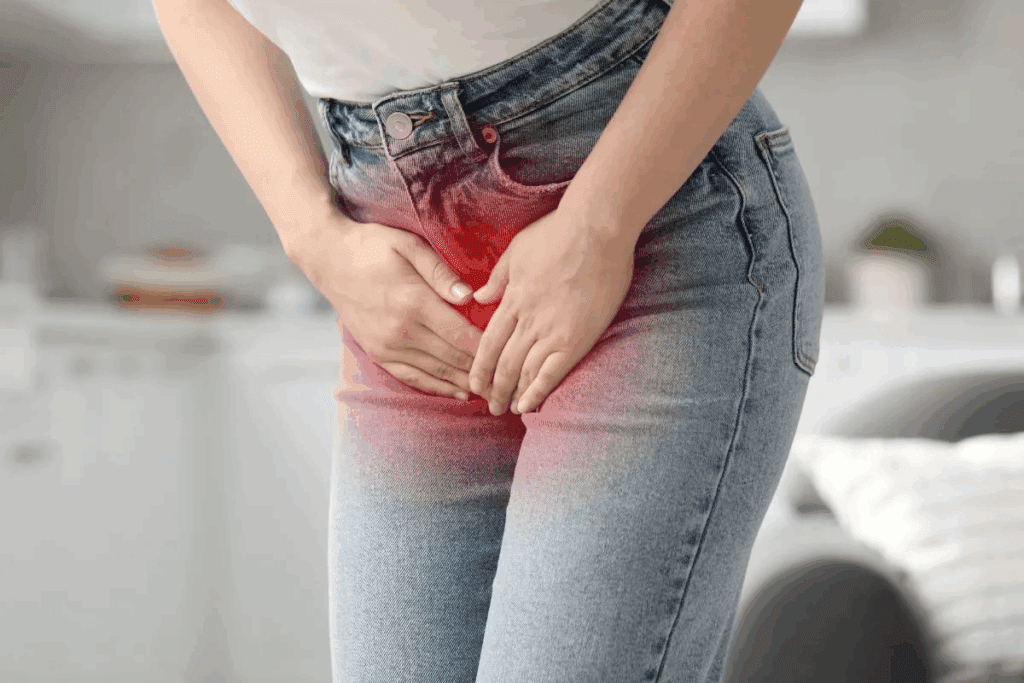
Discovering blood in your urine can be alarming. But knowing what causes it is the first step to getting better. Hematuria, or blood in urine, is a common issue. It makes up over 20 percent of all urological visits would a uti cause blood in urine.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a top reason for hematuria. The Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) says UTIs are more common in women. This is because a woman’s urethra is shorter. This makes it easier for bacteria to get into the bladder or kidney.
At Liv Hospital, we take a detailed look at hematuria. We make sure our patients get the right diagnosis and treatment. Knowing how UTIs and hematuria are linked is key to good care.
Key Takeaways
- UTIs are a common cause of hematuria, mostly in women.
- Hematuria can signal various conditions, from harmless to serious.
- Getting a professional medical check-up is vital for the right diagnosis.
- Liv Hospital is dedicated to innovative, patient-focused healthcare.
- Thorough investigation is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Blood in Urine (Hematuria)
Blood in urine, known as hematuria, is a sign that needs attention. It’s not a disease but a symptom of possible health issues. These issues must be checked by a doctor.
What is Hematuria?
Hematuria means there’s blood in your urine. It can show up in different amounts. Many people experience it at some point in their lives.
Prevalence and Statistics
About one in five people see a urologist for hematuria. The number of cases changes with age, gender, and other factors. Knowing these stats helps figure out if you should see a doctor.
Types of Hematuria: Visible vs. Microscopic
Hematuria comes in two types: gross hematuria and microscopic hematuria. Gross hematuria means you can see the blood, making your urine look pink, red, or cola-like. Microscopic hematuria is when you can’t see the blood but it shows up under a microscope.
It’s important to know the difference. Gross hematuria is more obvious and needs quick medical help. But microscopic hematuria also points to serious health issues that need to be checked.
The Urinary System: Structure and Function

The urinary system is a complex network of organs. It works together to eliminate waste and maintain health. It filters waste and excess fluids from the blood, regulates electrolyte levels, and keeps acid-base balance.
