Arthrosis, also known as osteoarthritis, is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions worldwide. It causes pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. These symptoms can greatly impact daily life.
As the protective cartilage at joint surfaces wears down, joint degeneration occurs. This can affect the bone structure underneath. It’s very common, affecting about 32.5 million people in the U.S.
Understanding the arthrosis definition and recognizing its symptoms early is key. It’s important for effective management and treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Arthrosis is synonymous with osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease.
- It affects millions worldwide, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
- The condition results from the progressive wear and tear of protective cartilage layers at joint surfaces.
- Early recognition of symptoms is key for effective management and treatment.
- Approximately 32.5 million people in the U.S. are affected by this condition.
Arthrosis Def: Understanding the Degenerative Joint Condition
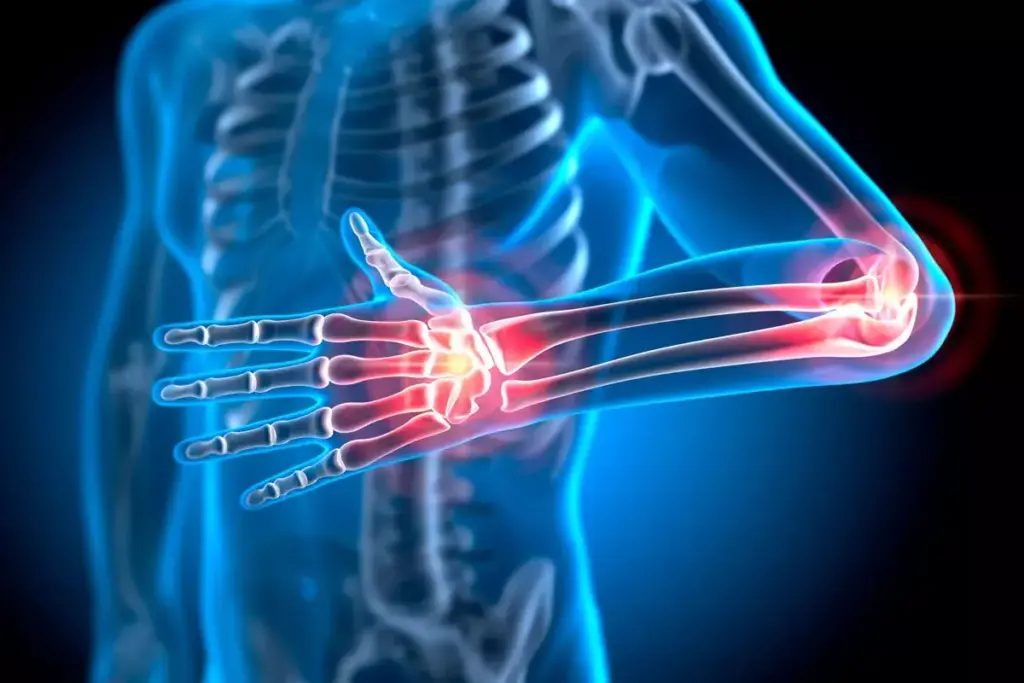
Arthrosis is a major cause of disability worldwide. It’s important to know its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. We’ll explore what arthrosis is, how it’s different from other joint problems, and its medical terms.
Medical Definition and Terminology
Arthrosis, also known as osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease, is when the cartilage in joints wears down. This leads to pain, stiffness, and less mobility. The term “arthrosis” is often used the same as osteoarthritis, but some say arthrosis is more about wear and tear without much inflammation.
Doctors use different names for arthrosis, like degenerative joint disease and osteoarthrosis. Knowing these terms helps in diagnosing and treating the condition. Key points about arthrosis include:
- Deterioration of joint cartilage
- Bone spurs or osteophytes formation
- Subchondral bone changes
- Joint inflammation (in some cases)
Arthrosis vs. Inflammatory Arthritis
It’s important to know the difference between arthrosis and inflammatory arthritis. Arthrosis is mainly about wear and tear, while inflammatory arthritis is about joint inflammation due to autoimmune diseases or infections.
The main differences between arthrosis and inflammatory arthritis are:
- Arthrosis: Characterized by degeneration of cartilage and bone, with minimal inflammation.
- Inflammatory Arthritis: Marked by significant inflammation, often due to autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis.
Knowing these differences is key for effective treatment plans. For arthrosis, treatment aims to reduce pain, improve joint function, and slow disease progression. In contrast, inflammatory arthritis treatment often includes anti-inflammatory drugs and DMARDs.
Causes and Risk Factors of Arthrosis
It’s important to know what causes arthrosis to prevent and manage it well. Arthrosis is a joint condition that gets worse over time. It’s caused by genetics, environment, and lifestyle.
Age, Weight, and Joint Stress
Age is a big risk factor for arthrosis. As we get older, our joints’ cartilage wears down. This leads to pain and stiffness. Being overweight or obese puts more stress on joints like hips, knees, and spine, making it worse.
Stress on joints from repetitive actions or injuries also plays a part. This stress can lead to arthrosis.
Keeping a healthy weight can lower the risk of arthrosis. Eating right and exercising regularly helps. Also, avoiding too much strain on joints and taking care of past injuries can help prevent it.
Genetic Factors and Gender Differences
Genetics play a big role in arthrosis risk. If your family has it, you’re more likely to get it. Scientists are studying how certain genes can make you more prone to it.
Women are more likely to get arthrosis, often after menopause. Hormones seem to play a part. Knowing this helps doctors tailor treatments for women.
Understanding arthrosis causes and risks helps us prevent and manage it. We can live healthier by taking care of our joints and being mindful of our genetics.
Symptoms and Affected Body Parts
It’s important to know the symptoms of arthrosis early. This helps in getting the right treatment. We will look at the common joints affected and the symptoms people face.
Common Joints Affected by Arthrosis
Arthrosis mainly hits joints that bear weight and are used a lot. The knees, hips, hands, neck, and wrists are often affected. We’ll see how arthrosis impacts these areas.
- Knees: Knee arthrosis causes knee pain and stiffness, making daily tasks hard.
- Hips: Hip arthrosis affects the hip joint, leading to pain and less mobility.
- Hands and Fingers: Hand and finger arthrosis makes everyday tasks tough due to finger pain and stiffness.
Pain, Stiffness, and Mobility Issues
The symptoms of arthrosis include pain, stiffness, and less mobility in the affected joints. We’ll explore these symptoms and their effects on patients.
- Pain: Pain is a main symptom, often felt during activity and sometimes at rest.
- Stiffness: Stiffness, mainly after rest or inactivity, is common.
- Mobility Issues: Reduced mobility comes from joint degeneration, making it hard to move the affected joint.
These symptoms can greatly affect a patient’s life. It’s key to see a doctor for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion: Understanding and Managing Arthrosis
It’s key to understand arthrosis to manage it well. Knowing the basics helps people deal with their diagnosis and treatment choices. Managing arthrosis means using treatments, making lifestyle changes, and trying alternative therapies to keep joints healthy.
Good care for arthrosis combines different treatments. Plans are made for each person, aiming to ease symptoms and improve life quality. By learning about arthrosis, people can take steps to keep their joints and overall health good.
We stress the need for a wide approach to handle arthrosis. This includes medical treatments and changes in lifestyle. This way, people can lessen the effects of arthrosis on their daily lives, leading to a better life quality.