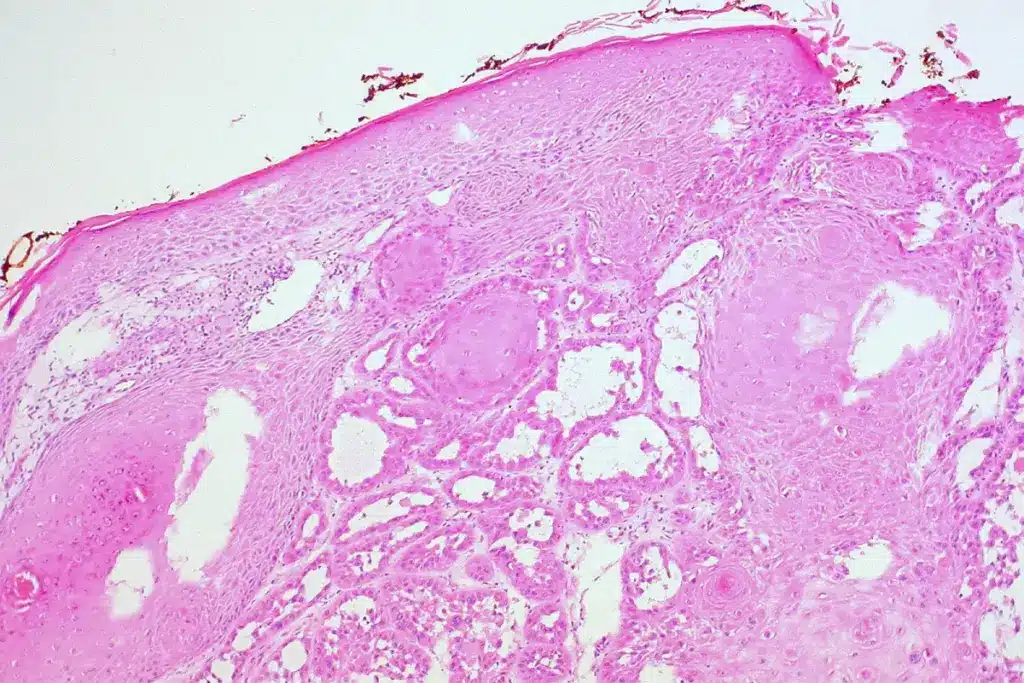
Adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) is a rare and complex cancer of the secretory glands. It grows slowly, often comes back, and can spread late. This makes it a tough condition to deal with.
At Liv Hospital, we’re dedicated to helping patients with ACC. We focus on the disease’s biology, causes, and treatments to get the best results.
Understanding ACC is key for both patients and doctors. While we don’t know the exact cause, research points to genetic and environmental factors.
Key Takeaways
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma is a rare type of cancer affecting the secretory glands.
- ACC can occur in various parts of the body, including the salivary glands, breast, skin, and respiratory tract.
- The exact cause of ACC is unknown, but genetic and environmental factors are likely involved.
- Understanding ACC’s biology is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment.
- Liv Hospital provides complete, team-based care for patients with ACC.
Understanding Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
Adenoid cystic carcinoma is a complex and rare cancer. It mainly affects the salivary glands. We will look into its details to give a full picture.
Definition and Classification
Adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) is a rare tumor found in the salivary glands. It has cystic, tubular, and solid patterns. These patterns help classify ACC, which affects its behavior and outcome.
The histological classification of ACC includes three main types:
- Tubular
- Cribriform
- Solid
Each type has its own traits. These traits can change how aggressive the tumor is and how well it responds to treatment.
Affected Demographics and Body Locations
ACC can strike at any age but is most common in adults aged 40 to 60. There’s a slight female predominance in ACC cases. It mainly hits the salivary glands but can also appear in the breast, skin, and respiratory tract.
Knowing who is at risk helps in catching ACC early. Key groups include:
- Adults aged 40-60
- Slightly more common in females
- Can occur in various body locations
Understanding these groups is key to early detection and treatment of ACC.
Causes and Risk Factors of Adenoid Cystic Cancer
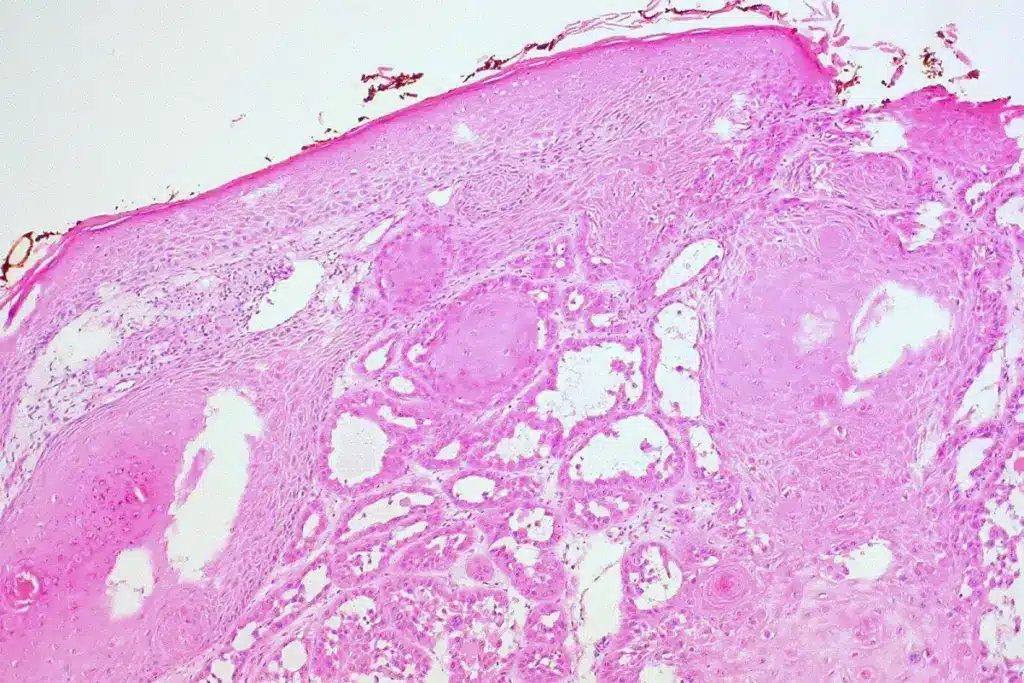
It’s important to know what causes adenoid cystic carcinoma to manage and treat it well. This cancer is complex and has many causes.
