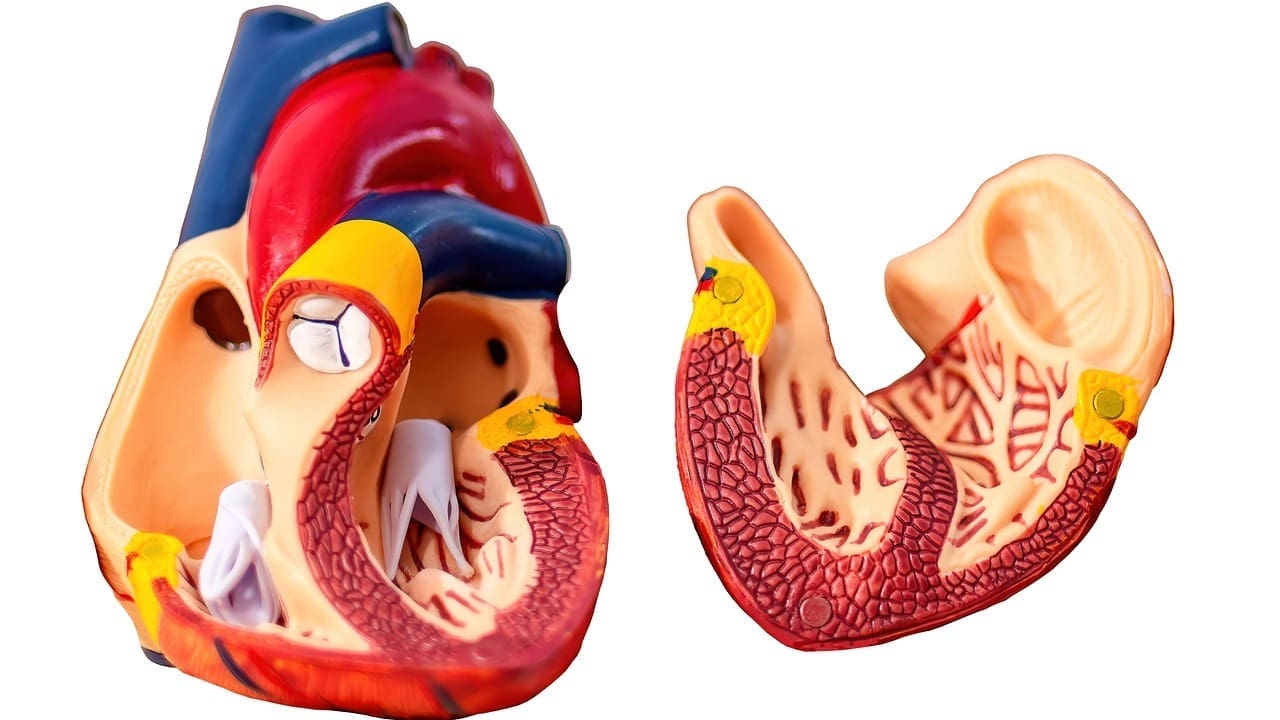
The ascending aorta is key to our heart’s function. It carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. It starts at the base of the left ventricle, right after the aortic valve. It’s about 5 cm long and 3 to 4 cm wide in adults.
The aorta, the biggest artery, starts in the left ventricle and goes down to the abdomen. The ascending aorta is the first part of it. It’s very important for blood flow.
Key Takeaways
- The ascending aorta is the first segment of the aorta, emerging from the left ventricle.
- It is typically 5 cm long and 3 to 4 cm in diameter in healthy adults.
- The aorta is the largest artery, extending from the heart to the abdomen.
- Understanding the ascending aorta’s anatomy is essential for diagnosing cardiovascular conditions.
- The ascending aorta plays a vital role in delivering oxygen-rich blood to the body.
