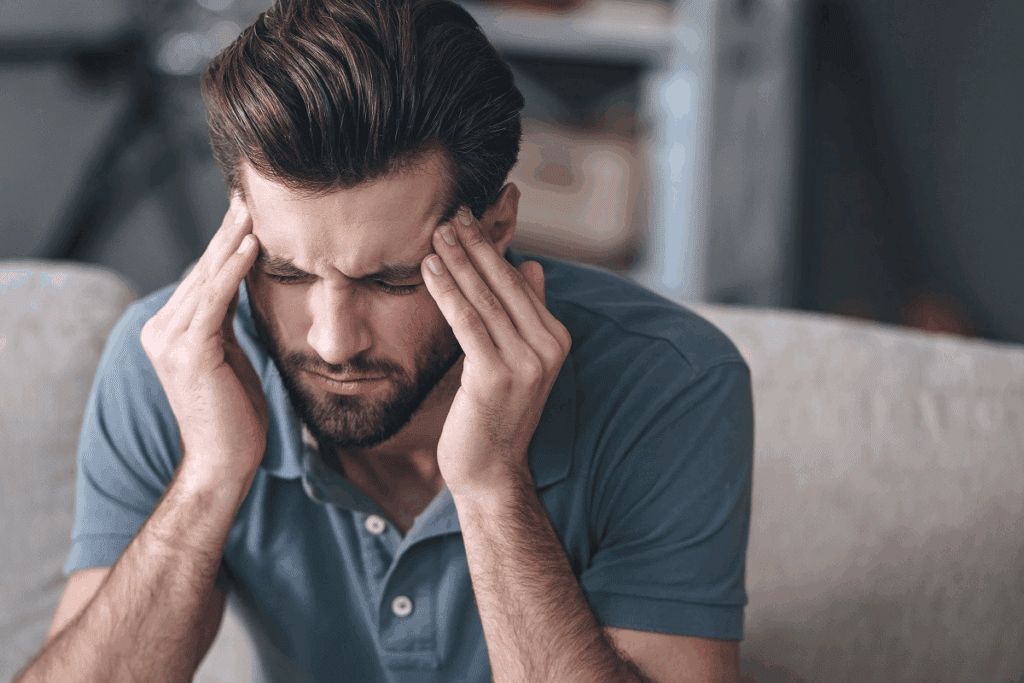
A severe headache can be a sign of a life-threatening condition. When a blood clot blocks blood flow in the brain’s veins, it can cause severe headache pain. Understand do blood clots cause headaches, how they develop, and when to seek urgent care.
Ischemic strokes happen when a clot blocks a blood vessel in the brain. They can be fatal if not treated quickly. It’s important to know how blood clots and headaches are connected to spot early warning signs.
Liv Hospital focuses on patients, giving them the latest care for blood clot-related symptoms. This ensures their safety and peace of mind.
Key Takeaways
- Severe headaches can be a sign of a life-threatening blood clot.
- Blood clots obstructing blood flow in the brain’s veins can cause debilitating headache pain.
- Ischemic strokes can be fatal if not treated promptly.
- Understanding the relationship between blood clots and headaches is important.
- Liv Hospital’s patient-centered approach ensures the latest care for blood clot-related symptoms.
Understanding Blood Clots and Their Formation
It’s important to know about blood clots and how they form. This knowledge helps us spot health risks early and prevent them. Blood clots are a serious medical issue that can affect our health a lot.
What Are Blood Clots?
Blood clots are like thick, gel-like clumps of blood. They form when the body tries to stop bleeding. This can happen from an injury or without a clear reason. Blood clots can be life-saving by stopping bleeding, but they can also be harmful if they block blood flow.
How and Why Blood Clots Form
The process of blood clotting is complex. It involves several steps that lead to the formation of a fibrin clot. Many things can trigger this process, like injuries, staying too long in one position, or genetic factors. “The formation of blood clots is a delicate balance between preventing excessive bleeding and avoiding unnecessary clotting,” say doctors.
Common Locations for Blood Clots
Blood clots can form in different parts of the body. They can appear in the deep veins of the legs (deep vein thrombosis or DVT), the lungs (pulmonary embolism), and the brain. Clots near the skin can be seen, but those deeper inside can’t.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) happens when a clot forms in a vein deep inside the body. It often occurs in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis. It’s key to know the signs of DVT because it can lead to serious problems like pulmonary embolism if the clot moves to the lungs.
