Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a rare soft tissue cancer. It affects people of all ages, but mostly children and teens. Every year, about 350 kids in the United States get RMS. This shows how important it is to know about this disease.
We will look into who might get rhabdomyosarcoma. We’ll talk about its causes and risk factors. While anyone can get RMS, some groups are more likely. By learning about RMS, we can understand it better.
Knowing about rhabdomyosarcoma helps find it early and treat it well. As we talk about who might get RMS, we’ll share how common it is. We’ll also see why knowing about it is so important.
Key Takeaways
- Rhabdomyosarcoma is a rare soft tissue cancer.
- It’s more common in children and adolescents.
- Understanding the causes and risk factors is key.
- RMS can happen to anyone, but some groups are more at risk.
- Finding it early is vital for good treatment.
Understanding Rhabdomyosarcoma: An Overview
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a rare cancer that comes from muscle cells. It’s a tough condition to deal with. We need to know a lot about it, like what it is, how it’s classified, and how common it is.
Definition and Classification
Rhabdomyosarcoma, or RMS, is a cancer that starts in muscle cells. It’s divided into types based on how it looks under a microscope. The main types are embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, and pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma. Each type acts differently and responds to treatment in its own way.
Doctors say knowing the type of RMS is key to treating it.
“Accurate diagnosis and classification of RMS are essential for effective management and improved patient outcomes.”
,Oncologist
| Subtype | Characteristics | Common Age Group |
| Embryonal RMS | Most common in children, resembles embryonic muscle | 0-10 years |
| Alveolar RMS | More common in adolescents and young adults, aggressive | 10-20 years |
| Pleomorphic RMS | Rare, more common in adults, highly malignant | Adults |
Incidence and Prevalence
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a rare cancer, making up about 3% of all childhood cancers. It’s most common in young kids and teens. The latest numbers show it affects about 4.5 kids per million under 20.
The types of RMS vary in how common they are. Embryonal RMS is the most common in kids, while alveolar RMS is more common in older kids and teens. Knowing this helps doctors find it early and treat it better.
As we learn more about rhabdomyosarcoma, it’s clear we need to understand it well. Knowing its definition, types, how common it is, and more helps us find better treatments and improve care for patients.
What is RMS Disease of Rhabdomyosarcoma
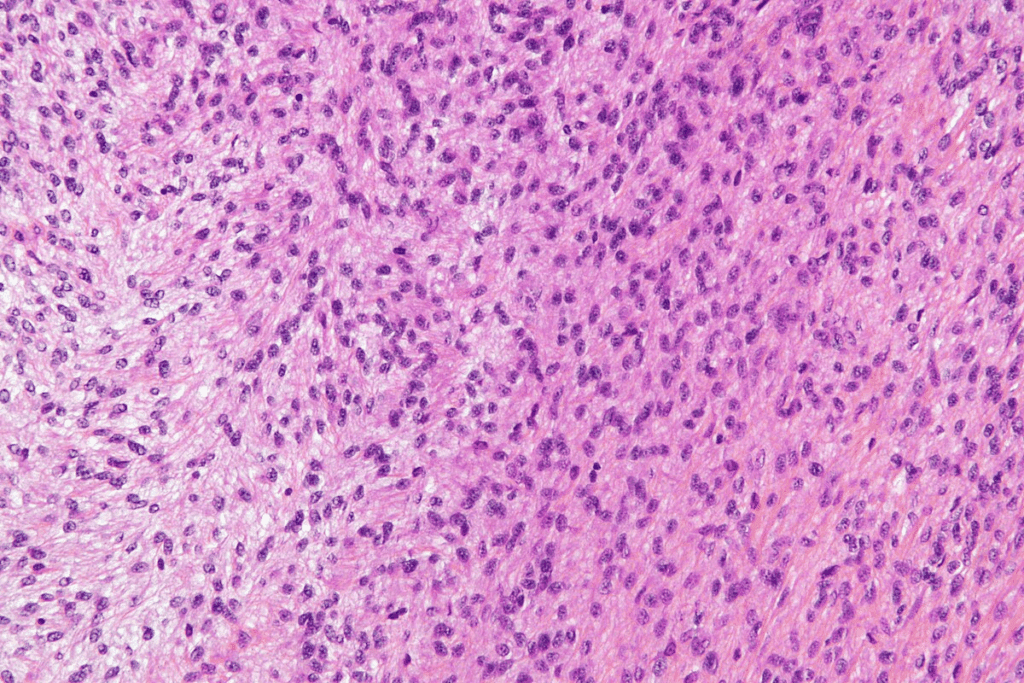
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a rare and complex cancer that affects muscle tissue. It’s important to know its medical definition, how it impacts the body, and what makes it different from other soft tissue sarcomas.
