For those with knee arthritis in just one area, unicompartmental knee arthroplasty, or partial knee replacement, is a good choice. This minimally invasive procedure keeps the healthy parts of the knee intact. Unlike full knee replacement, it’s becoming more popular because it has a faster recovery time.
Liv Hopsital offer top-notch healthcare, including support for patients from around the world. Our team is skilled in partial and total knee replacements. We aim to improve your mobility and quality of life.
Key Takeaways
- Partial knee replacement is a minimally invasive procedure that preserves healthy knee anatomy.
- It is a viable treatment option for patients with knee arthritis limited to one area.
- Recovery time is typically quicker compared to full knee replacement.
- Patients with intact knee ligaments and a BMI under 40 are typically eligible.
- Most patients can return to sports within 6 to 10 weeks.
Understanding Knee Anatomy and Function
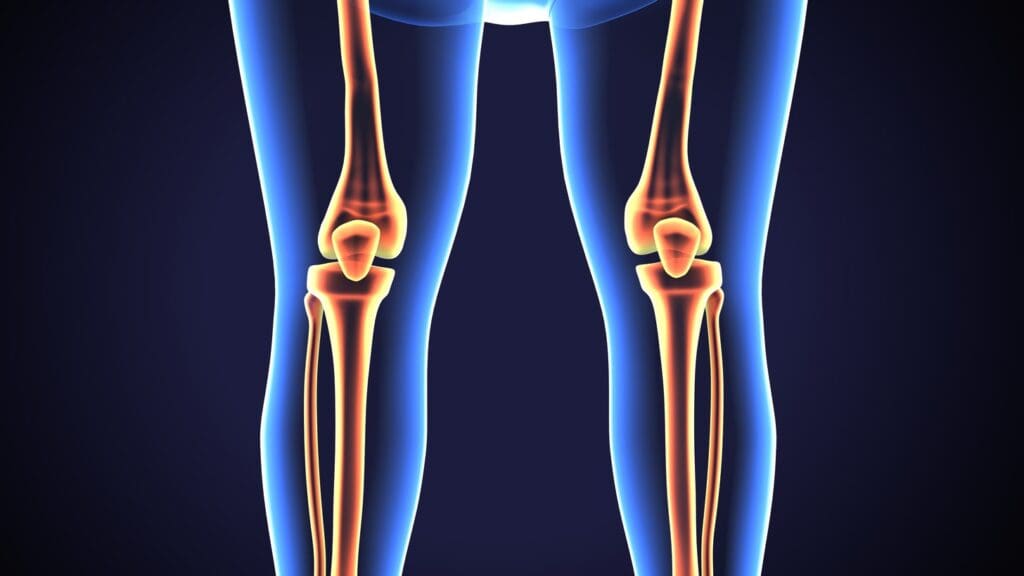
Knowing how the knee works is key to understanding its role in our bodies. The knee is a complex joint that helps us move and do daily tasks.
The Three Compartments of the Knee
The knee has three main parts: the medial, lateral, and patellofemoral compartments. Each part has its own job and structure.
The medial compartment is on the inside and carries a lot of our weight. The lateral compartment is on the outside and helps with side-to-side movement. The patellofemoral compartment is where the kneecap meets the femur, allowing us to bend and straighten our knees.
How Healthy Knees Work
Healthy knees work together, with bones, cartilage, ligaments, and muscles all playing a part. The articular cartilage helps the bones move smoothly.
The knee stays stable thanks to ligaments like the ACL and PCL, and the medial and lateral collateral ligaments.
Common Causes of Knee Deterioration
Knee problems can come from osteoarthritis, trauma, and overuse. Knowing these causes helps us prevent and treat knee issues.
Osteoarthritis wears down cartilage, causing pain. Trauma, like fractures or sprains, can also harm the knee. Overuse injuries are common in athletes or those who strain their knees a lot.
| Component | Function | Common Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Medial Compartment | Supports weight and facilitates movement | Osteoarthritis, injuries |
| Lateral Compartment | Allows for lateral movement and stability | Injuries, wear and tear |
| Patellofemoral Compartment | Enables knee bending and straightening | Patellofemoral pain syndrome, osteoarthritis |
What Is Partial Knee Surgery?
