At Liv Hospital, we know that getting ectasia of the thoracic aorta can worry you. Ectasia is when the aorta gets a bit wider but isn’t big enough to be called an aneurysm. It’s usually less than 3 cm wide.
We get it when you have questions about what it means for your health. Our team is here to help with the latest care and advice for this condition.
Ectasia of the thoracic aorta means the aorta is a bit wider than usual. But it’s not as big as an aneurysm. Knowing about it is key to staying healthy. We’re here to guide and support you.
Key Takeaways
- Ectasia of the thoracic aorta is a mild dilation of the aorta.
- It is not an aneurysm, typically measuring less than 3 cm in diameter.
- Understanding this condition is vital for patient health.
- Liv Hospital offers the latest care and protocols.
- Our team is dedicated to your safety and learning.
Understanding Thoracic Aortic Anatomy and Function
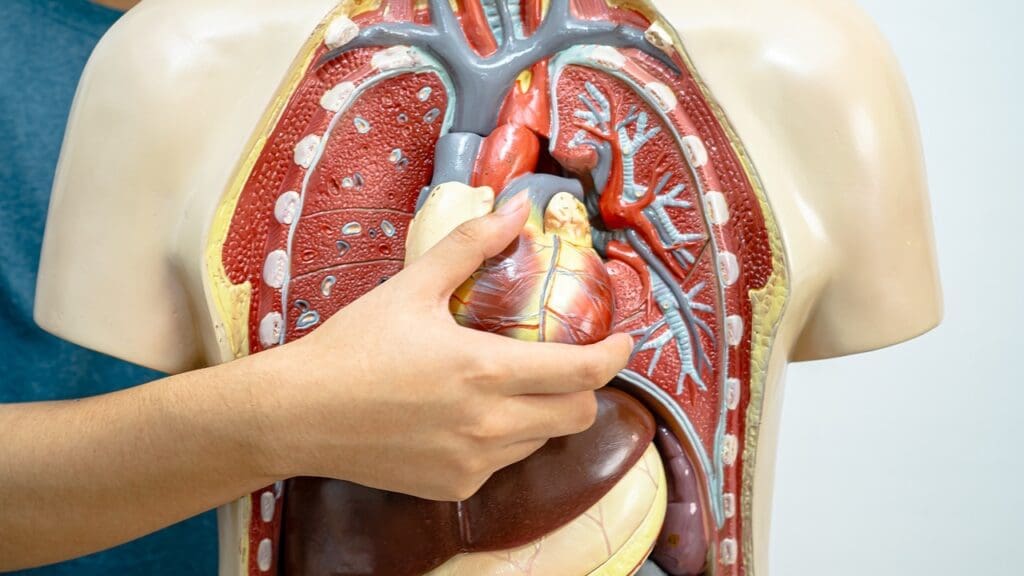
It’s important to know about the thoracic aorta’s anatomy and function. This artery starts in the heart’s left ventricle. It goes through the chest and into the belly, where it becomes the abdominal aorta.
Normal Aortic Structure and Dimensions
The thoracic aorta has a certain shape and size that’s key to its job. Normal aortic dimensions change with age, sex, and size. The diameter is usually between 2 and 3.5 cm. The part going up is a bit bigger than the part going down.
| Aortic Segment | Average Diameter (cm) |
|---|---|
| Ascending Aorta | 2.8-3.5 |
| Descending Aorta | 2.0-3.0 |
The Importance of Aortic Health
Keeping the aortic health in check is vital for heart health. Problems like ectasia or aneurysms can be serious. It’s important to watch for risks and catch diseases early.
Knowing the thoracic aorta’s normal shape and function helps doctors. They can then diagnose and treat aorta-related issues better. This leads to better health outcomes for patients.
What Is Ectasia of the Thoracic Aorta?
