Persistent right-sided abdominal pain, nausea, or digestive discomfort may signal gallbladder trouble. This condition affects millions worldwide. Early and accurate diagnosis is key to preventing serious complications and ensuring effective treatment.
How do you check for gallbladder issues? Learn about the 7 best, essential tests doctors use to check for problems and stones.
At Liv Hospital, we are dedicated to international standards and patient-first care. You get a thorough evaluation with the latest diagnostic tools. This helps you regain health and confidence.
Key Takeaways
- Accurate diagnosis of gallbladder problems requires a combination of clinical assessment and advanced diagnostic tests.
- Gallstones and functional disorders can be detected using various diagnostic tests.
- Liv Hospital uses international standards and evidence-based protocols for gallbladder diagnosis.
- Early diagnosis is key for effective treatment and preventing complications.
- Comprehensive evaluation at Liv Hospital helps patients regain health and confidence.
Gallbladder Problems: Signs and Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
It’s important to know the signs and symptoms of gallbladder problems early. The gallbladder helps with digestion. If it has issues, it can cause serious problems if not treated.
Common Gallbladder Conditions and Their Manifestations
Gallbladder problems can show up in different ways. These symptoms can be similar to other health issues. This makes it hard to diagnose. Common issues include gallstones, cholecystitis, and biliary dyskinesia.
Symptoms of gallbladder disease can include:
- Severe pain in the upper right abdomen
- Nausea and vomiting
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Fever and chills
- Abdominal tenderness
Warning Signs That Warrant Medical Attention
Some symptoms need you to see a doctor right away. Severe pain in the upper right abdomen, jaundice, fever, or persistent vomiting are signs to watch for. If you have these, get medical help fast.
It’s important to recognize these warning signs. This can help avoid serious problems like gangrene or perforation of the gallbladder. These issues need emergency surgery.
Risk Factors for Developing Gallstones and Gallbladder Disease
There are several factors that increase the risk of gallstones and gallbladder disease. These include:
| Risk Factor | Description |
| Obesity | Being significantly overweight increases the risk of gallstones. |
| Age | The risk of gallstones increases with age, after 40. |
| Family History | A family history of gallstones increases an individual’s risk. |
| Diet | A diet high in fat and low in fiber can contribute to gallstone formation. |
Knowing these risk factors can help prevent problems. It also helps in getting early diagnosis if symptoms show up.
The Diagnostic Journey: Why Proper Testing Matters
Getting a correct diagnosis is key to treating gallbladder problems well. The diagnostic journey includes tests to find gallbladder issues. It’s important for patients to know why these tests are needed.
Complications of Untreated Gallbladder Problems
Not treating gallbladder problems can lead to big issues. Infection and inflammation can cause a lot of pain and even be life-threatening. Also, untreated gallstones can block the bile duct, causing jaundice and harming the liver.
The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Getting a correct diagnosis is essential. It helps doctors tell apart different gallbladder problems and find gallstones or other issues. This leads to a better treatment plan, lowering the risk of complications and improving health outcomes.
What to Expect During the Diagnostic Process
Patients will go through various tests during the diagnostic process. These might include physical checks, blood tests, and imaging like ultrasound or CT scans. These tests help doctors understand the gallbladder’s condition, making it easier to diagnose and treat.
The diagnostic journey is a vital step in dealing with gallbladder problems. Knowing the importance of proper testing and the risks of not treating gallbladder issues helps patients make informed choices about their treatment.
Physical Examination: The First Step in Gallbladder Assessment
A thorough physical examination is key in the first steps to check for gallbladder disease. It helps doctors find signs and symptoms that might point to gallbladder problems.
What Your Doctor Will Look For During Examination
Your doctor will check for tenderness in the upper right abdomen. This is a common sign of gallbladder issues. They will also look for jaundice, like yellow skin and eyes, which can mean bile duct blockage.
The doctor might do a deep touch on the abdomen. This is to feel the gallbladder and the areas around it.
