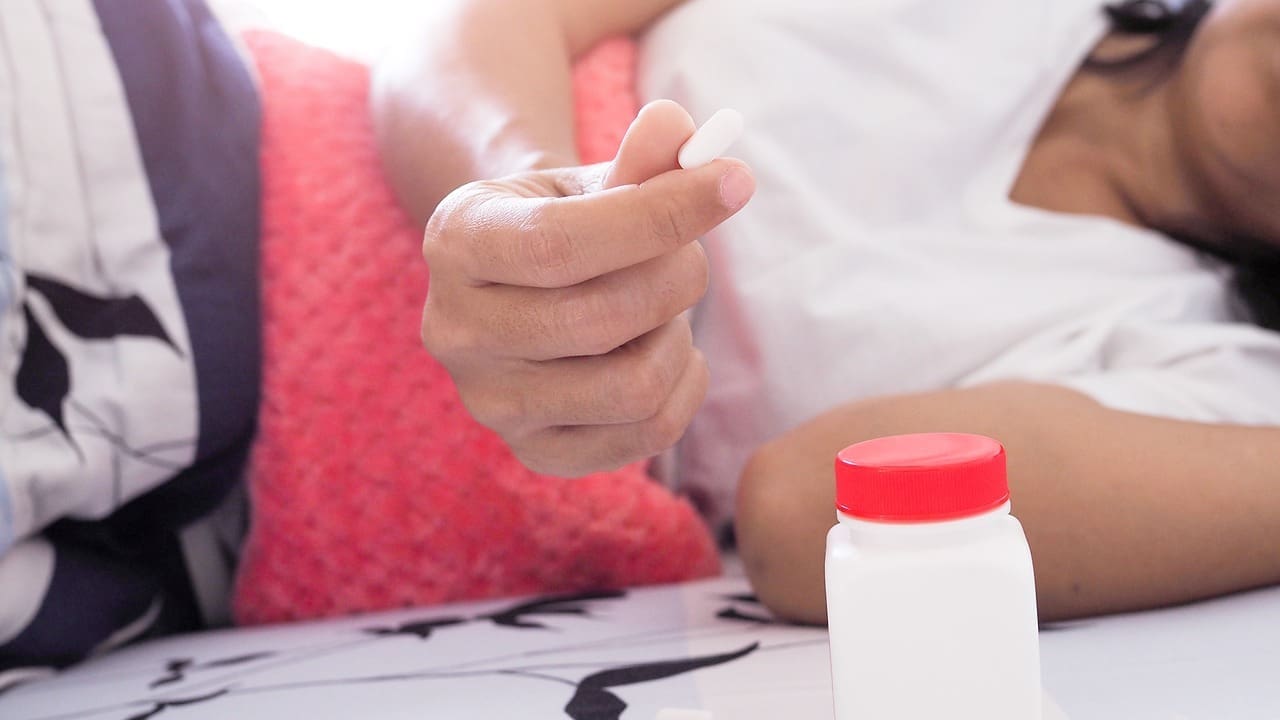
Feeling chest pain when breathing deeply can be scary. It’s important to know what to do next. At Liv Hospital, we stress finding out why you have chest pain before treating it.
Ibuprofen can help with chest pain caused by inflammation, like in acute pericarditis. But, taking it without knowing why you have chest pain is risky. You should always talk to a doctor first.
Dealing with chest pain can be hard. That’s why it’s key to talk to doctors. They can help find the best way to treat you.
Key Takeaways
- Chest pain when breathing deeply requires medical evaluation.
- Ibuprofen may be used for chest pain caused by inflammation.
- Underlying cause of chest pain must be diagnosed before treatment.
- Consulting a healthcare professional is critical for safe treatment.
- Liv Hospital offers full care for chest pain patients.
Understanding Chest Pain When Breathing Deeply
Deep breathing is a natural process. But, chest pain from it can signal a health issue. This pain can take many forms, making people worry about their health. We’ll look into what causes it and its symptoms.
What is Pleuritic Chest Pain?
Pleuritic chest pain is linked to the pleura, thin membranes around the lungs. It happens when these membranes get inflamed, often from infection or injury. The pain is sharp and gets worse with deep breaths or coughing. Pleuritic pain can be a sign of many health issues, like infections and inflammatory diseases.
