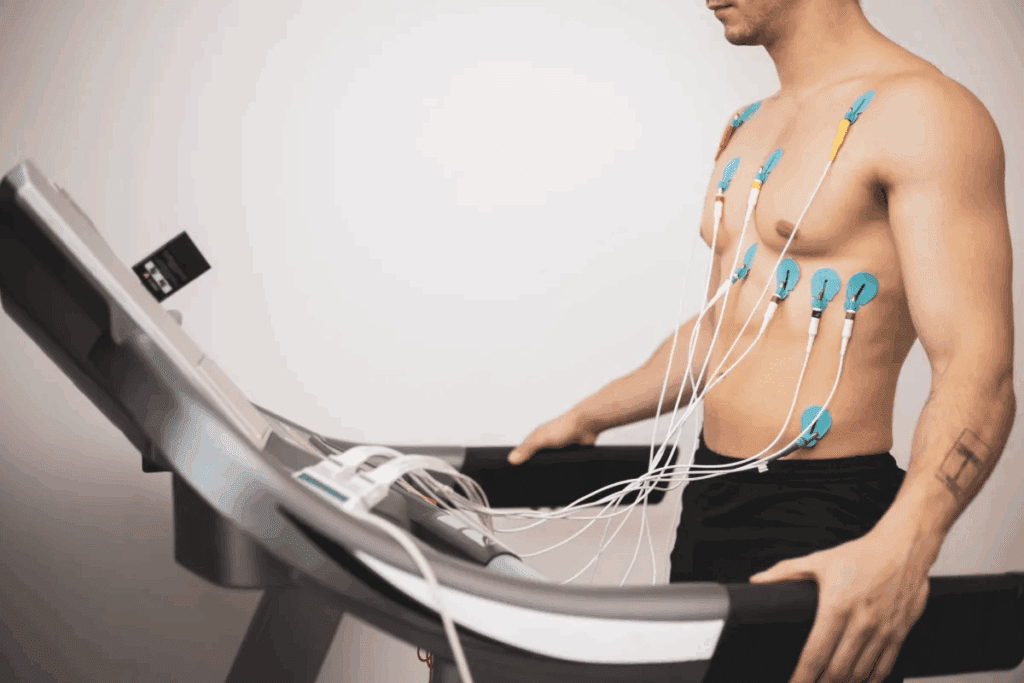
Learn what a nuclear treadmill stress test is, how it compares to dye and standard stress tests for the heart.
When heart health worries come up, getting a correct diagnosis is key. At Liv Hospital, we use top-notch heart care methods. This includes the nuclear treadmill stress test to check heart health and spot problems early.
A nuclear stress test is a special imaging test. It looks at blood flow to the heart when you’re resting and exercising. It uses a tiny bit of radioactive material to see how well the heart works.
We compare the nuclear treadmill stress test to other stress tests. This includes dye-based tests and standard exercise tests. We do this to give a full picture of heart health.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the purpose and benefits of a nuclear treadmill stress test.
- Learn how nuclear stress tests compare to other cardiac assessment methods.
- Discover how Liv Hospital’s advanced cardiac care can support your heart health.
- Find out what to expect from a nuclear stress test.
- Explore the role of imaging tests in diagnosing heart conditions.
Understanding Cardiac Stress Tests

It’s important for both patients and doctors to know about cardiac stress tests. These tests check how well the heart works when it’s under stress. This stress can come from exercise or medicine. They help find heart problems, plan treatments, and see if treatments are working.
The Purpose of Cardiac Stress Testing
Cardiac stress tests check how the heart performs when it’s working its hardest. This is key to spotting problems with blood flow to the heart. Such problems might mean coronary artery disease or other heart issues. Doctors use these tests to understand a patient’s heart health better.
Types of Cardiac Stress Tests Available
There are many types of cardiac stress tests, each with its own way of working. The most well-known include:
- Nuclear stress tests, which use a small amount of radioactive material to image the heart.
- Standard treadmill stress tests, which monitor heart activity while the patient exercises.
- Stress tests using dye or contrast agents, which enhance imaging to provide detailed pictures of the heart.
When Doctors Recommend Stress Testing
Doctors suggest stress tests for several reasons. They help diagnose heart disease, check heart risk, and see if treatments are working. They’re often recommended for people with heart symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath. Also, those at risk for heart disease might need a stress test.
