
A hernia in women happens when parts of the abdomen push through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. This usually happens in the pelvis or lower abdomen. It can be tricky to spot because the symptoms are not always clear.
Women with hernias often don’t have a visible bulge. This makes it tough to find out if someone has a hernia. So, hernias in women are often mistaken for other gynecological issues.
It’s important to know about hernias in women to catch them early. Liv Hospital is a trusted place for women to get help and advice on this issue.
Key Takeaways
- Hernias in women occur when abdominal contents protrude through a weakness in the abdominal wall.
- Subtle symptoms make hernias in women challenging to diagnose.
- Women with hernias may not exhibit a visible bulge, leading to frequent misdiagnosis.
- Liv Hospital offers expert care and guidance for women with hernias.
- Early recognition is essential for optimal health outcomes.
Understanding Female Real Hernia

It’s important to understand female real hernias to catch them early and treat them well. A female real hernia happens when an organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the belly wall. This can really affect a woman’s life, so knowing what causes it and how it shows up is key.
Definition and Anatomical Basics
A hernia is when the belly wall breaks, letting stuff bulge out. In women, hernias can pop up in the groin, navel, or through old scars. To get it, you need to know about the belly’s layers and how they can get weak.
Key anatomical structures are the fascia, muscles, and peritoneum. If these get weak, you can get a hernia. Pregnancy is a big risk factor because it stretches the belly wall, making hernias more likely.
“Pregnancy can increase the risk of developing hernias due to the stretching of the abdominal wall.”
How Abdominal Weaknesses Develop in Women
Women can get weak spots in their belly for many reasons. Pregnancy, being overweight, and past surgeries are some. Pregnancy stretches the belly, making muscles and fascia weak. Also, things that make you push hard on your belly, like coughing a lot or lifting heavy, can cause hernias too.
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Obesity and weight gain
- Previous abdominal surgeries
- Chronic conditions causing increased abdominal pressure
Knowing these risks helps prevent and catch hernias early in women.
The Most Common Hernia in Females: Types and Locations
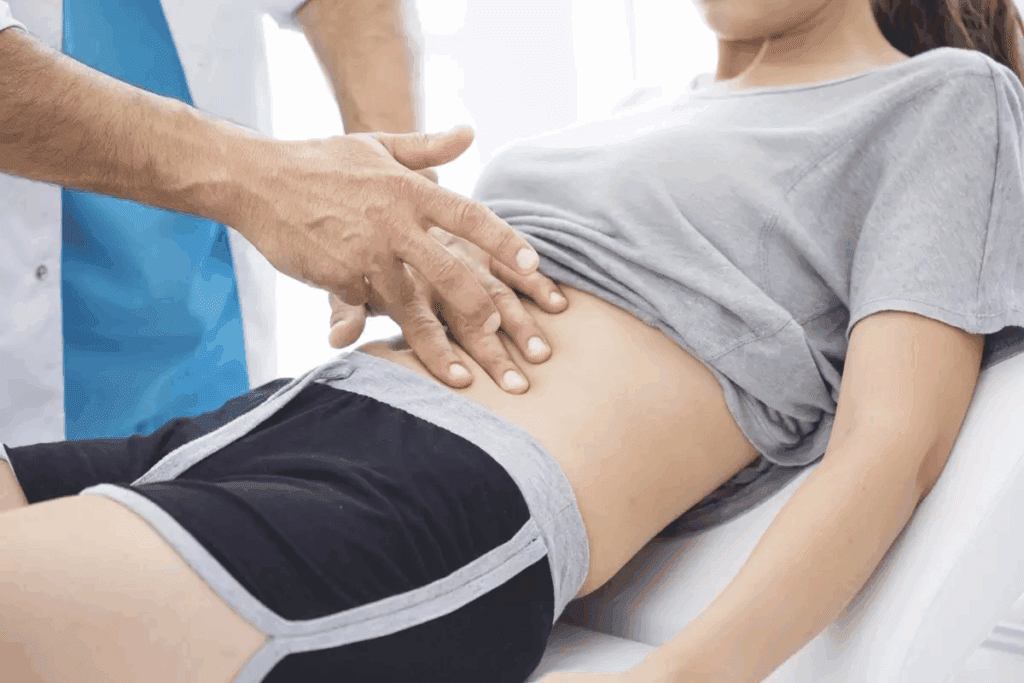
It’s important to know about the most common hernias in women. This knowledge helps doctors diagnose and treat them better. Each type of hernia has its own features and risks.
