When pain or numbness spreads from your neck to your arms, knowing about the C6 and C7 spine is key. The cervical spine, with seven vertebrae, is vital for neck movement and stability. The C6/C7 spine segment is very important, as it supports the base of the cervical spine.
At Liv Hospital, we understand how important this area is for your health. The C7 vertebra, with its distinctive spinous process, is easy to spot. It helps us diagnose and treat problems in this area. By studying the anatomy, nerve paths, and symptoms of the C6 and C7 region, we offer detailed care for those with discomfort or numbness.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the C6 and C7 spine region is key for diagnosing and treating related conditions.
- The C6/C7 spine segment anchors the base of the cervical spine, supporting neck movement and stability.
- The C7 vertebra has a prominent spinous process, making it a key landmark.
- Numbness or pain radiating from the neck to the arms can be related to the C6 and C7 region.
- Comprehensive care involves understanding the anatomy, nerve pathways, and symptoms associated with this area.
The Critical Role of C6 and C7 in Cervical Spine Function
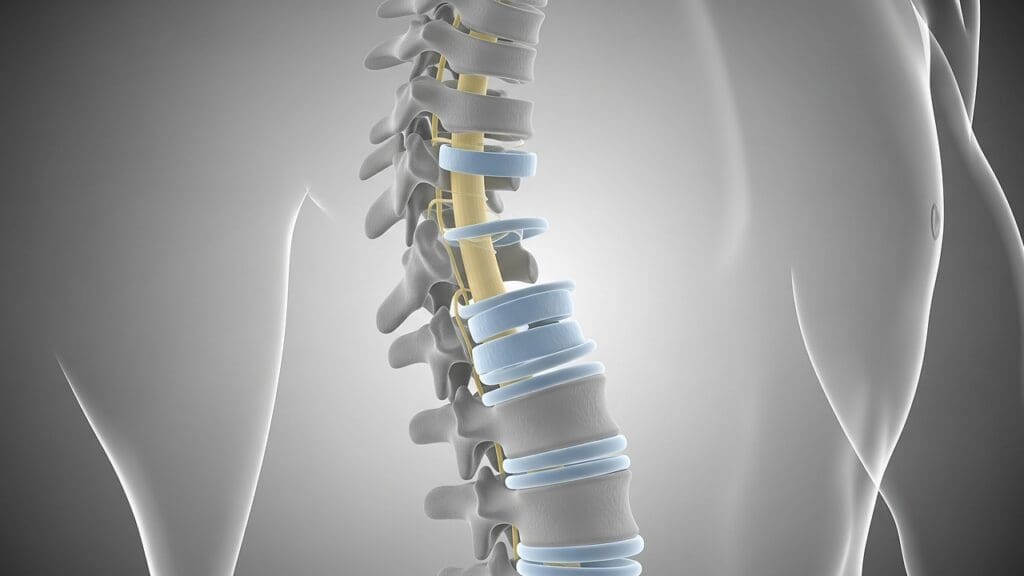
The C6 and C7 vertebrae are key to the cervical spine’s function. We’ll look at how they help the neck move and stay stable.
Transition Point: Where Middle Meets Lower Cervical Spine
The C6 and C7 vertebrae act as a transition point between the middle and lower cervical spine. This area is vital. It connects the more mobile upper and middle cervical spine with the more stable lower cervical spine.
The disc between C6 and C7 is key for this transition. It absorbs shock and allows smooth movement between the vertebrae. This disc, along with the surrounding facet joints, helps the segment flex, extend, and rotate.
Neck Movement and Stability Contributions
The C6 and C7 vertebrae play a big role in neck movement and stability. They help with flexion, extension, lateral bending, and rotation of the neck.
The unique anatomy of these vertebrae, including their articular surfaces and the intervertebral disc, makes this movement possible. The stability they provide is essential for keeping the spine aligned and preventing injuries.
Where is C6-C7 Located: Anatomical Landmarks and Identification
Knowing where C6-C7 is located is key for diagnosing and treating spinal issues. This part of the lower cervical spine is vital for neck movement and stability.
Palpating the Prominent C7 Spinous Process
The C7 vertebra, known as the “vertebra prominens,” has a unique spinous process. It’s easy to feel at the base of the neck. Here’s how to find it:
- Start by gently running your fingers down the back of the neck.
- At the base of the neck, you’ll feel a more noticeable bony projection.
- This is usually the spinous process of C7.