Partial knee surgery, also known as unicompartmental knee arthroplasty, is a less invasive method. It treats knee osteoarthritis in just one part of the knee.
Definition and Medical Terminology
Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty means replacing only the damaged part of the knee. It’s for those with damage in one area, like the inner, outer, or front part.
This surgery keeps more of your natural knee. It aims to preserve healthy bone and tissue. This can lead to better knee function and a more natural feel after surgery.
History and Development of the Procedure
The idea of partial knee replacement started in the 1970s. But, early versions didn’t always work well. This was due to old implant designs and surgical methods.
Now, thanks to better implant technology and surgical tools, results have greatly improved. Modern surgery uses computer-assisted and robotic-assisted methods. These help place implants more accurately, leading to better outcomes.
Current Techniques and Approaches
Today, partial knee surgery uses various methods. These include:
- Minimally invasive surgery to reduce damage and speed up recovery
- Advanced imaging to see the knee better during surgery
- Custom implants that fit each patient’s knee
These methods make partial knee surgery a good choice for many. It’s an option for those who might have only considered total knee replacement before.
Candidates for Partial Knee Replacement
Finding the right candidates for partial knee replacement means checking how severe and where the arthritis is. We look for people whose arthritis only affects one part of the knee. This makes them good candidates for this surgery.
Ideal Patient Profiles
Ideal candidates have arthritis in just one part of their knee. They often feel pain and stiffness in that area. If they haven’t gotten better with other treatments, surgery might help.
We check a patient’s medical history, do a physical exam, and use X-rays and MRI scans. This helps us see how damaged the knee is and what treatment is best.
Diagnostic Process
The diagnostic process is key to figuring out if someone needs partial knee replacement. It uses both clinical checks and imaging studies.
- Clinical evaluation: We look at symptoms, medical history, and do a physical exam to understand the knee’s state.
- Imaging studies: X-rays and MRI scans help us see inside the knee and check for damage or arthritis.
By using these tools, we can tell if someone is a good fit for partial knee replacement.
When Partial Knee Surgery Is Not Recommended
Partial knee replacement isn’t for everyone. If someone has severe arthritis in more than one part of the knee, they might need a total knee replacement instead.
| Condition | Suitability for Partial Knee Replacement |
|---|---|
| Arthritis in one compartment | Highly suitable |
| Arthritis in multiple compartments | Not suitable |
| Significant knee instability | Not recommended |
Orthopedic specialists say, “The success of partial knee replacement depends on choosing the right patients and doing the surgery carefully.” This shows how important it is to do a detailed check before surgery.
What Does a Partial Knee Replacement Look Like?
A partial knee replacement is made to look like the real knee. It uses new materials and careful surgery. This surgery only fixes the bad parts of the knee, keeping the good parts safe.
Components and Materials Used
These implants are made from metal and plastic. The metal parts are strong, like titanium or cobalt-chromium. They work well with the body’s tissues. The plastic part is for smooth movement, made from ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene.
Surgical Approach and Technique
The surgery for a partial knee replacement is smaller than for a total knee. Surgeons make a small cut, 3 to 5 inches, to get to the bad part of the knee. They remove the damaged parts and put in the new ones to fix the knee.
Visual Comparison to Natural Knee Structure
Looking at a partial knee replacement and a real knee, we see they try to keep the knee’s shape. The implant is made to work like the real knee. This helps the ligaments and tissues work better together.
This careful surgery means patients can recover faster. They might also have better results in the long run.
Full Knee Replacement Explained
Total knee replacement, or total knee arthroplasty, is a surgery that replaces the knee joint with artificial parts. It’s for those with severe arthritis or major knee damage. This damage affects many parts of the knee.
Total Knee Arthroplasty Defined
Total knee arthroplasty is a surgery that replaces the knee joint with artificial parts. These parts include the femoral, tibial, and patellar components. They are made to move like a natural knee.
We use the latest materials and methods to make sure the prosthetic knee lasts long and works well. The surgery is customized for each patient. This ensures the best results.
When Total Replacement Is Necessary
Total knee replacement is needed for severe arthritis or damage in many knee parts. This can make it hard to move and cause a lot of pain. It makes simple tasks hard to do.
