Feeling pain in your lower back and calf area can really disrupt your life. It’s not just a simple ache. It’s often a complex issue that needs a detailed approach.
At Liv Hospital, we help many patients with back and calf pain. We’re dedicated to giving you the insights and care you need. Simple practices like certain yoga stretches can offer relief and help you get through long days.
In this article, we’ll look at seven main reasons for these pains. We’ll help you understand why your lower back and legs hurt. And we’ll show you how to find effective relief.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the causes of combined back and calf pain
- Exploring the role of certain yoga stretches in pain relief
- Discovering the multidisciplinary approach at Liv Hospital
- Learning about patient-focused solutions for health
- Finding effective relief from lower back and leg pain
Understanding the Connection Between Back Pain and Calf Pain
It’s important to know how back pain and calf pain are linked. This helps in finding the right treatment. We need to look at the anatomy of the lower back and legs. Also, how pain signals move through our bodies.
Anatomy of the Lower Back and Legs
The lower back, or lumbar region, has five vertebrae. These vertebrae support a lot of our body’s weight. The lumbar spine includes vertebrae, discs, nerves, and muscles.
The vertebrae are separated by intervertebral discs. These discs help absorb shock and keep things flexible. Nerves from the lumbar spine go down to the legs. They control movement and feeling.
The calf muscles are at the back of the lower leg. They help us move and are connected to bones with tendons. The calf muscles work with other muscles to keep us stable and moving. Knowing how these areas work helps us find the cause of pain and treat it.
How Pain Signals Travel Through the Body
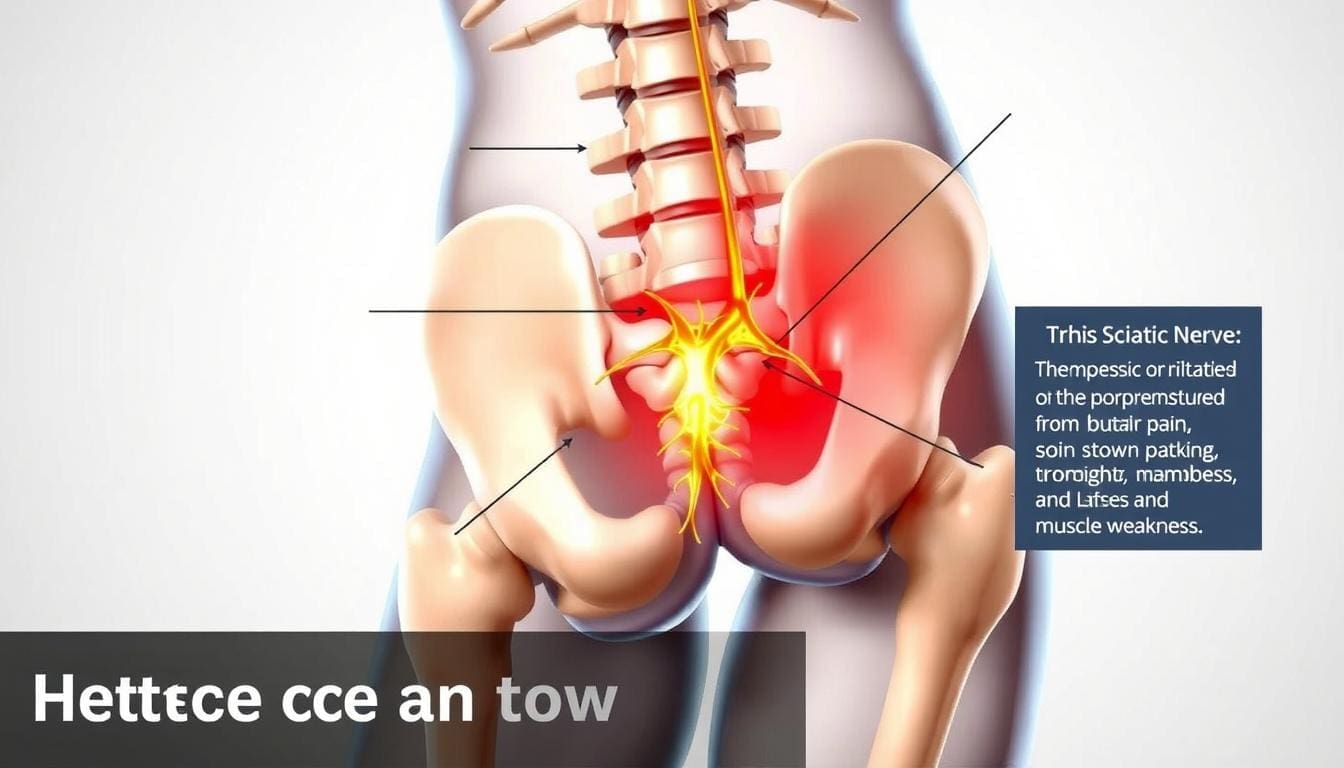
Pain signals travel through a network of nerves. When a nerve gets irritated or damaged, it sends a pain signal to the brain. The sciatic nerve is a common path for these signals. It runs from the lower back to the legs.