Relationship to Surrounding Structures
The C6-C7 segment is near many structures, like muscles, nerves, and blood vessels. Knowing these relationships helps in diagnosing and treating this area. The C6-C7 vertebrae are close to:
- The trachea and esophagus in front
- The scalene muscles on the sides
- Nerve roots that exit through the intervertebral foramina
Imaging Visualization of the C6-C7 Junction
Imaging studies are essential for seeing the C6-C7 junction. X-rays, MRI, and CT scans give detailed views of the vertebrae and soft tissues. These images help doctors:
- Check the alignment and health of the C6-C7 vertebrae
- Spot any degenerative changes or problems
- Plan the best treatment
By using both anatomy and imaging, we can accurately find and check the C6-C7 segment. This leads to better diagnosis and treatment of spinal conditions.
Anatomy of the C6 C7 Vertebrae: Structural Characteristics
The C6 and C7 vertebrae are key parts of the cervical spine. Each has special features that help them work well. We’ll look at what makes them different and how they keep the spine healthy.
Distinctive Features of C6 Vertebra
The C6 vertebra is the sixth one in the neck. It’s smaller than C7 and has a special shape. Its spinous process is split, which helps with neck movements.
C7 Vertebra: The Vertebra Prominens
The C7 vertebra is known for its long, noticeable spinous process. It’s longer than the others, making it easy to spot. Its bigger body helps it bear weight and stay stable.
Comparative Differences Between C6 and C7
C6 and C7 are different in the lower neck. C6 is smaller and has a split spinous process. C7 is bigger and has a single, long spinous process. These differences help them move and support the neck in different ways.
Knowing how C6 and C7 are built is key for fixing spine problems. Their special features are important for the spine’s health and function.
The Spinal C6 and C7 Intervertebral Disc: Function and Vulnerability
The intervertebral disc at C6-C7 is key for spinal flexibility and shock absorption. It’s made of a tough outer layer and a soft center. This setup helps the spine move smoothly and absorb shocks.
Composition and Biomechanical Properties
The disc at C6-C7 has unique biomechanical properties. The tough outer layer supports the spine, while the soft center absorbs shock. This is important for the spine’s normal function.
The disc’s composition helps it handle different stresses. But, the C6-C7 disc is more likely to get hurt. This is because it’s at the spot where the upper and lower spine meet.
Shock Absorption at the C6-C7 Motion Segment
The C6-C7 area is very mobile. The disc here is key for shock absorption. It helps protect the nerves during daily activities.
Age-Related Changes and Degenerative Processes
As we get older, the C6-C7 disc changes. It may shrink and not absorb shock as well. This can cause problems like disc herniation, where the soft center bulges out.
| Age Group | Common Disc Changes | Potential Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| 20-40 years | Mild degeneration, slight disc height loss | Occasional neck pain |
| 40-60 years | Moderate degeneration, noticeable disc height loss | Neck pain, occasional radiculopathy |
| 60+ years | Severe degeneration, significant disc height loss | Frequent neck pain, radiculopathy, possible myelopathy |
C6 and C7 Nerve Pathways: Motor and Sensory Distribution
Knowing how C6 and C7 nerves work is key to treating nerve problems. These nerves leave the spine at the C6-C7 level. They help control the arm and hand.
C6 Nerve Root: Innervation Patterns
The C6 nerve root helps muscles in the wrist and forearm. It controls the extensor carpi radialis brevis and others. This lets us extend the wrist and rotate the forearm.
C7 Nerve Pathway: Middle Finger and Triceps Function
The C7 nerve root helps with elbow bending and wrist bending. It mainly controls the triceps brachii for elbow bending. It also sends signals to the middle finger and parts of the index and ring fingers.
Muscle Groups Controlled by C6-C7 Nerves
The C6 and C7 nerves control muscles in the upper arm. Here’s a table showing the main muscle groups and their roles:
| Nerve Root | Muscle Group | Function |
|---|---|---|
| C6 | Extensor carpi radialis brevis | Wrist extension |
| C7 | Triceps brachii | Elbow extension |
| C6, C7 | Forearm muscles | Forearm supination and flexion |
For more details on spinal nerves, including C6 and C7, check out this resource on spinal nerve anatomy and physiology.
The C6-C7 Dermatome Map: Understanding Sensory Patterns
We look at the C6-C7 dermatome map to understand its sensory patterns. The C6 and C7 nerve roots control sensation in specific hand and arm areas.
C6 Dermatome: Thumb and Index Finger Distribution
The C6 dermatome usually covers the thumb and index finger. It’s in charge of feeling in these spots. Damage to the C6 nerve root can cause problems with feeling here.
C7 Dermatome: Middle Finger and Beyond
The C7 dermatome mainly affects the middle finger. It also reaches parts of the forearm and arm. Knowing where the C7 dermatome is helps doctors diagnose C7 nerve root issues.
Clinical Significance in Symptom Recognition
It’s key for doctors to know the sensory patterns of the C6-C7 dermatomes. This knowledge helps them diagnose and treat nerve problems at the C6-C7 level better.