Femoral Hernias: The Female Predominant Type
Femoral hernias are more common in women, often after they turn 65. They happen when tissue bulges through the femoral canal. Femoral hernias are a big concern for women because they can easily get cut off, which is a medical emergency.
Umbilical Hernias: Causes and Characteristics
Umbilical hernias often affect women, mainly those who have had many babies. They happen near the belly button and are linked to high abdominal pressure. Being overweight or having had surgery before can increase the risk of getting one.
Inguinal Hernias: Less Common but Significant
Inguinal hernias are less common in women than in men but are serious. They happen when tissue bulges through a weak spot in the groin area. Women’s inguinal hernias are harder to spot because they are smaller and show up differently than in men.
Incisional and Other Abdominal Hernias
Incisional hernias come through a scar or cut in the belly. Other hernias, like Spigelian and obturator hernias, are rarer but can be serious. They need careful diagnosis and treatment.
Can Women Get Hernias? Dispelling Myths
Many think hernias are rare in women, but research shows some types are more common in females. Hernias can happen to anyone, and it’s important to know the gender differences in hernia development.
Gender Differences in Hernia Development
While men get hernias more often, women are not immune. Femoral hernias are more common in women because of their wider pelvis. This wider pelvis can put extra strain on the femoral canal.
- Femoral hernias are more common in women than in men.
- Women are more likely to experience complications due to delayed diagnosis.
- The wider pelvis in women can increase the risk of certain types of hernias.
Why Hernias Are Often Overlooked in Women
Hernias in women are often missed or misdiagnosed. Symptoms can be vague, and doctors might not think of hernia first.
- Symptoms are often attributed to other gynecological conditions.
- Lack of awareness about hernias in women among some healthcare providers.
- The presentation of hernias can be different in women, making diagnosis challenging.
It’s key to spread the word about hernias in women. We must make sure doctors consider hernia when they see symptoms in female patients.
Unique Presentation: Why Hernias in Women Are Different
Hernias in women often show up differently than in men. This makes finding the right diagnosis tough. The main reason is the unique body shapes of men and women.
Anatomical Differences Affecting Presentation
The way the abdominal wall and nearby areas are built varies between genders. In women, hernias often pop up in spots that don’t show a bulge, like the femoral canal.
Key anatomical differences include:
- The broader pelvis in women, which can affect the distribution of abdominal pressure.
- The presence of the femoral canal, a possible weak spot.
- Differences in muscle and fascia structure.
The “No Bulge” Phenomenon in Female Hernias
One big challenge in spotting hernias in women is the “no bulge” phenomenon. Unlike men, who often have a visible bulge, women might not show this symptom.
The table below shows the main differences in how hernias appear in men and women:
| Characteristic | Male Hernias | Female Hernias |
| Visible Bulge | Common | Less Common |
| Typical Location | Inguinal region | Femoral or umbilical region |
| Symptoms | Often localized pain | Diffuse pain, sometimes radiating |
It’s key for doctors to know these differences to correctly diagnose and treat hernias in women.
Symptoms of Hernia in Female Patients
It’s important to know the symptoms of hernia in women to catch it early. Hernias in women can be different from those in men. This can lead to a delay in finding out what’s wrong.
