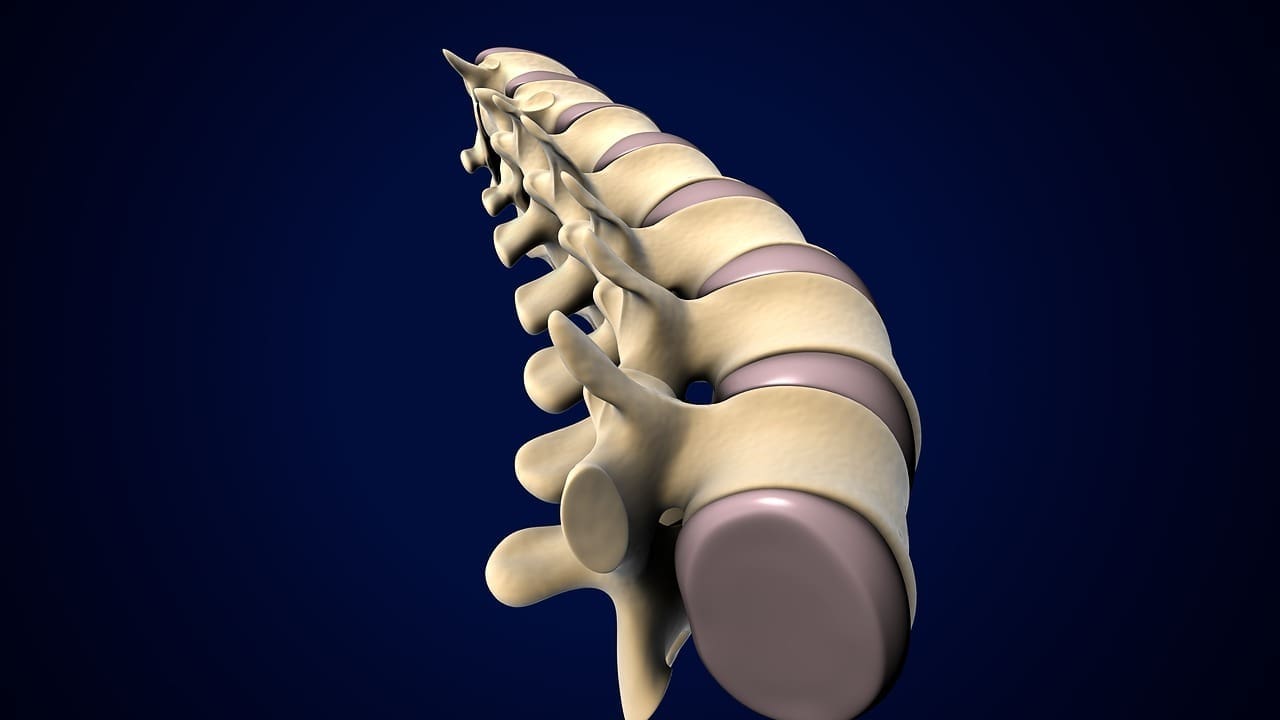
At Liv Hospital, we see many patients confused by slipped disc and herniated disc. These terms are often mixed up, but they mean different things in medical terms.
A herniated disc happens when the soft part of a spinal disc bulges out through a tear. A slipped disc, on the other hand, is a term used by non-medical people. It usually means the same thing as a herniated disc, or a milder issue like a disc bulge.
It’s important to know the difference between these conditions to get the right treatment. Research shows that discs at L4-L5 and L5-S1 are most likely to herniate. In this article, we’ll look at symptoms, causes, and treatments to help those seeking care.
Key Takeaways
- The terms “slipped disc” and “herniated disc” are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings.
- A herniated disc involves the soft center pushing out through a tear in the outer layer.
- Lumbar discs at L4-L5 and L5-S1 are most commonly affected by herniation.
- Understanding the differences between these conditions is key for effective treatment.
- Liv Hospital offers expert, patient-focused care for spinal disc problems.