To show the dermatome areas, here’s a table:
| Dermatome | Sensory Distribution |
|---|---|
| C6 | Thumb, Index Finger |
| C7 | Middle Finger, parts of forearm and arm |
Knowing the C6-C7 dermatome map is important for diagnosis and treatment. Doctors can give better care by understanding the specific sensory patterns of these dermatomes.
Common Symptoms of C6C7 Nerve Root Compression
Nerve root compression at C6C7 can cause many symptoms that affect daily life. We will look at common symptoms like pain, sensory issues, motor problems, and red flags that mean you need to see a doctor right away.
Pain Patterns: Neck, Shoulder, and Arm Radiation
Pain is a main symptom of C6C7 nerve root compression. It often starts in the neck and goes to the shoulder, arm, and sometimes the hand. Radicular pain can feel sharp or like shooting. It’s not just a simple neck ache but involves several areas.
Sensory Disturbances: Numbness and Tingling
People with C6C7 nerve root compression may feel numbness and tingling in their arm or hand. These feelings happen because the nerve root is compressed. This stops normal signals from getting through. Where these feelings are felt can help doctors figure out which nerve is affected.
Motor Symptoms: Weakness and Reflex Changes
Motor symptoms, like weakness and changes in reflexes, are common too. The muscles controlled by the C6 and C7 nerves may get weaker. This makes it hard to do everyday tasks. You might also notice reflexes that are less strong or missing.
Red Flag Symptoms Requiring Immediate Attention
While symptoms of C6C7 nerve root compression often come on slowly, some need quick action. Look out for sudden, severe pain, getting weaker, or problems with bladder or bowel control. Spotting these red flags is key to getting help fast and avoiding serious harm.
C7 Vertebrae Pain and Related Conditions
Understanding why C7 vertebrae hurt is key to fixing the problem. The C6-C7 part of the neck is often where pain starts. We’ll look at what can cause this pain and how it affects the C6-C7 area.
Cervical Disc Herniation at C6-C7
A herniated disc at C6-C7 can cause a lot of pain and other symptoms. This happens when the disc pushes on the C7 nerve root, leading to radiculopathy. You might feel pain, numbness, and weakness in your arm and hand.
The disc at C6-C7 is more likely to herniate because of its spot and the stress it gets. We’ll talk about how to diagnose and treat this issue.
Cervical Spondylosis and Foraminal Stenosis
Cervical spondylosis is a wear and tear condition that affects the neck, including C6-C7. It can cause foraminal stenosis, where the space for nerves gets smaller. This can lead to pain, numbness, and weakness.
Foraminal stenosis at C6-C7 can be found with imaging tests. Treatment can range from non-surgical methods to surgery.
Radiculopathy: When Nerve Roots Are Compressed
Radiculopathy happens when nerves get squished, causing pain, numbness, and weakness. At C6-C7, this can affect the middle finger and other areas.
We’ll cover what causes radiculopathy, its symptoms, and how to treat it.
Traumatic Injuries to the C6-C7 Segment
Car accidents or falls can hurt the C6-C7 area. These injuries can be mild or serious, like fractures or dislocations.
The treatment depends on how bad the injury is. It might include rest, physical therapy, or surgery.
| Condition | Symptoms | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
| Cervical Disc Herniation | Pain, numbness, weakness in arm and hand | Conservative management, surgery |
| Cervical Spondylosis | Pain, stiffness, numbness | Physical therapy, medication, surgery |
| Radiculopathy | Pain, numbness, weakness in specific dermatomes | Conservative management, interventional procedures |
| Traumatic Injuries | Pain, limited mobility, neurological symptoms | Immobilization, physical therapy, surgery |
Diagnostic Approaches for C6-C7 Spine Problems
Getting a correct diagnosis is key to treating C6-C7 spine issues. We use many methods to do this. These include clinical exams, imaging tests, and tests that check nerve function.
Clinical Examination Techniques
First, we do a detailed clinical exam. This includes looking at the patient’s health history and doing a physical check. We also check for nerve problems like numbness or weakness in the arms.
We might do special tests to see how well the muscles work and reflexes. For example, the Spurling’s test can show if a nerve is being pressed by checking if symptoms get worse when the neck is pressed.
Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRI, and CT Scans
Imaging tests are very important for finding out what’s wrong with the C6-C7 spine. We use different tests to see the spine and find the cause of symptoms.
| Imaging Modality | Primary Use |
|---|---|
| X-rays | Assessing bone structure and alignment |
| MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) | Visualizing soft tissues, including discs and nerves |
| CT (Computed Tomography) Scans | Evaluating bone detail and detecting fractures or stenosis |
Doctors say MRI is great for seeing soft tissue problems like disc herniations.
Electrodiagnostic Testing for Nerve Function
Tests like EMG and NCS check how nerves work and find damage. These tests help us understand how serious the nerve problem is. They help us decide the best treatment.
