors |
| Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) | Surgery to bypass blocked arteries | Good for complex disease, long-term benefits |
Emergency vs. Elective Stent Placement
Stent placement can be urgent or planned. Urgent placement is for heart attacks to open blocked arteries. Planned placement is for stable disease.
The choice between urgent and planned stent placement depends on the patient’s condition. Knowing the difference helps patients understand their treatment options.
Advanced Stent Procedures at Specialized Facilities
Liv Hospital is a top choice for heart care. We use the latest stent procedures and focus on keeping patients safe. We follow strict international standards to ensure the best care.
International Protocols for Stent Procedures
We follow international protocols closely. These rules are based on the newest research and trials. This means our patients get the safest and most effective treatments.
“The use of standardized protocols in stent procedures has been shown to significantly reduce complications and improve patient outcomes.” –
American Heart Association
Ensuring Patient Safety at Liv Hospital
Keeping patients safe is our main goal. We do this in many ways:
- Comprehensive pre-procedure evaluation
- State-of-the-art equipment and technology
- Highly trained and experienced medical staff
- Strict adherence to hygiene and safety protocols
| Safety Measure | Description | Benefit |
| Pre-procedure evaluation | Comprehensive assessment of patient health | Identifies possible risks |
| State-of-the-art equipment | Latest technology in stent procedures | Improves precision and safety |
Technological Advancements in Stent Procedures
The world of stent procedures is always changing. New technologies are key to these changes. Some important ones include:
- Drug-eluting stents that lower restenosis risk
- Bioresorbable stents for temporary support
- Advanced imaging for precise stent placement
These new technologies make stent procedures better and safer. At Liv Hospital, we keep up with these advancements. This way, our patients get the best care with the latest technology.
Conclusion: The Evolving Role of Stents in Cardiac Care
Stents have become key in treating heart disease, changing cardiac care. They keep getting better, making them safer and more effective.
Stents help keep blood flowing and arteries open. They also ease pain from angina. The future looks bright, with new stent technologies and treatments on the way.
Hospitals like Liv Hospital are leading the way in healthcare. They make sure patients get the best treatments. As heart care advances, stents will keep playing a big role in treating heart disease.
FAQ
What is a stent, and how does it work in the heart?
A stent is a small, mesh-like device. It’s inserted into a blocked or narrowed artery to restore blood flow. In the heart, stents keep coronary arteries open. This improves cardiac function and reduces symptoms like angina.
What is the difference between “stints” and “stents”?
“Stints” refers to a short time or a limited amount. “Stents,” on the other hand, are medical devices used to keep arteries open. The correct term for the medical device is “stent.”
What are the different types of heart stents available?
There are several types of heart stents. These include bare metal stents, drug-eluting stents, and bioresorbable stents. Each type has its own unique characteristics, advantages, and uses in medical practice.
How are stents used in medical practice beyond cardiology?
Stents are not just for cardiology. They are also used in other medical fields. This includes treating conditions like peripheral artery disease, kidney disease, and certain types of cancer.
What is the purpose of a stent in the heart?
The main purpose of a heart stent is to restore and maintain blood flow. This is in blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. It improves cardiac function, reduces symptoms, and prevents heart attacks.
Is a stent placement considered major surgery?
No, stent placement is not major surgery. It’s a minimally invasive procedure. It’s usually done using local anesthesia and involves a small incision.
What are the benefits of having a heart stent?
Having a heart stent offers several benefits. It relieves angina symptoms, prevents heart attacks, and improves overall health and functionality.
What are the risks and complications of heart stent placement?
Heart stent placement can have risks and complications. These include short-term issues like bleeding or infection. Long-term concerns include stent thrombosis or restenosis.
How do I recover from a heart stent procedure?
Recovering from a heart stent procedure involves several steps. These include immediate post-procedure care, long-term medication needs, and lifestyle adjustments. These support stent longevity.
When is a heart stent deemed necessary?
A heart stent is necessary when there’s significant blockage or narrowing of coronary arteries. It’s also needed when other treatments are not suitable or effective.
What materials are stents made of?
Stents are made from metal or a mix of metal and other materials. The material used depends on the stent type. Options include stainless steel, chromium-cobalt, and platinum-chromium.
How do I know if I’m a candidate for a heart stent?
To find out if you need a heart stent, you’ll need diagnostic tests. These include angiograms and stress tests. They assess the severity of coronary artery blockage or narrowing.
Can I undergo stent placement on an elective basis?
Yes, stent placement can be done on an elective basis. This is for patients with stable coronary artery disease. It can also be an emergency procedure for heart attacks or other acute coronary syndromes.
References
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2023, November 29). What Are Stents? https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/stents
- NHS. (2025, July 1). Coronary angioplasty and stent insertion – How it’s performed. https://www.nhs.uk/tests-and-treatments/coronary-angioplasty/what-happens/























