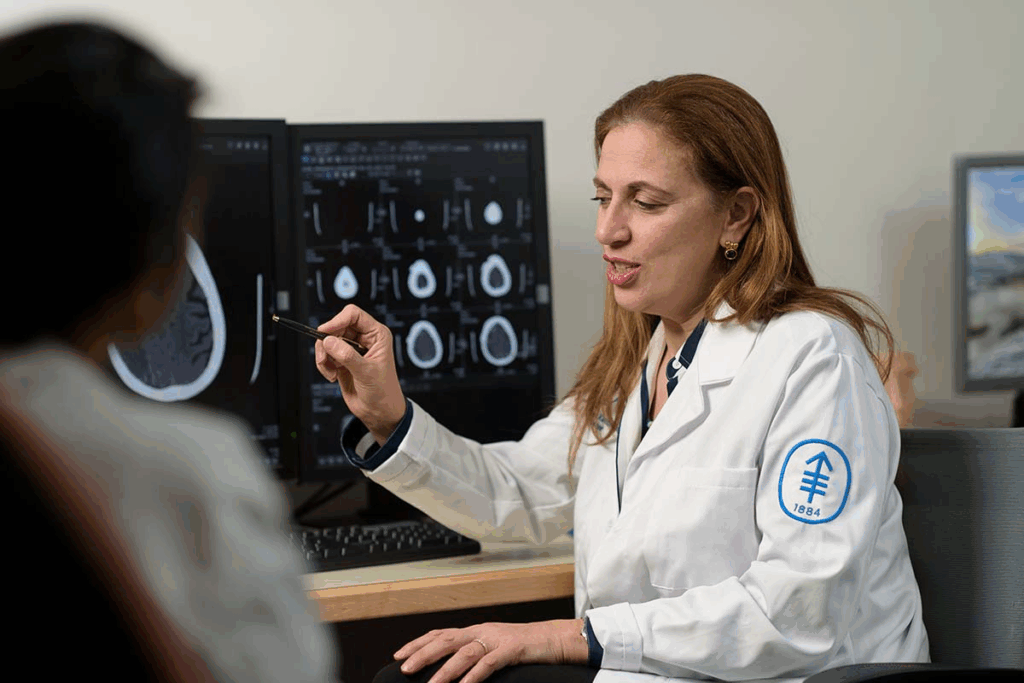
Imagine having a brain surgery while you’re fully awake and alert. This is true for many patients who have an awake craniotomy. It’s a type of neurosurgery where the patient is awake and can respond during the surgery.
During awake brain surgery, doctors remove damaged or diseased tissue carefully. They do this to keep important brain functions working. This surgery needs a very skilled team and a patient who can cooperate.
Key Takeaways
- Awake craniotomy is a type of neurosurgery performed while the patient is awake.
- The procedure requires a highly skilled neurosurgical team.
- Patients remain conscious and responsive during the brain operation.
- Awake brain surgery helps preserve critical brain functions.
- The procedure is used to treat various brain conditions.