The Ascending Aorta: Definition and Overview
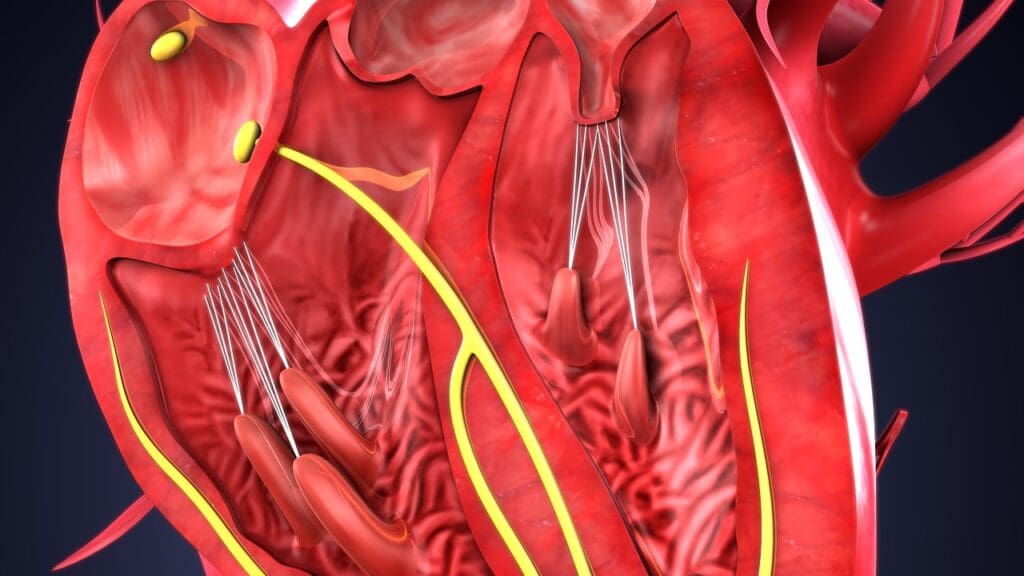
The ascending aorta is key to the heart’s function. It carries oxygen-rich blood to the body. It starts at the left ventricle of the heart, right after the aortic valve.
What Is the Ascending Aorta?
The ascending aorta is the first part of the aorta. It comes from the left ventricle. Its main job is to send oxygen-rich blood to the body. It’s about 5 cm long and has a diameter of 3 to 4 cm in adults.
Key Characteristics and Importance
The ascending aorta is vital for heart health. Its diameter (AO diameter) is key in checking heart health. Any issues with its size or shape can cause big problems.
Knowing the normal size and shape of the ascending aortic artery is important. It helps spot problems and diagnose heart issues.
The ascending aortic artery is essential for good blood flow. It plays a big role in keeping the heart and body healthy.
Anatomical Location of the Ascending Aorta
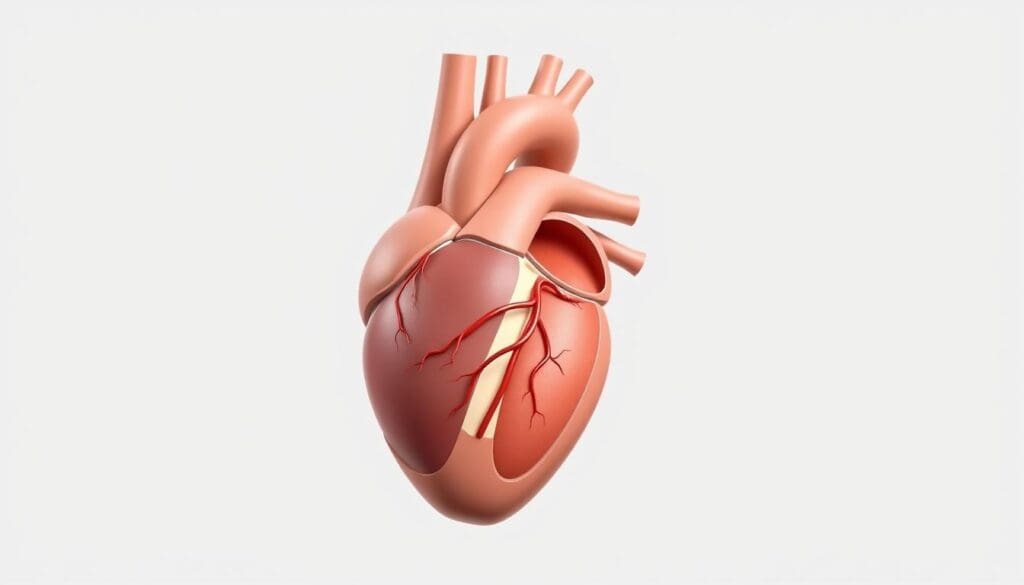
We will explore the anatomical location of the ascending aorta, a key part of heart health. The ascending aorta starts at the left ventricle and comes out right after the aortic valve. This spot is vital for its role in blood circulation.
Where Is the Ascending Aorta Located?
The ascending aorta is found in the thoracic cavity, starting from the left ventricle of the heart. It begins at the aortic valve and goes up to the sternal angle. Then, it turns into the aortic arch. Pictures often show it right above the left ventricle and before the aortic arch.
Diagrams and ascending aorta images are great for seeing where it is. They help us understand its close connection to other heart parts. These images show how close it is to the pulmonary trunk and where the right and left coronary arteries start.
Relationship to the Left Ventricle and Aortic Valve
The ascending aorta starts from the left ventricle right after the aortic valve. This valve is key for blood to flow only one way, from the left ventricle into the ascending aorta. The close bond between the ascending aorta, the left ventricle, and the aortic valve is essential for the heart to pump blood well.