When this nerve gets irritated, it can cause pain that spreads from the back to the calf. This is called sciatica. Knowing how pain signals move helps us figure out why we have back and calf pain.
Treating back pain and calf pain means finding and fixing the cause. This might include calf strain treatment, physical therapy, or medical help. By understanding the connection between back and calf pain, doctors can create better treatment plans for each patient.
Sciatica: A Primary Cause of Back Pain and Calf Pain
Sciatica is a pain that starts in the lower back and goes down to the legs. It’s a big reason for back and calf pain. We’ll look into what sciatica is, its symptoms, and how to treat it.
Understanding Sciatica
Sciatica isn’t a disease itself but a sign of something else. It happens when the sciatic nerve gets irritated or squished. This can be due to many things, like herniated discs or muscle tightness.
Some yoga poses, like the pigeon pose, can help. They stretch the hip flexors and glutes, which are often tight with sciatica. Stretching these areas might ease some of the pain.
Identifying Symptoms of Sciatica
Sciatica symptoms can differ from person to person. Common signs include sharp pain from the back to the leg. Some might feel numbness, tingling, or weakness in their leg.
Knowing the symptoms is key to managing back and calf pain. Spotting sciatica signs early can lead to better care and lifestyle changes to reduce pain.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Sharp Pain | Radiates from lower back through buttocks and down one leg |
| Numbness/Tingling | Sensation of pins and needles in the affected leg |
| Weakness | Muscle weakness in the leg, potentially affecting mobility |
Treating Sciatica
Treating sciatica means fixing the root cause. For some, this means physical therapy. This includes exercises to strengthen the back and improve flexibility.
In serious cases, doctors might use injections or surgery to ease nerve pressure. Other treatments like acupuncture or chiropractic care can also help some people.
Understanding sciatica is the first step to managing it. It’s important to talk to a healthcare professional to find the right treatment.
Lumbar Herniated Discs and Their Impact on Lower Extremities
Lower back pain and calf pain often come from lumbar herniated discs. This condition needs to be looked at closely. Herniated discs in the lower back can cause pain that spreads to the legs.
How Disc Herniation Occurs
Disc herniation happens when the soft center of the disc leaks out. This leak is through a tear in the outer layer. It can be caused by aging, wear and tear, or injury.
Key factors contributing to disc herniation include:
- Lifting heavy objects improperly
- Sudden, strenuous activities
- Genetic predisposition
- Degenerative disc disease
Recognizing Herniated Disc Symptoms
Symptoms of a herniated disc can vary. Common signs include:
- Pain in the lower back that radiates to the legs
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the legs or feet
- Weakness in the muscles of the legs
- Difficulty with bladder or bowel control in severe cases
It’s important to notice these symptoms early. This way, you can get the right medical care.
Managing Herniated Disc Pain
Managing herniated disc pain involves medical treatments and self-care. Remedies for back and calf pain include:
- Physical therapy to strengthen the back muscles and improve flexibility
- Pain relief medications to manage discomfort
- Epidural steroid injections to reduce inflammation
- Surgery in severe cases where other treatments have failed
Preventing back and calf pain means living a healthy lifestyle. This includes regular exercise, proper lifting, and a balanced diet. Stretching exercises, like the low lunge, can help stretch the hips and quadriceps. This provides deep relief.
Spinal Stenosis: When Narrowing Causes Widespread Pain
Spinal stenosis is when the spinal canal gets narrower. This can cause pain in the back and legs. We’ll look at what causes it, its symptoms, how it gets worse, and how to treat it.
Types of Spinal Stenosis
There are different types of spinal stenosis, based on where and why the narrowing happens. The most common types are:
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: This is in the lower back and is the most common.