“Electrodiagnostic testing is a key tool for checking nerve function and finding out how bad nerve damage is.”
– Neurologist
Differential Diagnosis Considerations
When we’re figuring out what’s wrong with the C6-C7 spine, we also think about other possible causes. We rule out other conditions that might look like or add to the spine problem. This includes other neck issues, shoulder problems, or nerve traps.
By using clinical exams, imaging, and nerve tests, we can find and treat C6-C7 spine problems well. This helps our patients get better and feel better.
Treatment Options for Cervical Spine C6 C7 Conditions
Treatment for C6-C7 spine conditions includes many options. These range from non-surgical to surgical methods. The right treatment depends on the condition’s severity, the patient’s health, and their preferences.
Conservative Management Approaches
Non-surgical treatments are often the first step. This includes:
- Physical therapy to improve range of motion, strengthen muscles, and enhance posture
- Pain management through medication and lifestyle modifications
- Chiropractic care and spinal manipulation
- Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and improving ergonomics
A spine specialist notes, “Non-surgical treatments can greatly help manage symptoms and improve life quality for those with C6-C7 conditions.”
“The goal is to alleviate pain and restore function without resorting to more invasive procedures unless absolutely necessary.”
Interventional Procedures
For those not helped by non-surgical methods, interventional procedures are considered. These include:
| Procedure | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Corticosteroid injections | Injecting steroids into the affected area to reduce inflammation | Reduces pain and inflammation |
| Nerve blocks | Injecting medication into or around nerves to block pain signals | Provides temporary pain relief |
| Radiofrequency ablation | Using heat generated by radio waves to lesion nerves and reduce pain | Long-term pain relief |
Surgical Interventions for C6-C7 Pathology
Surgery is for severe cases where other treatments have failed. It’s also used when there’s significant nerve damage. Surgical options include:
- Discectomy: Removing the herniated disc
- Spinal fusion: Stabilizing the spine by fusing vertebrae together
- Artificial disc replacement: Replacing the damaged disc with an artificial one
Surgical decisions are made on a case-by-case basis, considering the patient’s overall health, the severity of their condition, and their personal preferences.
Conclusion: Maintaining C6-C7 Spinal Health
Keeping the C6-C7 spinal segment healthy is key for your spine’s overall well-being. The C6 and C7 vertebrae are important for neck movement and stability. Any problems here can cause a lot of pain and limit your movements.
It’s important to live a healthy lifestyle to avoid issues with the c6/c7 spine. Regular exercise, good posture, and a balanced diet can lower the risk of spinal problems. By being proactive, you can keep your spinal c6 and c7 working well.
The c6 and c7 spine can face issues like disc herniation, spondylosis, and radiculopathy. Knowing how the c6 c7 vertebrae work is vital for preventing and managing these problems. By staying healthy and getting medical help when needed, you can keep your C6-C7 spine healthy for a long time.
What is the function of the C6 and C7 vertebrae in the cervical spine?
The C6 and C7 vertebrae help move the neck and keep it stable. They are a key part of the spine.
Where is the C6-C7 segment located in the spine?
The C6-C7 segment is in the lower part of the neck. The C7 vertebra is easy to spot because of its long spinous process.
What is the role of the intervertebral disc between C6 and C7?
The disc between C6 and C7 helps absorb shock. It makes movement smooth and cushions the vertebrae.
What are the symptoms of C6C7 nerve root compression?
Symptoms include neck, shoulder, and arm pain. You might also feel numbness, tingling, weakness, and changes in reflexes.
How are the C6 and C7 nerve roots distributed?
The C6 nerve root helps with wrist extension and forearm supination. The C7 nerve root helps with elbow extension and wrist flexion.
What is the C6-C7 dermatome map?
The C6 dermatome covers the thumb and index finger. The C7 dermatome covers the middle finger. Both provide sensation to the hand and arm.
How is C7 vertebrae pain diagnosed?
Doctors use clinical exams, imaging, and tests to check nerve function. This helps diagnose C7 vertebrae pain.
What are the treatment options for C6-C7 spine conditions?
Treatment depends on the condition and its severity. Options range from conservative methods to surgery.
How can C6-C7 spinal health be maintained?
Keep the spine healthy by living a healthy lifestyle. Exercise regularly and maintain good posture to prevent problems.
What are the common conditions affecting the C6-C7 segment?
Common issues include herniated discs, cervical spondylosis, and injuries. These can cause nerve compression and radiculopathy.
What is the significance of the C7 vertebra’s prominent spinous process?
The C7 vertebra’s long spinous process is a key landmark. It helps identify the C6-C7 junction.


