“Pleurisy, or inflammation of the pleura, is a common cause of pleuritic chest pain. It can result from infections, autoimmune disorders, or other conditions affecting the lungs or chest cavity.”
Common Symptoms and Sensations
People with pleuritic chest pain often say the pain feels sharp or stabbing. It can be in one spot on the chest and might spread to the shoulder or back. Other signs include:
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing
- Fever
- Fatigue
The pain’s strength can change, sometimes easing when holding one’s breath or pressing on it. But, seeing a doctor is key if the pain is bad or if you have other worrying symptoms.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Sharp Pain | Pain that is stabbing or sharp, often worsening with deep breaths |
| Localized Pain | Pain confined to a specific area of the chest |
| Radiating Pain | Pain that spreads to the shoulder or back |
Knowing these symptoms helps figure out what’s causing chest pain when breathing deeply. We’ll keep exploring causes and treatments next.
Potential Causes of Pain in Chest When Breathing In Deep

Chest pain while taking deep breaths can be concerning. It’s important to know why this happens. Pain that gets worse when lying down or with deep breaths is a red flag.
Musculoskeletal Causes
Muscle and bone issues often cause chest pain with deep breathing. Costochondritis is a common problem. It’s an inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone.
- Costochondritis: Inflammation of the cartilage connecting the ribs to the breastbone.
- Muscle strain: Overuse or injury to the muscles in the chest wall.
- Rib injuries: Bruised or fractured ribs can cause pain that worsens with deep breathing.
Respiratory Infections and Conditions
Respiratory infections and conditions can also lead to chest pain when breathing in deep. These include pneumonia, bronchitis, and pleurisy.
| Condition | Description | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Pneumonia | Infection inflaming the air sacs in one or both lungs. | Cough, fever, chest pain, difficulty breathing. |
| Pleurisy | Inflammation of the pleura, the two layers of tissue surrounding the lungs. | Sharp chest pain that worsens with breathing. |
| Bronchitis | Inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes. | Cough, mucus production, chest discomfort. |
Cardiovascular Causes
Heart problems can also cause chest pain when breathing deeply. Pericarditis and pulmonary embolism are examples. Pericarditis is inflammation of the sac around the heart. Pulmonary embolism is a blockage in a pulmonary artery.
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the pericardium, the sac around the heart.
- Pulmonary Embolism: Blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries.
Other Possible Causes
Other factors can also cause chest pain when breathing deeply. Anxiety and panic disorders can lead to chest tightness or discomfort.
Knowing the possible causes is key to finding the right treatment. If you have persistent or severe chest pain, see a doctor right away.
Chest Tightness When Deep Breathing: Is It Serious?
Feeling chest tightness when you breathe deeply can be scary. You might wonder if it’s a sign of something serious. It’s normal to feel worried, but it’s key to tell if it’s just a minor issue or if you need to see a doctor.
Differentiating Between Normal and Concerning Tightness
Chest tightness can come from many things, like muscle issues or heart problems. It’s important to figure out how serious it is. If it happens sometimes and goes away, it might not be a big deal. But if it keeps happening or feels really bad, you should check it out.
To know if it’s just normal or if you should worry, think about a few things:
- How tight does it feel? Is it just a little or really bad?
- How long does it last? Does it go away quickly or stay for a while?
- Are there other symptoms too? Like pain, feeling dizzy, or trouble breathing?
As one doctor said,
“Chest pain or tightness can mean many things, some of which are very serious. It’s always safer to be careful.”
Associated Symptoms to Watch For
When you feel chest tightness while breathing deeply, watch for other signs too. Important symptoms to look out for include:
- Sharp or stabbing pain that gets worse with deep breathing or moving
- Having trouble breathing or feeling short of breath
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded
- Pain spreading to your arm, neck, or jaw
If you notice any of these symptoms with chest tightness, get help right away. It’s always better to be safe when dealing with symptoms that could mean serious health problems.
Keep track of when these symptoms happen, how bad they are, and what makes them better or worse. This info is very helpful when you talk to a doctor.
How to Know When Chest Pain is Serious
Knowing when chest pain is serious is key. Look out for red flags and know when to get help fast. Chest pain can be different, so it’s important to tell harmless pain from serious issues.