Knowing this relationship is key for diagnosing and treating problems with the ascending aorta and nearby areas. The close connection of these parts shows how complex and connected the heart and blood system are.
Physical Dimensions and Structure
Knowing the size of the ascending aorta is key for diagnosing heart problems. It’s a vital part of the aorta that starts from the left ventricle of the heart.
Length and Diameter of the Ascending Aorta
The ascending aorta is usually about 5 cm long. It’s 3 to 4 cm wide in healthy adults. These sizes can change with age, sex, and health.
The width of the ascending aorta is very important. It helps doctors spot and track aortic diseases.
Ascending Thoracic Aorta Diameter Measurements
Measuring the ascending thoracic aorta’s width is vital for heart checks. It helps find issues like aneurysms or swelling. The normal width is between 2.1 and 4.1 cm, but it can vary.
| Dimension | Average Measurement | Normal Range |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 5 cm | 4.5-5.5 cm |
| Diameter | 3.5 cm | 3-4 cm |
The Ascending Aortic Artery and Blood Flow
The ascending aorta is key in the circulatory system. It carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body. It’s the largest artery, making sure oxygenated blood reaches the rest of the body. We’ll look at how it works in circulation and its link to cardiac output.
Function in Circulation
The ascending aorta’s main job is to move oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body. It gets this blood from the left ventricle through the aortic valve. Then, it spreads this blood to the systemic circulation, giving vital organs and tissues the oxygen they need.
This process is vital for good circulation and heart health. Problems with the ascending aorta, like dilation or aneurysm, can harm blood flow and heart function.
Relationship to Cardiac Output
The cardiac output, or the heart’s blood pumping rate, is tied to the ascending aorta. The aorta gets blood from the left ventricle, and its ability to handle and spread this blood impacts cardiac output. A healthy ascending aorta is key for good cardiac output, ensuring blood is efficiently pumped around the body.
It’s important to understand the link between the ascending aorta and cardiac output for heart health. By keeping the ascending aorta healthy, doctors can better treat heart conditions.
Relationship Between the Ascending Aorta and Other Cardiac Structures
It’s important to know how the ascending aorta connects with other heart parts. This knowledge helps doctors find and treat heart problems. The ascending aorta links with several key parts of the heart, which is key for heart health.
The Ascending Aorta and Coronary Arteries
The ascending aorta is connected to the coronary arteries. These arteries start from the aortic root and go to the heart muscle. This connection is vital for the heart to work right, as it brings oxygen and nutrients.
Diagrams show how close the ascending aorta is to the right and left coronary arteries. This shows how these parts work together.
Proximity to the Pulmonary Trunk
The ascending aorta is near the pulmonary trunk. The pulmonary trunk carries blood from the heart to the lungs. This close connection shows the heart’s complex structure.
The Pericardium and the Ascending Aorta
The ascending aorta is covered by the pericardium. The pericardium protects the heart and keeps it in place. The bond between the pericardium and the ascending aorta is key for heart health.
In summary, the ascending aorta is linked to many heart parts, like the coronary arteries, pulmonary trunk, and pericardium. Knowing these connections is essential for treating heart issues. It shows how important the ascending aorta is for heart health.
The Ascending Arch of Aorta: Transition to the Aortic Arch
The ascending aorta leads to the aortic arch, a key point in blood flow. This change is not just a simple move; it’s a vital spot where the aorta starts to send blood to the upper body.
Anatomical Boundaries
The transition from the ascending aorta to the aortic arch is marked by certain landmarks. The ascending aorta ends at the sternal angle, turning into the aortic arch. This area is important because it starts the aortic arch, which then branches into several key arteries.
The aortic arch curves and gives off major arteries. These arteries supply the head and upper limbs. The brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid artery, and left subclavian artery are among them. Knowing these boundaries is key for diagnosing and treating heart issues.
Functional Significance
The transition from the ascending aorta to the aortic arch is vital for blood distribution. The aortic arch is a key structure, ensuring the brain and upper limbs get enough blood. Any problems here can cause serious health issues, like reduced blood flow to important areas.
We understand the importance of this vascular change for heart health. The aortic arch is essential in the blood flow path, and its correct function is vital for our well-being.
Imaging and Visualization of the Ascending Aorta
Seeing the ascending aorta is key for diagnosing heart issues. We use different imaging methods to check its shape and how it works. This is important for taking care of our patients.
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
Many imaging methods help us see the ascending aorta. Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are top choices. They give us detailed views of the aorta’s size and shape, helping us spot heart diseases.
CT scans give us clear pictures of the aorta, letting us measure its size and look for problems. MRI, with its soft tissue contrast, lets us see the aorta’s wall and nearby areas in detail.
