Cardiology is the medical specialty focused on the heart and the cardiovascular system. It involves the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels. These conditions include coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), and valve disorders. The field covers a broad spectrum, from congenital heart defects present at birth to acquired conditions like heart attacks.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Cardiology is the medical specialty that focuses on diagnosing, treating, and preventing diseases of the heart and blood vessels. These conditions—often grouped under the term cardiovascular disease—include coronary artery disease, heart failure, heart rhythm problems, heart valve disorders, and high blood pressure. A cardiology department brings together specialists, advanced tests, and treatments to protect your heart health, manage emergencies, and support long-term care.

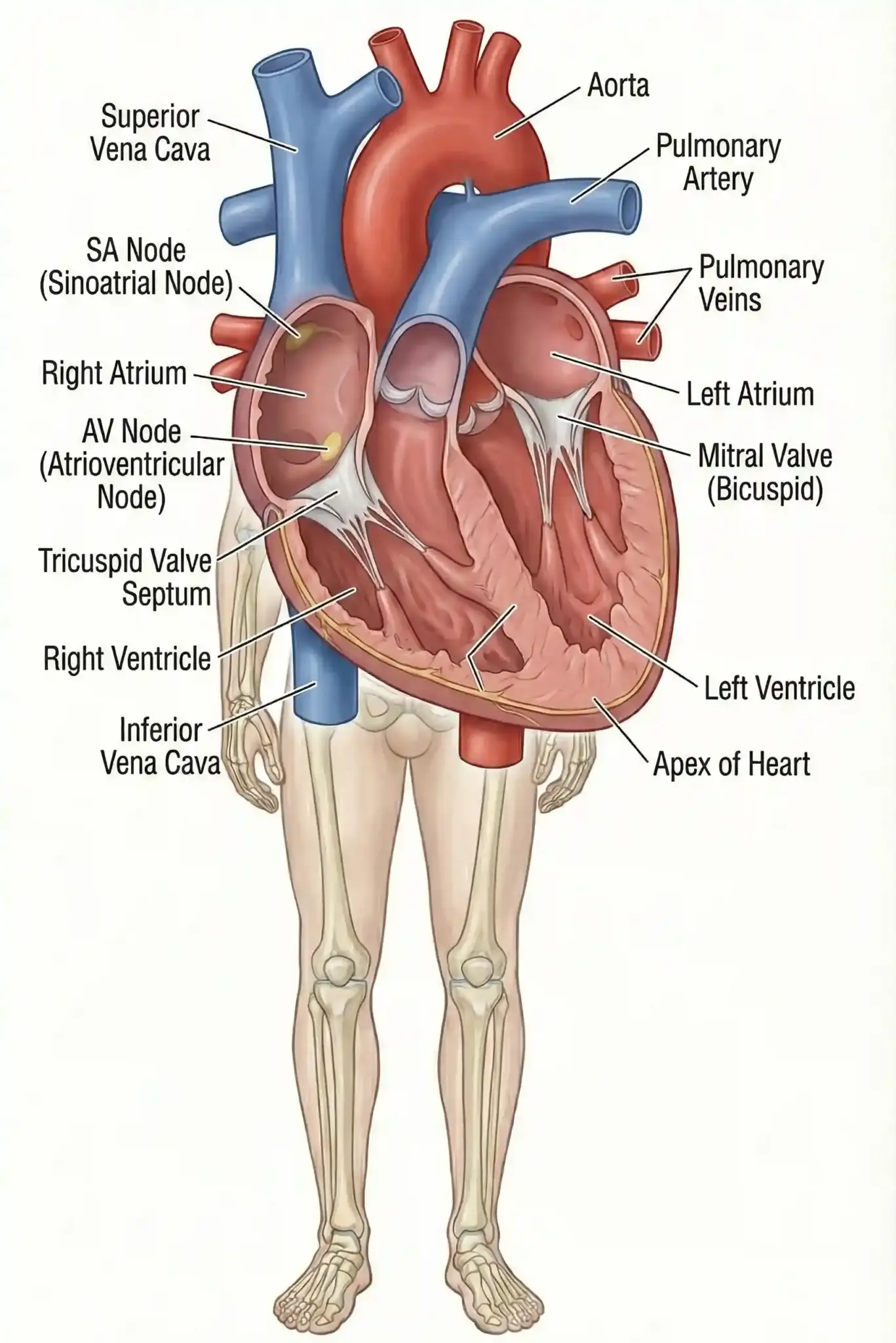
Cardiology deals with the entire cardiovascular system: the heart muscle, heart valves, electrical conduction system, and the arteries and veins that carry blood throughout the body. Cardiologists evaluate symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, dizziness, fainting, and leg swelling to determine whether they are caused by heart or vascular problems.
Common conditions managed in cardiology include:
Some hospitals also collaborate closely with vascular surgery, cardiac surgery, neurology, and emergency medicine to manage strokes, aortic aneurysms, and other complex cardiovascular problems.
Cardiology is a medical (non-surgical) specialty, while cardiac surgery focuses on operations on the heart and major blood vessels. Cardiologists diagnose heart disease, prescribe medications, perform many catheter-based procedures, and coordinate long-term care, but they do not perform open-heart surgery. Cardiac surgeons operate to bypass blocked arteries, repair or replace valves, correct structural problems, or implant certain devices.
Many heart patients are followed primarily by cardiologists, with cardiac surgeons involved only when surgery is needed. Together, these teams decide which patients benefit most from medications and minimally invasive procedures and which require open or hybrid surgery.