Understanding Spinal Disc Anatomy
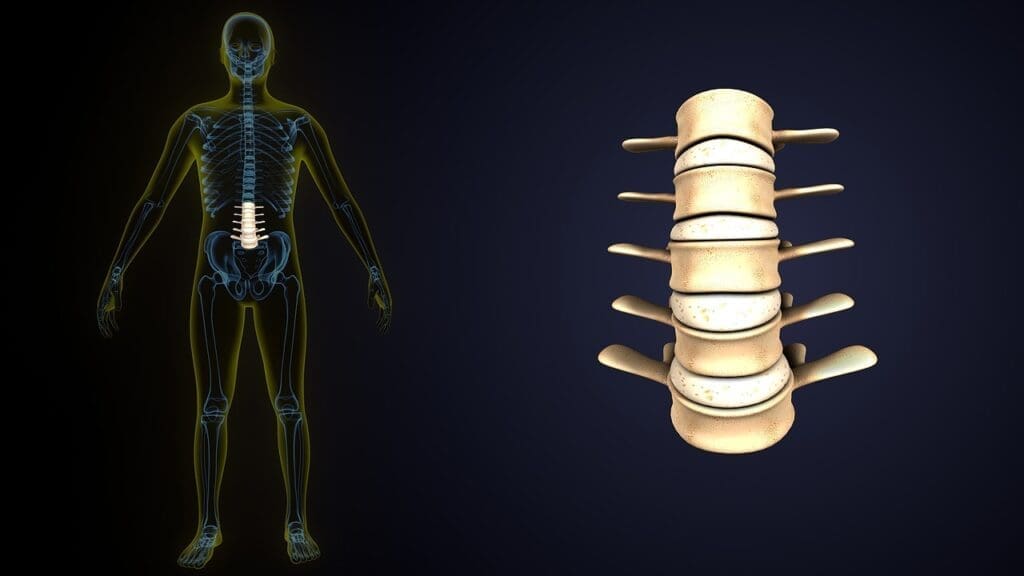
To understand the difference between a slipped disc and a herniated disc, we need to know about spinal discs. These discs are key parts of our spine. They support our body, help us move, and absorb shock.
Structure of a Healthy Spinal Disc
A healthy spinal disc has two main parts: the nucleus pulposus and the annulus fibrosus. The nucleus pulposus is soft and gel-like, helping to absorb shock. The annulus fibrosus, a tougher ring, keeps the disc’s shape and holds the nucleus in place.
Function of Spinal Discs in the Vertebral Column
Spinal discs do many things for our spine. They act as shock absorbers, spreading pressure evenly. They also help us move by allowing bending, twisting, and rotation. Plus, they keep the spacing between vertebrae right, so nerves can move freely.
Common Locations for Disc Problems
Disc problems often happen in the lumbar and cervical regions of the spine. The lumbar area, which bears our weight, is more prone to issues. The L4-L5 and L5-S1 levels are usually affected.
| Spinal Region | Common Disc Issues | Typical Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Lumbar | Herniated discs, degenerative disc disease | Lower back pain, sciatica |
| Cervical | Herniated discs, bulging discs | Neck pain, radiating pain to arms |
Slipped Disc vs Herniated Disc: Key Differences
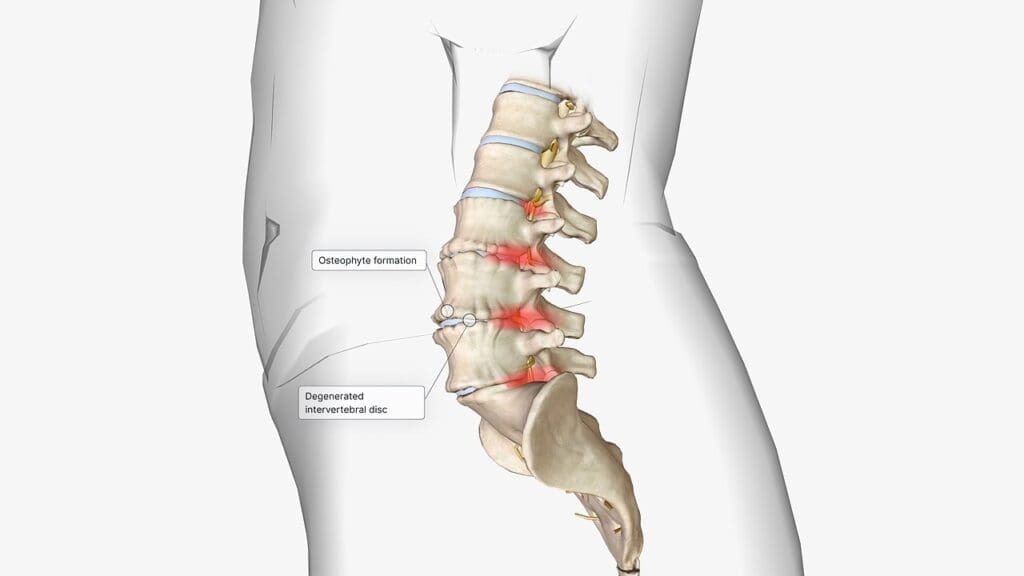
The terms “slipped disc” and “herniated disc” are often mixed up, but they mean different things in medicine. Knowing these differences is key for the right diagnosis and treatment.