The Relationship Between Blood Clots and the Brain
The brain needs a steady blood supply to function. Blood clots can disrupt this, causing serious problems. They can harm brain function, leading to severe health issues.
Blood Supply to the Brain
The brain gets its blood from arteries branching from the carotid and vertebral arteries. This network is key for delivering oxygen and nutrients. Any blockage, like a blood clot, can damage tissues or even kill cells.
The cerebral arteries feed different brain parts. For example, the anterior cerebral artery goes to the frontal and parietal lobes’ medial surfaces. The middle cerebral artery covers a big part of the brain’s lateral surface.
Cerebral Venous System
The cerebral venous system drains deoxygenated blood from the brain to the heart. It has superficial and deep veins that empty into the dural venous sinuses. Cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) happens when a clot forms in these sinuses or veins, blocking blood flow.
CVT can cause headaches, seizures, and even stroke. Symptoms vary based on where and how big the clot is.
Blood-Brain Barrier and Clotting
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) keeps the brain’s environment stable. It’s a selective barrier between blood and the brain’s fluid. Blood clots can damage the BBB, causing swelling and serious problems.
- Blood clots can irritate brain tissue, causing seizures.
- They can also cause fever, if there’s an infection or inflammation.
- Clots can damage local tissues due to lack of blood flow.
Knowing how blood clots affect the brain is key for treating conditions like cerebral venous thrombosis.
Do Blood Clots Cause Headaches? The Direct Connection
Blood clots can cause headaches, but it’s not that simple. The link between blood clots and headaches involves many factors. These include how the body works and how the brain reacts.
Mechanisms Behind Clot-Induced Headaches
A blood clot can block blood flow, leading to tissue damage or swelling. In the brain, this can cause pain. Cerebral vein thrombosis (CVT) is a serious condition where a clot forms in brain veins. It can lead to severe headaches.
“The headache from cerebral vein thrombosis is very severe,” a study says. It can also cause nausea, vomiting, and seizures. This shows how serious blood clot headaches can be.
Cerebral Vein Thrombosis and Pain
Cerebral vein thrombosis can cause a lot of pain because it blocks blood flow. This blockage can raise pressure inside the skull, leading to headaches. The pain is often very bad and can have other symptoms too.
Distinguishing Clot-Related Headaches from Other Types
It’s important to tell apart headaches from blood clots from other types. Clot-related headaches start suddenly and are very intense. They might also have other symptoms or problems with the nervous system.
Doctors look for signs like sudden start, intense pain, and other symptoms to tell them apart. Knowing the difference is important for the right treatment.
Types of Blood Clots That Commonly Cause Headaches
It’s important to know about the different blood clots that can cause headaches. These clots can form in the brain or other parts of the body. They can lead to various symptoms.
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST)
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST) is a blood clot in the cerebral venous sinuses. It can cause severe headaches and other symptoms like seizures and vision changes. Risk factors include oral contraceptives, clotting disorders, and head trauma.
Carotid Artery Thrombosis
Carotid Artery Thrombosis is a blood clot in the carotid artery. This artery supplies blood to the brain. Symptoms include headaches, transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), or strokes. A clot here can reduce blood flow to the brain.
Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis
Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis is similar to CVST. It involves a blood clot in the dural venous sinuses. Symptoms include headaches, papilledema, and other neurological issues. Quick diagnosis and treatment are key to avoid long-term damage.
Common Symptoms Across Types
- Severe headaches
- Neurological deficits
- Vision changes
- Seizures
Blood clots can also occur in less common places like the buttocks or throat. A clot in the buttocks can cause pain and swelling. A clot in the throat can make swallowing or breathing hard.
Knowing the types of blood clots and their symptoms is key for quick medical help. If you or someone you know has symptoms like severe headache, trouble speaking, or weakness in limbs, get medical help right away.
Warning Symptoms That Accompany Blood Clot Headaches
It’s important to know the warning signs of blood clot headaches. These symptoms can be severe and affect many parts of your body. They can even harm your brain and overall health.
Neurological Symptoms
Blood clots in the brain can cause serious problems. One scary sign is seizures. Studies show that some people with blood clots in the brain can have seizures. If you have a seizure, get help right away.
Other signs include feeling confused, having trouble speaking, or feeling weak on one side. These happen because the clot blocks blood flow to the brain. This can damage brain tissue or make it not work right.
Systemic Symptoms
Blood clots can also cause symptoms all over the body. For example, a fever might happen. This is because your body is fighting the clot. But not all clots cause fever. Some conditions, like infections, can lead to fever.