The Reality of Awake Brain Surgery
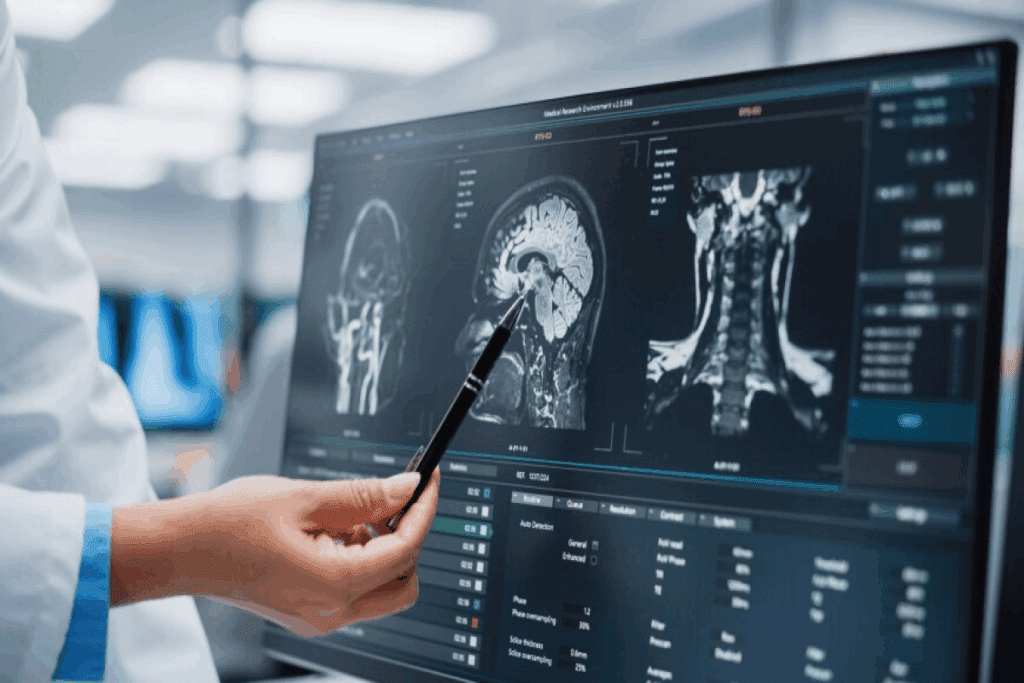
Being awake during brain surgery might sound scary, but it’s true for many patients. They undergo awake craniotomy. This complex surgery needs the patient’s help and the team’s skill.
What Exactly Is Awake Craniotomy?
Awake craniotomy is a type of brain surgery. It lets neurosurgeons open the skull while the patient is awake. This way, they can work on hard-to-reach brain areas with more accuracy.
Historical Development of the Technique
The awake craniotomy has a long history, starting in the early 1900s. At first, many doubted it. But as surgery techniques got better, so did the use of awake craniotomy.
Now, it’s a key part of brain surgery. It helps both patients and doctors a lot.
Year | Milestone in Awake Craniotomy |
1930s | First recorded instances of awake craniotomy |
1960s | Advancements in neurosurgical techniques increase adoption |
2000s | Modern anesthesia and monitoring techniques enhance safety |
Why Patients Need to Be Awake During Brain Operations
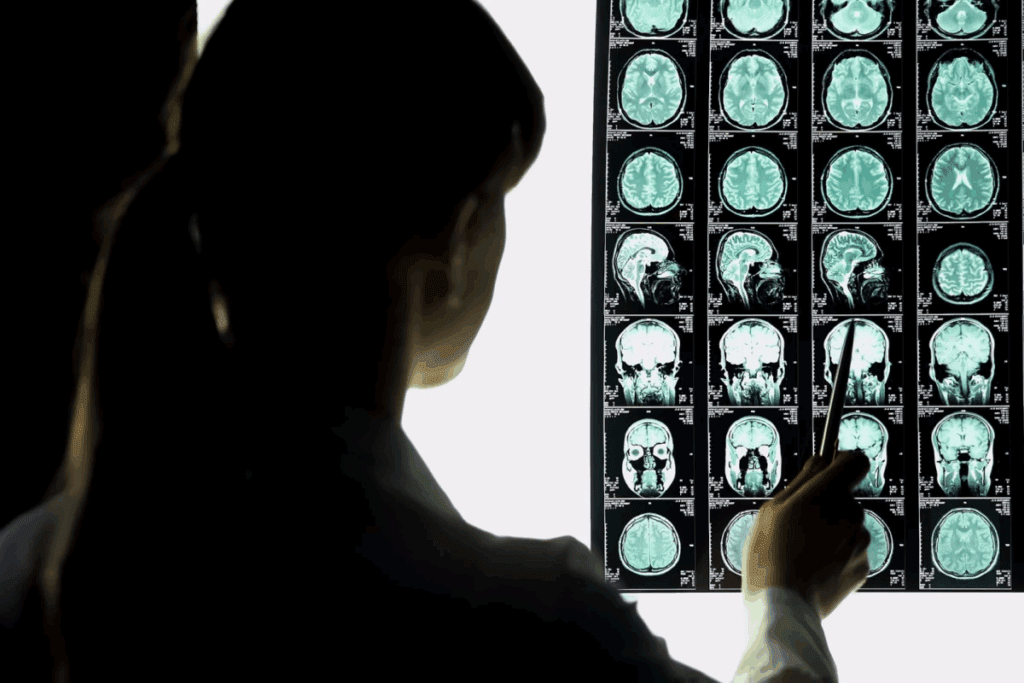
Patients must stay awake during brain surgery to keep important brain functions safe. This lets neurosurgeons watch how the brain reacts in real-time. It helps ensure that key functions are not harmed during the surgery.
