Hernias are a common medical issue that can take many forms.can a hernia cause diarrhoeaEating After Hernia Surgery: Recovery From Inguinal Hernia Surgery These include inguinal, femoral, umbilical, epigastric, hiatal, and incisional hernias. The most common sign of a hernia is a soft swelling or bulge under the skin. This bulge is often only visible when standing and goes away when lying down.
Liv Hospital stresses the need for modern medical care for hernia-related issues. This includes digestive problems like diarrhea.
Key Takeaways
- Hernias can occur in various forms, including inguinal, femoral, and hiatal hernias.
- Some hernias may cause digestive problems, such as diarrhea.
- Liv Hospital prioritizes patient-focused care and up-to-date academic protocols.
- A soft swelling or bulge under the skin is a common sign of a hernia.
- Proper medical care is essential for addressing hernia-related issues.
Understanding Hernias: Definition and Basic Concepts
A hernia happens when an organ or tissue bulges through a weak spot in the muscle or connective tissue. This weak spot is usually where the tissue should be held in place. Hernias can occur in different parts of the body, leading to various types.
What Constitutes a Hernia?
A hernia is when an organ or tissue bulges through a weak spot in the muscle or fascial layer. This can happen due to congenital conditions, injury, or strain. Hernias are classified based on their location and the nature of the bulge.
Several factors can lead to hernia development. These include:
- Increased pressure within the abdominal cavity
- Weakness in the abdominal wall, which can be congenital or acquired
- Aging, as the muscles and tissues naturally weaken over time
Common Locations for Hernia Development
Hernias often occur in the abdominal region. Specific areas include:
- The groin area, where inguinal hernias occur
- The navel, where umbilical hernias are found
- The upper stomach, associated with epigastric hernias
It’s important to understand the different types of hernias and their characteristics. For example, an umbilical hernia is a tissue bulge near the belly button. It usually goes away by age 5 in children. But, it can cause problems in adults if not treated.
Different Types of Hernias and Their Characteristics
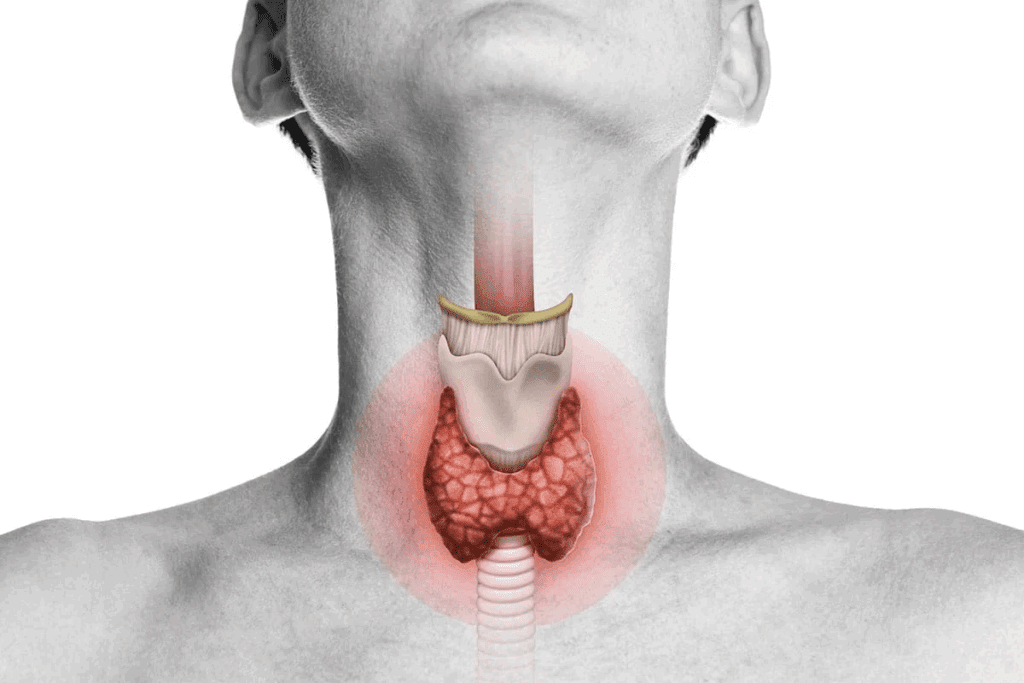
Knowing about the many types of hernias is key for diagnosis and treatment. Hernias can happen in different parts of the body. Their traits greatly affect symptoms and possible problems.
Inguinal Hernias
Inguinal hernias are very common. They happen when tissue, like part of the intestine, pushes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles. Most inguinal hernias happen in men, but women can get them too. Symptoms include a bulge in the groin area, which hurts, mainly when coughing, bending, or lifting heavy things.