Nausea and vomiting are also signs. These can be very uncomfortable. They might mean your brain is under too much pressure or there’s another problem with the clot.
It’s key to watch for these signs and get medical help fast. Quick action can make a big difference for people with blood clot headaches.
The Connection Between Migraines and Blood Clots
Studies have found a link between migraines and a higher risk of blood clots. This is important for understanding the risks of migraines.
Migraines as a Risk Factor
Migraines are more than just headaches. They are a neurological condition that can affect the body in many ways. People with migraines, and those with aura, might be at a higher risk of blood clots.
Key findings include:
- Increased risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Higher incidence of pulmonary embolism
- Association with other cardiovascular conditions
The exact reasons for this link are being studied. Several factors are thought to play a role.
Distinguishing Migraines from Clot-Related Headaches
It’s important to tell migraines apart from headaches caused by blood clots. Both can be very painful, but they have different signs and symptoms.
Characteristics of clot-related headaches:
- Sudden onset, often described as “thunderclap”
- Severe, unrelenting pain
- Associated neurological deficits
Migraines start more slowly and often come with aura, nausea, and sensitivity to light and sound.
Shared Mechanisms and Pathways
Research shows that migraines and blood clots share some common causes. These include:
- Endothelial dysfunction
- Inflammation and oxidative stress
- Hypercoagulability
Learning about these shared causes can help in preventing and managing both conditions.
As research goes on, doctors can better care for patients with migraines. This might help lower the risk of blood clots.
Can You Have a Blood Clot Without Symptoms?
Yes, it’s possible to have a blood clot without any symptoms. This is a big worry because blood clots can cause serious health problems if not treated quickly.
Silent Blood Clots
Silent blood clots are clots that form without any noticeable symptoms. They can happen in different parts of the body, like the legs, lungs, and brain. It’s hard to find these clots because they don’t show symptoms.
Some people might not feel anything until the clot has grown or broken loose. For example, a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) might not show pain or swelling until it’s very big.
Risk Factors for Asymptomatic Clots
There are several things that make it more likely to get silent blood clots. These include:
- Genetic predisposition to clotting disorders
- Prolonged periods of immobility, such as during long flights or bed rest
- Surgery or trauma
- Cancer and its treatment
- Obesity and smoking
Knowing these risk factors can help people prevent blood clots and stay aware of their health.
Incidental Discovery of Blood Clots
Asymptomatic blood clots are often found by accident during medical tests. For instance, a CT scan or MRI might show a clot in the lungs or legs.
Finding blood clots by accident shows how important regular health checks are. It’s key to talk to a doctor about any worries.
In summary, while blood clots can be without symptoms, knowing the risks and taking steps to prevent them can help avoid serious problems.
Are Blood Clots Visible? Physical Signs to Watch For
Spotting the signs of blood clots can save lives. These clots can appear in different parts of the body. Knowing these signs is key for quick action and treatment.
External Visibility of Superficial Clots
Some blood clots can be seen on the skin’s surface. These superficial clots look like red, swollen veins or lumps. They might feel warm or hot and hurt when touched.
A clot in a vein can make a limb swell, turn red, and hurt. This is a clear sign something is wrong.
Swelling and Skin Changes
Blood clots can make a limb swell because they block blood flow. The skin around the clot might turn red or purple. It can also feel warm or hot.
These changes often come with pain or tenderness. Watching for these signs is important. They could mean a serious problem.
In severe cases, swelling can be huge. The skin might look tight and shiny. If you see these signs, along with trouble moving the limb, get help fast.
Unusual Locations and Their Appearance
Blood clots can show up in odd places, and look different each time. For example, a clot in the cerebral venous sinus might not be seen but can cause headaches, confusion, and seizures. On the other hand, a clot in a limb will likely cause visible swelling and skin changes.
Some blood clots are invisible but just as dangerous. These “silent” clots can break loose and travel to vital areas. This can lead to serious problems like pulmonary embolism or stroke.
Blood Clots in Uncommon Locations
Blood clots in unusual spots, like the buttocks or throat, are tricky to spot. They can be very serious.
Blood clots can happen anywhere in the body. When they show up in rare places, finding and treating them gets harder. Knowing the signs and risks is key to getting help fast.
Blood Clot in Buttocks: Symptoms and Recognition
A blood clot in the buttocks hurts a lot. It can also swell, feel tender, and be painful. Spotting these signs early is important to avoid bigger problems.
- Localized Pain: Pain that is confined to the buttock area.
- Swelling: Visible swelling or enlargement of the buttock.