- Cervical Spinal Stenosis: This affects the neck.
- Central Spinal Stenosis: This is when the central canal of the spine narrows.
- Foraminal Spinal Stenosis: This happens when the nerve root canals narrow.
Knowing the type of spinal stenosis you have is key to finding the right treatment.
Symptoms and Progression
The symptoms of spinal stenosis vary based on where and how much it narrows. Common symptoms include:
- Pain, numbness, or tingling in the back, legs, or buttocks.
- Weakness in the legs or feet.
- Difficulty walking or standing for long periods.
As spinal stenosis gets worse, these symptoms can get worse too. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing symptoms.
Treatment Approaches for Stenosis
Treating spinal stenosis involves both non-surgical and surgical methods. Non-surgical methods include:
- Physical therapy to strengthen the core and improve flexibility.
- Pain management through medication.
- Lifestyle changes, like maintaining a healthy weight and improving posture.
If non-surgical methods don’t work, surgery might be needed to relieve nerve pressure. Strengthening core stabilizers can help relieve back and calf muscle pain. It’s important for both non-surgical and post-surgical care.
Understanding spinal stenosis and its treatments can help find relief from pain. It’s important to talk to a healthcare professional to find the best treatment for you.
Degenerative Disc Disease and Its Effects
As we get older, our spines wear out, leading to degenerative disc disease. This condition affects the spinal discs, which cushion the vertebrae. Over time, these discs can shrink, lose flexibility, and even crack or bulge, causing pain.
The Aging Spine and Disc Degeneration
The spine has vertebrae and discs between them. As we age, these discs can degenerate. This can be sped up by genetics, lifestyle, and past injuries.
Several factors contribute to disc degeneration, including:
- Age-related wear and tear
- Genetic predisposition
- Smoking and other lifestyle factors
- Previous spinal injuries or trauma
Identifying Degenerative Disc Disease
Symptoms of degenerative disc disease vary. Some people may not feel pain, while others have chronic back or calf pain. Common signs include:
- Persistent back pain that worsens over time
- Pain or numbness in the legs or calves
- Reduced flexibility or stiffness in the back
Diagnosing this disease involves medical history, physical exam, and imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans.
Managing Long-Term Disc Degeneration
Managing degenerative disc disease needs a multi-faceted approach. Some cases may not need aggressive treatment, while others might need surgery.
Conservative management strategies include:
- Physical therapy to improve flexibility and strength
- Pain management through medication or injections
- Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight and improving posture
Building strong feet is also key for stability and biomechanics. This can help lessen the effects of degenerative disc disease. With a focus on overall care and management, people can reduce symptoms and improve their life quality.
Muscle Strains and Cramps: Overexertion and Deficiencies
When we push too hard or don’t get enough minerals, our back and calf muscles can hurt. Muscle strains happen when fibers get stretched or torn. Cramps are when muscles contract without us wanting them to, and they can be very painful.
Causes of Muscle Strains in Back and Calves
Muscle strains in the back and calves can come from sudden or severe movements, overuse, or bad posture. Heavy lifting, bending, or quick changes in direction can cause strains. Not warming up or cooling down properly also raises the risk.
Some yoga poses can help by stretching hip muscles, which might lower strain risk. For example, poses that stretch the hamstrings and hip flexors can make muscles more flexible and strong.
Dehydration and Mineral Deficiencies
Not drinking enough water and not getting enough minerals can make muscles cramp and strain. When we’re dehydrated, our muscles get irritable and cramp more. Not having enough potassium, magnesium, and calcium can also cause muscle cramps.
Drinking enough water and eating foods rich in minerals can help avoid muscle cramps. Drinking water and eating bananas (for potassium), nuts (for magnesium), and dairy (for calcium) are good practices.
Recovery and Prevention Strategies
To get better from muscle strains and cramps, rest, stretch, and strengthen are key. Gentle stretching can ease tension, and strengthening can make muscles stronger.
Preventing it is better than treating it. Regular exercise, staying hydrated, and a balanced diet are important. Doing exercises that improve flexibility and strength, like yoga or Pilates, can help a lot.
| Prevention Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Stretching | Incorporating stretching exercises into your daily routine | Improves flexibility, reduces muscle tension |
| Strengthening Exercises | Engaging in exercises that strengthen back and calf muscles | Enhances muscle resilience, supports posture |
| Adequate Hydration | Drinking sufficient water throughout the day | Reduces muscle irritability, prevents cramps |
| Balanced Diet | Consuming a diet rich in essential minerals | Prevents mineral deficiencies, supports muscle health |
Understanding why muscle strains and cramps happen and using good recovery and prevention methods can help. Adding exercises for back pain relief and calf strain treatment to your routine can be very helpful.