Medical Definition of RMS
RMS is caused by abnormal growth of skeletal muscle cells. This leads to tumors in various parts of the body. If not treated, it can spread to other areas. The medical definition of RMS highlights its origin in skeletal muscle cells, making it unique among sarcomas.
How RMS Affects Muscle Tissue
RMS starts with uncontrolled cell growth, forming tumors. This disrupts normal muscle development and function. The impact on muscle tissue varies based on the RMS type and location.
There are different RMS subtypes, like embryonal and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Each has its own effects on muscle tissue.
Distinguishing RMS from Other Soft Tissue Sarcomas
It’s key to tell RMS apart from other soft tissue sarcomas for accurate diagnosis and treatment. RMS is identified by its origin in skeletal muscle cells. This makes it different from sarcomas that start in other soft tissues.
Understanding RMS’s unique traits is essential for effective treatment. By understanding the differences, healthcare professionals can offer better care.
Types of Rhabdomyosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is divided into different subtypes. This helps doctors tailor treatments to each patient. RMS is a complex disease with various subtypes. Each subtype has its own unique features and behavior.
Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma
Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma is the most common type in kids. It often shows up in the head, neck, or genitourinary tract. It looks like embryonic muscle tissue.
Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma
Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma is more common in teens and young adults. It usually appears in the arms, trunk, or perineal area. This type is aggressive and linked to certain genetic changes.
Other Subtypes: Pleomorphic and Spindle Cell
Pleomorphic and spindle cell Rhabdomyosarcoma are other types. Pleomorphic RMS is more common in adults and has very abnormal cells. Spindle cell RMS is rare but has a better outlook, often found in the paratesticular region or head and neck.
To understand the differences, let’s look at a comparative table.
| Subtype | Common Age Group | Typical Locations | Prognosis |
| Embryonal | Children | Head and Neck, Genitourinary Tract | Variable |
| Alveolar | Adolescents and Young Adults | Extremities, Trunk, Perineal/Perianal Region | Generally Poor |
| Pleomorphic | Adults | Extremities, Trunk | Poor |
| Spindle Cell | Children and Adults | Paratesticular Region, Head and Neck | Favorable |
Rhabdomyosarcoma in Children
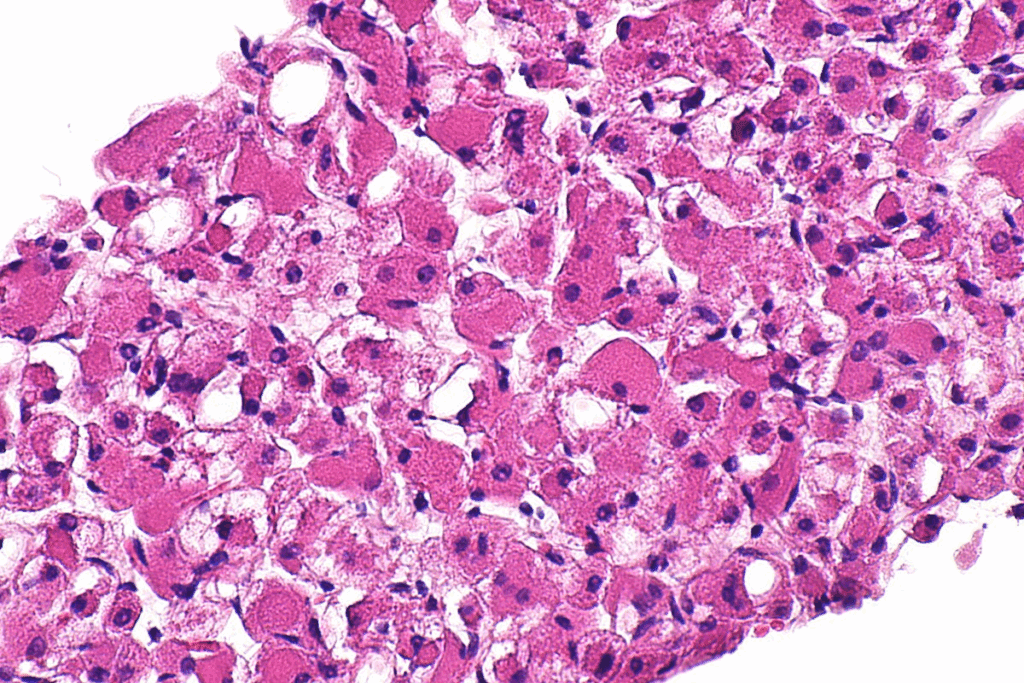
RMS, or rhabdomyosarcoma, is the most common soft tissue sarcoma in kids. We’ll look into how it affects children. This includes how common it is, where it usually happens, and what’s special about treating kids.
Prevalence in Pediatric Populations