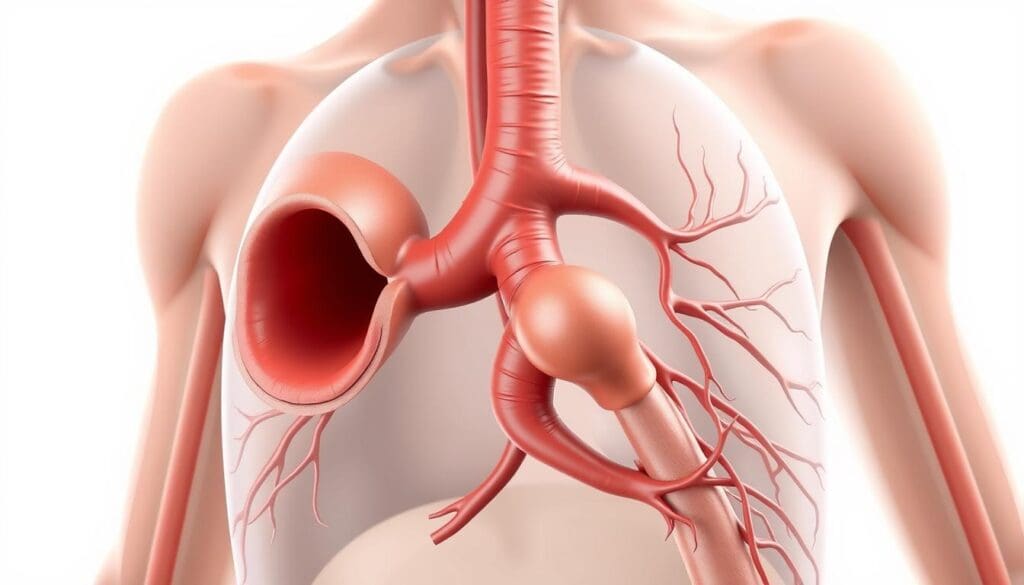
It’s important to know about ectasia of the thoracic aorta for heart health. Ectasia means the aorta gets wider. This can lead to serious health issues. We’ll look into what it is, why it matters, and how common it is.
Definition and Clinical Significance
Ectasia of the thoracic aorta means the aorta gets bigger. It can lead to more serious problems like aneurysms. Early detection and monitoring are key to avoid worse problems.
Differentiating Between “Mildly Ectatic” and Aneurysmal Changes
It’s important to tell the difference between mildly ectatic and aneurysmal changes. Both involve the aorta getting wider, but one is more serious. Mildly ectatic changes are less severe, while aneurysmal changes are more serious and might need surgery.
Prevalence and Epidemiology
Ectasia of the thoracic aorta is more common in older adults. It’s linked to high blood pressure and other heart risks. The frequency of thoracic aortic ectasia varies among different groups, showing the need for specific screening and care plans.
Knowing about the prevalence and epidemiology helps doctors find and help at-risk groups. This way, they can take the right steps to manage their health.
Causes and Risk Factors of Thoracic Aortic Ectasia
It’s important to know the causes and risk factors of thoracic aortic ectasia. This condition makes the thoracic aorta widen. Many factors can influence this.
Age-Related Degenerative Changes
Age is a big risk factor for thoracic aortic ectasia. As we get older, our aortic walls lose elasticity and strength. This can cause the aorta to dilate. Age-related wear and tear on the aortic wall is a main cause of ectasia.
Hypertension and Cardiovascular Conditions
Hypertension is a major risk factor for thoracic aortic ectasia. High blood pressure strains the aortic wall, speeding up degeneration. Other heart conditions, like atherosclerosis, also raise the risk. Controlling high blood pressure is key to stopping aortic ectasia from getting worse. For more on symptoms and causes.
Genetic and Connective Tissue Disorders
Genetics play a big role in thoracic aortic ectasia. Certain conditions, like Marfan syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, increase the risk. These disorders weaken the aortic wall, making it more prone to dilation.
Other Contributing Factors
Other factors can also lead to thoracic aortic ectasia. Lifestyle choices, like smoking and high cholesterol, can harm heart health. We also look at the role of genetic screening for those with a family history of aortic issues.
Types and Anatomical Variations of Ectatic Thoracic Aorta
It’s important to know the different types and how the thoracic aorta can change. This helps doctors diagnose and treat the condition better. The changes in the aorta can affect different parts, leading to different health issues.