Pelvic and Lower Abdominal Pain Patterns
Women with hernias often feel pain in their pelvis and lower belly. This pain can change in how bad it is and how often it happens. Sometimes, the pain gets worse when you do certain things.
Common Pain Patterns:
- Pelvic pain that goes to the groin or thigh
- Lower belly pain that gets worse when lifting or bending
- Pain that gets more uncomfortable with physical activity
Discomfort Characteristics: Aching, Burning, and Sharp Pain
The pain from hernias in women can feel like a dull ache, burning, or sharp. The kind of pain you feel can tell you about the type and how bad the hernia is.
| Pain Type | Description | Possible Causes |
| Aching | Dull, persistent discomfort | Early stages of hernia, mild protrusion |
| Burning | Sharp, intense pain | Irritation of nerves, incarcerated hernia |
| Sharp | Sudden, severe pain | Strangulation, severe incarceration |
Activity-Related Symptoms and Triggers
Many activities can make symptoms of hernia in women worse. Knowing what these are can help manage the condition.
Common Triggers:
- Lifting heavy objects
- Bending or straining
- Coughing or sneezing
- Physical exercise, like activities that strengthen the core
By knowing these symptoms and triggers, doctors can give better diagnoses and treatment plans for women with hernias.
Hernia Lower Left Abdomen Female: Specific Concerns
Diagnosing hernias in the lower left abdomen of female patients needs a deep understanding. Hernias in this area are tricky because their symptoms are not clear and the abdominal anatomy is complex.
Distinguishing Features of Left-Sided Hernias
Left-sided hernias in the lower left abdomen have unique signs. They often cause pain or discomfort in the left lower abdomen. The pain gets worse with physical activity, coughing, or straining. You might also feel a heavy or pressured feeling in the groin or lower abdomen.
In women, left-sided hernias can be hard to spot because of other gynecological issues. A detailed clinical check-up and a keen eye for diagnosis are key.
Differential Diagnosis with Other Conditions
When diagnosing left-sided hernias, it’s important to tell them apart from other causes of lower left abdominal pain. These include diverticulitis, ovarian cysts, endometriosis, and inflammatory bowel disease. A thorough diagnostic process is vital to avoid mistakes and get the right treatment.
“The clinical presentation of hernias in women can be subtle and may not always include a palpable mass, making diagnosis more challenging.” – Dr. Jane Smith, General Surgeon
To correctly diagnose left-sided hernias, doctors might use imaging like ultrasound or MRI. These tests can confirm a hernia and rule out other issues.
- Ultrasound: Good for spotting hernias and checking their size and content.
- MRI: Offers detailed views of the abdominal wall, helping spot hernias not seen on ultrasound.
By knowing the unique signs of left-sided hernias and using a detailed diagnostic method, doctors can better diagnose and treat female patients with hernias in the lower left abdomen.
Early Stage Female Real Hernia: Detection Challenges
Finding hernias early in women is hard because the first signs are often small. Women don’t always show the same symptoms as men. This makes it harder to diagnose.
Subtle Initial Manifestations
Women with hernias might not have the usual bulge seen in men. Instead, they might feel mild discomfort or pain. This can be confused with other health issues.
As one study found, “The absence of a clear bulge can lead to delays in diagnosis.”
Some common first signs include:
- Pelvic or lower abdominal pain
- Aching or burning sensations
- Discomfort during physical activities
Progression Timeline and Warning Signs
Knowing how a hernia grows is key to catching it early. Hernias can take time to develop. Spotting early warning signs can help women get help sooner.
Important warning signs are:
- Increasing pain or discomfort
- Pain that gets worse with activity
- Nausea or vomiting in severe cases
As a medical expert once said,
“Prompt recognition of hernia symptoms can significantly improve treatment outcomes.”
So, it’s vital for women to know these signs. If they have ongoing or severe symptoms, they should see a doctor.
When to Worry About Hernia Pain Female: Red Flags
It’s important for women to know the signs of hernia problems. Hernias can cause serious issues if not treated right away.
