Spinal disc problems can be confusing and scary. A herniated disk happens when the soft disk between vertebrae tears. This lets the soft stuff inside leak and press on nerves nearby.
At Liv Hospital, we use top-notch medical imaging to show these changes clearly. Our team helps patients grasp their situation. This makes it easier for them to decide on their treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Herniated disks occur when the disk between vertebrae tears and the inner substance leaks.
- Advanced medical imaging helps diagnose and treat spinal disc issues.
- Understanding herniated disk images is key for accurate diagnosis.
- Liv Hospital’s expertise supports patients in making informed care decisions.
- Clear visuals of spinal disc changes aid in patient education.
Understanding Spinal Disc Anatomy and Pathology
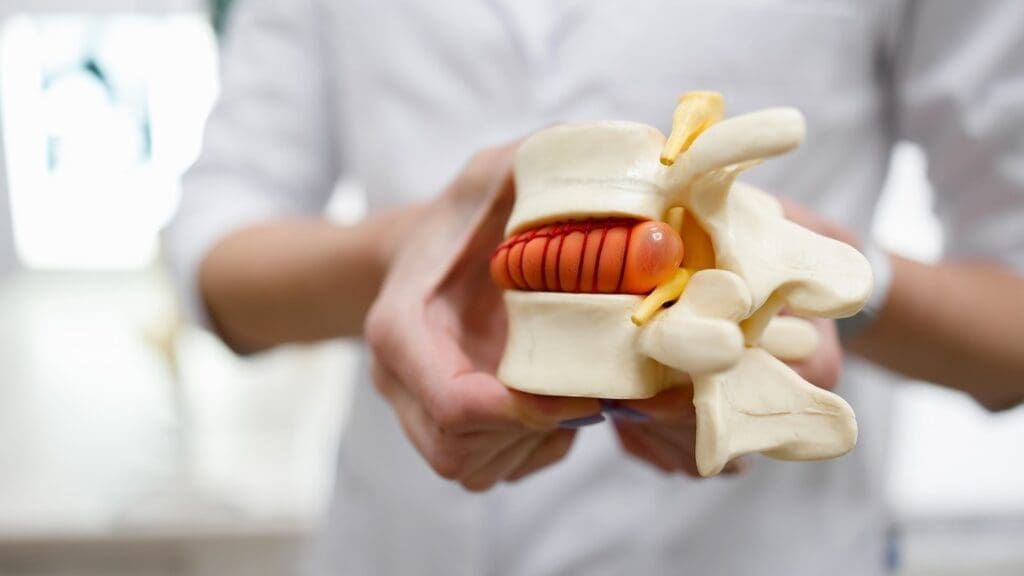

To understand what a herniated disc looks like, we need to know about spinal discs first. These discs are between the vertebrae in our spine. They act as shock absorbers.
Normal Disc Structure and Function
A normal spinal disc has two main parts. The nucleus pulposus is the soft, gel-like center. The annulus fibrosus is the tougher, outer layer. They work together to absorb shock and keep the spine stable.
Mechanisms of Disc Injury and Degeneration
Disc injury and degeneration can happen for many reasons. Heavy lifting, sudden twisting, or age-related wear and tear are common causes. When the annulus fibrosus tears, the nucleus pulposus can bulge out, causing a herniated disc.
Risk Factors for Disc Herniation
Several factors can lead to disc herniation. These include:
- Genetic predisposition
- Age-related degeneration
- Heavy lifting or bending
- Sudden injury or trauma
Knowing these risk factors helps in preventing and diagnosing disc herniation. Modern imaging like MRI, CT, and X-ray are key. They help see disc problems and check for nerve compression and spinal alignment issues.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetic Predisposition | Family history can play a role in disc degeneration and herniation. |
| Age-related Degeneration | As we age, the spinal discs naturally degenerate, increasing the risk of herniation. |
| Heavy Lifting or Bending | Lifting heavy objects or bending can put significant stress on the spinal discs. |
Herniated Disk Images: Visual Characteristics in Medical Scans

Looking at medical scans, we find key signs of herniated disks. These signs help doctors know how bad the damage is and how it affects nerves.