What Medical Professionals Mean by “Herniated Disc”
A herniated disc happens when the soft center of the spinal disc leaks out. This leak is through a tear in the outer layer. It can hurt nearby nerves, causing pain, numbness, or weakness. Doctors call this specific problem a herniated disc, which they can spot with MRI or CT scans.
The Non-Medical Term “Slipped Disc”
The term “slipped disc” is not a real medical term. It’s used to describe a herniated or bulging disc in simple terms. But “slipped disc” doesn’t really tell you what’s wrong, which can confuse people about their diagnosis.
Why Terminology Matters in Diagnosis
Using the right words is very important in medicine. Studies show that the words used can change how a problem is treated. Getting the diagnosis right means using clear, specific language. This ensures patients get the right care for their issue. Knowing the difference between a slipped disc and a herniated disc shows how important it is to understand medical terms.
- Accurate diagnosis depends on precise terminology.
- Clear language ensures appropriate treatment plans.
- Understanding medical terms improves patient care.
By knowing the difference between these terms, patients can understand their diagnosis better. This leads to better care.
Types of Disc Problems Explained
Spinal disc issues come in many forms, each with its own set of challenges. We’ll look at herniated discs, bulging discs, degenerative disc disease, and disc sequestration and extrusion.
Herniated Discs: When the Nucleus Pushes Through
A herniated disc happens when the soft inner part of the disc leaks out. This can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the back and legs. Key symptoms include:
- Sharp pain in the lower back or neck
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the extremities
- Weakness in the muscles
Bulging Discs: Protrusion Without Rupture
Bulging discs happen when the disc pushes out without tearing. This can be painless or cause mild to moderate discomfort. It’s essential to monitor bulging discs as they can lead to more serious problems if not managed well.
Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease is when spinal discs lose their shape and function over time. Studies show it’s linked to imbalances in the body’s repair and inflammation processes. Treatment options include conservative management and physical therapy.
Disc Sequestration and Extrusion
Disc sequestration is when a disc fragment breaks off and moves away. Disc extrusion is when the disc bulges out a lot. Both can cause a lot of pain and neurological symptoms, often needing medical help.
Different Types of Bulging Discs
Knowing the types of bulging discs is key for the right diagnosis and treatment. Each type has its own set of symptoms and treatment options.
Circumferential Bulges: Even Protrusion
Circumferential bulges happen when the disc bulges evenly around its whole edge. This is often due to wear and tear on the disc.
Focal Bulges: Partial Protrusion
Focal bulges are when only part of the disc bulges out. These can cause more problems if they press on nerves.
Broad-Based Bulges
Broad-based bulges involve a big part of the disc bulging out, over 25% of its edge. They can also press on nerves.
Distinguishing Bulges from Herniations
It’s important to tell bulging discs apart from herniated discs. Herniated discs have a bigger problem with the disc’s outer layer. Accurate diagnosis is vital for the right treatment.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Knowing what causes disc problems is key to preventing and treating them. We’ve found several main factors that lead to disc issues.
Age-Related Degeneration
As we get older, our spinal discs change naturally. They lose water, becoming less flexible and more likely to crack. This can cause degenerative disc disease, a common issue in older adults.
Traumatic Injuries
Events like falls or car accidents can hurt the spinal discs right away. A sudden impact can cause herniation or other injuries.