Understanding Ascending Aorta Labeled Images
It’s important to understand labeled images of the ascending aorta. On these images, the aorta is seen above the left ventricle and before the aortic arch. Knowing these landmarks helps us spot any issues or differences.
Labeled images help doctors and radiologists find the ascending aorta and its connection to other heart parts. This is vital for planning surgeries and tracking heart conditions.
Measuring AO Diameter in Clinical Practice
Measuring the ascending aorta’s diameter is a big part of heart checks. Getting the right measurements is key for diagnosing aortic problems like dilatation or aneurysm. We use CT and MRI to get these precise measurements.
The diameter is measured at certain spots, like the sinotubular junction or the mid-ascending aorta. These measurements are important for tracking disease and planning treatments.
Medical Terminology and International Nomenclature
Terms for the ascending aorta differ in many languages and medical traditions. This issue is common in medical talk worldwide. Knowing these differences is key for correct diagnosis, treatment, and research across languages and places.
The ascending aorta has different names in various medical terms. For example, in Latin, it’s called “aorta ascendens,” a term used in many languages. This Latin term is important because it’s the base for many international medical terms.
Aorta Ascendens: Latin Terminology
The Latin term “aorta ascendens” is common in medical books and classes. It’s the standard term in many anatomy and medical texts. Latin helps healthcare workers talk clearly across languages.
Aorta Ascendente: Spanish Terminology
In Spanish-speaking areas, the ascending aorta is called “aorta ascendente.” This name is similar to the Latin “aorta ascendens.” This similarity makes it easier to translate and understand medical info.
Other Regional Variations in Terminology
Other languages also have their names for the ascending aorta. For instance, in French, it’s “aorte ascendante,” and in German, “aufsteigende Aorta.” These differences show how important it is to know local terms when talking about health or working together globally.
We need to know about these differences for better global health talk. By understanding and using different terms, we can help patients, do better research, and work better together worldwide.
Conclusion: The Critical Role of the Ascending Aorta in Cardiovascular Health
The ascending aorta is key in moving oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body. It’s a vital part of the heart system. Problems here can cause serious heart issues, like aneurysms and dissections.
Knowing about the ascending aorta is important for good heart care. We’ve looked at its structure, function, and how it affects heart health. This shows its big role in keeping our hearts working right.
The ascending aorta is closely linked to other heart parts, like the left ventricle and coronary arteries. This makes it even more important for blood flow. Recognizing its role helps doctors diagnose and treat heart problems better. This leads to better health for patients.
In short, the ascending aorta is a critical part of heart care. Understanding its role helps us give top-notch medical care. This is key for patients from around the world who need advanced treatments.
What is the ascending aorta?
The ascending aorta is the first part of the aorta. It starts from the left ventricle of the heart. It’s key in sending oxygen-rich blood to the body.
Where is the ascending aorta located?
It’s found at the heart’s base. It begins right after the aortic valve. You can see it above the left ventricle and before the aortic arch on images.
What are the normal dimensions of the ascending aorta?
It’s usually 5 cm long. In healthy adults, it’s about 3 to 4 cm wide. Knowing these sizes helps spot problems and diagnose heart issues.
What is the function of the ascending aorta in blood flow and circulation?
It carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body. Its work is linked to how well the heart pumps blood.
How is the ascending aorta related to other cardiac structures?
It’s connected to the coronary arteries, which start from the aortic root. It’s also near the pulmonary trunk and surrounded by the pericardium, a sac around the heart.
What imaging modalities are used to visualize the ascending aorta?
CT and MRI scans show detailed images of the aorta. Knowing how to read these images helps doctors diagnose and track heart conditions.
What is the significance of the transition from the ascending aorta to the aortic arch?
The aorta ends at the aortic arch. This arch has branches that supply the head and arms. Knowing this helps doctors diagnose and treat heart issues.
What are some regional variations in terminology for the ascending aorta?
It’s called “aorta ascendens” in Latin and “aorta ascendente” in Spanish. Knowing these names helps doctors talk clearly and make accurate diagnoses.
References
- Kenhub (Ascending Aorta) : https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/ascending-aorta
- Wikipedia (Ascending aorta) : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ascending_aorta
- Radiopaedia (Ascending aorta) : https://radiopaedia.org/articles/ascending-aorta?lang=us
- UF Health (Aorta Anatomy) : https://ufhealth.org/conditions-and-treatments/aorta-anatomy
- University of Minnesota Visible Heart Lab (Ascending Aorta) : https://www.vhlab.umn.edu/atlas/aorta/ascending-aorta/index.shtml




