Ascending Thoracic Aortic Ectasia
Ectasia in the ascending part of the thoracic aorta is a big worry. It’s close to the heart and can harm heart function. Ascending thoracic aortic ectasia needs close watch and treatment to avoid serious problems.
Ectatic Descending Thoracic Aorta
The descending part of the thoracic aorta can also change. These changes might be linked to different risks and outcomes. Knowing about ectatic descending thoracic aorta helps doctors find the best treatment.
Fusiform Ectasia Patterns
Fusiform ectasia means the aorta gets wider in a uniform way. This can happen in different parts of the thoracic aorta. Fusiform ectasia patterns help doctors understand how severe the condition is.
Mild Ectasia vs. Moderate Dilation
Telling mild ectasia from moderate dilation is key for planning treatment. The table below shows the main differences:
| Characteristics | Mild Ectasia | Moderate Dilation |
|---|---|---|
| Aortic Diameter | Slightly increased | Noticeably enlarged |
| Clinical Implication | Lower risk | Higher risk |
| Management | Monitoring | Active treatment |
We understand how complex the ectatic thoracic aorta is. Accurate diagnosis and the right treatment are vital for better patient care.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
Understanding the symptoms of thoracic aortic ectasia is key for early treatment. This condition can show up in different ways. It’s important to know the possible signs and symptoms.
Common Symptoms When Present
When symptoms appear, they might include chest pain, back pain, or trouble breathing. This is because the expanding aorta can press on or move other structures. Sometimes, symptoms of aortic regurgitation can happen if the ectasia affects the aortic root.
Asymptomatic Presentation and Incidental Findings
Many people with thoracic aortic ectasia don’t show symptoms. It’s often found by chance during imaging for other reasons. Regular health checks and screenings are vital, even more so for those at risk.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you have sudden, severe chest or back pain, get medical help right away. This could mean a serious issue like aortic dissection. Also, if you have a family history of aortic problems or other risk factors, see a doctor.
Spotting symptoms early can greatly improve treatment and outcomes. We stress the need to know the signs and get medical help when needed.
Diagnostic Approaches for Ectasia of Thoracic Aorta
We use many methods to find ectasia of the thoracic aorta. This ensures we can detect and watch it closely. Finding this condition involves first checking, then using advanced scans, and measuring carefully.
Initial Assessment and Physical Examination
The first step is a detailed medical history and physical check-up. Our healthcare providers look for signs like high blood pressure or heart disease history.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Advanced scans are key in finding thoracic aortic ectasia. We use different scans to see the aorta and measure it.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scans
CT scans give detailed pictures of the aorta. This is very helpful for spotting ectasia and tracking it.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI is another great tool for finding aortic ectasia. It gives clear images without harmful radiation, perfect for long-term checks.
Echocardiography Options
Echocardiography, like transthoracic and transesophageal, checks aortic size and function. This is very useful for seeing how ectasia affects the heart.
Measurement Criteria and Diagnostic Standards
Getting an accurate diagnosis needs standard measurements. We stick to set rules to make sure we diagnose and track thoracic aortic ectasia the same way every time.
- Measurements are taken at different points along the thoracic aorta.
- These measurements are compared to what’s normal for age and size.
- By taking measurements over time, we can see if it’s getting worse.
By using these methods together, we can spot and keep an eye on thoracic aortic ectasia. This helps us act quickly if needed.
Management and Monitoring Strategies
We have a detailed plan for managing thoracic aortic ectasia. It includes regular imaging, medication, and lifestyle changes. Our plan is made just for each patient to ensure the best care and lower the risk of problems.
Regular Imaging Follow-up Protocols
Keeping an eye on thoracic aortic ectasia with regular imaging is key. We suggest CT or MRI scans to watch the aortic diameter. The scan frequency depends on the patient’s condition and ectasia severity.
Blood Pressure Control and Medication
Managing blood pressure is vital for thoracic aortic ectasia care. We might give medications to keep blood pressure in check. This helps ease the aortic wall’s strain, slowing ectasia and preventing more issues.
Lifestyle Modifications for Aortic Health
Changing your lifestyle is important for managing thoracic aortic ectasia. We recommend a healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking. These steps can help prevent aortic dilation and boost heart health.