Rhabdomyosarcoma is the top soft tissue sarcoma in kids. Most cases happen in kids under 10. It’s a big part of childhood cancers, so early detection is key.
RMS can show up in many places, but some spots are more common in kids. Knowing this helps doctors diagnose and treat better.
Common Sites of Occurrence
In kids, RMS often pops up in the head and neck, the genitourinary tract, and limbs. These areas are more likely to be affected.
| Site of Occurrence | Characteristics |
| Head and Neck | Often presents with symptoms like swelling, pain, or difficulty swallowing |
| Genitourinary Tract | May cause urinary obstruction or other urinary symptoms |
| Limbs | Typically presents as a palpable mass or swelling |
Unique Considerations for Children
Treating RMS in kids requires special thought. Age, tumor location and size, and the child’s health are all important. Treatment usually includes surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation, tailored for each child.
It’s also important to think about the long-term effects of treatment. Kids are more likely to face growth issues, fertility problems, and a higher risk of secondary cancers.
Understanding RMS in kids helps us improve diagnosis, treatment, and support for families. Our aim is to give kids the best care possible, tailored to their needs.
Demographic Patterns in Rhabdomyosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) shows clear patterns in its demographics. These patterns are key to understanding its causes and how well it can be treated. They help us find out who is at higher risk and how to best diagnose and treat them.
Age Distribution and Risk
The age when RMS occurs changes with the type of RMS. Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma is most common in kids under 10. On the other hand, alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is seen more in older kids and teens. Knowing this helps us catch it early and treat it better.
RMS is most common in childhood, with a spike again in late teens. This pattern suggests different causes for RMS at different ages.
Gender and Ethnic Considerations
Gender and ethnicity also affect RMS patterns. RMS is a bit more common in boys than girls. There are also ethnic differences in who gets certain types of RMS.
For example, some genetic traits are more common in certain ethnic groups. This might affect how often RMS occurs. Knowing these differences helps us target our screening and treatment efforts.
By studying RMS demographics, we can find at-risk groups and improve early detection and treatment. This research also helps us understand RMS causes and how to prevent it.
Genetic Predisposition to Rhabdomyosarcoma
Genetic predisposition is key in Rhabdomyosarcoma development. Certain hereditary syndromes and mutations raise the risk. Research has uncovered the complex genetic factors behind this disease.
