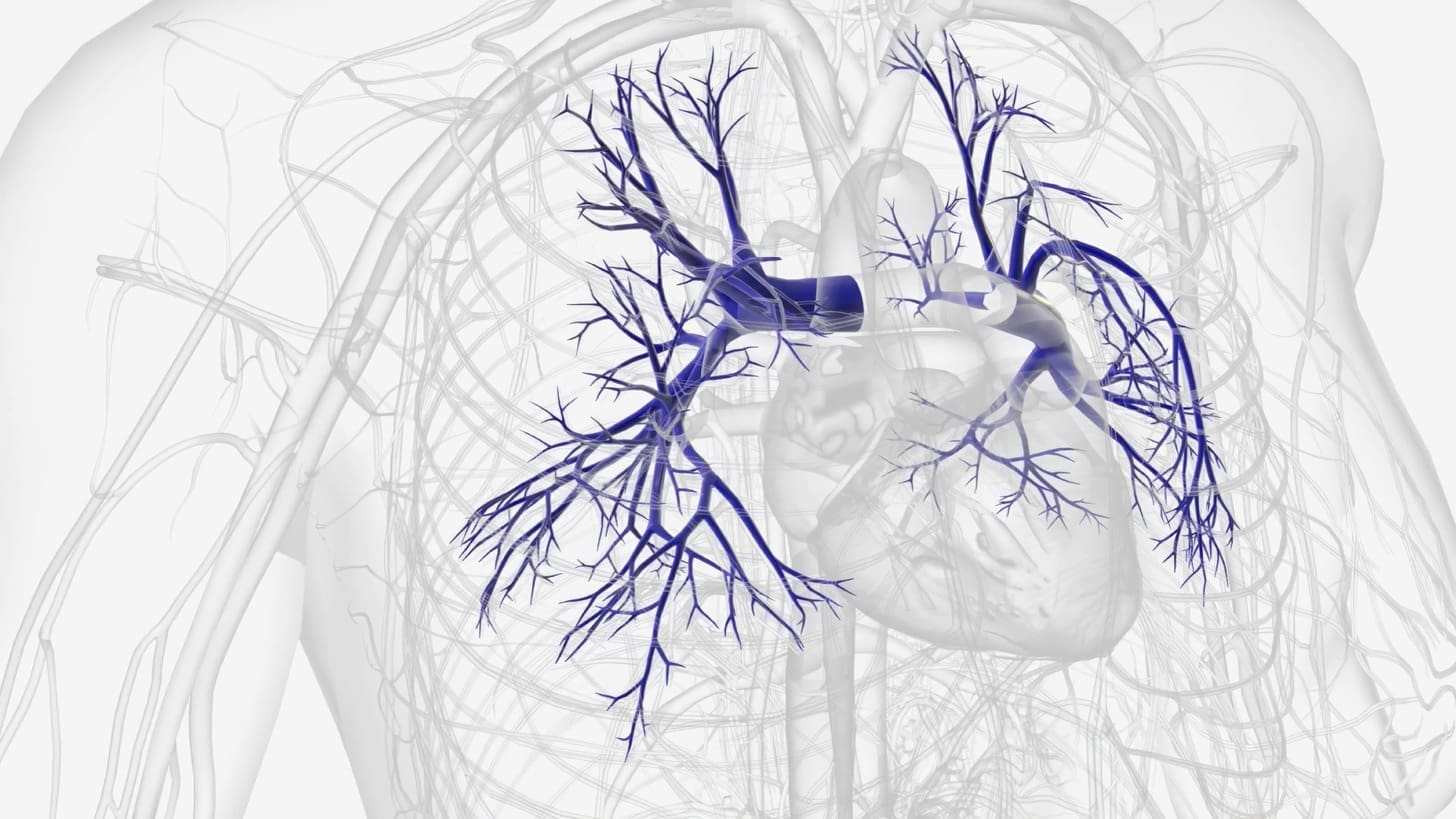
At Liv Hospital, we know how vital accurate vascular diagnosis is. Angiography, a special X-ray method, shows the blood vessels’ structure and finds issues.