Murphy’s Sign and Other Clinical Indicators
Murphy’s sign is a key sign of gallbladder disease. The doctor will ask you to breathe deeply while they press on your abdomen. If you feel pain and stop breathing as the gallbladder touches their fingers, it’s a positive sign.
Other signs include muscle tension in the abdomen and rebound tenderness. These can mean irritation in the peritoneum.
Critical Information to Share With Your Healthcare Provider
It’s important to share all the details with your doctor. This includes:
- A full list of your symptoms, when they started, and how bad they are.
- Any past health issues, like liver or bile duct problems.
- History of surgeries or procedures.
- What medicines you’re taking and any allergies.
Sharing this info helps your doctor make a better diagnosis and plan the right treatment.
| Clinical Indicator | Description | Significance |
| Murphy’s Sign | Tenderness upon deep palpation during inhalation | Positive sign indicative of gallbladder disease |
| Jaundice | Yellowing of skin and eyes | May indicate bile duct obstruction |
| Guarding | Muscle tension in the abdominal wall | Suggests peritoneal irritation |
Blood Tests: What Laboratory Work Reveals About Gallbladder Function
Blood tests are key in diagnosing gallbladder problems. They show signs of infection, inflammation, and liver issues. These can all be linked to gallbladder disease.
Liver Function Tests and Bilirubin Levels
Liver function tests (LFTs) check for liver damage or disease. They look at enzymes and proteins in the blood, like bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase. High levels can mean liver problems or bile duct blockages, often tied to gallbladder issues.
Bilirubin levels are very important for gallbladder health. High bilirubin can mean bile duct blockages, usually from gallstones. This can cause jaundice, a yellow skin and eye condition.
Complete Blood Count for Detecting Infection and Inflammation
A complete blood count (CBC) is vital for diagnosing gallbladder problems. It checks blood components like white blood cells. A high white blood cell count can show gallbladder infection or inflammation, known as cholecystitis.
- A CBC can help diagnose acute cholecystitis, a condition where the gallbladder becomes inflamed.
- It can also detect signs of chronic inflammation.
Limitations: Why Blood Work Alone Cannot Diagnose Gallstones
Blood tests offer insights into gallbladder health but have limits. They can’t confirm gallstones on their own. Ultrasound and other imaging tests are needed to see gallstones.
Blood tests hint at gallbladder problems but aren’t enough for a full diagnosis. A complete diagnosis includes blood tests, imaging, and a doctor’s evaluation.
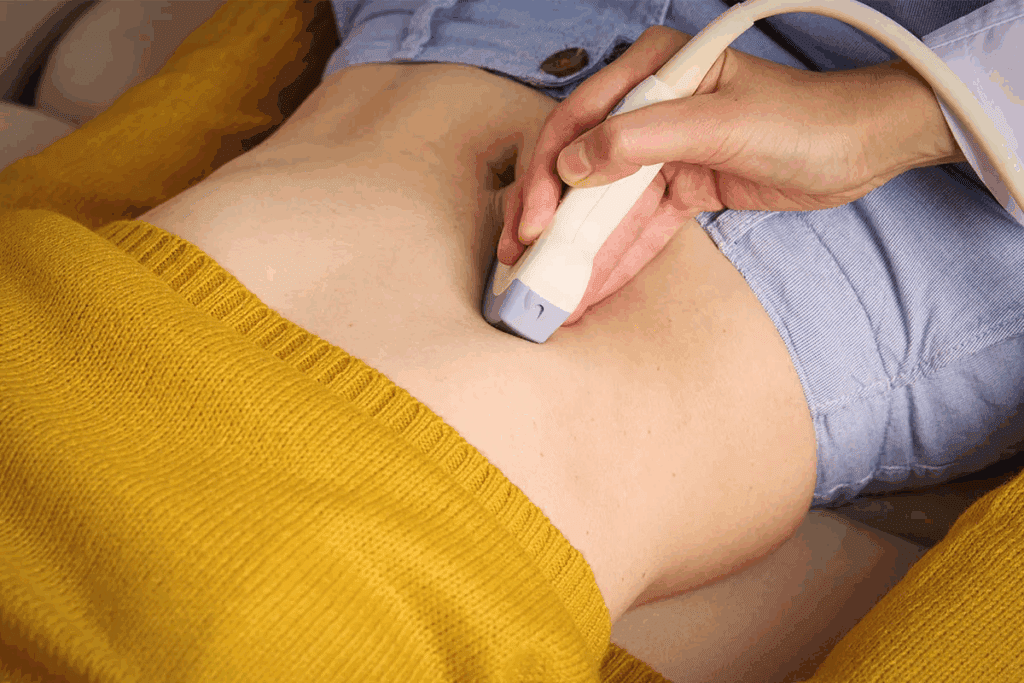
Ultrasound: The Gold Standard for Gallstone Detection
Gallbladder ultrasound is the top choice for finding gallstones. It gives clear images that help doctors decide on treatment. This method is safe and accurate, making it very popular.