Red Flag Symptoms
Some symptoms with chest pain are red flags. They mean you need to see a doctor right away. These include:
- Severe or Prolonged Pain: Pain that’s really bad, lasts a long time, or gets worse.
- Difficulty Breathing: Feeling out of breath or tired even when sitting or doing light activities.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Feeling like you might faint or dizzy.
- Pain Radiating to Other Areas: Pain spreading to arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
When Should I Go to ER for Chest Pain?
Go to the ER if you have any of these:
- Chest pain that’s really bad, doesn’t go away, or has other scary symptoms.
- Symptoms that get worse or happen with activity.
- Heart disease risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, or family heart history.
| Symptom | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Severe Chest Pain | Pain that’s really bad and might spread | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Difficulty Breathing | Feeling out of breath or tired sitting or resting | Go to the ER |
| Dizziness | Feeling faint or dizzy | Seek medical help immediately |
Chest Pain That Worsens When Lying Down
Chest pain that gets worse when lying down might mean pericarditis or pleurisy. If your pain gets worse in this position, see a doctor to find out why.
Understanding chest pain and knowing when it’s serious can save lives. If you’re not sure, it’s better to be safe and get checked by a doctor.
How Ibuprofen Works in the Body
Ibuprofen is a key player in treating chest pain. It’s a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It’s known for its pain relief and anti-inflammatory effects.
Anti-inflammatory Mechanism
Ibuprofen stops the body from making prostaglandins. These are substances that cause pain and swelling. It does this by blocking the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme.
By lowering prostaglandin levels, ibuprofen reduces swelling and pain. Doctors say its anti-inflammatory effect is great for conditions with a lot of swelling.
This makes ibuprofen a good choice for managing chest pain caused by swelling.
Pain-Relieving Properties
Ibuprofen’s pain relief comes from blocking COX enzymes. This action cuts down on prostaglandin production. It helps in reducing swelling and directly affects pain pathways.
This means it can help with deep breath chest pain and other types of pain.
| Pain Type | Ibuprofen’s Effect |
|---|---|
| Inflammatory Pain | Reduces inflammation by inhibiting prostaglandin production |
| Musculoskeletal Pain | Relieves pain by blocking COX enzymes |
Duration and Onset of Action
Ibuprofen starts working fast, usually within 30 minutes to an hour. Its pain relief can last 4 to 6 hours, depending on the type and dose. Knowing this can help manage pain in chest when breathing deeply.
Understanding how ibuprofen works helps in deciding if it’s right for chest pain. It’s important to weigh its benefits and risks, considering any health conditions or other medications.
Can I Take Ibuprofen for Chest Pain? When It May Help
Many people wonder if ibuprofen can help with chest pain that gets worse when they breathe deeply. We’ll look into when ibuprofen might be a good choice for chest pain. We’ll also cover the right amount to take and how long it might take to feel better.
Appropriate Scenarios for Ibuprofen Use
Ibuprofen can be helpful for chest pain caused by inflammation. It’s good for:
- Costochondritis – inflammation of the cartilage connecting the ribs to the breastbone
- Pleurisy – inflammation of the lining surrounding the lungs
- Musculoskeletal strain or injury
But, always talk to a doctor before taking ibuprofen for chest pain. This is to make sure you don’t have a more serious issue that needs a different treatment.
Dosage Considerations
Adults usually take 200 to 400 mg of ibuprofen every 4 to 6 hours as needed. It’s important to stick to the dosage on the label or what your doctor tells you.
| Condition | Initial Dose | Maximum Daily Dose |
|---|---|---|
| General Pain Relief | 200 mg | 1200 mg |
| Inflammatory Conditions | 400 mg | 2400 mg |
Expected Relief Timeline
Ibuprofen usually starts working in 30 minutes to an hour. The pain relief can last 4 to 6 hours. This depends on the dose and how your body reacts.
Key Points to Remember:
- Always consult a healthcare professional before taking ibuprofen for chest pain.
- Follow the recommended dosage to minimize possible side effects.
- Keep an eye on your symptoms. If they get worse or you notice concerning side effects, seek medical help.
When Ibuprofen Is Not Recommended for Chest Pain
Ibuprofen is good for many pains, but not all. It’s not always safe for chest pain, mainly for certain people.