To understand the differences between these tests, let’s look at a comparison table:
| Test Type | Methodology | Key Benefits |
| Nuclear Stress Test | Uses radioactive tracers to image the heart. | Provides detailed images of heart function and blood flow. |
| Standard Treadmill Stress Test | Monitors heart activity during exercise. | Assesses heart function under stress; widely available. |
| Stress Test with Dye/Contrast | Enhances imaging with contrast agents. | Offers clear images of heart structure and function. |
What Is a Nuclear Treadmill Stress Test?

The nuclear treadmill stress test is a complex medical test. It combines exercise with nuclear imaging to check how well the heart works under stress.
This test helps see if the heart muscle gets enough blood, mainly when you’re active. It spots areas where blood flow might be low. This could mean heart disease or other heart problems.
Definition and Basic Procedure
This test has two parts: walking on a treadmill and using a small radioactive tracer. First, the tracer is injected into a vein. It then builds up in the heart muscle based on blood flow.
While walking on the treadmill, the exercise gets harder. This stresses the heart. We then see how the heart works under stress compared to when it’s at rest.
The Role of Radioactive Tracers
The test uses a radioactive tracer like technetium-99m or thallium-201. These tracers give off gamma rays. A special camera called a gamma camera or SPECT scanner catches these rays.
The tracer shows up in the heart muscle. Areas with less uptake might have ischemia or scar tissue. This info is key for diagnosing heart disease and planning treatment.
How Exercise Is Incorporated
Exercise is key in the nuclear treadmill stress test. Patients walk on a treadmill. The speed and incline increase to make the heart work harder. We aim for a heart rate based on age and fitness.
For those who can’t exercise, there’s pharmacological stress testing. This uses medicines to mimic exercise’s effects on the heart.
Equipment and Technology Used
The main tools for this test are a treadmill, an ECG monitor, and a nuclear imaging camera (SPECT or PET scanner). It also needs radioactive tracers and software to analyze the heart’s function.
| Equipment | Description | Function |
| Treadmill | Exercise device | To stress the heart through physical exercise |
| ECG Monitor | Electrocardiogram machine | To monitor heart activity during the test |
| SPECT/PET Scanner | Nuclear imaging camera | To capture images of the heart’s blood flow and function |
By using these technologies together, we get a full picture of the heart’s function. This helps us spot problems early.
The Science Behind Nuclear Imaging
Nuclear imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials to see how the heart works. It’s key in stress tests, showing how the heart handles stress. This helps doctors understand the heart’s blood flow and function.
How Radioactive Tracers Work in the Body
Radioactive tracers are substances that give off radiation. This radiation is picked up by special imaging tools. When given through a vein, these tracers move through the blood and stick to the heart muscle.
Parts of the heart with less blood flow take up less tracer. Areas with normal blood flow take up more. This difference helps doctors see how well the heart is working.
Types of Imaging Used (SPECT vs. PET)
There are two main types of nuclear imaging for heart stress tests: SPECT and PET. SPECT uses a gamma camera to capture gamma rays from the tracer. This gives a 3D view of the heart.
PET, on the other hand, catches positrons from the tracer. It gives clearer images and more detailed info on heart metabolism and blood flow.
Both SPECT and PET have their benefits. SPECT is more common because it’s cheaper and easier to find. PET, though, offers better image quality and accuracy.
| Imaging Type | Description | Advantages |
| SPECT | Uses gamma camera to detect gamma rays | Widely available, lower cost |
| PET | Detects positrons emitted by tracer | Higher resolution, quantitative accuracy |
Radiation Exposure Levels
One worry about nuclear imaging is radiation. The dose from a stress test depends on the tracer and the test’s details. We aim to keep doses low to protect patients while getting clear images.
We know radiation is a big concern. But we’re careful to keep doses low. This way, we get top-notch images without risking our patients’ health.
Standard Treadmill Stress Tests Explained
Standard treadmill stress tests are key to understanding heart health. They check how the heart works when it’s stressed, usually through exercise.
Procedure and Monitoring Methods
We watch a patient’s electrocardiogram (ECG), blood pressure, and heart rate on a treadmill. The exercise gets harder to stress the heart. This helps us see how it performs under different conditions.
The test happens in a place like a hospital or diagnostic center. There, we can keep a close eye on the patient’s vital signs and change the test if needed.
What Standard Tests Can and Cannot Detect
Standard treadmill stress tests can spot coronary artery disease and heart attack risks. They also check if treatments for heart issues are working. But, they don’t show detailed heart images or functions.