Procedure for Gallbladder Ultrasound
Getting a gallbladder ultrasound is easy. Patients often need to not eat for a few hours before. This makes the gallbladder easier to see.
A technician puts gel on the belly and uses a transducer to take pictures. This helps them see the gallbladder well.
Key steps in the ultrasound procedure include:
- Preparation: Patients may be required to fast for 4-8 hours before the test.
- Application of gel: A clear gel is applied to the abdomen to facilitate the transmission of sound waves.
- Imaging: The technician uses a transducer to capture images of the gallbladder from multiple angles.
What Ultrasound Can Detect
Ultrasound is great at finding problems in the gallbladder. It can spot gallstones, thick walls, and sludge. This info is key for choosing the right treatment.
The capabilities of ultrasound include:
- Detecting gallstones of various sizes and compositions.
- Identifying gallbladder wall thickening, which can be a sign of inflammation or other conditions.
- Visualizing biliary sludge, which can be a precursor to gallstone formation.
Accuracy and Limitations of Ultrasound
Ultrasound is very good at finding gallstones, with accuracy rates of 95% to 98%. But, how well it works can depend on the technician, the equipment, and the patient’s health.
| Diagnostic Feature | Accuracy Rate |
| Gallstones Detection | 95-98% |
| Gallbladder Wall Thickening | 80-90% |
| Biliary Sludge Detection | 70-85% |
Even though ultrasound is very useful, it has its limits. Sometimes, more tests are needed to make sure of a diagnosis or to get more details about the gallbladder and bile ducts.
CT Scans: When 3D Imaging Is Necessary for Gallbladder Diagnosis
Ultrasound is often the first choice for checking the gallbladder. But, CT scans are key for detailed 3D images when more is needed. They’re very useful in complex cases or when complications are thought of.
Indications for Computed Tomography in Gallbladder Assessment
CT scans aren’t usually the first choice for gallbladder issues. But, they’re vital in some situations. This includes when there’s a chance of gallbladder cancer, pancreatitis, or complications from gallstones.
They’re also helpful when ultrasound can’t make a clear diagnosis. Or when you need to know how severe the gallbladder disease is.
Key indications for CT scans in gallbladder assessment include:
- Suspected gallbladder cancer or other malignancies
- Complications from gallstones, such as pancreatitis or choledocholithiasis
- Unclear diagnosis after ultrasound
- Assessing the severity of gallbladder disease
- Evaluating the gallbladder and surrounding structures in complex cases
What CT Scans Can Reveal That Ultrasound Might Miss
CT scans have big advantages over ultrasound in some cases. They give clear images of the gallbladder and nearby areas. This can show problems or conditions that ultrasound might miss.