Key Visual Markers of Disc Herniation
In these images, we see a bulge of disc material outside its usual spot. This looks like a dark bulge on MRI scans. It can press on spinal nerves. We check the size and where the herniation is, and if it’s pressing on nerves or narrowing the spinal canal.
Dark Bulges and Protrusions in Imaging
Dark bulges and protrusions show disc herniation. They can cause pain, weakness, numbness, or tingling in the leg or foot. Seeing these bulges helps us know how serious the herniation is.
Spinal Canal Narrowing Visualization
Spinal canal narrowing, or stenosis, shows up as a smaller spinal canal in scans. This can press on the spinal cord or nerves, making symptoms worse. By looking at herniated disk images, we can see how much the canal is narrowed and what it means for nerve pressure.
Knowing these visual signs is key to diagnosing and treating herniated disks. By studying image herniated disc details, doctors can create better treatment plans. This helps to ease symptoms and improve patient care.
What Does a Slipped Disc Look Like in Diagnostic Imaging?
It’s key to know what a slipped disc looks like in imaging for good treatment and care. We use MRI, CT, and X-ray to see how far the disc is out of place and how it affects nearby areas.
Defining Characteristics of Slipped Discs
A slipped disc, or herniated disc, shows up as a bulge or protrusion on scans. Key features include the disc material going beyond its usual spot and possibly pressing on nerves nearby.
Altered Spinal Alignment in Images
Slipped discs can cause the spine to be off-kilter, seen on imaging. This misalignment comes from the disc being out of place or the body trying to adjust.
Common Locations for Disc Displacement
Disc displacement happens in different spine areas, but some spots are more likely. Here’s a table showing common places and what they’re like:
| Spinal Region | Frequency of Disc Displacement | Typical Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Lumbar Spine | High | Lower back pain, sciatica |
| Cervical Spine | Moderate | Neck pain, radiating arm pain |
| Thoracic Spine | Low | Mid-back pain, rare |
Doing heavy lifting, pushing, or bending a lot can make disc displacement more likely. Knowing what slipped discs look like in imaging helps doctors plan better treatments.
Ruptured Disc Visualization: Fragmented Material and Nerve Compression
Medical imaging shows how a ruptured disc affects nerves. This can cause a lot of pain. We’ll see how imaging helps understand the rupture’s severity.
Visual Signs of Complete Disc Rupture
A complete disc rupture shows fragmented material outside the disc. In images, this looks like displaced or extruded disc material. This material can press on nerves, causing pain.
Tracking Displaced Disc Material in the Spinal Canal
Medical imaging tracks the disc material in the spinal canal. This helps doctors understand nerve compression. They can then plan the best treatment.
Acute vs. Chronic Rupture Appearances
Disc ruptures look different based on their type. Acute ruptures show more inflammation and different MRI signals. Chronic ruptures may look scarred. Knowing these differences helps doctors choose the right treatment.
Bulging Disc Appearance: Early Signs and Progression
Bulging discs in medical images can signal a problem. They look like a uniform bulge beyond the normal disc area. Sometimes, they don’t cause any pain, or the pain is mild.
How Bulging Differs from Herniation in Images
Bulging discs are different from herniated ones. Bulging discs spread out more evenly, while herniated discs have a specific spot that bulges. This makes bulging discs look like a general bulge in images, and herniated discs look like a specific bulge.
Detecting Subtle Disc Changes Before Full Herniation
It’s important to catch small changes in discs early. MRI can show these changes, like a disc getting thinner or changing color. It can also spot tiny cracks in the disc.
Monitoring Bulging Discs Over Time
Keeping an eye on bulging discs is key. By using imaging over time, doctors can see how discs change. This helps them decide the best course of action. Here’s a table showing the main differences between bulging and herniated discs:
| Characteristics | Bulging Disc | Herniated Disc |
|---|---|---|
| Disc Protrusion | Generalized, uniform bulge | Focal, localized protrusion |
| Symptoms | Often asymptomatic or mild | Moderate to severe symptoms |
| Imaging Findings | Diffuse disc margin extension | Localized displacement of disc material |
Knowing how bulging discs look and change helps doctors act fast. This can stop further damage and serious problems.