Femoral Hernias
Femoral hernias happen just below the inguinal ligament, where the femoral artery goes into the thigh. These hernias are more common in women and linked to higher pressure inside the belly. Femoral hernias are risky because they can easily get stuck or cut off blood flow.
Umbilical Hernias
Umbilical hernias are around the belly button (navel) and are more common in babies, but adults can get them too. In adults, umbilical hernias are often linked to being overweight, having many babies, or other conditions that raise belly pressure. Symptoms include a visible bulge or swelling around the navel, which might hurt.
Epigastric Hernias
Epigastric hernias are in the upper midline of the belly, between the navel and the breastbone. These hernias are quite rare and usually show as a small, painless bulge. They can cause discomfort, mainly after eating.
To better understand these hernias, let’s look at a comparison table:
| Hernia Type | Common Location | Typical Symptoms | Risk Factors |
| Inguinal | Groin area | Bulge, pain when coughing or lifting | Men, age, family history |
| Femoral | Below inguinal ligament | Pain, risk of incarceration | Women, increased abdominal pressure |
| Umbilical | Around the navel | Visible bulge, pain | Infants, obesity, multiple pregnancies |
| Epigastric | Upper midline abdomen | Small bulge, discomfort after eating | Relatively rare, associated with abdominal wall defects |
It’s important to know that while these hernias differ, they can all lead to serious problems if not treated right. Knowing the specific type of hernia and its traits is key to finding the best treatment.
Can a Hernia Cause Diarrhea? Exploring the Connection
To understand if hernias can cause diarrhea, we need to know how different hernias affect our digestive system. Hernias happen when an organ or tissue bulges through a weak spot in the muscle or tissue that usually keeps it in place. While hernias often cause abdominal pain, their link to diarrhea is more complicated.
Mechanisms Behind Hernia-Related Digestive Symptoms
Hernias can become more common with age, physical strain, or weak abdominal muscles. Some hernias can mess with how our intestines move, leading to diarrhea. This is because they can block part of the bowel or put pressure on it.
Here are some main ways hernias can affect our digestion:
- Mechanical pressure on the intestines, which can cause bowel obstruction or slow digestion.
- Increased abdominal pressure, making symptoms like diarrhea worse.
- Irritation or inflammation of the herniated tissue, which can change our bowel habits.
If a hernia is not treated, it can become strangulated. This is a serious problem that can cause severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and even life-threatening issues. Symptoms include fever, diarrhea, and trouble passing gas or having a bowel movement.
Research Evidence on Hernia-Diarrhea Relationship
Research shows that some hernias are more likely to cause digestive problems, like diarrhea. For example, hiatal hernias can lead to gastroesophageal reflux. This can indirectly affect how we go to the bathroom.
Studies have found:
- Many patients with hernias have gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea.
- The type and location of the hernia can affect how likely and severe digestive symptoms are.
- Fixing hernias with surgery can often help with digestive problems, including diarrhea.
It’s important to understand the connection between hernias and diarrhea for proper treatment. By knowing how hernias can affect our digestion, doctors can better help patients with these symptoms.
Hiatal Hernias: The Primary Culprit for Digestive Disturbances
Hiatal hernias often cause digestive problems. They happen when part of the stomach pushes up into the chest. This can lead to issues like acid reflux, ulcers, and Barrett’s esophagus.
How Hiatal Hernias Affect Stomach Function
Hiatal hernias can mess with how the stomach works. When the stomach bulges into the chest, it can make the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) not work right. This can cause gastroesophageal reflux, leading to heartburn and regurgitation.
This can also change how food moves through the digestive system. It might cause diarrhea or constipation, making things worse.
Gastroesophageal Reflux and Bowel Changes
Gastroesophageal reflux is a big problem with hiatal hernias. It can cause esophagitis, strictures, and other issues. It can also mess with bowel habits, leading to diarrhea.
Liv Hospital uses the latest medical methods and teamwork to treat hiatal hernias. They might suggest lifestyle changes, medicines, or surgery to fix the hernia.
Symptoms Specific to Hiatal Hernias
Symptoms of hiatal hernias include heartburn, regurgitation, and trouble swallowing. Some people might feel chest pain, thinking it’s heart-related. Changes in bowel habits, like diarrhea or constipation, can also happen.
It’s key to know these symptoms to diagnose and treat hiatal hernias. By tackling the root cause, doctors can help patients feel better and improve their digestion.