Hereditary Syndromes Associated with RMS
Certain genetic syndromes increase Rhabdomyosarcoma risk. For example, Li-Fraumeni syndrome significantly raises cancer risk, including RMS. This rare disorder is caused by TP53 gene mutations.
“The link between Li-Fraumeni syndrome and Rhabdomyosarcoma shows the need for genetic screening,” medical researchers say.
Specific Genetic Mutations
Specific genetic mutations also raise Rhabdomyosarcoma risk. Genes like PAX3-FOXO1 and PAX7-FOXO1 are often mutated in alveolar RMS. These mutations disrupt normal cell function, causing tumors.
Family History as a Risk Factor
A family history of cancer, like Rhabdomyosarcoma, is a big risk factor. Studies show people with such a history face higher RMS risk. This makes family history key in assessing risk.
Understanding Rhabdomyosarcoma’s genetic predisposition helps spot high-risk individuals. It also guides the development of targeted treatments. As research digs deeper, we’re getting closer to better prevention and treatment.
Environmental Risk Factors
Studies show that environmental factors are key in rhabdomyosarcoma development. It’s important to understand these factors to fight this disease.
Prenatal and Early Life Exposures
Exposure to toxins before birth and in early life may raise RMS risk. Pesticides and industrial pollutants are linked to higher RMS risk in kids. A study found that prenatal pesticide exposure increases RMS risk in children.
Early life ionizing radiation exposure is also linked to RMS. The exact how is being studied. It’s thought that such exposure may cause genetic changes that lead to RMS.
Other Environmental Considerations
Other factors like workplace chemicals also play a role in RMS risk. For example, vinyl chloride, used in PVC production, is linked to cancer risk, including RMS.
Lifestyle and environmental factors like diet and infections may also affect RMS risk. Eating fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is good for health and may protect against RMS.
| Environmental Factor | Potential Risk | Evidence |
| Prenatal exposure to pesticides | Increased risk of RMS in children | Correlational studies |
| Early life exposure to ionizing radiation | Increased risk of RMS | Epidemiological studies |
| Workplace exposure to certain chemicals (e.g., vinyl chloride) | Increased risk of various cancers, potentially RMS | Occupational health studies |
Research is ongoing to understand RMS’s complex causes. Knowing these risk factors helps in creating prevention and early detection plans.
Recognizing Symptoms of Rhabdomyosarcoma
The symptoms of rhabdomyosarcoma depend on where and how big the tumor is. Spotting these symptoms early is key for quick diagnosis and treatment.
Common Presenting Signs
Rhabdomyosarcoma shows up in different ways, based on where the tumor is. Common signs include:
- A swelling or lump in the affected area
- Pain or tenderness
- Impaired function of the affected muscle or limb
These signs can look like other health issues. So, it’s important to see a doctor for a correct diagnosis.
Symptoms by Anatomical Location
The symptoms of rhabdomyosarcoma change based on where the tumor is. Here are some common symptoms for different areas:
| Location | Common Symptoms |
| Head and Neck | Swelling, pain, difficulty swallowing, or protrusion of the eye |
| Genitourinary Tract | Urinary obstruction, hematuria, or a palpable mass |
| Limbs | Swelling, pain, or limited mobility |
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you or your child has any lasting or odd symptoms, get medical help. Early diagnosis is key for effective treatment and better results.
Key indicators to seek medical help include:
- A lump or swelling that doesn’t go away
- Persistent pain
- Unexplained bleeding or discharge
Seeing a doctor quickly can greatly impact the diagnosis and treatment of rhabdomyosarcoma.
Diagnostic Process for Rhabdomyosarcoma
The process to diagnose rhabdomyosarcoma is detailed. It includes several steps like initial assessment, imaging, biopsy, and staging. A mix of clinical checks, imaging, and lab tests is needed to find this condition.
Initial Assessment and Physical Examination
The first step is a detailed medical history and physical check-up. Doctors look for signs like swelling, pain, or a mass. This helps decide if more tests are needed.