Comparing Herniated Disc Pictures: Bulging vs. Slipped vs. Ruptured
It’s important to know the differences between bulging, slipped, and ruptured discs for the right treatment. We’ll look at pictures to show how each condition is different.
Side-by-Side Visual Comparison of Disc Pathologies
Bulging discs show a uniform bulge beyond the normal disc area. Slipped or herniated discs have a more specific displacement of disc material. Ruptured discs have a complete tear of the annulus fibrosus, with the nucleus pulposus material leaking out.
Severity Spectrum in Disc Imaging
The severity of disc problems can be seen on a spectrum, from mild bulging to complete rupture. Studies show MRI is over 95 percent accurate for diagnosing herniated discs. T2-weighted images are best for showing protrusion, edema, and structural changes.
Clinical Implications of Different Visual Presentations
A leading medical expert says, “The way herniated discs look on images is key for treatment planning.”
“Choosing between non-surgical and surgical options often depends on how severe the disc problem is and if nerves are compressed.”
Surgical options might include removing part of the disk that presses on nerves. Sometimes, the whole disk is replaced with bone, and a metal plate is added for support.
By studying herniated disc pictures and understanding their clinical implications, we can make more accurate diagnoses. This helps us create better treatment plans.
MRI Technology: 95% Accuracy in Herniated Disc Diagnosis
MRI is a top tool for finding herniated discs, with a 95% accuracy rate. This high accuracy is key for good treatment plans and patient care. We’ll look at how MRI, with T1 and T2 images, advanced methods, and contrast, helps achieve this accuracy.
T1 vs. T2-Weighted Images for Optimal Disc Visualization
T1 and T2 images are key in MRI. T1 images show body structures clearly. T2 images spot soft tissue changes, like disc protrusions and swelling. T2 images show how far disc herniation goes and any structural changes.
Advanced MRI Protocols for Disc Pathology
New MRI methods improve finding disc problems. These methods show disc shape and how it affects nearby nerves better.
Contrast Enhancement in Complex Cases
For tough cases, contrast agents help more. They show different disc issues and inflammation. This is great when the diagnosis is hard or when checking nerve compression.
Using these MRI techniques, doctors can diagnose herniated discs more accurately. This leads to better treatment plans for patients.
CT Scans and X-rays: When and How They Visualize Disc Problems
Understanding CT scans and X-rays is key to diagnosing spinal disc issues. These tools give important insights into the spine. Yet, they have their own strengths and weaknesses.
Advantages for Bony Changes and Calcification
CT scans are great for spotting bony changes and calcification in disc problems. They show detailed images of the spine’s bones. This helps doctors see issues like bone spurs or hardened disc material.
Limitations and Appropriate Applications of X-rays
X-rays are good for initial checks but have limits with soft tissues like discs. They’re better for looking at bones and alignment. For example, X-rays can spot vertebral fractures or misalignments.
Radiation Considerations in Imaging Selection
Choosing between CT scans and X-rays means thinking about radiation. CT scans use more radiation than X-rays. So, the choice depends on what’s needed for diagnosis and the patient’s situation.
- CT scans are ideal for bony changes and calcification.
- X-rays are better for initial assessments and bony structure evaluation.
- Radiation exposure varies between CT scans and X-rays.
Herniated Disc Diagrams and Educational Imaging
Herniated disc diagrams are key in teaching patients about their condition and treatment. They help patients grasp their situation, making it easier for them to talk with doctors.
Annotated Images for Patient Education
Annotated images are great for teaching patients. They show the details of a herniated disc, helping patients see what’s happening. This can make them feel less scared and more likely to follow treatment plans.
We use these images to show how big the herniation is and how it affects nerves.
3D Reconstructions and Cross-Sectional Views
Advanced imaging like 3D reconstructions and cross-sections gives deep looks at herniated discs. These views are super helpful in tricky cases. They show exactly where and how big the herniation is, which is key for planning surgery.