For such cases, partial knee replacement might not be enough. It only fixes one part of the knee. Total knee replacement fixes the whole knee.
Components and Surgical Approach
The parts used in total knee replacement work together to fix the knee. The femoral and tibial components replace the damaged surfaces. The patellar component covers the kneecap for smooth movement.
Our surgery is planned with great care and precision. This ensures the prosthetic parts fit right and stay in place. This detail is key for a successful surgery and recovery.
Understanding the parts and how the surgery is done helps patients see the complexity and benefits of this procedure.
Partial Versus Full Knee Replacement: Key Differences
When thinking about knee replacement surgery, it’s important to know the differences between partial and full knee replacement. We’ll look at how they differ in surgery, keeping the knee natural, long-term results, and cost.
Surgical Invasiveness Comparison
Partial knee replacement is less invasive than full knee replacement. It only replaces the damaged part of the knee. Full knee replacement, on the other hand, replaces the whole knee joint.
Studies show that partial knee replacement leads to quicker recovery times and less tissue damage than total knee replacement. This is because partial knee replacement uses a smaller incision, causing less disruption to the surrounding tissue and muscles.
This can mean less post-operative pain and a faster return to normal activities.
Preservation of Natural Knee Structures
Partial knee replacement has the advantage of preserving natural knee structures. It only replaces the damaged part, leaving the healthy parts intact. This can make the knee feel and function more naturally after surgery.
- Retains healthy bone and cartilage
- Preserves ligaments and surrounding tissue
- Can result in a more natural knee motion
Long-term Outcomes and Durability
Both partial and full knee replacements have good long-term outcomes. But, the durability of the implant and patient satisfaction can differ. Partial knee replacement patients often report higher satisfaction rates because their knee feels more natural.
| Outcome | Partial Knee Replacement | Full Knee Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Recovery Time | Generally quicker | Typically longer |
| Preservation of Knee Structures | Retains healthy parts | Replaces entire knee joint |
| Long-term Satisfaction | Often higher | Varies |
Cost Considerations
The cost of partial versus full knee replacement can vary a lot. The initial cost of the implant and surgery might be similar. But, partial knee replacement often results in lower rehabilitation costs because of quicker recovery times and less need for extensive physical therapy.
In conclusion, choosing between partial and full knee replacement depends on several factors. These include the extent of knee damage, patient health, and personal preferences. Understanding these differences can help patients make an informed decision about their treatment options.
Recovery Time for Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee replacement surgery is becoming more popular. This is because it has a faster recovery time than total knee replacement. The reason is its less invasive nature, which keeps more of the natural knee structure intact.
Immediate Post-Operative Period
Right after surgery, patients usually stay in the hospital for a few days. They are watched closely for any problems and pain is managed well. Good pain control helps them start rehab sooner.
Patients start moving their knee and doing simple exercises. This keeps the knee flexible and strengthens the muscles around it. It also helps prevent stiffness and aids in healing.
Short-term Recovery Milestones
In the short term, patients hit several recovery milestones. Within a few weeks, they can walk without help, though they might use a cane. By six weeks, they can do daily tasks more easily.
- Resume driving within 2-4 weeks
- Return to light physical activities by 6-8 weeks
- Gradually increase exercise intensity under professional guidance
Long-term Rehabilitation Process
The long-term rehab for partial knee replacement includes more physical therapy. Physical therapy is key to getting back to normal. It helps strengthen the knee and improve flexibility.
Patients see ongoing improvements in their knee function for months after surgery. Full recovery can take up to 6 months. But, many feel better in the first 3 months.
Comparison to Total Knee Replacement Recovery
Partial knee replacement has a faster recovery than total knee replacement. It causes less post-operative pain and lets patients get back to normal activities sooner.
Research shows patients with partial knee replacement have better knee function and are happier. But, the choice between partial and total knee replacement depends on the patient’s knee damage and health.
Latest Advancements in Knee Replacement Technology
New technologies in knee replacement are changing how we treat knee problems. These advancements have made partial knee replacement surgeries more accurate and effective.
Robotic-Assisted Partial Knee Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery is a big step forward in knee replacement. It allows for greater precision and minimally invasive procedures. This can lead to faster recovery times and better results for patients.