Anatomy of the Urinary Tract
The urinary tract includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Each part has a vital role in urine production and elimination. The kidneys filter waste and excess fluids from the blood, producing urine. The ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder through peristalsis. The bladder stores urine until it’s eliminated. The urethra is the tube through which urine leaves the body.
How Urine is Produced and Eliminated
Urine production starts in the kidneys. Waste products and excess substances are filtered from the blood. This involves filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
Once produced, urine flows through the ureters into the bladder. It’s stored until the body is ready to eliminate it. The process of urination involves the bladder muscle and the urethral sphincter working together.
The Body’s Natural Defense Mechanisms
The urinary system has natural defense mechanisms. These include the flushing effect of urine flow. It helps remove bacteria and other pathogens from the urinary tract.
The lining of the urinary tract also produces substances. These substances inhibit bacterial growth and adherence. Understanding these defense mechanisms is key to preventing urinary tract infections (UTIs).
What is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection in the urinary system. This system includes the kidneys, bladder, and connecting tubes. UTIs are usually caused by bacteria and can affect different parts of the urinary tract.
Common Causes of UTIs
UTIs happen when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra. The most common bacteria is Escherichia coli (E. coli). Other factors that can lead to UTIs include:
- Bacterial entry through the urethra
- Poor hygiene
- Sexual activity
- Use of certain types of birth control
Knowing these causes helps prevent UTIs.
Risk Factors for Developing UTIs
Some people are more likely to get UTIs due to certain risk factors. These include:
| Risk Factor | Description |
| Gender | Women are more likely to develop UTIs due to their shorter urethra. |
| Age | Older adults are more susceptible to UTIs. |
| Medical Conditions | Conditions like diabetes and kidney stones can increase the risk. |
Types of UTIs: Lower vs. Upper Tract Infections
UTIs can be classified into lower and upper tract infections based on the location of the infection.
- Lower Tract Infections: These occur in the bladder and urethra. Cystitis is a common type of lower UTI.
- Upper Tract Infections: These occur in the kidneys and are known as pyelonephritis. Upper UTIs are more serious and can lead to complications if not treated promptly.
Understanding the differences between lower and upper UTIs is essential for appropriate treatment and management.
Would a UTI Cause Blood in Urine?
When bacteria infect the urinary tract, they cause an inflammatory response. This can lead to hematuria, which is blood in the urine. It’s a common sign of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs).
The Inflammatory Response in UTIs
The body’s defense against infection is the inflammatory response. In UTIs, this response is triggered by bacteria in the urinary tract. The inflammation can cause red blood cells to leak into the urine, leading to hematuria. Doctors say, “The inflammation can damage blood vessels in the urinary tract, making them more likely to bleed.”
The body fights infection by activating immune cells and releasing chemicals. These chemicals make blood vessels more open. This allows red blood cells to leak into the urine.
How Bacteria Damage Blood Vessels
Bacteria from UTIs stick to the urinary tract lining and start an infection. As they grow, they damage the cells lining the urinary tract. This damage can disrupt blood vessels, causing bleeding. The bacteria also release toxins that make the damage worse.
In some cases, the infection can lead to more severe problems. For example, pyelonephritis, an infection of the kidney, can also cause hematuria.
Frequency of Hematuria in UTI Cases
Hematuria is a common symptom in UTI patients. Studies show that many people with UTIs will have some blood in their urine.
“Hematuria is present in approximately 40-60% of patients with UTIs, though the severity varies.”
The amount and severity of hematuria can depend on several factors. These include the type of bacteria and the person’s health.
It’s important to understand the link between UTIs and hematuria for proper treatment. We’ll look at how to diagnose and treat it in the next sections.
White Blood Cells and Blood in Urine
Seeing white blood cells and blood in your urine is a warning sign. White blood cells are part of your immune system. They show up in urine when there’s an infection or inflammation.
The Relationship Between White Blood Cells and UTIs
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) cause your body to send white blood cells to fight off bacteria. This is known as pyuria. It’s a sign that your body is fighting an infection.
Key points about white blood cells and UTIs:
- White blood cells are a sign of the body’s response to infection.
- Pyuria is a common indicator of UTI.
- The presence of white blood cells can vary depending on the severity of the infection.
Blood vs. Pyuria: Understanding the Difference
Hematuria (blood in urine) and pyuria (white blood cells in urine) are different. Hematuria can be caused by many things, like infections or stones. Pyuria is more linked to infections and inflammation.
It’s important to tell the difference between hematuria and pyuria to find the cause.