- Tenderness: The area may be tender to the touch.
If you notice these signs, get medical help right away. They can figure out what’s wrong and how to fix it.
Throat and Neck Blood Clots
Blood clots in the throat or neck are very dangerous. They’re close to important parts of the body. Symptoms include trouble swallowing, swelling, or pain in the neck or throat.
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing.
- Pain or discomfort in the neck or throat.
- Visible swelling or bruising.
If you have these symptoms, get help fast. They could mean a serious problem.
Other Rare Locations
Blood clots can also show up in places like the arms, liver, or brain. Each spot has its own symptoms and challenges.
For example, a clot in the arm might cause pain, swelling, and color changes. A clot in the liver can lead to belly pain and jaundice.
Knowing about blood clots in these areas helps catch them early. This can prevent serious problems.
Life-Threatening Complications: When Blood Clots Can Kill You
Blood clots can cause severe, life-threatening problems if not treated quickly. They can block blood flow, leading to serious health issues. These issues can be fatal if not treated fast enough.
Stroke and Cerebrovascular Events
A blood clot in the brain can cause a stroke. This happens when the brain’s blood supply is cut off. It can lead to cerebrovascular events, causing brain damage or death. The damage depends on where and how big the clot is.
Pulmonary Embolism
A pulmonary embolism happens when a blood clot travels to the lungs. It blocks blood flow there. This can be deadly if not treated right away. Symptoms include sudden breathlessness, chest pain, and coughing up blood.
Heart Attack and Cardiac Complications
Blood clots can also cause a heart attack. This happens when a clot blocks blood to the heart muscle. It forms in the coronary arteries, damaging or killing heart tissue. Quick medical help is key to avoid long-term heart problems.
Timeline and Progression of Serious Complications
The time it takes for serious complications to develop can vary. It depends on the clot’s location, size, and the person’s health. Knowing these factors helps in quick diagnosis and treatment.
In summary, blood clots can lead to serious problems like stroke, pulmonary embolism, and heart attack. It’s important to recognize the signs and get medical help right away to avoid fatal outcomes.
Conclusion: When to Seek Emergency Care for Headaches
Severe headaches can be a sign of a serious problem, like a blood clot. Knowing when to get emergency care is key to avoiding big issues.
If you have a sudden, really bad headache, or one with symptoms like confusion or vision problems, get help right away. This is very important.
Other signs that mean you need to see a doctor fast include a headache with fever, stiff neck, or throwing up. If you usually get migraines or have other health issues, watch for any changes in your headaches.
Deciding when to get emergency care for headaches is a big deal. It can mean the difference between life and death. If you’re not sure, it’s always better to be safe and get medical help. Quick action can really help people with serious conditions like blood clots.
FAQ
Are blood clots visible?
Some blood clots, like superficial ones, can be seen under the skin. Others, like deep vein thrombosis, might not be visible.
Do blood clots cause swelling?
Yes, blood clots can cause swelling. This happens more often in limbs or areas where fluid can build up.
Can a blood clot cause headaches?
Yes, certain blood clots, like cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, can lead to headaches. This is due to the pressure and inflammation they cause in the brain.
Can blood clots cause seizures?
Yes, blood clots in or around the brain can cause seizures. This is because they put pressure on the brain or cause inflammation.
Can you have a blood clot and not know it?
Yes, it’s possible to have a blood clot without symptoms. This often happens with small clots or those in areas that don’t cause immediate harm.
Can a blood clot cause nausea?
Yes, blood clots can cause nausea. This is more common if the clot is related to a condition affecting the brain or gastrointestinal system.
Can a blood clot kill you?
Yes, a blood clot can be deadly if it breaks loose and travels to critical areas. For example, the lungs (pulmonary embolism) or brain (stroke).
What are the symptoms of a blood clot in the buttocks?
Symptoms of a blood clot in the buttocks include pain, swelling, and tenderness in the affected area.
Can blood clots cause fever?
Yes, in some cases, blood clots can cause a low-grade fever. This is more likely if there’s an associated infection or inflammation.
What are the symptoms of a throat blood clot?
Symptoms of a blood clot in the throat include difficulty swallowing, pain, and swelling in the neck.
Do blood clots cause headaches?
Certain types of blood clots, like those in the cerebral venous sinuses, can cause headaches.
Can blood clots cause migraines?
While migraines are a headache disorder, research suggests people with migraines might be at higher risk for venous thrombosis. This involves blood clots.



