Preserving Critical Brain Functions
Keeping patients awake is key to saving brain functions like language and motor skills. When awake, patients can respond to tasks. This helps surgeons avoid damaging important brain areas.
Language and Motor Skills Protection
Surgeons test language and motor skills by asking patients to speak or move. This feedback is key to protecting the brain’s function areas.
Cognitive Function Assessment
Awake surgery also lets surgeons check cognitive function. This is important for seeing how the surgery affects the brain. It helps make adjustments to keep cognitive abilities safe.
Medical Conditions Requiring Awake Surgery
Some medical issues need awake brain surgery. These include brain tumors, epilepsy, and movement disorders. Awake surgery is more precise and safer for these conditions.
Brain Tumors in Eloquent Areas
Brain tumors in key areas need careful surgery. Awake surgery helps remove tumors without harming vital functions.
Epilepsy and Movement Disorders
Awake surgery treats epilepsy and movement disorders too. Patients’ feedback helps surgeons avoid damaging brain areas involved in these conditions.
“The ability to perform surgery on an awake patient is a game-changer in neurosurgery, allowing us to treat complex conditions with greater precision and safety.”
Understanding the need for awake brain surgery helps both patients and doctors. It shows the advanced benefits and complexities of this technique.
The Complete Brain Operation Process
The brain operation process includes getting ready before surgery, managing anesthesia, and watching over patients after. This careful plan helps make sure surgeries go well, even when patients need to stay awake.
Preoperative Preparation and Assessment
Getting ready for surgery is key. Patients have tests like MRI and CT scans to help doctors plan. They also share their medical history and go through physical exams to spot any risks.
Before surgery, patients learn what to expect. This helps lower their stress and makes sure they’re ready for the surgery.
Anesthesia Management During Surgery
Managing anesthesia is very important, more so in awake neurosurgery. The team uses a special method called “awake craniotomy anesthesia.” It has two parts: sedation and awake management.
Initial Sedation Phase
In the first part, patients get sedatives to relax. This makes them comfortable but able to follow commands if needed.
Awake Phase Management
In the second part, patients are fully awake. This part needs careful management to keep them comfortable and cooperative. Surgeons can do important parts of the surgery while patients are awake, making adjustments as needed.
Immediate Post-Procedure Monitoring
After surgery, patients are watched closely in a recovery area. Medical staff look for any signs of problems, like brain issues or reactions to anesthesia. Post-operative care is tailored to each patient to help them recover smoothly.
Monitoring includes checking vital signs and doing neurological tests. Pain management is also a big focus, with medication given as needed to keep patients comfortable.
Patient Experiences During Awake Neurosurgery
Patients going through awake neurosurgery feel both physical and emotional sensations. These feelings can change a lot, based on the surgery type, the patient’s health, and how ready they are mentally.
Physical and Psychological Sensations
Patients might feel anything from a little discomfort to pain during the surgery. This depends on the operation’s stage and the brain area being worked on. They might also feel anxious, scared, or disconnected from what’s happening.