Every year, over 2 million people get angiography worldwide. It’s the top choice for checking blood vessels. We aim to give top-notch care by explaining angiography’s medical meaning and its part in keeping blood vessels healthy.
Key Takeaways
- Angiography is a special X-ray technique for seeing blood vessels.
- It is seen as the best way to diagnose blood vessel problems.
- More than 2 million angiography procedures happen every year globally.
- Liv Hospital is dedicated to providing top-notch vascular diagnostics.
- Angiography helps find issues in blood vessels.
What Is Angiography
Angiography is a way to see inside blood vessels. It helps doctors find and fix problems in the blood system. This tool is key in today’s medicine, letting doctors see the blood vessels up close.
The Basic Concept and Medical Definition
Angiography uses dye and X-rays to show blood vessel images. It spots blockages and other issues. Doctors say it’s changed how they see blood vessels, making it easier to find problems.
Angiography helps us find and treat many blood vessel issues. It uses X-rays, dye, and special software to see inside the blood system. This helps doctors understand and fix vascular problems.
Common Terminology and Spelling Variations
There are many ways to spell and say angiography. You might see “angiograpgy,” “angiograph,” “angiograpghy,” “agiography,” or “engiography.” But they all mean the same thing: a way to see inside blood vessels.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Angiography | Standard medical term for vascular imaging |
| Angiograpgy | Common misspelling of angiography |
| Angiograph | Alternative term, often used informally |
| Agiography | Variant spelling, less commonly used |
Knowing these different words is important. It helps doctors and patients talk clearly about angiography. We need to make sure everyone understands what angiography is and how it helps.
The Historical Development of Angiography
The journey of angiography has seen many medical breakthroughs and tech advancements. It has changed a lot from its early days to today’s advanced state.
Origins and Early Applications
Angiography started with early X-ray tech to see blood vessels. The process of recording an X-ray of blood vessels began in the early 1900s. These first angiography tests were risky but started a new era in checking blood vessels.
At first, angiography was used to learn about blood vessel anatomy and find big vascular problems. As it got better, x-ray angiography showed how important it was for doctors to see inside blood vessels. This helped them diagnose and treat vascular diseases better.
Evolution into Modern Practice
Angiography has made huge strides over the years. Better imaging tech and contrast media have made it safer and more precise. Now, thanks to digital subtraction angiography and other new tools, angiography is much safer.
Today, angiography is seen as the gold standard in vascular diagnosis. It lets doctors see blood vessels very clearly. We’re always looking for ways to make angiography even safer and more effective.
How Angiography Works: The Science Behind the Procedure
To understand angiography, we need to know the science behind it. It uses X-ray technology and contrast dye. This method lets doctors see the blood vessels in detail.
X-rays capture images of blood vessels. Contrast dye makes these images clearer. Together, they help doctors see any problems in the blood vessels.
X-ray Technology in Vascular Imaging
X-ray technology is key in angiography. It helps capture images of blood vessels. X-ray imaging uses X-ray beams that go through the body.
These beams are absorbed differently by different tissues. This is how X-rays help see blood vessels. The images are then made clearer for doctors to look at.
The Role of Contrast Dye in Visualization
Contrast dye is very important in angiography. It makes blood vessels stand out on X-ray images. The dye is injected through a catheter into the bloodstream.
The dye absorbs X-rays in a way that makes blood vessels show up better. This helps doctors find and diagnose problems more easily.
| Component | Function in Angiography |
|---|---|
| X-ray Technology | Captures images of blood vessels using X-ray beams |
| Contrast Dye | Enhances visibility of blood vessels by absorbing X-rays differently |
| Catheter | Delivers contrast dye directly to the area of interest |
Angiography combines X-ray technology and contrast dye. This makes it a powerful tool for doctors. It helps them see and treat blood vessel problems better.