Some key benefits of CT scans include:
- Detailed imaging of the gallbladder wall and surrounding tissues
- Detection of small stones or sludge in the bile ducts
- Visualization of complications such as gangrene or perforation
- Assessment of adjacent structures like the pancreas and liver
Preparing for a Gallbladder CT Scan
Getting ready for a CT scan of the gallbladder is simple. You might need to fast for a few hours. This helps get better images. Sometimes, contrast material is used to make the gallbladder and nearby areas clearer.
Tell your doctor about any medicines you’re taking, like for kidney disease or diabetes. Also, let them know if you’re pregnant or might be. This can change if you should have a CT scan.
Understanding CT scans’ role in diagnosing gallbladder problems helps patients. It shows how these tests help in the diagnostic process.
MRI and MRCP: Advanced Imaging for Bile Duct Evaluation
MRI and MRCP are key tools for checking bile duct issues. They give doctors detailed views of the bile ducts. This helps in diagnosing and treating related problems.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Gallbladder Assessment
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive test. It uses magnets and radio waves to show internal organs clearly. For gallbladder checks, MRI shows the bile ducts, gallbladder, and nearby tissues.
This is key for spotting issues like gallstones, inflammation, or tumors. The test involves lying in an MRI machine. It takes many images of the belly area. Then, radiologists study these images to find any problems.
MRI is great for those who can’t have CT scans or ultrasounds because of health issues.
The Role of MRCP in Visualizing Bile Ducts
MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography) is a special MRI for bile and pancreatic ducts. It gives clear images of these ducts. Doctors can see blockages, narrowings, or other issues.
MRCP is very useful for finding problems like primary sclerosing cholangitis or bile duct stones.
When Doctors Recommend MRI Over Other Imaging Tests
Doctors might choose MRI or MRCP over other tests in some cases. For example, if a patient can’t have CT scan contrast dyes because of allergies, MRI is safer. MRI also shows soft tissues better. This makes it great for complex bile duct issues or seeing how far a disease has spread.
In summary, MRI and MRCP are vital for checking bile duct problems. They offer detailed images of the bile ducts and nearby areas. This makes them essential in today’s medicine.
How Do You Check for Gallbladder Issues: The HIDA Scan Explained
A HIDA scan is a test that checks the gallbladder and bile ducts. It uses a special tool to see how well the gallbladder works and how bile moves. This helps doctors find problems.
Understanding the Hepatobiliary Iminodiacetic Acid Scan Procedure
The HIDA scan starts with a small amount of radioactive material being injected into a vein. This material goes through the liver and into the bile ducts, gallbladder, and small intestine. A camera tracks this material to show the gallbladder and bile ducts.
The patient lies on a table while the camera takes pictures. The test can last from 30 minutes to several hours. This depends on what the doctor needs to know.
Key aspects of the HIDA scan procedure include:
- Injection of a radioactive tracer
- Use of a gamma camera to track the tracer’s movement
- Imaging of the gallbladder and bile ducts
- Potential use of a medication to stimulate gallbladder contraction
Measuring Gallbladder Ejection Fraction and Function
The HIDA scan also checks the gallbladder ejection fraction (GBEF). This is how much bile is moved from the gallbladder into the small intestine. A good GBEF is above 35-40%.
If the GBEF is low, it might mean the gallbladder isn’t working right. This could be due to chronic disease or other issues. Doctors use GBEF to see if the gallbladder is working well.
Interpreting HIDA Scan Results and What They Mean
The results of a HIDA scan can show a lot about the gallbladder and bile ducts. It can help find problems like:
- Gallbladder dysfunction
- Obstruction of the bile ducts
- Cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder)
- Leaks or fistulas in the biliary system
Doctors look at the scan results along with the patient’s symptoms and medical history. If the results are not normal, more tests or treatment might be needed.
| Condition | HIDA Scan Findings |
| Gallbladder Dysfunction | Low gallbladder ejection fraction |
| Bile Duct Obstruction | Delayed or absent flow of tracer into the small intestine |
| Cholecystitis | Failure of the gallbladder to visualize or abnormal tracer uptake |
Doctors say the HIDA scan is very helpful. It gives important information about the gallbladder and bile flow. This helps doctors decide the best treatment for patients with gallbladder disease.