Pain Management Reality
Managing pain well is key during awake neurosurgery. Local anesthesia is used to numb the scalp and brain areas. But, some patients might feel pressure or discomfort.
Emotional Responses
Patients’ emotional reactions can be very different. Some might feel anxious or scared, while others stay calm. Preoperative counseling and support from the team help manage these feelings.
Interacting with the Surgical Team
Talking and working with the surgical team is very important in awake neurosurgery. Patients do specific tasks during the surgery. This helps the surgeons understand and protect important brain functions.
Types of Tasks Performed
Patients might do simple things like moving a limb or more complex tasks like speaking or reading. These tasks help the team identify and keep safe vital brain areas.
Patient Testimonials
Many patients say they had a good experience with awake neurosurgery. They thank the team for their professionalism and support. They say clear communication and care are key during the procedure.
Aspect of Experience | Patient Feedback |
Pain Management | Generally positive, with some reporting mild discomfort |
Emotional Support | Highly valued; helped in managing anxiety and fear |
Interaction with Surgical Team | Positive; appreciated clear instructions and support |
Advanced Brain Mapping Techniques
Brain mapping has grown a lot, helping a lot in awake neurosurgery. New brain mapping methods help doctors find important brain spots with great accuracy. This makes surgeries safer and more effective.
Functional MRI and Preoperative Planning
Functional MRI (fMRI) is a way to see brain function without hurting it. It checks blood flow changes in the brain. Doctors use it before surgery to know the brain’s layout and how it works.
This info is key for planning the surgery. It helps doctors know which parts to keep safe.
Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring
Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring (IONM) watches the nervous system during surgery. It uses direct cortical stimulation and electrocorticography. These methods help map brain functions as surgery happens.
Direct Cortical Stimulation
Direct cortical stimulation uses electricity to find brain spots for important tasks. This includes moving, talking, and feeling. It’s vital for keeping these functions safe during surgery.
Electrocorticography
Electrocorticography (ECoG) records brain electrical activity right from the surface. It finds seizure spots and maps brain functions. This info helps guide the surgery.
Weighing the Risks and Benefits
It’s important to know the risks and benefits of awake neurosurgery before deciding. This surgery lets patients stay awake during parts of the operation. It helps surgeons see how the brain works in real-time, which can lead to better results.
Advantages of Awake Neurosurgery
Awake neurosurgery has many good points. It can lead to better brain function and fewer problems after surgery. This is because surgeons can see how the brain works while they operate.
Improved Functional Outcomes
The main good thing about awake neurosurgery is that it can make patients do better after surgery. Surgeons can avoid hurting important parts of the brain. This is shown in a study in the Journal of Neurosurgery.
“The awake craniotomy technique has revolutionized the field of neurosurgery, enabling surgeons to operate with greater precision and accuracy.”
Reduced Neurological Deficits
Awake neurosurgery also means fewer brain problems after surgery. Surgeons watch the brain closely during surgery. This helps them avoid causing more damage.
Potential Complications and Concerns
Even though awake neurosurgery has many benefits, it also has risks. These include seizures during surgery and how it might affect a person’s mind.
Intraoperative Seizures
One big risk is seizures during surgery. These can happen because of how the brain is being tested. Doctors and anesthesiologists need to be ready to handle these seizures quickly.
Psychological Impact
Being awake during surgery can also affect a person’s mind. They might feel scared or stressed. But, with the right help and support, many people can handle these feelings well.
In summary, awake neurosurgery is a complex choice. It has many benefits, like better brain function and fewer problems after surgery. But, it also has risks like seizures and how it might affect a person’s mind.
Recovery Journey After Brain Surgery
After brain surgery, patients start a long recovery journey. It includes time in the hospital and then rehabilitation. This journey is key to getting back to health and function.
Hospital Stay and Early Recovery
The first part of recovery happens in the hospital. Here, doctors and nurses watch over the patient closely.