When You Have Blood in Urine but No Infection
Sometimes, people have blood in their urine without a UTI. This could be due to kidney stones, bladder stones, or even cancer. A doctor needs to check to find out why.
Having blood in urine without an infection means you need more tests. These include:
- Imaging studies to check for structural problems.
- Urine tests to look for hidden infections.
- Cystoscopy to examine the bladder and urethra.
Low White Blood Cell Count with Hematuria
A low white blood cell count (leukopenia) with hematuria is a serious sign. It might mean your immune system is weak or there’s another health problem. Doctors will do a full check-up to find out why.
Knowing about white blood cells and blood in urine helps doctors diagnose and treat you right. If you have symptoms like hematuria or pyuria, see a doctor for help.
Diagnosing the Cause of Blood in Urine
Figuring out why there’s blood in your urine needs a detailed medical check-up. Doctors look at many possible reasons, from simple infections to serious diseases like cancer.
Urine Tests and Cultures
The first step is usually urine tests and cultures. These tests find infections, check for abnormal cells, and spot other signs that show what’s causing the blood.
Urine cultures are key for finding UTIs. They show which bacteria are causing the infection. A study in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology found they’re very important for deciding how to treat UTIs.
Understanding Negative Urine Cultures with Blood Present
Some people with blood in their urine might have negative urine cultures. This means no bacteria were found, even though there’s blood. It’s a mystery that needs more looking into.
The American Urological Association says, “Even with negative urine cultures, blood in the urine doesn’t mean there’s no infection or other problems. More tests are usually needed.”
Imaging Studies and Further Testing
If tests don’t show what’s causing the blood, imaging studies might be suggested. Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI can spot problems like stones or tumors in the urinary tract.
A study in the Journal of Urology showed imaging is key for finding the cause of blood in urine. It helps spot stones and tumors.
The Diagnostic Process
Diagnosing hematuria involves many steps. Doctors use tests, look at your medical history, and do a physical exam. They use all this info to find out why there’s blood in your urine.
A clinical guideline says, “A careful approach to checking for hematuria is vital. It helps find the real cause and treat it right.”
Other Common Causes of Blood in Urine
UTIs are a common reason for blood in urine. But, other conditions can also cause it. Knowing these can help with diagnosis and treatment.
Kidney and Bladder Stones
Kidney and bladder stones are hard deposits that can cause pain and bleeding. They can scratch the lining of the urinary tract, leading to blood. The pain is often severe, felt in the flank or lower abdomen.
“The pain from kidney stones is very severe,” say doctors. Stones moving can cause micro-tears, leading to bleeding.
Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
BPH, or enlarged prostate, makes the prostate gland bigger. This can block urine flow. Straining to urinate can cause blood vessels to rupture, leading to blood in the urine.
An enlarged prostate also raises the risk of UTIs. Symptoms include frequent urination, weak flow, and feeling like the bladder isn’t empty.
Kidney Disease
Kidney disease affects the kidneys’ function and structure. Some types, like glomerulonephritis, can cause blood in the urine. Kidney disease can damage the glomeruli, leading to blood in the urine.
Medications and Other Factors
Some medications can cause blood in urine as a side effect. Anticoagulants, for example, can increase bleeding risk. Some chemotherapy drugs, like cyclophosphamide, can irritate the bladder and cause bleeding.
Other factors, like trauma, exercise, and diet, can also lead to blood in urine. It’s important to see a healthcare provider to find the cause.
When Blood in Urine May Indicate Cancer
Blood in urine can be scary and might mean cancer. This symptom, called hematuria, needs a detailed check to find the cause. Cancer is a big worry that should be looked at right away.
Types of Cancer Associated with Hematuria
Many cancers can cause blood in urine. Bladder and kidney cancers are the most common. Bladder cancer often makes urine look bloody. Kidney cancer might not always show blood in the urine.
Ureteral and urethral cancers can also cause blood in urine, but they are rarer. Knowing the exact cancer is key for the right treatment.
Bladder Cancer: Risk Factors and Prevalence
Bladder cancer is a big reason for blood in urine. Smoking, chemicals, and bladder infections increase risk. Men and older people are more likely to get it.
Bladder cancer rates vary worldwide. Places with more smoking and chemical exposure have higher rates. Finding it early can help a lot.