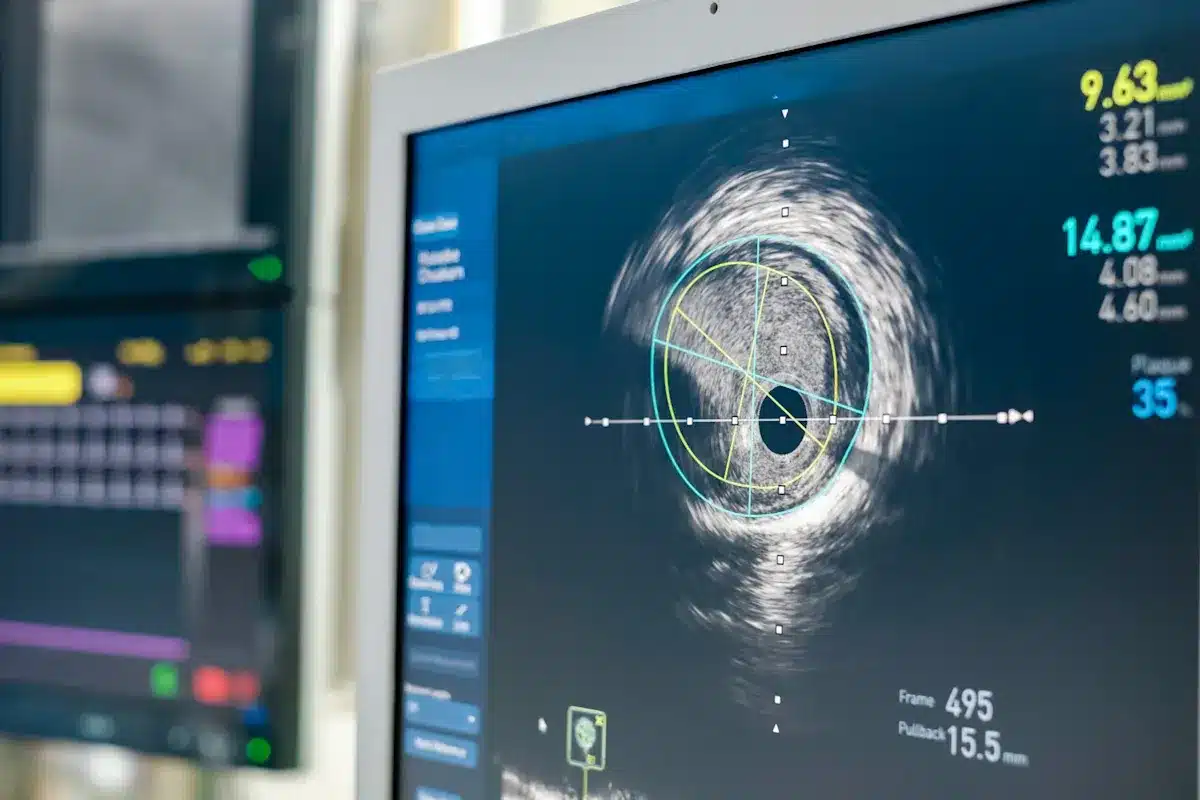
A modern cardiology department offers much more than one-time consultations. Services range from routine check-ups and risk assessment to emergency care for heart attacks and complex procedures such as coronary angiography, angioplasty, and device implantation.
Core cardiology services typically include:
These services help patients receive coordinated evaluation, treatment, and follow-up in one integrated heart center.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.