“The HIDA scan has become an essential component in the diagnosis and management of gallbladder disorders, providing a non-invasive means to assess gallbladder function and identify any issues.”
— Dr. John Smith, Gastroenterologist
Endoscopic Procedures: ERCP and Endoscopic Ultrasound
ERCP and endoscopic ultrasound are key in diagnosing and treating gallbladder and bile duct issues.
When Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Is Needed
ERCP is a detailed procedure for bile and pancreatic duct problems, like gallbladder disease.
It’s useful when tests like ultrasound or CT scans show blockages or narrowings.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications of ERCP
ERCP is used for both checking and treating issues. It lets doctors see the bile and pancreatic ducts with contrast material.
It also helps in removing gallstones, widening narrow ducts, and putting in stents to keep ducts open.
| Procedure | Diagnostic Use | Therapeutic Use |
| ERCP | Visualize bile and pancreatic ducts | Remove gallstones, dilate narrowed ducts, place stents |
| Endoscopic Ultrasound | Detailed imaging of gallbladder and bile ducts | Guide fine-needle aspiration for tissue diagnosis |
Endoscopic Ultrasound for Detailed Gallbladder Imaging
EUS gives clear images of the gallbladder and bile ducts. It helps in diagnosing gallbladder disease and guides tissue diagnosis.
EUS is great for checking gallbladder cancer and how it affects nearby areas.
Conclusion: Taking Action for Your Gallbladder Health
Gallbladder health is key for feeling good overall. Finding out if you have gallbladder issues is the first step to getting better. This involves several tests, like physical checks, blood work, and scans.
If you keep feeling bad, you need to see a doctor fast. Ignoring gallbladder problems can cause serious issues, like pancreatitis or cholecystitis. Knowing how to get checked and why it’s important helps keep your gallbladder in top shape.
Don’t wait to see a doctor if you’re not feeling right. A correct diagnosis helps doctors figure out the best treatment. This might mean surgery or other treatments.
By focusing on your gallbladder health and getting help when you need it, you can avoid big problems. Getting the right treatment is essential for a healthy gallbladder and a better life.
FAQ
What tests show gallbladder problems?
Tests like ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, MRCP, HIDA scans, and endoscopic procedures can show gallbladder issues.
How do you check a gallbladder?
To check a gallbladder, doctors use physical exams, lab tests, and imaging like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI.
Will blood work show gallbladder problems?
Blood tests can hint at gallbladder problems. They include liver function tests and complete blood count. But, they can’t confirm gallstones or disease.
Which blood test shows gallstones?
No blood test directly shows gallstones. But, liver function tests and bilirubin levels can suggest gallbladder issues.
What is the role of ultrasound in detecting gallstones?
Ultrasound is key for finding gallstones. It shows stones, wall thickening, and sludge in the gallbladder well.
How is a HIDA scan used to diagnose gallbladder problems?
A HIDA scan checks the gallbladder’s ejection fraction and function. It helps diagnose cholecystitis or biliary dyskinesia.
When is ERCP used to diagnose and treat gallbladder problems?
ERCP is used to see the bile ducts, diagnose choledocholithiasis, or perform treatments.
What is the importance of accurate diagnosis for gallbladder problems?
Accurate diagnosis is key to avoid complications like cholecystitis, pancreatitis, or gallbladder cancer. It guides the right treatment.
How do doctors assess gallbladder function during a physical examination?
Doctors look for signs like Murphy’s sign, tenderness, or guarding in the right upper quadrant. These signs indicate gallbladder disease.
What are the risk factors for developing gallstones and gallbladder disease?
Risk factors include obesity, family history, age, ethnicity, and certain medical conditions like diabetes or liver disease.
What are the common signs and symptoms of gallbladder problems?
Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and jaundice. They vary based on the condition.

