Contraindications with Certain Conditions
Some medical conditions mean you should not take ibuprofen for chest pain. People with stomach ulcers or bleeding problems are at higher risk. Also, those with kidney disease should talk to their doctor first, as ibuprofen can harm kidneys.
It’s also not good for people who are dehydrated or at risk of dehydration. This can harm the kidneys even more.
Risks for Patients with Cardiovascular Disease
For those with heart problems, ibuprofen can be risky. It can raise blood pressure and cause fluid buildup, making heart failure worse. Long-term use can also raise the chance of heart attack and stroke.
If you have heart disease and chest pain, talk to your doctor before taking ibuprofen. They can find the safest option for you.
Potential Interactions with Other Medications
Ibuprofen can react badly with other medicines. For example, it can make bleeding more likely when taken with blood thinners. It can also cause problems with antidepressants and other pain relievers.
Always tell your doctor about all your medicines before starting ibuprofen. This includes prescription drugs, over-the-counter meds, and herbal supplements.
If your chest pain gets worse when you lie down or breathe deeply, get help right away. Knowing why you have chest pain is key to treating it right.
Heart Pain When Inhaling: Specific Conditions and Treatments
Feeling heart pain when you inhale can be scary. We need to look into possible causes and treatments. We’ll talk about pericarditis, pulmonary embolism, and costochondritis, and how to treat them.
Pericarditis and Ibuprofen Use
Pericarditis is when the sac around your heart gets inflamed. It can cause sharp chest pain. This pain might feel better when you sit up and lean forward, but gets worse when you lie down or take deep breaths. Ibuprofen is often used to treat it because it reduces inflammation and eases pain.
We usually start with ibuprofen for pericarditis because it works well. But, we need to watch how the patient responds and change the treatment if needed.
Pulmonary Embolism Considerations
Pulmonary embolism is when something blocks an artery in your lungs. It can cause sudden chest pain that gets worse with deep breaths. Unlike pericarditis, pulmonary embolism is a serious emergency that needs quick medical help.
Ibuprofen might help with some symptoms, but it’s not a cure for pulmonary embolism. If you think you might have it, you need to see a doctor right away.
Costochondritis Management
Costochondritis is when the cartilage between your ribs and sternum gets inflamed. It can cause chest pain that might feel like heart pain. The pain usually gets worse with deep breathing or moving.
For costochondritis, we often use pain relief medicines like ibuprofen. We might also suggest physical therapy or other treatments to help manage the symptoms.
Here’s a quick overview of the conditions and their treatments:
| Condition | Primary Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Pericarditis | Sharp chest pain improving when sitting up | Ibuprofen for inflammation and pain relief |
| Pulmonary Embolism | Sudden onset chest pain worsening with deep breaths | Immediate medical attention; anticoagulant therapy |
| Costochondritis | Chest pain worsening with movement or deep breaths | Ibuprofen for pain relief; physical therapy |
It’s important to know why you’re feeling heart pain when you inhale. We’ve looked at pericarditis, pulmonary embolism, and costochondritis. We’ve also talked about how ibuprofen can help with some of these conditions.
Does Advil Help With Chest Pain? Comparing Options
Chest tightness and pain can be unsettling. Many turn to Advil as a possible solution. We’ll look into whether Advil works for chest pain and compare it with other options.
Advil vs. Generic Ibuprofen
Advil is a brand name for ibuprofen, which also comes in generic forms. Both have the same active ingredient, ibuprofen. The main difference is in inactive ingredients and how they’re made.
Key similarities between Advil and generic ibuprofen:
- Same active ingredient (ibuprofen)
- Similar mechanism of action (anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving)
- Comparable efficacy in treating pain and inflammation
Choosing between Advil and generic ibuprofen often depends on personal preference and cost. Generic versions are cheaper. Brand names like Advil might offer specific formulations or packaging that some prefer.
Other OTC Pain Relievers for Chest Pain
Other over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers can also help with chest pain. These include:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- Aspirin
- Naproxen (Aleve)
Each has its own uses, warnings, and side effects. For example, aspirin is not good for people with certain bleeding disorders or those taking certain medications.
Prescription Alternatives
In some cases, prescription medications are needed for chest pain. These can include:
- Stronger NSAIDs (e.g., prescription-strength ibuprofen or naproxen)
- Muscle relaxants for musculoskeletal causes of chest pain
- Other prescription pain relievers
Always talk to a healthcare provider before starting any new medication, including prescription options. They can figure out why you’re experiencing chest pain and suggest the best treatment.