Cardiovascular diseases are among the leading causes of death and disability worldwide, but many serious events such as heart attacks and strokes are preventable or can be limited with early care. Risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and obesity may cause no symptoms for years while gradually damaging blood vessels and the heart. Detecting problems early allows time to adjust lifestyle, start medications, and plan procedures before irreversible damage occurs.
Prompt treatment also greatly improves outcomes during emergencies. For example, opening a blocked coronary artery quickly during a heart attack can save heart muscle and reduce the risk of heart failure, while rapid treatment of severe arrhythmias or heart failure can be life-saving.
You should seek cardiology evaluation if you have symptoms that may suggest heart or vascular disease or if you carry multiple risk factors even without symptoms. Common reasons to see a cardiologist include chest pain or pressure, shortness of breath with minimal exertion, palpitations, fainting or near-fainting, unexplained fatigue, and leg swelling.
Other situations where cardiology assessment is recommended include:
Even if you feel well, checking your heart health may be advisable if you have multiple risk factors or plan to start an intensive exercise program later in life.
Cardiology is not only about treating acute events; it also focuses on long-term management to prevent new problems and stabilize existing disease. This often involves regular follow-up visits, medication adjustments, monitoring with tests, and close coordination with primary care, endocrinology, and other specialties.

A structured approach helps patients understand their condition and participate actively in protecting their heart health.

At a comprehensive center such as Liv Hospital Cardiology, patients can access emergency care, advanced diagnostics, interventional procedures, and rehabilitation under one roof. The department typically includes subspecialties such as interventional cardiology, heart failure and cardiomyopathy, electrophysiology (for rhythm problems), and imaging. Close collaboration with cardiac surgery, intensive care, and other departments supports care for complex cases, including acute coronary syndromes, valve disease, and congenital heart problems.
For international patients, medical records and previous test results can often be reviewed before arrival to plan a focused evaluation and treatment schedule. During your stay, consultations, tests, and procedures are organized efficiently, and you receive a clear summary of findings, medications, and follow-up recommendations to share with your doctors at home.