First 48 Hours Post-Surgery
The first 48 hours are very important. Medical staff look for any problems or bad reactions to the surgery. Patients are closely watched to manage pain and any immediate issues.
Managing Initial Side Effects
Side effects like nausea, headache, and tiredness are treated with medicine and rest. The medical team helps find ways to lessen these effects and aid in a smooth recovery.
Long-Term Rehabilitation Process
After leaving the hospital, patients need a long-term rehab to fully recover.
Physical Therapy Requirements
Physical therapy is key to getting back strength, mobility, and coordination. A therapy plan is made just for the patient’s needs.
Cognitive Rehabilitation
Cognitive rehab helps fix any brain function issues from the surgery. It works on memory, attention, and solving problems.
Rehabilitation Component | Description | Goals |
Physical Therapy | Regaining physical strength and mobility | Improve mobility, reduce pain |
Cognitive Rehabilitation | Restoring cognitive functions | Enhance memory, attention, problem-solving |
Speech Therapy | Addressing communication issues | Improve speech clarity, comprehension |
Alternative Approaches to Neurosurgery
The field of neurosurgery is evolving with new, advanced techniques. While traditional surgery under general anesthesia is key, new methods are being used. They aim to improve results and lower risks.
Advanced Imaging and Navigation Systems
Advanced imaging and navigation systems have changed neurosurgery. Tools like functional MRI and intraoperative MRI help locate brain structures. This lets surgeons work with more precision in complex areas.
- Precise tumor resection: Ensuring maximal removal of tumors while preserving critical brain functions.
- Reduced risk of neurological damage: By accurately mapping brain areas responsible for vital functions.
- Enhanced patient safety: Through real-time monitoring and adjustments during surgery.
When Traditional Surgery Under General Anesthesia Is Preferred
Even with new methods, traditional surgery under general anesthesia is often the best choice. This is true for:
- Complex aneurysms or AVMs: Conditions that require a high level of control and stability, often best achieved under general anesthesia.
- Pediatric neurosurgery: Children often require general anesthesia to ensure they remain calm during delicate procedures.
- Emergency situations: Acute trauma or hemorrhage may necessitate immediate surgery under general anesthesia.
Neurosurgeons use their knowledge to choose the best method for each patient. This approach helps improve outcomes and recovery.
Conclusion: The Evolving Landscape of Neurosurgery
The field of neurosurgery is always getting better. New techniques and technologies are being developed to help patients more. Awake brain surgery is a big step forward, helping with complex brain conditions.
Awake craniotomy has shown great results in keeping brain functions safe. It uses advanced tools like functional MRI and neurophysiological monitoring. These tools make brain surgeries more precise.
Neurosurgery, including brain and neurological surgery, is getting more advanced. This progress will keep going, thanks to research and new tech. Patients can look forward to better treatments and results in the future.
Are you awake during neurosurgery?
Imagine having a brain surgery while you’re fully awake and alert. This is true for many patients who have an awake craniotomy. It’s a type of neurosurgery where the patient is awake and can respond during the surgery.
During awake brain surgery, doctors remove damaged or diseased tissue carefully. They do this to keep important brain functions working. This surgery needs a very skilled team and a patient who can cooperate.
Key Takeaways
- Awake craniotomy is a type of neurosurgery performed while the patient is awake.
- The procedure requires a highly skilled neurosurgical team.
- Patients remain conscious and responsive during the brain operation.
- Awake brain surgery helps preserve critical brain functions.
- The procedure is used to treat various brain conditions.
The Reality of Awake Brain Surgery
Being awake during brain surgery might sound scary, but it’s true for many patients. They undergo awake craniotomy. This complex surgery needs the patient’s help and the team’s skill.
What Exactly Is Awake Craniotomy?
Awake craniotomy is a type of brain surgery. It lets neurosurgeons open the skull while the patient is awake. This way, they can work on hard-to-reach brain areas with more accuracy.