Compared to nuclear stress tests, these don’t use radiation. This makes them safer for some patients. Yet, they might miss some heart problems, mainly in those with certain health histories.
Advantages and Limitations
Standard treadmill stress tests are non-invasive, affordable, and give quick results. But, they’re not for everyone. They’re not good for patients with certain health issues or those who can’t exercise.
In summary, standard treadmill stress tests are a great tool for heart health. Knowing how they work, what they can find, and their limits helps us see their value in keeping our hearts healthy.
Stress Tests Using Dye or Contrast Agents
Cardiac stress tests with dye or contrast agents are more detailed. These agents make the heart’s structure and function clearer. This leads to more accurate diagnoses.
How Contrast Agents Enhance Imaging
Contrast agents highlight areas of the heart with good blood flow. They help spot ischemic or damaged areas. This is key during stress tests to see how the heart performs under stress.
Enhanced Imaging: Contrast agents greatly improve stress test images. This is vital for diagnosing heart diseases and other conditions.
Types of Dye Used in Cardiac Testing
There are many contrast agents or dyes for cardiac stress tests. Each has its own use and benefits. The right dye depends on the test’s needs and the patient’s health.
| Type of Dye | Characteristics | Applications |
| Iodine-based contrast | High-density contrast for clear imaging | Commonly used in CT scans and angiography |
| Gadololinium-based contrast | Used for MRI scans, provides detailed soft tissue imaging | Ideal for assessing cardiac structure and function |
| Barium-based contrast | Used for certain types of cardiac imaging, like esophageal studies | Limited use in stress tests, more in gastrointestinal studies |
Contrast vs. Radioactive Tracers
Contrast agents and radioactive tracers are used in cardiac imaging. They serve different purposes. Knowing their differences helps choose the right tool.
Radioactive tracers are used in nuclear stress tests to check heart blood flow. Contrast agents are for stress echocardiography or CT scans. The choice depends on the patient’s needs and the technology available.
Comparing Nuclear, Dye, and Standard Stress Tests
It’s important to know the differences between nuclear, dye, and standard stress tests. This helps patients make better choices for their heart health. The right test depends on the patient’s health history and current state.
Diagnostic Accuracy Comparison
Nuclear stress tests are very accurate, great for finding coronary artery disease. They show detailed images of the heart’s blood flow. This helps doctors spot problems.
Standard stress tests are simpler and less expensive. They work well as a first step to check the heart’s function during exercise.
Dye or contrast-enhanced stress tests give even clearer images of the heart. The choice between these tests depends on what the doctor needs to see.
Risk Profiles of Each Test
Nuclear stress tests involve a small amount of radiation, which is safe. Standard stress tests are mostly safe but can be risky for those with severe heart disease.
Dye or contrast-enhanced tests might cause rare allergic reactions. They can also be risky for people with kidney disease.
Cost and Insurance Coverage
The cost of stress tests varies a lot. Nuclear tests are pricier because of the radioactive tracers and tech. Standard tests are the cheapest.
Insurance coverage also changes based on the test and the patient’s plan. Many plans cover nuclear tests for certain heart issues.
Which Test Is Right for Different Patients
The right test depends on many things. This includes the patient’s health history, symptoms, and what doctors think might be wrong. For example, those at high risk for heart disease might get a nuclear test.
Patients who can’t exercise might get pharmacological stress tests. These tests mimic exercise without needing to move.
Choosing a stress test should always be a team effort. A doctor will consider the patient’s needs and situation to decide the best test.
Preparing for a Nuclear Treadmill Stress Test
To have a smooth and effective nuclear treadmill stress test, patients need to follow certain steps. It’s important to prepare well to get accurate results and avoid risks.
Pre-Test Instructions
Before the test, it’s key to know and follow your doctor’s pre-test instructions. These steps are to keep you safe and make sure the test works well.
- Disclosure of Medical History: Tell your doctor about any health issues, allergies, or medicines you’re taking.
- Medication Management: Some medicines might need to be changed or stopped before the test. Your doctor will tell you what to do.
Dietary and Medication Restrictions
What you eat and drink before the test is important. Patients are usually told not to eat, drink, or smoke for 4-6 hours before. This helps make sure the test results are accurate.
“Fasting before a nuclear stress test is key for accurate results. It lets us see how the heart works under stress without recent food or drink affecting it.”
What to Wear and Bring
Wear comfy clothes and good shoes for walking or running. Choose loose, comfy clothes and sturdy shoes for the treadmill. You might also need to bring medical records or test results.