Abdominal Hernias and Their Impact on Bowel Function
Abdominal hernias can really mess with your digestion. They happen when an organ or tissue bulges through a weak spot in the belly wall. The effect on your bowels depends on the hernia’s type and where it is.
Mechanical Interference with Intestinal Movement
Abdominal hernias can slow down or block food in your digestive system. This is because they put pressure on your intestines. This pressure can cause a bunch of problems, like pain, nausea, and changes in how often you go to the bathroom.
In some cases, it can even cause more serious issues. These include bowel obstruction or strangulation of the hernia.
Partial Bowel Obstruction Symptoms
Partial bowel obstruction is a big problem with hernias. You might feel:
- Intermittent abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Bloating and gas
These symptoms happen because the hernia is blocking part of your intestine. This messes up the normal flow of food and waste.
Hernia in the Lower Left Stomach Area
Hernias can pop up in different spots, like the lower left stomach area. These can be tough because they can press on the sigmoid colon. This can mess with your bowel habits and cause discomfort.
A table summarizing the key aspects of abdominal hernias and their impact on bowel function is provided below:
| Hernia Type | Location | Impact on Bowel Function |
| Inguinal Hernia | Groin area | Potential for bowel obstruction |
| Umbilical Hernia | Near the belly button | Possible interference with intestinal movement |
| Incisional Hernia | Through a previous surgical incision | Risk of bowel strangulation |
It’s important to know about the different hernias and how they affect your bowels. This helps doctors figure out the best way to treat you. By understanding the symptoms and risks, doctors can help you feel better and avoid more problems.
Recognizing Hernia Symptoms Beyond Diarrhea
Hernias are not just about visible bulges; they can cause a variety of symptoms depending on their type. Understanding these symptoms is key for early detection and treatment.
Common Symptoms Across Different Hernia Types
While symptoms can vary, there are common signs across different hernias. These include:
- A visible bulge or swelling in the affected area
- Discomfort or pain, often when coughing, lifting, or bending over
- A feeling of heaviness or pressure in the abdomen
- In some cases, gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or changes in bowel movements
It’s essential to note that not all hernias present with a visible bulge. Some may cause discomfort or pain without any noticeable swelling, making diagnosis more challenging.
When Symptoms Indicate a Medical Emergency
Certain symptoms can indicate a medical emergency, like a strangulated hernia. These include:
- Severe pain or tenderness in the hernia area
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- A hernia that becomes red, purple, or dark
- Inability to push the hernia back in or if it becomes incarcerated
Immediate medical attention is required if any of these symptoms occur. A strangulated hernia can lead to serious complications, including tissue death.
Recognizing hernia symptoms and knowing when they’re a medical emergency can greatly improve outcomes. If you’re experiencing any unusual or severe symptoms, it’s vital to seek medical evaluation promptly.
Stages of Hernia Development and Symptom Progression
It’s key to understand how hernias progress. Each stage has its own risks and symptoms. Knowing this helps spot complications early.
From Reducible to Incarcerated Hernias
At first, many hernias are reducible. This means they can be pushed back into the belly. But, if ignored, they can turn into incarcerated hernias.
An incarcerated hernia is trapped and can’t be pushed back. It causes a lot of pain and can lead to serious issues.
The chance of a hernia becoming incarcerated goes up with age and physical strain. It’s vital to watch for symptoms and get help if you notice severe pain or tenderness.
Strangulated Hernias: A Serious Complication
A strangulated hernia is a serious problem. It happens when the blood supply to the hernia is cut off. This is a medical emergency that needs quick action.
Symptoms include severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. If a hernia becomes strangulated, surgery is needed right away to save the tissue.
Going from a reducible hernia to an incarcerated or strangulated one shows why quick medical help is so important. Spotting the signs early can prevent serious problems.
Diagnosing Hernias When Digestive Symptoms Are Present Symptoms Are Present
Diagnosing hernias when you have digestive symptoms is complex. Symptoms can vary and might be caused by other issues in the gut.
Physical Examination Techniques
A detailed physical exam is the first step. Doctors use different methods to find hernias. They look for tenderness or masses.
Liv Hospital believes in a team effort for complex cases. This way, all possible causes are checked.
Key Physical Examination Techniques:
- Visual inspection for visible bulges or swelling
- Palpation to detect masses or tenderness
- Cough test to observe changes in the hernia size
Imaging Studies for Hernia Confirmation
Imaging studies are key to confirm a diagnosis. Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI are common tools used.
| Imaging Modality | Advantages | Limitations |
| Ultrasound | Non-invasive, cost-effective, real-time imaging | Operator-dependent, limited depth penetration |
| CT Scan | High-resolution images, useful for complex cases | Radiation exposure, higher cost |
| MRI | Excellent soft tissue differentiation, no radiation | Higher cost, claustrophobia issues |
“The choice of imaging modality depends on the clinical context and the suspected type of hernia.”