Imaging Studies
Imaging is key in finding rhabdomyosarcoma. Ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans show where and how big the tumor is. These images help plan treatment and understand the tumor’s size.
Biopsy and Pathological Examination
A biopsy is vital to confirm rhabdomyosarcoma. A tissue sample is taken and checked under a microscope. Pathologists look for specific signs, like cross-striations, to make the diagnosis.
- Fine-needle aspiration biopsy
- Core needle biopsy
- Incisional or excisional biopsy
Staging and Risk Stratification
After confirming the diagnosis, the next step is to find out the stage and risk level. Staging checks how far the tumor has spread. This info is key for planning treatment and predicting how well the patient will do.
- Stage 1: Localized disease, completely resected
- Stage 2: Localized disease, microscopic residual
- Stage 3: Localized disease, gross residual or regional disease
- Stage 4: Distant metastatic disease
Knowing how rhabdomyosarcoma is diagnosed is important. It helps get the right treatment and improves patient outcomes.
Treatment Approaches for Rhabdomyosarcoma
Treating rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) means using surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy together. Each treatment is chosen based on the patient’s specific needs.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is key in treating RMS. It aims to remove the tumor completely. The type of surgery needed depends on the tumor’s location and size.
- Tumor resection with wide margins to ensure removal of all cancerous cells
- Lymph node dissection in cases where cancer has spread to the lymph nodes
- Reconstructive surgery to restore function and appearance after tumor removal
Radiation Therapy Protocols
Radiation therapy targets and kills cancer cells that can’t be removed surgically. It also helps prevent the cancer from coming back. The treatment plans for RMS are very detailed.
- External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) is commonly used to deliver precise doses of radiation to the tumor site.
- Brachytherapy, where small radioactive sources are placed near or within the tumor, may be used in certain cases.
Chemotherapy Regimens
Chemotherapy is vital in treating RMS, even for tumors that can’t be fully removed. Chemotherapy regimens for RMS often include a mix of drugs.
- Vincristine, Actinomycin-D, and Cyclophosphamide (VAC) is a common chemotherapy regimen.
- Other drugs like Doxorubicin and Etoposide may be added or used in alternative regimens based on the patient’s response and risk stratification.
Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials
New treatments for RMS are being researched, with several promising options in clinical trials. These include targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and new chemotherapy agents.
Joining clinical trials can give patients access to new treatments. It’s important for patients and their families to talk about the benefits and risks with their doctors.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The outlook for rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) changes a lot based on several important factors. Knowing these factors helps patients and their families deal with the disease’s challenges.
Factors Affecting Prognosis
Several elements impact the prognosis of RMS. These include:
- Type of RMS: The subtype, like embryonal or alveolar, greatly affects the prognosis.
- Stage at Diagnosis: How far the disease has spread at diagnosis is key.
- Response to Treatment: How well the tumor responds to treatment is a big indicator of long-term success.
- Age of the Patient: Age can change the prognosis, with younger patients often doing better than older ones.
Survival Statistics by Type and Stage
Thanks to better treatments, survival rates for RMS have gone up. But, survival rates differ based on the type and stage of RMS:
- Embryonal RMS: Usually has a better outlook, mainly in young kids.
- Alveolar RMS: Often has a worse prognosis because it’s more aggressive.
- Localized Disease: Patients with localized RMS tend to live longer than those with spread disease.
Long-term Outcomes and Recurrence
Long-term results for RMS patients depend on many things. These include how well the first treatment worked and if the disease comes back. Coming back is a big worry, mainly in the first few years after treatment.
- Regular check-ups are key to catch any signs of coming back.
- Survivors might face late effects from treatment, needing ongoing support.
We stress the need for full care for RMS patients. This care should cover both the physical and emotional sides of their journey. By knowing what affects prognosis and survival, patients and their families can better handle RMS’s complexities.
Living with Rhabdomyosarcoma
Getting a diagnosis of rhabdomyosarcoma starts a tough journey. It needs strength, hope, and a strong support system. To live with RMS, you need a full care plan. This includes medical treatment, managing side effects, follow-up care, and psychosocial support.