Repetitive Movements and Poor Posture
Doing the same movements over and over can wear down the spine. This is often due to bad posture or jobs that involve heavy lifting or bending.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics can also play a part in disc problems. People with a family history of back issues might be more likely to have disc problems.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Discs |
|---|---|---|
| Age-Related Degeneration | Natural aging process affecting disc health | Loss of water content, reduced flexibility |
| Traumatic Injuries | Sudden, forceful impacts on the spine | Immediate damage, possible herniation |
| Repetitive Movements | Repeated strain on the spinal discs | Wear and tear speed up |
| Genetic Predisposition | Family history influencing disc health | Higher risk of disc problems |
By knowing these risk factors, we can take steps to avoid them. This can help keep our spines healthy and improve our overall well-being.
Symptoms: How Herniated and Bulging Discs Differ
It’s important to know the symptoms of herniated and bulging discs to get the right treatment. Both affect the spinal discs but show different signs.
Pain Patterns and Intensity
The pain from herniated and bulging discs can vary. Herniated discs usually cause sharp, intense pain because they press on nerves. Bulging discs, on the other hand, might lead to a dull, widespread pain.
Key differences in pain patterns include:
- Herniated discs: Sharp, shooting pain that radiates along the nerve pathway
- Bulging discs: Dull, aching pain that may be more widespread
Neurological Symptoms: Numbness and Weakness
Neurological symptoms are more common in herniated discs. This is because they directly press on nerves. Symptoms can include:
- Numbness or tingling sensations
- Muscle weakness
Functional Limitations
Both conditions can limit how you function. But herniated discs often cause more severe restrictions. This is due to intense pain or nerve problems.
When Symptoms Require Immediate Medical Attention
Some symptoms need quick medical help. These include:
- Sudden onset of severe pain
- Progressive numbness or weakness
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
Most Commonly Affected Spinal Regions
Disc problems can happen anywhere in the spine. But some areas get hit more often. The spine has three main parts: cervical, thoracic, and lumbar. Each part has its own special traits and is more likely to have disc issues.
Lumbar Disc Problems (L4-L5 and L5-S1)
The lumbar area, mainly the L4-L5 and L5-S1 levels, sees a lot of disc herniation. This is because these spots take a lot of stress. Studies show most lumbar disc herniations happen here, often because of wear and tear and sudden injuries.
Cervical Disc Issues
Cervical disc problems are common too, mainly in the lower neck. These can cause neck pain and arm symptoms. Poor posture and repetitive strain often play a role.
Thoracic Disc Conditions
Thoracic disc issues are less common but serious. The thoracic spine is usually stable. But when disc problems do happen, they can cause big problems.
Why Certain Areas Are More Vulnerable
Some spine areas are more likely to have disc problems. This is because of stress, wear and tear, and genetics. Knowing this helps in preventing and treating these issues.
Disc problems can affect different spine areas, with the lumbar region being the most common. “The lumbar spine carries a lot of the body’s weight and stress,” say spinal health experts. This makes it more likely to have disc issues.
Diagnostic Approaches for Disc Problems
Diagnosing disc problems involves several steps. We use clinical evaluation and advanced imaging. This helps us find the right treatment for each patient.
Physical Examination Techniques
Our first step is a thorough physical exam. We check range of motion, muscle strength, and reflexes. Tests like the straight leg raise help spot lumbar disc herniation.
Imaging Studies: MRI, CT, and X-rays
Imaging is key to confirming disc problems. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) shows disc anatomy and herniations. Computed Tomography (CT) scans and X-rays check bones and rule out other issues.
Electromyography and Nerve Conduction Studies
In some cases, we use electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (NCS). These tests check nerve function. They help us understand the extent of nerve damage.
Differential Diagnosis Considerations
We also look at other possible causes of symptoms. This includes degenerative joint disease, spinal stenosis, or peripheral neuropathy. A detailed exam helps us rule out these conditions and find the right diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Disc Conditions
There are many ways to treat disc conditions. Each method has its own benefits and things to think about. The right treatment depends on how bad the condition is, the patient’s health, and what they prefer.
Conservative Management Approaches
Conservative management is often the first step. It aims to lessen symptoms and improve function without surgery. We suggest rest, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies like chiropractic care or acupuncture.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy is key in managing disc conditions. A custom exercise plan can strengthen spine muscles, boost flexibility, and cut down pain. We team up with physical therapists to create safe and effective plans for our patients.
Medications for Pain and Inflammation
Medicines help manage pain and inflammation from disc conditions. We might prescribe NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, or oral steroids to ease symptoms.