Historical Development of the Technique
The awake craniotomy has a long history, starting in the early 1900s. At first, many doubted it. But as surgery techniques got better, so did the use of awake craniotomy.
Now, it’s a key part of brain surgery. It helps both patients and doctors a lot.
Year | Milestone in Awake Craniotomy |
1930s | First recorded instances of awake craniotomy |
1960s | Advancements in neurosurgical techniques increase adoption |
2000s | Modern anesthesia and monitoring techniques enhance safety |
Why Patients Need to Be Awake During Brain Operations
Patients must stay awake during brain surgery to keep important brain functions safe. This lets neurosurgeons watch how the brain reacts in real-time. It helps ensure that key functions are not harmed during the surgery.
Preserving Critical Brain Functions
Keeping patients awake is key to saving brain functions like language and motor skills. When awake, patients can respond to tasks. This helps surgeons avoid damaging important brain areas.
Language and Motor Skills Protection
Surgeons test language and motor skills by asking patients to speak or move. This feedback is key to protecting the brain’s function areas.
Cognitive Function Assessment
Awake surgery also lets surgeons check cognitive function. This is important for seeing how the surgery affects the brain. It helps make adjustments to keep cognitive abilities safe.
Medical Conditions Requiring Awake Surgery
Some medical issues need awake brain surgery. These include brain tumors, epilepsy, and movement disorders. Awake surgery is more precise and safer for these conditions.
Brain Tumors in Eloquent Areas
Brain tumors in key areas need careful surgery. Awake surgery helps remove tumors without harming vital functions.
Epilepsy and Movement Disorders
Awake surgery treats epilepsy and movement disorders too. Patients’ feedback helps surgeons avoid damaging brain areas involved in these conditions.
“The ability to perform surgery on an awake patient is a game-changer in neurosurgery, allowing us to treat complex conditions with greater precision and safety.”
Understanding the need for awake brain surgery helps both patients and doctors. It shows the advanced benefits and complexities of this technique.
The Complete Brain Operation Process
The brain operation process includes getting ready before surgery, managing anesthesia, and watching over patients after. This careful plan helps make sure surgeries go well, even when patients need to stay awake.
Preoperative Preparation and Assessment
Getting ready for surgery is key. Patients have tests like MRI and CT scans to help doctors plan. They also share their medical history and go through physical exams to spot any risks.
Before surgery, patients learn what to expect. This helps lower their stress and makes sure they’re ready for the surgery.
Anesthesia Management During Surgery
Managing anesthesia is very important, more so in awake neurosurgery. The team uses a special method called “awake craniotomy anesthesia.” It has two parts: sedation and awake management.
Initial Sedation Phase
In the first part, patients get sedatives to relax. This makes them comfortable but able to follow commands if needed.
Awake Phase Management
In the second part, patients are fully awake. This part needs careful management to keep them comfortable and cooperative. Surgeons can do important parts of the surgery while patients are awake, making adjustments as needed.
Immediate Post-Procedure Monitoring
After surgery, patients are watched closely in a recovery area. Medical staff look for any signs of problems, like brain issues or reactions to anesthesia. Post-operative care is tailored to each patient to help them recover smoothly.
Monitoring includes checking vital signs and doing neurological tests. Pain management is also a big focus, with medication given as needed to keep patients comfortable.
Patient Experiences During Awake Neurosurgery
Patients going through awake neurosurgery feel both physical and emotional sensations. These feelings can change a lot, based on the surgery type, the patient’s health, and how ready they are mentally.
Physical and Psychological Sensations
Patients might feel anything from a little discomfort to pain during the surgery. This depends on the operation’s stage and the brain area being worked on. They might also feel anxious, scared, or disconnected from what’s happening.
Pain Management Reality
Managing pain well is key during awake neurosurgery. Local anesthesia is used to numb the scalp and brain areas. But, some patients might feel pressure or discomfort.