Differential Diagnosis: Ruling Out Other Causes
When digestive symptoms are present, ruling out other causes is important. Doctors must consider diseases like inflammatory bowel disease or diverticulitis.
A thorough diagnostic process is essential. It helps in accurate diagnosis and planning the right treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Hernia Symptoms
Knowing the difference between urgent and non-urgent hernia symptoms is key. Hernias can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe pain. It’s important to know when to seek medical help.
Urgent vs. Non-Urgent Symptoms
Not all hernia symptoms need immediate attention. But, some signs are urgent. Severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and trouble passing gas or having a bowel movement are urgent. These could mean a strangulated hernia, a serious issue that needs quick treatment.
On the other hand, mild discomfort, a bulge in the abdomen or groin, or feeling of heaviness or pressure might not be urgent. Yet, it’s important to see a healthcare professional. Watch your symptoms and get medical advice if they get worse or change.
| Symptom | Urgency Level | Action |
| Severe pain, nausea, vomiting | High | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Mild discomfort, bulge in abdomen or groin | Low to Moderate | Schedule a doctor’s visit |
What to Expect During Your Doctor’s Visit
At your doctor’s visit forhernia symptoms, expect a detailed check-up. The doctor will do a physical exam and might check for a bulge. They might also do imaging studies like an ultrasound or CT scan to confirm the diagnosis and see how severe the hernia is.
Tell your doctor everything about your symptoms. Share when they started, how bad they are, and what makes them better or worse. This helps your doctor figure out the best treatment for you.
Treatment Approaches for Hernias Causing Diarrhea
For hernias causing diarrhea, treatment plans are made just for you. They use the latest medical methods. At places like Liv Hospital, a team of experts works together to give you the best care.
Conservative Management Options
If your hernia isn’t too serious, conservative management might be suggested. This includes:
- Changing your diet to ease symptoms
- Making lifestyle changes to feel better
- Watching the hernia for any signs of trouble
These steps can often keep symptoms under control and stop things from getting worse.
Surgical Interventions: Traditional vs. Minimally Invasive
If other methods don’t work or your hernia is complex, surgical intervention is needed. There are two main types of surgery:
- Traditional Open Surgery: This uses a bigger cut to directly fix the hernia.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: This uses small cuts, a camera, and special tools to fix the hernia.
Most doctors prefer the minimally invasive method. It’s known for causing less pain, quicker recovery, and fewer complications.
What Do They Do for a Hernia During Surgery?
During hernia surgery, the main goal is to repair the hernia. This is done by:
- Pushing the bulging tissue back into place
- Fixing the weak spot, often with mesh
- Strengthening the area around it to prevent it from happening again
The type of surgery depends on the hernia’s type, size, and your health.
Post-Treatment Expectations for Digestive Symptoms
After treatment, whether it’s non-surgical or surgery, symptoms should start to get better. If you had surgery, following postoperative care instructions is key. It helps you heal well and avoids problems.
Digestive issues like diarrhea should get better as you heal. Sometimes, you might need to adjust your diet to manage symptoms.
Knowing about treatment options and what to expect after treatment helps you make informed choices. This is important for managing hernias that cause diarrhea.
Recovery and Long-Term Outcomes After Hernia Treatment
Knowing how long it takes to recover from hernia treatment is key. It helps patients set realistic goals and make smart choices about their health.
Timeline for Symptom Resolution
The time it takes for symptoms to get better varies. It depends on the hernia type, treatment, and the patient’s health. Usually, symptoms start to improve in a few weeks after surgery. But, it might take longer to get back to normal activities.
Immediate Post-Surgery Recovery: Right after surgery, patients might feel pain, swelling, and bruising. Doctors use medicine and rest to help manage pain.
Short-Term Recovery: Within 1-2 weeks, patients can start doing light activities. How fast you recover depends on your age, health, and if you have any complications.
Potential Complications and Recurrence Rates
Hernia treatment works well most of the time. But, there are risks of complications and recurrence.Medical organization says knowing these risks helps manage expectations and ensures proper care.
| Complication | Description | Prevention/ Management |
| Infection | Bacterial infection at the surgical site | Antibiotics, proper wound care |
| Recurrence | Hernia reoccurs at the same site | Proper surgical technique, lifestyle modifications |
| Chronic Pain | Long-term pain or discomfort | Pain management strategies, potentially further surgery |
Follow-up Care Recommendations
Follow-up care is vital for recovery. Patients should see their doctor regularly. This helps monitor healing and address any issues quickly.