Risk Stratification Approaches
It’s important to figure out the right management for each patient. We look at the ectasia’s size and location, the patient’s medical history, and overall health. This helps us create a treatment plan that meets the patient’s unique needs and risks.
Treatment Options and Interventions
There are many ways to treat thoracic aortic ectasia. These range from simple management to complex surgeries. The right treatment depends on the size and location of the ectasia, the patient’s health, and symptoms.
Medical Management Approaches
For many, the first step is medical management. This means controlling blood pressure with medicine and lifestyle changes. Regular imaging tests also help monitor the condition. Keeping blood pressure in check is key to slowing the ectasia’s growth.
Surgical Considerations and Timing
Surgery is needed when the ectasia is at high risk of rupture or dissection. The decision to operate depends on the aorta’s size and the patient’s health. New surgical methods have made aortic repairs safer and more effective.
Innovative Treatment Developments
New treatments for thoracic aortic ectasia are being researched. This includes less invasive procedures and new materials for repairs.
“The future of aortic treatment lies in personalized medicine and minimally invasive techniques,” says a leading cardiovascular surgeon.
Liv Hospital’s Specialized Approach to Aortic Conditions
At Liv Hospital, we focus on a team-based approach to aortic conditions. Our experts work together to offer complete care. We use the latest technology and methods to ensure the best results for our patients.
| Treatment Approach | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Management | Control of blood pressure and regular monitoring | Slows progression, reduces risk of complications |
| Surgical Intervention | Repair or replacement of the affected aorta | Prevents rupture or dissection |
| Innovative Treatments | Less invasive procedures and new materials | Improved outcomes, reduced recovery time |
Conclusion: Living with Thoracic Aortic Ectasia
Living with thoracic aortic ectasia means understanding the condition well. We’ve looked at what it is, why it happens, and how to diagnose it. It’s key to get a correct diagnosis and keep an eye on it.
Managing the condition is important. This includes regular check-ups, controlling blood pressure, and making lifestyle changes. These steps help lower the risk of serious problems and make life better.
At Liv Hospital, we aim to give top-notch healthcare. We help international patients with advanced treatments and care. Our team creates custom plans for each patient, aiming for the best results for those with thoracic aortic ectasia.
What is ectasia of the thoracic aorta?
Ectasia of the thoracic aorta is when the aorta in your chest gets wider. It’s not as big as an aneurysm. This condition can worry people, so it’s key to understand its health impact.
How does ectasia differ from an aneurysm?
Ectasia is a milder form of aorta widening. It’s not as big as an aneurysm. We tell them apart by the aorta’s size and symptoms.
What are the risk factors for developing thoracic aortic ectasia?
Risk factors include getting older, high blood pressure, and certain genetic conditions. Some genetic syndromes also raise the risk.
Can thoracic aortic ectasia be asymptomatic?
Yes, many people with it don’t show symptoms. It’s often found by chance during tests. Regular check-ups are vital to catch it early.
How is thoracic aortic ectasia diagnosed?
Doctors use CT scans, MRI, or echocardiography to diagnose it. These tests help check the aorta’s size and watch for changes.
What are the management strategies for thoracic aortic ectasia?
Management includes regular tests, controlling blood pressure, and lifestyle changes. We tailor plans to meet each patient’s needs.
Are there any treatment options available for thoracic aortic ectasia?
Treatments vary from medical management to surgery, based on the condition’s severity. We keep up with new treatments to offer the best care.
How does Liv Hospital approach the treatment of aortic conditions?
Liv Hospital uses a specialized team approach for aortic conditions. Our experts work together to give patients the best care.
What is the significance of monitoring and managing thoracic aortic ectasia?
Monitoring and managing it are key to avoid complications. Regular follow-ups and sticking to treatment plans are essential.
Can lifestyle modifications help manage thoracic aortic ectasia?
Yes, healthy eating, exercise, and stress management can help. We guide patients on these changes as part of their treatment.
References
- Cedars-Sinai (Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm) : https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/t/thoracic-aortic-aneurysm.html




