Robotic systems help surgeons perform complex surgeries with better accuracy. They provide a detailed 3D image of the knee. This helps in planning and executing the surgery more precisely.
Improved Materials and Designs
New materials and implant designs are also key to better knee replacement outcomes. These advancements make implants more durable and compatible with the body. This reduces complications and improves implant longevity.
Some important improvements include:
- More durable and wear-resistant materials
- Enhanced implant designs for better fit and function
- Improved fixation methods for greater stability
| Material | Characteristics | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Titanium Alloys | High strength, low elasticity | Improved durability and reduced risk of implant loosening |
| Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene | Enhanced wear resistance | Longer implant lifespan and reduced risk of osteolysis |
| Ceramic Materials | High hardness, low friction | Reduced wear and improved joint mobility |
Patient-Specific Implants
Patient-specific implants are another big leap in knee replacement technology. These implants are made to fit each patient’s unique anatomy. This can lead to better outcomes and higher patient satisfaction.
To make these implants, a detailed 3D model of the patient’s knee is created. This model is used to design and make implants that meet the patient’s specific needs.
Future Directions in Knee Surgery
The future of knee surgery looks promising. We can expect more advancements in knee replacement technology. Some areas to watch include:
- Further improvements in robotic-assisted surgery
- Advances in biomaterials and implant design
- Increased use of patient-specific implants
- Integration of artificial intelligence in surgical planning and execution
As these technologies improve, we can look forward to even better results for patients undergoing knee replacement surgery.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision About Knee Surgery
It’s key to know the difference between partial and total knee replacement when thinking about surgery. We’ve looked at what each procedure is, who it’s best for, and how to recover.
When you’re thinking about knee surgery, think about the good and bad of each choice. Partial knee replacement is less invasive and might mean a quicker recovery. But, total knee replacement might be needed for more serious damage.
Talking to your doctor is the first step in making a choice. They can help you decide based on your knee damage, health, and how you live. This way, you pick the best option for you.
Understanding the details of partial versus total knee replacement is important. It helps you move forward and improve your life.
What is partial knee replacement surgery?
Partial knee replacement surgery replaces only the damaged part of the knee. This keeps the healthy parts intact.
How does partial knee replacement differ from total knee replacement?
Partial knee replacement only fixes the damaged part of the knee. Total knee replacement, on the other hand, replaces the whole knee joint.
What are the benefits of partial knee surgery?
Partial knee surgery is less invasive. It keeps the knee’s healthy parts intact. This can lead to a faster recovery than total knee replacement.
Who is a good candidate for partial knee replacement?
People with osteoarthritis or damage in just one part of the knee are good candidates. They should have little to no instability or deformity in the knee.
What is the recovery time for partial knee replacement?
Recovery from partial knee replacement is usually quicker. Most people can get back to normal activities within a few weeks to months.
How does the recovery process compare to total knee replacement?
Recovery from partial knee replacement is often less intense and shorter. It tends to involve less pain and fewer complications than total knee replacement.
What are the latest advancements in knee replacement technology?
New advancements include robotic-assisted surgery and better materials and designs. These aim to improve the surgery’s accuracy and outcomes.
What is robotic-assisted partial knee surgery?
Robotic-assisted partial knee surgery is a minimally invasive method. It uses a robotic system for precise and accurate surgery.
Are there any cost considerations for partial knee replacement compared to total knee replacement?
Partial knee replacement might cost less upfront. But, overall costs can vary. This depends on factors like the need for future surgeries and rehabilitation costs.
How do I make an informed decision about knee surgery?
Consider the extent of knee damage, your overall health, and personal preferences. Talk to an orthopedic surgeon to find the best treatment for you.
What is the difference between partial and full knee replacement in terms of long-term outcomes?
Both can offer long-term pain relief and improved function. The choice depends on the extent of damage and your overall health.
Can I undergo partial knee replacement if I have severe arthritis?
No, partial knee replacement is not for severe arthritis affecting multiple parts of the knee. Total knee replacement might be a better option.




