Alternative Treatments for Chest Pain When Breathing Deeply
There are many alternative treatments for chest pain when breathing deeply. These include various therapies and self-care practices. They can help alongside traditional treatments to ease pain and boost well-being.
Other Medications to Consider
Other than ibuprofen, there are other medicines for chest pain. These include:
- Acetaminophen: Good for pain relief, safe when NSAIDs are not.
- Nitroglycerin: Used for angina, it relaxes and widens blood vessels.
- Antibiotics: If pain is from a bacterial infection, antibiotics are used.
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy is key for chest pain, often from muscle issues. It includes:
- Stretching exercises: To loosen muscles and reduce tension.
- Strengthening exercises: To support the chest area’s muscles.
- Manual therapy: Massage or manipulation to ease pain and improve movement.
Home Remedies and Self-Care Strategies
Home remedies and self-care can help with chest pain. These include:
- Applying heat or cold: To the area to lessen pain and swelling.
- Rest: Staying away from activities that make pain worse.
- Relaxation techniques: Like meditation or deep breathing to lower stress.
Breathing Techniques and Posture Adjustments
Improving breathing and posture can help with chest pain. Techniques include:
- Diaphragmatic breathing: Strengthens the diaphragm and boosts lung capacity.
- Pursed-lip breathing: Slows breathing and lowers stress.
- Postural correction: Keeping good posture to ease strain on the chest and breathing muscles.
By adding these alternative treatments to your plan, you can find relief from chest pain. This can greatly improve your life quality.
Conclusion
Knowing if you can take ibuprofen for chest pain when breathing deeply is key. We’ve talked about why you might feel chest pain, like from muscles, lungs, or heart issues. Ibuprofen might help with some pains, but finding the real cause is critical for the right treatment.
If you feel pain in your chest when you breathe deeply, knowing when to get help is important. We’ve listed signs that mean you should see a doctor right away. If your pain gets worse or you have other bad symptoms, get medical help fast.
In short, while ibuprofen might work for some chest pains, it’s not for all. Always talk to a doctor to figure out the best treatment for you. This way, you get the care you need to feel better.
Can ibuprofen help with chest pain when breathing deeply?
Ibuprofen might ease chest pain from deep breathing, like in pericarditis. But, you should know why you’re feeling pain before taking it.
What is pleuritic chest pain?
Pleuritic chest pain gets worse with deep breaths or coughs. It’s often from the pleura, the lung lining’s inflammation.
What are the possible causes of chest pain when breathing deeply?
Chest pain from deep breathing can be from muscle or bone issues, lung infections, heart problems, or other issues like pulmonary embolism or costochondritis.
How can I tell if chest tightness when deep breathing is serious?
Look for signs like trouble breathing, dizziness, or severe pain. If you see these, get medical help right away.
When should I go to the ER for chest pain?
Go to the ER for chest pain if it’s severe, you can’t breathe well, feel dizzy, or gets worse when lying down. These are serious signs.
Can I take ibuprofen for heart pain when inhaling?
Ibuprofen might help heart pain from inhaling, like in pericarditis. But, talk to a doctor first, and be careful if you have heart disease.
Does Advil help with chest pain?
Advil, or ibuprofen, can ease chest pain from inflammation. But, always follow the dose and talk to a doctor if the pain doesn’t go away or gets worse.
Are there other treatments for chest pain when breathing deeply?
Yes, there are other treatments like different medicines, physical therapy, home remedies, and self-care. This includes breathing exercises and changing how you sit or stand.
Can I take ibuprofen with other medications for chest pain?
Always check with a doctor before mixing ibuprofen with other medicines. This is because of possible bad reactions, special warnings, or risks with certain health issues or heart disease.
How does ibuprofen work to relieve chest pain?
Ibuprofen reduces inflammation and pain by its anti-inflammatory action. This makes it a good option for chest pain from inflammatory conditions.
What are the risks of using ibuprofen for chest pain?
Using ibuprofen for chest pain can have risks. These include bad reactions with other medicines, warnings for certain health issues, and dangers for people with heart disease.
Reference:
https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682159.html
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11572456




