The Complete Angiography Process Explained
We will walk you through the angiography process, from start to finish. Knowing each step can ease your worries and make the experience smoother.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before an angiography, several steps are taken. Informed consent is given after explaining the procedure’s risks and benefits. Patients are advised to:
- Fast for a certain period before the procedure
- Disclose any allergies, specially to contrast dye
- Inform their doctor about medications they’re taking
- Arrange for someone to drive them home after the procedure
The access site, usually in the groin or arm, is cleaned and prepared for the procedure.
During the Angiography Procedure
During the angiography, the patient lies on an X-ray table. The access site is numbed with local anesthesia. A catheter is inserted into the blood vessel and guided to the area of interest using X-ray imaging. Once in place, contrast dye is injected to visualize the blood vessels. X-ray images are then captured to diagnose any vascular conditions.
Post-Procedure Care and Recovery
After the procedure, the catheter is removed, and pressure is applied to the access site to prevent bleeding. Patients are monitored for a period to check for any immediate complications. Post-procedure care includes:
- Resting for several hours to allow the access site to heal
- Monitoring the access site for signs of bleeding or infection
- Following up with their doctor as instructed
Most patients can resume their normal activities within a day or two. Strenuous activities may need to be avoided for a longer period.
Different Types of Angiography Procedures
Angiography isn’t a single procedure; it has many forms for different medical needs. We use various angiography types to diagnose and treat vascular conditions. This ensures patients get the right care for their condition.
Coronary Angiography
Coronary angiography is key for seeing the heart’s blood supply. It spots blockages or issues in the heart’s arteries. It’s vital for finding coronary artery disease, a big cause of heart attacks.
In this procedure, a dye is injected into the heart’s arteries through a catheter. X-rays then show the arteries and any blockages. This info helps decide the best treatment, like angioplasty or stenting.
Cerebral Angiography
Cerebral angiography looks at the brain’s blood vessels. It’s key for finding issues like cerebral vasospasm, aneurysms, and AVMs. It gives clear images of the brain’s blood structure, helping with diagnosis and treatment plans.
A catheter is inserted into a leg blood vessel and guided to the brain’s arteries. Then, dye is injected, and X-rays are taken. This helps neurosurgeons and radiologists plan treatments.
Pulmonary Angiography
Pulmonary angiography checks the lungs’ blood supply. It’s critical for spotting pulmonary embolism, a serious condition where a clot blocks a lung artery. It’s the top choice for finding pulmonary embolism.
| Procedure | Indications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Coronary Angiography | Coronary artery disease, blockages | Detailed visualization of coronary arteries |
| Cerebral Angiography | Cerebral vasospasm, aneurysms, AVMs | Precise diagnosis of cerebral vascular conditions |
| Pulmonary Angiography | Pulmonary embolism | Accurate diagnosis of pulmonary embolism |
Peripheral Angiography
Peripheral angiography looks at blood vessels outside the heart and brain, usually in the legs. It helps find peripheral artery disease (PAD), where narrowed or blocked vessels reduce limb blood flow. It guides treatments like angioplasty and stenting to improve blood flow.
As we’ve seen, different angiography procedures are key for diagnosing and treating various vascular issues. Understanding each type’s specific uses and benefits helps healthcare providers offer targeted care.
Medical technology keeps improving, and angiography is likely to get even better. For now, it remains a vital part of vascular diagnosis and treatment.
Medical Conditions Diagnosed Through Angiography
Angiography helps us find and treat serious vascular diseases. It’s a key tool in medicine that lets doctors see inside blood vessels. This helps them spot conditions that could cause big health problems if not treated.
Vascular Blockages and Atherosclerosis
Angiography is great for finding blockages and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis happens when plaque builds up in arteries. This can lead to heart attacks or strokes. Doctors use angiography to see where and how bad these blockages are.