Kidney and Other Urological Cancers
Kidney cancer, or renal cell carcinoma, is another cause of blood in urine. Smoking, being overweight, and some genes raise risk. Not everyone with kidney cancer will see blood in their urine.
Ureteral and urethral cancers are rarer but can also cause blood in urine. They share symptoms with other cancers and need careful testing.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Attention
Hematuria might mean cancer, but other signs are urgent. Look out for ongoing or coming back blood in urine, pain while peeing, needing to pee a lot, and losing weight without trying.
If you see these signs, get medical help fast. Early action can make a big difference for cancer patients.
Treatment and Prevention of UTIs and Hematuria
UTI treatment and prevention are key to reducing hematuria. Managing UTIs well is important. It helps ease symptoms and prevents complications.
Antibiotic Therapy for UTIs
Antibiotic therapy is the main treatment for UTIs. It targets the bacteria causing the infection. The right antibiotic depends on the bacteria and the infection’s severity.
It’s vital to finish all antibiotics as directed. This ensures the infection is fully cleared and prevents it from coming back.
Managing UTI Symptoms and Pain
Managing UTI symptoms is also important for comfort. This includes pain relief medications and staying hydrated. Hydration helps flush out bacteria.
Some people find relief with heat therapy. Applying a warm heating pad to the lower abdomen can help.
Preventive Strategies to Reduce UTI Risk
Preventing UTIs is essential to lower hematuria risk. Preventive strategies include drinking lots of water and practicing good hygiene. Also, urinating after sex is important.
- Drinking cranberry juice may help prevent UTIs in some individuals.
- Avoiding irritating feminine products can also reduce UTI risk.
- For recurrent UTIs, low-dose antibiotic prophylaxis may be recommended.
Follow-up Care and Monitoring
After a UTI, follow-up care is critical. It ensures the infection is fully treated and watches for complications like persistent hematuria.
Regular visits to a healthcare provider are important. They help in early detection and management of urinary tract issues.
Conclusion: When to Seek Medical Attention
If you see blood in your urine, you should get medical help right away. Hematuria can mean you have a urinary tract infection (UTI) or another serious issue. These need quick medical checks.
We’ve talked about UTIs and hematuria a lot. We covered their causes, signs, how doctors find them, and how to treat them. Knowing when to go to the doctor is key if you have these symptoms.
Seeing blood in your pee, or feeling pain when you pee, means you should see a doctor. A doctor will do tests to find out what’s wrong. Then, they’ll give you the right treatment.
Getting help early can stop problems and make you feel better. By going to the doctor when you need to, you get the care you need. This helps keep you healthy.
FAQ
Does blood in urine mean cancer?
Blood in urine, or hematuria, can hint at cancer but isn’t always a sign. It can stem from UTIs, kidney stones, or other issues. If you see blood in your urine, see a doctor for a check-up.
Can a bladder infection cause blood in urine?
Yes, bladder infections can lead to blood in urine. The infection can damage blood vessels in the urinary tract, causing hematuria.
What cancers cause blood in urine?
Cancers like bladder, kidney, and other urological cancers can cause blood in urine. If you notice blood, get a full check-up to find out why.
Does a UTI cause blood in urine?
UTIs can lead to blood in urine, but it’s not always the case. The severity of the infection and your health play a role.
Can you pee blood with a UTI?
Yes, UTIs can cause blood in urine. The infection can damage blood vessels in the urinary tract, leading to bleeding.
Would a UTI cause blood in urine?
UTIs can cause blood in urine, more so if severe or untreated. Quick medical help is key to avoid complications and ease symptoms.
Is blood in urine a sign of UTI?
Blood in urine might mean a UTI, but it’s not the only reason. Kidney stones or cancer can also cause it. A proper diagnosis is needed to find the cause.
What is the difference between hematuria and pyuria?
Hematuria is blood in urine, while pyuria is white blood cells in urine. Both can point to a UTI or other issues.
Can you have blood in urine but no infection?
Yes, you can have blood in urine without an infection. Kidney stones, cancer, or certain meds can also cause it.
What does it mean when you have blood in urine and low white blood cells?
Blood in urine and low white blood cells can mean many things. It could be a UTI, kidney disease, or cancer. A detailed check-up is needed to find the cause.
References
Government Health Resource. (2025). Does a UTI Cause Blood in Urine What. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/community/for-patients/common-illnesses/uti.html


