Symptoms Requiring Urgent Medical Evaluation
Some symptoms mean you need to see a doctor fast. These include:
- Severe or getting worse pain
- Vomiting or feeling sick
- Fever or feeling cold
- A tender or painful lump in the belly
- Abdominal tenderness or guarding
If you notice any of these, get medical help right away.
Complications of Untreated Hernias in Women
Ignoring hernias can cause big problems. These include:
- Strangulation: When the blood supply to the hernia is cut off, causing tissue death.
- Incarceration: When the hernia gets trapped and can’t go back inside.
- Obstruction: A blockage of the intestine, causing severe pain, vomiting, and constipation.
These issues can be very serious and need quick medical help.
Emergency Situations: Recognizing Strangulation
Strangulation is a serious emergency. Look out for these signs:
- Severe pain at the hernia site
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- A tender, red, or discolored lump
If you think you have strangulation, get to the emergency room fast. Quick action can prevent serious problems and save lives.
Diagnosis Challenges: Hernias vs. Gynecological Conditions
Diagnosing hernias in women is tough because symptoms can look like other gynecological issues. The female body’s complexity and similar symptoms make it hard to get a correct diagnosis. This often leads to wrong or late diagnoses.
Common Misdiagnoses in Female Patients
Hernias in women are often mistaken for conditions like ovarian cysts, endometriosis, or pelvic inflammatory disease. Symptoms like pelvic pain or lower abdominal discomfort are shared. Getting the right diagnosis needs a careful look and thorough check-up.
Comprehensive Diagnostic Approach
It’s important to use a detailed approach to tell hernias apart from gynecological issues. This includes a full medical history, physical exam, and imaging tests. Doctors should always think of hernia when seeing women with belly or pelvic pain.
The physical exam should focus on the groin and belly. The cough test can help spot hernias by showing a bulge or tenderness.
Advanced Imaging Techniques for Accurate Diagnosis
Modern imaging is key in diagnosing hernias in women. Ultrasound is often first because it’s safe and good at showing soft tissues. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is used for tricky cases or when ultrasound doesn’t help.
Computed Tomography (CT) scans might be used in some cases, like for finding complications or other causes of symptoms. The right imaging depends on the situation and what’s suspected.
Treatment Options for Abdominal Hernia in Women
Understanding and treating abdominal hernias in women is key. The right treatment depends on the hernia’s type, size, and the woman’s health.
Conservative Management Approaches
Women with small, painless hernias might not need surgery. Instead, they can watch the hernia and make lifestyle changes. These changes help reduce strain on the belly and manage any discomfort.
Lifestyle adjustments are important. They include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce abdominal pressure
- Avoiding heavy lifting or bending
- Managing chronic coughing or constipation
- Engaging in appropriate physical activity to strengthen abdominal muscles
Surgical Techniques and Innovations
For many, surgical repair is the best option. Modern surgery offers quick recovery and fewer risks.
There are several surgical methods:
- Open repair: A traditional method involving a single incision
- Laparoscopic repair: Minimally invasive surgery using several small incisions
- Robotic repair: An advanced form of laparoscopic surgery with enhanced precision
| Surgical Method | Benefits | Recovery Time |
| Open Repair | Effective for large hernias, straightforward technique | Typically 4-6 weeks |
| Laparoscopic Repair | Less invasive, reduced risk of infection, quicker recovery | Usually 1-3 weeks |
| Robotic Repair | High precision, less tissue damage, faster recovery | Generally 1-2 weeks |
Recovery Considerations Specific to Women
Recovery times can vary. Women should focus on post-operative care. This includes managing pain, wound care, and gradually getting back to normal activities.
Knowing about hernia treatments helps women make better choices. They can consider the hernia type, health, and personal preferences when choosing a treatment.
Risk Factors and Prevention of Hernias in Women Abdomen
Several risk factors can lead to abdominal hernias in women. It’s important to know these factors to catch and manage them early.