Vascular blockages can happen in many places, like the heart or legs. Angiography lets doctors find these blockages. They can then decide the best way to fix them and keep blood flowing.
Aneurysms and Vascular Malformations
Angiography is also key for finding aneurysms and vascular malformations. An aneurysm is a bulge in a blood vessel that can burst. Vascular malformations are odd blood vessel growths that can cause health problems. Angiography lets doctors see these clearly, helping them plan the best treatment.
Blood Clots and Circulation Issues
Angiography also helps find blood clots and check on blood flow. Blood clots can block blood flow and cause serious problems. Doctors can then treat these clots with the right medicine or surgery to fix the flow.
In short, angiography is very important for finding and treating many vascular diseases. It gives doctors clear pictures of the blood vessels. This helps them make the right diagnosis and treatment plans, which improves patient care.
Angiography by the Numbers: Global Usage and Statistics
Angiography is key in finding vascular problems, with many procedures done worldwide each year. It’s a vital tool in medicine, giving insights into blood vessel health that were hard to get before.
The Gold Standard in Vascular Diagnosis
Angiography is top for diagnosing blood vessel issues because it shows detailed images. It’s trusted by doctors everywhere for its accuracy and reliability.
Key benefits of angiography include:
- High-resolution imaging of vascular structures
- Accurate diagnosis of vascular blockages and diseases
- Guiding minimally invasive treatments and interventions
Worldwide Procedure Frequency and Trends
More angiography procedures are done every year, thanks to more heart diseases and better technology.
Some important stats on angiography use worldwide are:
- Over 2 million angiography procedures are done annually worldwide.
- Most are for heart artery disease, showing its commonness.
- There’s a rise in using angiography for blood vessel disease in the legs, due to more older people.
These trends show how important angiography is in healthcare today. It helps in diagnosing and guiding treatments. As technology gets better, we’ll see more uses of angiography and better care for patients.
Patient Experience and Comfort During Angiography
Ensuring patient comfort is our top priority during angiography. Medical teams take all necessary steps to make sure patients are safe and comfortable. We know that medical procedures can cause anxiety, so we strive to make the angiography process as smooth as possible.
Anesthesia and Sedation Options
There are various anesthesia and sedation options available to ensure patient comfort. The choice depends on the procedure, the patient’s health, and their needs. Local anesthesia is often used to numb the area where the catheter is inserted, reducing discomfort.
Sedation options are also available to help patients relax. For example, conscious sedation allows patients to stay awake but feel relaxed. The level of sedation can be adjusted to keep patients comfortable throughout the procedure.
What Patients Can Expect During the Procedure
On the day of the angiography, patients arrive a few hours early. They are greeted by our medical team, who explain the procedure and answer any questions. The necessary equipment is then prepared.
During the procedure, patients lie on an X-ray table. The area for the catheter is cleaned and numbed. The catheter is inserted under imaging guidance, and a contrast dye is used to see the blood vessels.
After the procedure, patients are monitored for any complications. The medical team then provides instructions on post-procedure care and any follow-up appointments.
| Aspect of Care | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Procedure Preparation | Patients are informed about the procedure, and any necessary preparations are made. | Reduces anxiety, ensures patient is well-prepared. |
| Anesthesia and Sedation | Local anesthesia and sedation options are used to minimize discomfort. | Enhances patient comfort, reduces pain. |
| Post-Procedure Care | Monitoring and care after the procedure to prevent complications. | Ensures patient safety, promotes recovery. |
We focus on patient comfort and experience to make angiography safe and effective. Our goal is to help patients receive the care they need with minimal stress and discomfort.
Recent Advancements in Angiography Technology
Recent angiography tech has changed vascular diagnostics a lot. It makes things more accurate and safer. This change helps doctors diagnose and treat vascular issues better.