Using Visual Aids in Treatment Planning
Visual aids do more than teach; they help plan treatments too. They show the disc and its impact on the spine, helping doctors come up with better plans. This might include surgery to remove the part of the disk pressing on nerves.
We use these tools to make treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs. This makes it more likely for treatments to work well.
Herniated Disc Lower Back Swelling: Identifying Inflammatory Changes
A herniated disc in the lower back can cause a lot of swelling and inflammation. This swelling is not just a simple reaction. It’s a complex process involving many biochemical and cellular changes.
Edema Patterns Around Herniated Discs
Edema patterns around herniated discs can differ a lot from person to person. Advanced imaging techniques help us see these patterns. They are key to understanding how much inflammation and nerve compression there is.
Tracking Healing Progress Through Sequential Imaging
Sequential imaging is very important for tracking how herniated discs heal. By looking at changes in swelling and inflammation over time, we can see if treatments are working. We can then make changes if needed.
Correlation Between Swelling and Symptom Severity
Studies have found a link between swelling and how bad symptoms are. Here’s a table showing this link:
| Degree of Swelling | Symptom Severity |
|---|---|
| Mild | Minimal pain, limited mobility |
| Moderate | Noticeable pain, reduced mobility |
| Severe | Significant pain, limited mobility, possible neurological problems |
This table shows why knowing the link between swelling and symptoms is so important. By watching these factors closely, we can give our patients the best care possible.
“The relationship between herniated disc swelling and symptom severity is complex and multifactorial. Advanced imaging techniques are essential for understanding this correlation and guiding treatment decisions.”
Conclusion: Advances in Herniated Disc Imaging and Diagnosis
Advances in herniated disc imaging have greatly improved how we diagnose and treat these issues. At Liv Hospital, we use the latest imaging technologies. This helps us give accurate diagnoses and create effective treatment plans.
We are committed to top-notch healthcare for all our patients, including those from abroad. Our advanced imaging tools, like MRI and CT scans, help us see herniated discs clearly. This lets us understand how severe the problem is.
Thanks to these imaging advances, we can find the real causes of back pain. Then, we can plan treatments that target the problem. While we can’t promise results, a healthy lifestyle and exercise can help prevent problems with the discs.
We aim to give our patients the best care and support. This way, they can get the best possible results from their treatment.
What does a herniated disc look like in medical imaging?
A herniated disc shows up as a bulge or protrusion on scans like MRI or CT. It often presses on nearby nerves, leading to symptoms.
How do herniated discs differ from bulging discs in images?
Herniated discs have a clear rupture or bulge. Bulging discs just look like a general bulge without a rupture.
What are the visual signs of a ruptured disc in diagnostic imaging?
A ruptured disc looks like fragmented disc material on scans. It can also show severe nerve compression.
Can MRI accurately diagnose herniated discs?
Yes, MRI is very accurate, about 95%, in spotting herniated discs. It uses T1 and T2-weighted images.
How do CT scans and X-rays visualize disc problems?
CT scans show bony changes and calcification related to disc wear. X-rays are less detailed but can hint at disc problems, like height loss.
What does a slipped disc look like in diagnostic imaging?
A slipped disc, like a herniated disc, shows as a bulge or protrusion. It can change spinal alignment and press on nerves.
How are inflammatory changes associated with herniated disc lower back swelling identified?
Edema patterns around herniated discs on MRI show inflammation. This can link to how severe symptoms are.
What is the role of herniated disc diagrams and educational imaging?
Images with notes, 3D views, and cross-sections help patients understand their condition. They also guide treatment plans by showing disc problems clearly.
How do imaging technologies track healing progress in herniated discs?
Imaging, like MRI, can follow changes in disc and inflammation over time. This helps see how healing is going.
What are the advantages of using MRI for herniated disc diagnosis?
MRI gives detailed images of soft tissues like discs and nerves without radiation. It’s best for finding herniated discs and nerve issues.
References
- Wikipedia (Disc herniation) : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disc_herniation
- Radiopaedia (Disc Herniation) : https://radiopaedia.org/articles/disc-herniation?lang=us




