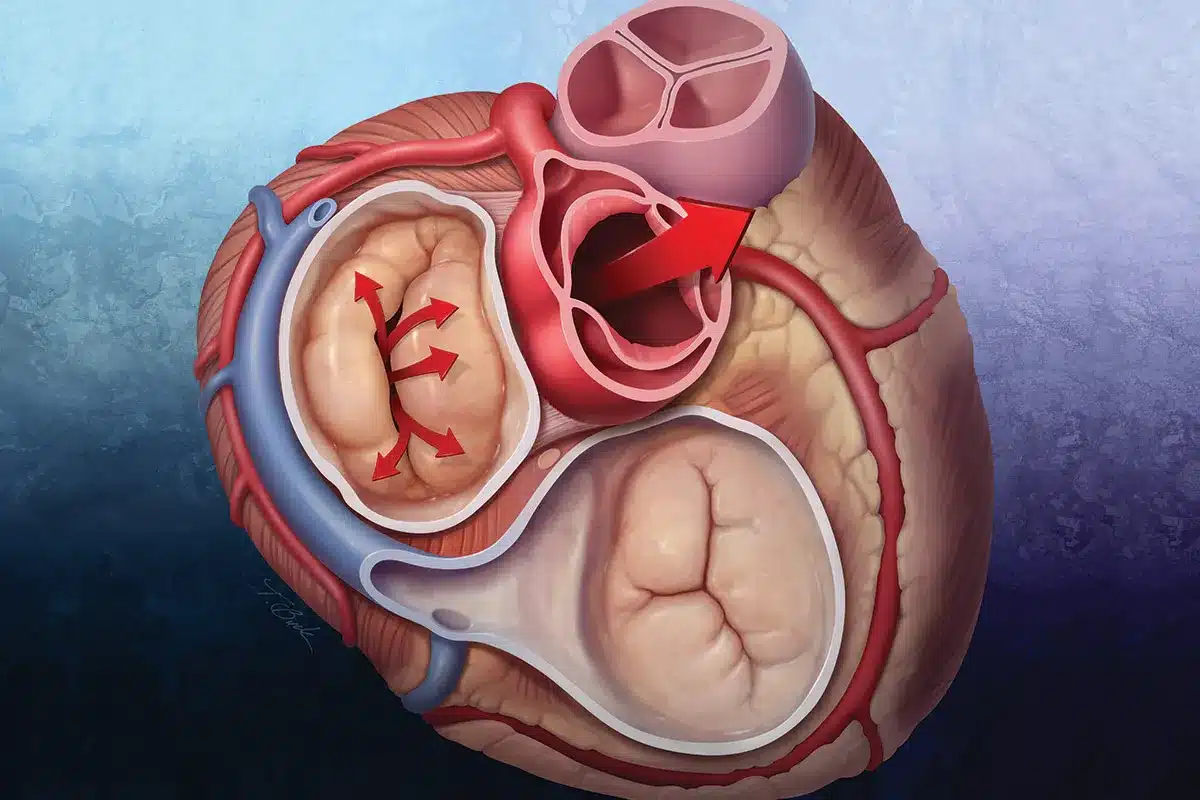
A heart attack is a plumbing problem in which blood flow to the heart is blocked, while cardiac arrest is an electrical problem in which the heart stops beating unexpectedly.
Valves may need replacement if they become too tight (stenosis) to let blood through or too leaky (regurgitation) to hold blood back, causing the heart to overwork.
The ejection fraction is the percentage of blood your heart pumps out with each contraction and is used to assess how well your heart pumps.
While some heart muscle damage is permanent, lifestyle changes and medications can halt the progression of the disease and, in some cases, improve arterial health.
A pacemaker monitors the heart’s natural rhythm and sends an electrical pulse to prompt a heartbeat if it detects that the heart is beating too slowly or missing beats.

What is RFR? Resting Full Cycle Ratio. Get best vital definitions. This new index helps spot dangerous artery issues fast. Amazing tech for you. Radio

Every year, over 1 million heart catheterizations are done in the U.S. This makes it a common way to check and treat heart problems. If

Recent studies show that taking aspirin every day can lower the risk of heart attacks and strokes. This has made people curious about aspirin’s heart-protective
It’s important to know about rare heart conditions to help patients. We look into these uncommon diseases, their traits, and the help available for those

Did you know the National Institutes of Health (NIH) gives out billions in grants each year? Knowing when Federal Financial Reports (FFRs) are due is
A resting heart rate between 60-100 beats per minute is seen as normal for adults. Yet, research shows that a lower resting heart rate links

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)