Vascular Issues: When Blood Flow Is the Problem
Vascular problems can cause pain in the lower back and calves. It’s important to know why. Issues like Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) can really hurt your quality of life. They can cause pain and might lead to serious problems if not treated.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep Vein Thrombosis is when a blood clot forms in the deep veins, usually in the legs. It can cause pain, swelling, and warmth. DVT is serious because the clot can travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
Key symptoms of DVT include:
- Swelling in the affected leg
- Pain or tenderness in the leg
- Warmth or redness of the skin
- Visible veins
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Peripheral Artery Disease happens when the arteries in the legs get narrowed or clogged. This leads to pain when walking or exercising. PAD is a sign of a bigger problem, like heart disease.
Common symptoms of PAD include:
- Leg pain when walking (claudication)
- Coldness or numbness in the legs
- Weak or absent pulses in the legs
- Sores or wounds that won’t heal
Urgent Warning Signs
Both DVT and PAD have symptoms that need quick medical help. It’s important to know these signs to avoid serious problems.
Warning signs that require immediate medical attention:
- Severe pain or swelling in one leg
- Chest pain or difficulty breathing (possible pulmonary embolism)
- Severe coldness or paleness of the leg
- Sudden weakness or difficulty walking
Understanding and treating vascular problems can help manage back and calf pain. Recognizing DVT and PAD symptoms early can prevent serious issues. This can greatly improve your life quality.
Inflammatory Conditions Affecting the Back and Legs
It’s important to know about inflammatory conditions to tackle back and leg pain. These conditions can cause a lot of discomfort and affect how well you live. We’ll look into these issues and talk about how to manage inflammation.
Arthritis and Its Many Forms
Arthritis is a term for many inflammatory joint conditions. The most common types affecting the back and legs are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. Each type needs its own treatment plan.
Osteoarthritis is a joint disease that can cause pain and stiffness in the spine and legs. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that can make joints inflamed, affecting the back and legs. Ankylosing spondylitis mainly affects the spine, causing inflammation and potentially leading to vertebrae fusion.
Inflammatory Treatment Approaches
Dealing with inflammatory conditions requires a variety of strategies. Treatments often include medicines, lifestyle changes, and physical therapy. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often used to lessen inflammation and pain.
Changing your lifestyle can also help. This includes staying at a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and eating an anti-inflammatory diet. Physical therapy is also helpful, as it can make joints more flexible and stronger.
- Medications: NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and biologic agents
- Lifestyle modifications: diet, exercise, weight management
- Physical therapy: exercises to improve flexibility and strength
By understanding different types of arthritis and using a wide range of treatments, people can manage their symptoms better. This helps improve their quality of life. It’s essential to manage these conditions well to reduce pain and prevent damage.
Effective Treatments for Back Pain and Calf Pain
Managing back pain and calf pain needs a mix of medical treatments, physical therapy, and self-care. Finding the right treatment can be tough. But, by trying these options, you can find the best relief for your pain.
Medical Interventions
Medical treatments are key for back pain and calf pain, mainly if it’s due to a medical issue. Always talk to a healthcare expert to find the best treatment.
Some common medical treatments include:
- Medications: Pain relievers, muscle relaxants, and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage pain and discomfort.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical options may be considered to address underlying issues such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
| Treatment | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Medications | Pain relievers and muscle relaxants | Reduces pain and discomfort |
| Injections | Corticosteroid injections | Decreases inflammation |
| Surgery | Surgical procedures for severe conditions | Addresses underlying issues |
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy is a great way to manage back pain and calf pain. It’s important to have a personalized exercise plan that fits your needs.
Key parts of physical therapy include:
- Core Strengthening: Exercises that strengthen the core muscles can help alleviate back pain.
- Stretching: Gentle stretching can improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques such as massage and mobilization can help relieve pain and improve mobility.
Home Remedies and Self-Care
Home remedies and self-care are also important for managing back pain and calf pain. Adding these to your daily routine can help a lot.