Emotional Responses
Patients’ emotional reactions can be very different. Some might feel anxious or scared, while others stay calm. Preoperative counseling and support from the team help manage these feelings.
Interacting with the Surgical Team
Talking and working with the surgical team is very important in awake neurosurgery. Patients do specific tasks during the surgery. This helps the surgeons understand and protect important brain functions.
Types of Tasks Performed
Patients might do simple things like moving a limb or more complex tasks like speaking or reading. These tasks help the team identify and keep safe vital brain areas.
Patient Testimonials
Many patients say they had a good experience with awake neurosurgery. They thank the team for their professionalism and support. They say clear communication and care are key during the procedure.
Aspect of Experience | Patient Feedback |
Pain Management | Generally positive, with some reporting mild discomfort |
Emotional Support | Highly valued; helped in managing anxiety and fear |
Interaction with Surgical Team | Positive; appreciated clear instructions and support |
Advanced Brain Mapping Techniques
Brain mapping has grown a lot, helping a lot in awake neurosurgery. New brain mapping methods help doctors find important brain spots with great accuracy. This makes surgeries safer and more effective.
Functional MRI and Preoperative Planning
Functional MRI (fMRI) is a way to see brain function without hurting it. It checks blood flow changes in the brain. Doctors use it before surgery to know the brain’s layout and how it works.
This info is key for planning the surgery. It helps doctors know which parts to keep safe.
Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring
Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring (IONM) watches the nervous system during surgery. It uses direct cortical stimulation and electrocorticography. These methods help map brain functions as surgery happens.
Direct Cortical Stimulation
Direct cortical stimulation uses electricity to find brain spots for important tasks. This includes moving, talking, and feeling. It’s vital for keeping these functions safe during surgery.
Electrocorticography
Electrocorticography (ECoG) records brain electrical activity right from the surface. It finds seizure spots and maps brain functions. This info helps guide the surgery.
Weighing the Risks and Benefits
It’s important to know the risks and benefits of awake neurosurgery before deciding. This surgery lets patients stay awake during parts of the operation. It helps surgeons see how the brain works in real-time, which can lead to better results.
Advantages of Awake Neurosurgery
Awake neurosurgery has many good points. It can lead to better brain function and fewer problems after surgery. This is because surgeons can see how the brain works while they operate.
Improved Functional Outcomes
The main good thing about awake neurosurgery is that it can make patients do better after surgery. Surgeons can avoid hurting important parts of the brain. This is shown in a study in the Journal of Neurosurgery.
“The awake craniotomy technique has revolutionized the field of neurosurgery, enabling surgeons to operate with greater precision and accuracy.”
Reduced Neurological Deficits
Awake neurosurgery also means fewer brain problems after surgery. Surgeons watch the brain closely during surgery. This helps them avoid causing more damage.
Potential Complications and Concerns
Even though awake neurosurgery has many benefits, it also has risks. These include seizures during surgery and how it might affect a person’s mind.
Intraoperative Seizures
One big risk is seizures during surgery. These can happen because of how the brain is being tested. Doctors and anesthesiologists need to be ready to handle these seizures quickly.
Psychological Impact
Being awake during surgery can also affect a person’s mind. They might feel scared or stressed. But, with the right help and support, many people can handle these feelings well.
In summary, awake neurosurgery is a complex choice. It has many benefits, like better brain function and fewer problems after surgery. But, it also has risks like seizures and how it might affect a person’s mind.
Recovery Journey After Brain Surgery
After brain surgery, patients start a long recovery journey. It includes time in the hospital and then rehabilitation. This journey is key to getting back to health and function.
Hospital Stay and Early Recovery
The first part of recovery happens in the hospital. Here, doctors and nurses watch over the patient closely.
First 48 Hours Post-Surgery
The first 48 hours are very important. Medical staff look for any problems or bad reactions to the surgery. Patients are closely watched to manage pain and any immediate issues.