Managing Side Effects of Treatment
RMS treatment is tough, with surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. It’s key to manage side effects to keep quality of life good. Effective side effect management needs a team of healthcare experts working together.
Side effects like fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and infection risk are common. Knowing these side effects helps patients and families prepare. For example, nutrition counseling helps with diet changes, and psychological support helps with emotional challenges.
Follow-up Care and Monitoring
After treatment, follow-up care is key to watch health and catch any problems early. Regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare team are important. They help spot issues quickly and take action.
Follow-up care includes visits, tests, and procedures based on the patient’s risk and treatment history. This ongoing check-up is vital for the best outcomes and to address any concerns or symptoms.
Psychosocial Support for Patients and Families
RMS affects not just the patient but also their family and loved ones. Psychosocial support is a big part of care, helping with emotional, social, and psychological needs. Support can be counseling, support groups, or online resources.
Access to psychosocial support boosts well-being for patients and families. It helps them deal with RMS challenges. By focusing on mental health and support, we can build resilience and improve life quality for those with rhabdomyosarcoma.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS), a rare and aggressive cancer that affects muscle tissue. Knowing about RMS is key for early detection and treatment. Our look into RMS shows how important it is to know its causes and risk factors.
Diagnosing and treating RMS involves many steps, like surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Each treatment plan is made for the person, based on the disease’s type and stage. Knowing the causes and risk factors helps us better treat RMS and improve patient results.
As we learn more about RMS, raising awareness is vital. Early detection and good care can greatly help those affected. We’re dedicated to top-notch healthcare and support for patients from around the world.
FAQ
What is rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS)?
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a cancer that affects muscle tissue. It mostly happens in kids and teens but can also affect adults. It starts in the muscle cells of soft tissues.
What are the different types of rhabdomyosarcoma?
There are several types of RMS. The most common is embryonal RMS, found in kids. Alveolar RMS is more common in teens and young adults.
What are the symptoms of rhabdomyosarcoma?
Symptoms depend on where the tumor is. You might notice swelling, pain, or a lump. Other signs include trouble swallowing, urinary issues, or vision problems.
How is rhabdomyosarcoma diagnosed?
Doctors use imaging studies like MRI or CT scans and a biopsy to diagnose RMS. They also do a pathological exam. Staging and risk stratification help decide the best treatment.
What are the treatment options for rhabdomyosarcoma?
Treatment for RMS includes surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. The plan depends on the tumor’s type, stage, and location, and the patient’s health.
What is the prognosis for rhabdomyosarcoma?
Prognosis varies based on the type, stage, and treatment response. Kids with localized RMS usually have a better outlook than those with metastatic disease. Survival rates have improved with better treatments.
Are there any genetic risk factors for rhabdomyosarcoma?
Yes, genetic syndromes like Li-Fraumeni syndrome and specific mutations can raise the risk. Family history also plays a role in some cases.
Can environmental factors contribute to the development of rhabdomyosarcoma?
Prenatal and early life exposures, along with other environmental factors, may increase the risk. But the exact causes are not fully understood.
How can patients and families cope with rhabdomyosarcoma?
Managing side effects and getting psychosocial support are key. Access to care and support services can greatly improve life quality.
Why is awareness and early detection important for rhabdomyosarcoma?
Early detection and awareness are vital for better treatment outcomes and survival. Recognizing symptoms and getting medical help quickly can make a big difference.
References
- Shrestha, A., Spector, L. G., & Flanders, W. D. (2013). Early life factors and risk of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 22(3), 595-603. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3854857/
- Martin-Giacalone, B. A., Li, H., Scheurer, M. E., et al. (2024). Germline genetic testing and survival outcomes among children with rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. JAMA Network Open, 7(3), e244170. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2816828


