Genetic Mutations in MYB and MYBL1 Genes
Studies have found specific genetic changes in the MYB and MYBL1 genes in most ACC tumors. These changes are key in how the cancer grows and spreads. The MYB gene is linked to many cancers, and its mutation in ACC is a big factor in the cancer’s traits.
These genetic changes affect how the tumor grows and spreads. Knowing about these changes helps doctors find better treatments for ACC patients.
Metastatic Patterns and Lymph Node Involvement
Adenoid cystic carcinoma can spread to distant places like the lungs and bones. But, it rarely involves lymph nodes. How ACC spreads is key in planning treatment.
The metastatic ability of ACC means patients need close follow-up. Finding metastasis early is vital for better treatment plans. A team approach, including surgery and radiation, is often needed to fight metastatic ACC.
Understanding the causes and risk factors of adenoid cystic carcinoma helps doctors create better treatment plans. This is based on genetic changes and how the cancer spreads.
Conclusion
Adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) is a rare and complex cancer. It needs careful attention and management. ACC has malignant cells and often spreads through nerves.
Imaging like CT and MRI is key in diagnosing and planning treatment. They help see how the cancer grows and affects important body parts.
The best treatment for ACC is surgery, sometimes followed by radiation. A team of doctors and support for patients are important. For more on ACC, including causes and treatments, see this case report.
Understanding and tackling ACC’s complexities helps us offer top-notch care worldwide. Early detection and treatment are key to better outcomes. A full care plan is vital for managing this complex disease.
FAQ
What is adenoid cystic carcinoma?
Adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) is a rare, slow-growing form of cancer that most commonly develops in the salivary glands of the head and neck. However, it can also appear in the breast, skin, lungs, or uterus. It is characterized by its tendency to grow along nerves (perineural invasion
What are the causes of adenoid cystic carcinoma?
The exact cause is currently unknown. Unlike many other cancers, it is not strongly linked to lifestyle habits like smoking or alcohol use. It is primarily driven by genetic rearrangements, most notably a fusion of the MYB and NFIB genes.
What are the risk factors for developing adenoid cystic carcinoma?
There are very few established risk factors for ACC. It occurs slightly more often in women than men and is typically diagnosed in middle-aged or older adults (ages 40–60), though it can affect people of any age. It does not appear to be hereditary.
How does adenoid cystic carcinoma metastasize?
Unlike many cancers that spread through the lymph nodes, ACC primarily spreads through the bloodstream. It is also unique for its “skipping” nature, where it travels along nerves. The most common site for distant metastasis is the lungs, followed by the liver and bones.
What are the treatment options for adenoid cystic carcinoma?
Treatment is usually multi-modal:
Surgery: The primary treatment, aiming for wide “clear margins” to remove the tumor.
Radiation Therapy: Often used after surgery to kill remaining microscopic cells, especially since ACC frequently involves nerves.
Systemic Therapy: Chemotherapy or targeted therapies may be used for advanced or metastatic cases, though their effectiveness is currently limited.
Can adenoid cystic carcinoma be cured?
While ACC has a high 5-year survival rate because it grows slowly, it is known for late recurrence (sometimes 10–20 years after initial treatment). Because of this persistent nature, many doctors view it as a chronic condition that requires lifelong monitoring rather than a definitive “cure.”
How is adenoid cystic carcinoma diagnosed?
Physical Exam: Checking for lumps or facial numbness.
Imaging: MRI or CT scans to determine the tumor’s size and nerve involvement.
Biopsy: A Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) or core biopsy is required to confirm the diagnosis by looking at the cells under a microscope.
What is the role of genetic testing in adenoid cystic carcinoma?
Genetic testing is becoming vital for identifying the MYB-NFIB fusion gene, which helps confirm the diagnosis. In advanced cases, genomic profiling can help doctors identify specific mutations that might make a patient eligible for clinical trials or targeted drug therapies.
What kind of support is available for patients with adenoid cystic carcinoma?
Because ACC is rare, specialized support is key:
Patient Advocacy Groups: Organizations like the ACC Research Foundation (ACCRF) provide resources and connect patients.
Multidisciplinary Teams: Access to oncologists, surgeons, and neurologists who specialize in rare head and neck cancers.
Palliative Care: Focused on managing pain and side effects from nerve involvement.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4741919/[1