Duration and Scheduling Considerations
The whole process, from getting ready to recovering, takes a few hours. Plan to spend at least half a day at the testing facility. Try to schedule the test when you can rest afterwards, as you might feel tired.
By following these tips, you can make sure your nuclear treadmill stress test is safe and effective. This helps your healthcare team make the best decisions for your care.
The Complete Nuclear Stress Test Procedure
The nuclear stress test procedure has several steps. It starts with preparation and ends with recovery. This helps us check your heart health. We’ll walk you through each step so you know what to expect.
Before the Exercise Component
Before the test starts, we get you ready. We inject a small amount of radioactive tracer into your vein. This tracer helps us see the heart’s blood flow.
During the Treadmill Phase
After the tracer is in, you’ll walk on a treadmill. It gets faster and steeper to stress your heart. Our team watches your heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG. We aim to reach a target heart rate or see symptoms that match your usual condition.
The Imaging Process
When you reach the peak stress, the tracer spreads through your heart. Then, you lie on a table for imaging. Our camera takes pictures of your heart, showing good blood flow and blockages. We do this again at rest to compare your heart’s function.
Recovery and Post-Test Monitoring
After imaging, you start the recovery phase. Our team keeps an eye on your vital signs. When your heart rate and blood pressure go back to normal, the test is over. You’ll get instructions on what to do next and any follow-up appointments.
Our experienced team is here to make sure you’re safe and comfortable. We know medical tests can be scary. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
Pharmacological Nuclear Stress Tests
When exercise isn’t an option, pharmacological nuclear stress tests are a reliable way to check heart health. This method is great for those who can’t exercise because of health issues or mobility problems.
Alternatives for Patients Who Cannot Exercise
For people who can’t do the exercise needed in traditional stress tests, pharmacological tests are a key tool. These tests use medicine to make the heart work like it does during exercise. This lets doctors check how well the heart works under stress.
Pharmacological stress testing is good for more patients. It includes those with severe mobility issues, chronic pain, or other conditions that stop them from exercising well.
Medications Used to Simulate Exercise
Several medicines are used in pharmacological nuclear stress tests to mimic exercise. These include:
- Adenosine: It makes blood vessels wider, like exercise does.
- Regadenoson: It causes blood vessels to widen, like exercise does, by acting on adenosine receptors.
- Dobutamine: It makes the heart beat faster and stronger, like exercise does.
Doctors pick these medicines based on the patient’s health and what they want to find out.
Comparing Exercise vs. Pharmacological Testing
Both exercise-based and pharmacological nuclear stress tests have their benefits. They are chosen based on the patient’s health and needs.
Exercise stress tests are often preferred because they give a more natural look at how the heart works during exercise. But, pharmacological stress tests are very useful for those who can’t exercise. They give important information for diagnosis.
Doctors decide which test to use based on the patient’s health, how mobile they are, and their heart concerns.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Nuclear stress tests are useful, but they come with risks. It’s important for patients to know these risks to make good choices about their health.
Radiation Exposure Concerns
One big worry is radiation from these tests. The tracers used can slightly raise cancer risk. But, the amount of radiation is usually low.
We do our best to keep radiation low. We use the smallest amount of tracer needed for a good test.
Exercise-Related Risks
The test’s exercise part can be risky for some. It might cause heart problems or low blood pressure. In rare cases, it could lead to heart attack or arrest.
We watch patients closely during the test. We’re ready to act fast if needed.
Allergic Reactions to Tracers
Some might be allergic to the tracers. This can cause mild to severe reactions. It’s rare but can happen.
We check for allergies before the test. We’re ready to handle any bad reactions.
Managing and Minimizing Risks
We follow strict rules to keep risks low. This includes choosing the right patients, watching them closely, and caring for them after the test.
| Risk | Mitigation Strategy |
| Radiation Exposure | Using the lowest effective dose of radioactive tracer |
| Exercise-Related Complications | Close monitoring during the test and having emergency equipment on hand |
| Allergic Reactions | Screening for allergies and being prepared to respond to adverse reactions |
By knowing the risks and taking steps to reduce them, we make sure nuclear stress tests are safe and helpful.
Interpreting Nuclear Stress Test Results
When you get a nuclear stress test, doctors look at your heart’s images. They check how your heart works when it’s stressed and when it’s calm. This helps them see if your heart is healthy.