Age-Related Risk Factors
Age is a big risk for hernias in women. As women get older, their abdominal muscles weaken. Women over 50 are at higher risk because of muscle weakness and age.
Pregnancy and Childbirth Considerations
Pregnancy and childbirth can weaken abdominal muscles. This risk grows with each pregnancy. Good prenatal care and postpartum recovery can help lower these risks.
Lifestyle Modifications and Preventive Strategies
Changing your lifestyle can help prevent hernias. Keeping a healthy weight, avoiding heavy lifting, and managing coughs or sneezes are key. Also, eating foods high in fiber can prevent constipation, a risk factor for hernias.
- Eating a balanced diet to maintain a healthy weight
- Avoiding smoking to reduce chronic coughing
- Engaging in regular, gentle exercise to strengthen core muscles
Core-Strengthening Exercises for Prevention
Doing exercises that strengthen the core can lower hernia risk. Exercises like planks and pelvic tilts target the abdominal muscles. Start slowly and increase intensity gradually to avoid injury.
By knowing the risks and taking preventive steps, women can lower their chance of getting hernias. Being aware and proactive is key to keeping the abdomen healthy.
Conclusion
It’s key to understand female real hernias for women’s health. These conditions can really affect life quality if not treated or diagnosed right.
Hernias in women are complex. They have unique signs and are hard to diagnose. This shows we need more awareness and education.
Women can help keep their belly healthy by knowing the signs, risks, and treatments. This way, they can avoid problems linked to female real hernias.
Getting a correct diagnosis and treatment on time is vital for managing hernias. This highlights the need for a full approach to women’s health, including knowing about hernias.
FAQ
What is a hernia in women?
A hernia in women happens when an organ or tissue bulges through a weak spot in the belly wall. This can cause pain and discomfort.
Can women get hernias?
Yes, women can get hernias, though they’re less common than in men. They can appear in the groin, navel, or belly wall.
What are the most common types of hernias in females?
Females often get femoral, umbilical, inguinal, and incisional hernias.
What are the symptoms of a hernia in women?
Women with hernias might feel pain or discomfort in their pelvis and lower belly. This pain can get worse when they cough, lift, or bend.
How is a hernia diagnosed in women?
Diagnosing hernias in women can be tricky. It’s because they might not show a bulge and can look like other gynecological issues. Doctors use a detailed approach, including physical exams and imaging, to figure it out.
What are the treatment options for abdominal hernias in women?
Women with abdominal hernias have several treatment options. These include non-surgical methods, surgery, and new ways to repair hernias. The best choice depends on the hernia’s type, size, and how serious it is.
Can hernias be prevented in women?
While some risks can’t be changed, women can lower their chances of getting a hernia. They can do this by keeping a healthy weight, exercising, and strengthening their core muscles.
When should I worry about hernia pain in women?
If a woman’s hernia pain is severe, doesn’t go away, or comes with other symptoms like nausea or fever, she should seek help right away. Any red flags or signs of serious problems need immediate medical attention.
What are the complications of untreated hernias in women?
Untreated hernias in women can cause serious problems. These include strangulation, bowel obstruction, or incarceration. These issues need emergency care.
How can I reduce my risk of developing a hernia?
To lower your risk of getting a hernia, live a healthy lifestyle. Eat well, exercise regularly, and avoid heavy lifting or bending.
Are there any specific concerns related to hernias in the lower left abdomen in women?
Yes, hernias in the lower left abdomen in women can be hard to diagnose. This is because they can look like other conditions. A thorough diagnostic process is needed to accurately diagnose and treat these hernias.
References
Andrews, S., et al. (2013). Gallstone size e related to the incidence of post-cholecystectomy retained bile duct stones. Surgery Journal, 5(3), 143-147. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1743919113000484