Interventional Procedures
For those who don’t get better with conservative methods, we consider interventional procedures. These include epidural steroid injections or nerve blocks to reduce inflammation and pain.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is for severe cases that haven’t improved with other treatments. Options might be discectomy, spinal fusion, or artificial disc replacement. We talk about the risks and benefits with our patients to choose the best option.
We take a detailed and patient-focused approach to treating disc conditions. We work with each patient to create a treatment plan that meets their specific needs and goals.
Common Misconceptions About Disc Problems
We often hear wrong ideas about spinal disc issues, like “slipped” and “herniated” discs. These wrong ideas can confuse people. They can also change how patients see their health problems and treatment choices.
Is a Slipped Disc the Same as a Herniated Disc?
Many people mix up “slipped disc” and “herniated disc.” But they’re not the same. A herniated disc happens when the soft center of the disc pushes out. A slipped disc is a simpler term for different disc problems.
Myths About Disc Healing and Recovery
Some think disc problems can’t be fixed and that recovery is impossible. But, many disc issues can be managed well with the right treatment and care.
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| Disc problems always require surgery. | Many disc issues can be treated without surgery. |
| Once a disc is damaged, it’s always a problem. | With the right care, many people see big improvements. |
Misconceptions About Activity Restrictions
While some activities might need to be cut back, lying in bed all day isn’t usually needed. Gentle exercises and physical therapy can help a lot in getting better.
Understanding Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes
The outlook for disc problems varies a lot. It depends on the specific issue and the person. Knowing what to expect long-term helps patients make better choices for their health.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into the differences between slipped and herniated discs. We’ve covered their symptoms, causes, how they’re diagnosed, and treatment options. Knowing about these disc issues is key for the right care.
A herniated disc happens when the soft center bulges out, causing pain. On the other hand, a slipped disc isn’t a real medical term. It’s just another way to say a disc has bulged or herniated. The signs, reasons, and how they’re found out differ. Treatments range from simple care to surgery.
We aim to have given a clear view of disc problems. This should help readers understand their condition better. Knowing the difference between slipped and herniated discs helps find the best treatment. This can greatly improve one’s health.
Is a slipped disc the same as a herniated disc?
“Slipped disc” is a term often used but not medical. It can mean either a herniated or bulging disc. A herniated disc is when the soft center pushes through the tough outer layer. We make sure to explain the difference to help with diagnosis.
What are the common causes of disc problems?
Many things can cause disc problems. These include getting older, injuries, repetitive actions, bad posture, and genetics. Knowing these causes helps in preventing and managing disc issues.
How do herniated and bulging discs differ in terms of symptoms?
Herniated discs usually cause sharp pain and nerve symptoms. This is because the soft center presses on nerves. Bulging discs might cause more general pain and discomfort.
What are the treatment options for disc conditions?
Treatments range from non-surgical methods like physical therapy to surgery. The choice depends on the disc problem’s severity and the patient’s needs.
Are there different types of bulging discs?
Yes, there are several types of bulging discs. Each type has its own characteristics and treatment needs.
How are disc problems diagnosed?
Doctors use physical exams, imaging like MRI and CT scans, and nerve tests to diagnose. They also rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
Can disc problems be prevented?
Some risks like age and genetics can’t be changed. But, a healthy lifestyle and avoiding injuries can lower the risk of disc problems.
What are the most commonly affected spinal regions for disc problems?
The lower back, or lumbar region, is most often affected. The neck, or cervical region, is also common. The middle back, or thoracic region, is less often affected.
Are there any misconceptions about disc healing and recovery?
Yes, many believe in myths about disc healing. It’s important to know the truth about recovery and what to expect.
What is the difference between a herniated disc and a ruptured disc?
A herniated disc means the soft center pushes through the tough outer layer. A ruptured disc is a more severe breach that can lead to disc sequestration. Knowing the difference is key for the right treatment.
Is a bulging disc the same as a slipped disc?
A bulging disc means the disc bulges without rupturing. “Slipped disc” is a non-specific term. While a bulging disc is a type of “slipped disc,” not all “slipped discs” are bulging. It’s important to clarify these terms for accurate diagnosis and treatment.

