Understanding Test Images
The images from a nuclear stress test are key to finding heart problems. They show how blood moves to your heart muscle at rest and when you’re stressed. Abnormal blood flow can mean your heart muscle isn’t getting enough oxygen. This could point to heart disease or other heart issues.
What Different Results Mean
Test results can be normal or show problems. Normal results mean your heart is working well, with no big blockages. But, if the results are abnormal, it might mean you have heart disease or damage.
| Result Type | Description | Possible Implications |
| Normal | Normal blood flow at rest and during stress | Low risk of coronary artery disease |
| Abnormal | Reduced blood flow during stress | Possible coronary artery disease or heart damage |
| Ischemia | Reduced blood flow to specific areas of the heart during stress | May indicate blockages or significant coronary artery disease |
Next Steps After Abnormal Results
If your test shows problems, your doctor will talk about what it means. They might suggest more tests, like a coronary angiogram, to see your heart’s arteries better.
Follow-up Testing
You might need more tests to confirm the diagnosis or plan treatment. These could include other imaging tests or procedures to check your heart’s health.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on what your doctor finds. It could be lifestyle changes, medicines, or procedures like angioplasty. Your healthcare team will help you create a plan that’s right for you.
Conclusion
We’ve looked at various cardiac stress tests. These include nuclear treadmill stress tests, standard treadmill tests, and those using dye or contrast agents. Each test has its own way of checking for heart disease.
A nuclear stress test with contrast shows how well the heart works under stress. It helps doctors find where blood flow might be low. This info is key for creating a good treatment plan.
Knowing the differences between these tests helps patients make better choices. By picking the right test, patients get accurate diagnoses and timely care. This can greatly improve their health outcomes.
In short, a heart stress test with contrast is a key tool for checking heart health. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of each test. This way, you can choose the best option for you.
FAQ
What is a nuclear treadmill stress test?
A nuclear treadmill stress test is a test that combines exercise on a treadmill with nuclear imaging. It checks how well the heart works under stress. It helps find coronary artery disease and see how blood flows through the heart.
How does a nuclear stress test differ from a standard treadmill stress test?
A nuclear stress test uses a small amount of radioactive tracer to see the heart’s blood flow. A standard treadmill stress test uses an electrocardiogram (ECG) and physical symptoms. The nuclear test gives more detailed images of the heart’s blood flow.
What is the role of radioactive tracers in a nuclear stress test?
Radioactive tracers help see the heart’s blood flow and function. They are injected into the blood and build up in the heart muscle. This allows for detailed imaging with a special camera.
How do I prepare for a nuclear treadmill stress test?
To prepare, wear comfy clothes and shoes. Avoid caffeine and tell your doctor about any medications or health conditions. You might also need to skip eating for a few hours before the test.
What are the possible risks and side effects of a nuclear stress test?
Risks include radiation exposure and allergic reactions to the tracer. There’s also a chance of exercise-related problems. But these risks are low, and steps are taken to reduce them.
How do I understand my nuclear stress test results?
A doctor will interpret your test results. They’ll look at the images and data from the test. Then, they’ll talk to you about what it means and what steps to take next.
What is the difference between SPECT and PET scans in nuclear stress tests?
SPECT and PET are imaging techniques used in nuclear stress tests. SPECT is more common and shows detailed heart blood flow images. PET scans offer even higher resolution and are used for more complex cases.
Can I undergo a nuclear stress test if I have certain medical conditions?
It depends on your health conditions. Tell your doctor about any health issues, like kidney disease or allergies. They’ll decide if the test is right for you.
How long does a nuclear treadmill stress test take?
The test usually takes a few hours. This includes getting ready, exercising on the treadmill, and imaging. The actual treadmill time is about 7-12 minutes.
Are there alternatives to exercise-based nuclear stress tests?
Yes, there are pharmacological nuclear stress tests for those who can’t exercise. These tests use medications to mimic exercise’s effects on the heart.
What is the cost of a nuclear stress test, and is it covered by insurance?
The cost varies by location and provider. Many insurance plans cover nuclear stress tests when they’re medically necessary. Check with your insurance to see what’s covered.
How does a nuclear stress test compare to a stress test using dye or contrast agents?
Nuclear stress tests use radioactive tracers, while some tests use dye or contrast agents. The choice depends on the diagnostic needs and the patient’s situation.
References:
- ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Blood vessels – an overview. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/immunology-and-microbiology/blood-vessels




