Digital Subtraction Angiography
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) is a big step forward. It makes blood vessels clearer by removing background images. This gives doctors a detailed look at blood vessel problems.
- DSA gives clear images with less background noise.
- It lets doctors see things in real-time during procedures.
- It uses less dye, which lowers the risk of problems.
3D Rotational Angiography
3D Rotational Angiography is another key improvement. It shows blood vessels in 3D, helping doctors plan treatments better. The 3D images can be turned and viewed from different sides, giving a full view of complex blood vessel structures.
- 3D Rotational Angiography makes complex blood vessel structures clearer.
- It helps in precise planning for procedures.
- It improves how vascular diseases are assessed.
Minimally Invasive Approaches
There have also been big steps in minimally invasive methods. These methods use smaller cuts and cause less damage, leading to faster recovery and fewer complications. Using the wrist for angiography is becoming more common, making the experience better for patients.
We’re seeing a big change in angiogrpahy with these new advancements. Vascular diagnostics are getting more precise and easier for patients. As tech keeps getting better, we’ll see even more progress in treating vascular conditions.
Conclusion: The Future of Angiography in Vascular Diagnostics
Angiography is a key tool in vascular diagnostics. It helps doctors see inside the body’s blood vessels. Knowing what angiography is and how it works is important for everyone involved.
The future of angiography is bright. New technologies and techniques are being developed. These advancements have already improved patient care, like a 96% success rate in stent placement. We can look forward to even more progress in this field.
As medicine keeps changing, so will our understanding of angiography. We’ll see new technologies that make angiography even better. The term angiography medical term will keep meaning precise and accurate medical imaging.
What is angiography?
Angiography is a way to see inside blood vessels. It uses a contrast dye and X-ray images to show the blood vessel’s details. This helps doctors find and fix problems in the blood vessels.
What is the medical definition of angiography?
Angiography is a medical test. It uses X-rays and a contrast dye to see blood vessels. This helps doctors find blockages or other issues.
What are the different types of angiography procedures?
There are many types of angiography. These include looking at the heart, brain, lungs, and legs. Each type focuses on different parts of the body.
How does angiography work?
Angiography uses X-rays and dye to see blood vessels. The dye is injected into the vessels. Then, X-rays capture clear images of the vessels.
What is the role of contrast dye in angiography?
Contrast dye is key in angiography. It makes blood vessels stand out. This helps doctors spot problems like blockages.
What can patients expect during an angiography procedure?
Patients get local anesthesia and might be sedated. A catheter is inserted, dye is injected, and X-rays are taken. This is to see the blood vessels clearly.
What are the benefits of digital subtraction angiography?
Digital subtraction angiography makes images clearer. It removes background tissue and bone. This leads to more accurate diagnoses.
How is angiography used in diagnosing vascular conditions?
Angiography helps find vascular problems like blockages and aneurysms. It gives detailed images. This helps doctors plan the best treatment.
What are the recent advancements in angiography technology?
New tech in angiography includes digital subtraction and 3D imaging. These advancements make procedures safer and more accurate.
Is angiography a painful procedure?
Angiography is not painful. Patients are numbed where the catheter goes. Some might feel a bit uncomfortable or anxious, but sedation helps.
What is the recovery time after an angiography procedure?
Recovery time varies. Most patients rest for a few hours and go home the same day. It depends on the procedure.
Can angiography be used to treat vascular conditions?
Yes, angiography can treat conditions like blockages. It can do this through procedures like angioplasty and stenting during the exam.
What is the difference between angiography and angioplasty?
Angiography is for looking at blood vessels. Angioplasty is for fixing narrowed or blocked vessels. Angioplasty often happens during angiography.
References
- Coronary angiography. Retrieved from: https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/tests/coronary-angiography
- Coronary angiography. Retrieved from: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003876.htm
- Coronary angiogram. Retrieved from: https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/coronary-angiogram
- CTangiography. Retrieved from: https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/angioct?PdfExport=1