Some effective home remedies include:
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Proper Posture: Maintaining good posture can reduce strain on your back and legs.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help strengthen muscles and improve overall health.
By combining these methods, you can create a complete plan to manage your back pain and calf pain effectively.
When to See a Doctor for Back Pain and Calf Pain
Knowing when to seek medical help for back pain and calf pain is key. Many cases can be managed at home. But, some symptoms need quick medical attention to avoid serious issues.
Red Flag Symptoms
There are specific symptoms that mean you should see a doctor right away. These include:
- Severe pain that doesn’t get better with rest or medicine
- Numbness or tingling in the legs or groin area
- Weakness in the legs or feet that makes walking or balance hard
- Loss of bladder or bowel control, which is a medical emergency
- Fever with back pain, which could mean an infection
If you have any of these symptoms, get medical help fast. Quick action can greatly improve your outcome and prevent lasting harm.
What to Expect at Your Appointment
At your doctor’s visit for back pain and calf pain, you’ll get a thorough check-up. This usually includes:
- Talking about your medical history to find any underlying issues
- A physical exam to check pain, strength, and flexibility
- Diagnostic tests like X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to see the spine and soft tissues
- Talking about your symptoms and lifestyle to find out what might be causing them
Your doctor will then suggest a treatment plan just for you. This might include physical therapy, medicine, lifestyle changes, or sometimes surgery.
It’s also key to do stability training and strengthen your feet. These steps can help prevent future back pain and calf pain. They improve your posture, balance, and muscle strength.
Conclusion
Understanding why we get back and calf pain is key to managing it. This article has looked at several reasons, like sciatica and herniated discs. These can cause a lot of discomfort.
Knowing the cause helps us find the right treatment and make lifestyle changes. Adding exercises for back pain to our daily routine can really help. Simple stretches and exercises can lessen pain and stop it from coming back.
We urge everyone to take charge of their back and calf pain. Combining doctor visits with self-care can lead to lasting relief. Managing pain well needs a mix of treatments, and we’re here to help guide you.
What are the common causes of back pain and calf pain?
Back pain and calf pain can come from sciatica, herniated discs, and spinal stenosis. Other causes include degenerative disc disease, muscle strains, vascular issues, and inflammatory conditions.
How does sciatica cause back pain and calf pain?
Sciatica happens when the sciatic nerve gets irritated or compressed. This causes pain that spreads from the lower spine to the buttocks and legs.
What are the symptoms of a lumbar herniated disc?
Symptoms include back pain, calf pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the legs. This depends on where and how severe the herniation is.
How is spinal stenosis diagnosed and treated?
Doctors use MRI or CT scans to diagnose spinal stenosis. Treatment can be conservative, like physical therapy and pain management. In severe cases, surgery is needed.
Can degenerative disc disease be managed without surgery?
Yes, managing degenerative disc disease often involves physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and pain management. Sometimes, minimally invasive procedures are used.
How can muscle strains and cramps be prevented?
To prevent muscle strains and cramps, stay hydrated, get enough minerals, warm up before exercise, and avoid overexertion.
What are the warning signs of vascular issues like DVT or PAD?
Warning signs include sudden swelling, pain, or discoloration in the legs. For PAD, leg pain during walking that goes away with rest is a sign.
How are inflammatory conditions like arthritis treated?
Treatment for arthritis includes medications to reduce inflammation, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. In some cases, injections or surgery are used to manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
What are the effective treatments for back pain and calf pain?
Treatments include pain management medications, physical therapy, and home remedies like heat or cold therapy. These help strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
When should I seek medical attention for back pain and calf pain?
Seek medical attention for sudden severe pain, numbness or weakness in the legs, loss of bladder or bowel control, or pain with fever or trauma.
What can I expect during a doctor’s appointment for back pain and calf pain?
Expect a detailed medical history, physical exam, and possibly diagnostic tests like X-rays or MRI. You’ll also discuss treatment options tailored to your condition.
How can I relieve back and calf muscle pain at home?
Rest, apply heat or cold packs, do gentle stretching, and use over-the-counter pain relievers. Maintaining a healthy weight also helps reduce strain.
Are there exercises that can help alleviate back pain and calf pain?
Yes, exercises like stretching, strengthening the core and leg muscles, and low-impact activities like walking or swimming can help alleviate pain and improve function.
References
Healthline: Lower Back and Leg Pain: Causes, Treatments, and More






