By understanding the recovery process and following up with care, patients can get the best results. This also helps avoid complications.
Preventing Hernias and Managing Digestive Symptoms
To prevent hernias, making lifestyle modifications and dietary adjustments is key. These changes help keep your digestive system healthy. They also lower the chance of getting hernias and ease digestive problems.
Lifestyle Modifications for Hernia Prevention
Changing your lifestyle can help prevent hernias. Here are some important steps:
- Keep a healthy weight to ease pressure on your abdominal muscles.
- Stay away from heavy lifting and bending to avoid straining your abdominal wall.
- Quit smoking to boost your health and reduce coughing, which can harm your abdominal muscles.
- Manage chronic conditions like constipation to avoid straining during bowel movements.
By making these lifestyle changes, you can lower your risk of getting a hernia.
Dietary Adjustments to Minimize Symptoms
Changing what you eat is vital for managing digestive symptoms linked to hernias. Here are some tips:
- Eat more fiber to prevent constipation and keep bowel movements regular.
- Stay away from foods that upset your stomach, like spicy or fatty foods.
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals to ease stomach pressure and improve digestion.
- Drink plenty of water to prevent constipation and support your digestive health.
These dietary changes can help lessen symptoms like diarrhea and discomfort from certain hernias.
Physical Activity Guidelines for Hernia Patients
Right physical activity is important for health and can help prevent hernias. Here are some guidelines:
- Do regular, low-impact exercises like walking or swimming to stay healthy without straining your abdominal muscles.
- Avoid high-impact activities or heavy lifting that can strain your abdominal wall.
- Do exercises that strengthen your core muscles, like gentle abdominal exercises, for extra support.
- Slowly increase your physical activity to avoid sudden strain on your body.
By following these physical activity guidelines, you can support your health and lower the risk of hernias.
Conclusion: Understanding the Relationship Between Hernias and Digestive Health
It’s key to understand how hernias and digestive health are connected. Different types of hernias can lead to symptoms like diarrhea. This happens because of mechanical issues or other factors.
Liv Hospital stresses the need for a team effort in treating hernias. They point out that a complete care plan is vital. Knowing which hernias cause digestive problems and the treatment choices is critical for doctors.
By recognizing the connection between hernias and digestive health, patients can get the right treatment. This improves their life quality. A team-based care approach helps avoid complications and reduces the chance of hernias coming back.
FAQ
What kind of hernia is most likely to cause diarrhea?
Hiatal hernias often cause digestive issues like diarrhea. This is because they affect stomach function and lead to reflux.
Can a hernia cause diarrhea?
Yes, some hernias can cause diarrhea. This is true for hernias in the abdominal cavity or those that press on the intestines.
What are the different types of hernias?
There are many types of hernias. These include inguinal, femoral, umbilical, epigastric, and hiatal hernias. Each has its own characteristics and risks.
How do hernias affect bowel function?
Hernias in the abdomen can block the intestines. This can lead to symptoms like changes in bowel habits.
What are the symptoms of a hernia in the lower left stomach area?
Symptoms include a bulge, discomfort, and pain. Digestive issues can also occur, depending on the hernia’s size and location.
How is a hernia diagnosed when digestive symptoms are present?
Doctors use physical exams and imaging like ultrasound or CT scans. They also rule out other causes of symptoms.
When should I seek medical attention for hernia symptoms?
Seek help for severe pain, vomiting, or bowel obstruction. Even mild discomfort or bulges should be checked by a doctor.
What are the treatment options for hernias causing diarrhea?
Treatment can be non-surgical or surgical. Options include lifestyle changes and surgery, which can be traditional or minimally invasive.
What can I expect during hernia surgery?
Surgery involves pushing the bulge back and reinforcing the area. This is often done with mesh.
How long does it take for digestive symptoms to resolve after hernia treatment?
Recovery time varies. It depends on the hernia type and treatment. But many see relief soon after treatment.
Can hernias be prevented?
Preventing all hernias is not possible. But, staying healthy, avoiding heavy lifting, and managing coughing can help reduce risk.
What are the possible complications of untreated hernias?
Untreated hernias can cause serious problems. These include incarceration, strangulation, and bowel obstruction. This shows why timely treatment is key.
References
Muleta, J., et al. (2024). A rare case of bile leak due to type 2 duct of Luschka injury: Diagnosis and intervention. Journal of Surgical Case Reports. Retrieved from https://academic.oup.com/jscr/article/2024/3/rjae179/7632948



