Managing Initial Side Effects
Side effects like nausea, headache, and tiredness are treated with medicine and rest. The medical team helps find ways to lessen these effects and aid in a smooth recovery.
Long-Term Rehabilitation Process
After leaving the hospital, patients need a long-term rehab to fully recover.
Physical Therapy Requirements
Physical therapy is key to getting back strength, mobility, and coordination. A therapy plan is made just for the patient’s needs.
Cognitive Rehabilitation
Cognitive rehab helps fix any brain function issues from the surgery. It works on memory, attention, and solving problems.
Rehabilitation Component | Description | Goals |
Physical Therapy | Regaining physical strength and mobility | Improve mobility, reduce pain |
Cognitive Rehabilitation | Restoring cognitive functions | Enhance memory, attention, problem-solving |
Speech Therapy | Addressing communication issues | Improve speech clarity, comprehension |
Alternative Approaches to Neurosurgery
The field of neurosurgery is evolving with new, advanced techniques. While traditional surgery under general anesthesia is key, new methods are being used. They aim to improve results and lower risks.
Advanced Imaging and Navigation Systems
Advanced imaging and navigation systems have changed neurosurgery. Tools like functional MRI and intraoperative MRI help locate brain structures. This lets surgeons work with more precision in complex areas.
- Precise tumor resection: Ensuring maximal removal of tumors while preserving critical brain functions.
- Reduced risk of neurological damage: By accurately mapping brain areas responsible for vital functions.
- Enhanced patient safety: Through real-time monitoring and adjustments during surgery.
When Traditional Surgery Under General Anesthesia Is Preferred
Even with new methods, traditional surgery under general anesthesia is often the best choice. This is true for:
- Complex aneurysms or AVMs: Conditions that require a high level of control and stability, often best achieved under general anesthesia.
- Pediatric neurosurgery: Children often require general anesthesia to ensure they remain calm during delicate procedures.
- Emergency situations: Acute trauma or hemorrhage may necessitate immediate surgery under general anesthesia.
Neurosurgeons use their knowledge to choose the best method for each patient. This approach helps improve outcomes and recovery.
Conclusion: The Evolving Landscape of Neurosurgery
The field of neurosurgery is always getting better. New techniques and technologies are being developed to help patients more. Awake brain surgery is a big step forward, helping with complex brain conditions.
Awake craniotomy has shown great results in keeping brain functions safe. It uses advanced tools like functional MRI and neurophysiological monitoring. These tools make brain surgeries more precise.
Neurosurgery, including brain and neurological surgery, is getting more advanced. This progress will keep going, thanks to research and new tech. Patients can look forward to better treatments and results in the future.
FAQ
What is awake brain surgery?
Awake brain surgery, also known as awake craniotomy, is a procedure where the patient stays awake. This lets the team watch the brain’s functions live.
Why is brain surgery performed while the patient is awake?
It’s done to keep important brain functions like speech and motor skills safe. This is key for surgeries in areas that control these functions.
What are the benefits of awake neurosurgery?
It offers precise tumor removal and less risk to brain areas. Recovery times are also faster. Plus, it lets the team watch brain functions in real-time.
What are the risks associated with awake neurosurgery?
Risks include anxiety and discomfort. There’s also a chance of seizures, bleeding, or infection. But, the benefits usually outweigh these risks.
How long does brain surgery typically take?
Surgery time varies. It depends on the procedure’s complexity and the patient’s needs. Some surgeries last hours, while others are quicker.
What is the recovery process like after brain surgery?
Recovery involves a hospital stay and rest. The length of stay and recovery time vary based on health and procedure complexity.
Are there alternative approaches to neurosurgery?
Yes, there are. Advanced imaging and navigation systems help guide the team. Sometimes, general anesthesia is preferred based on the patient’s needs.
How is brain mapping used in awake brain surgery?
Brain mapping identifies critical areas. It uses functional MRI and neurophysiological monitoring to map brain functions.
Can I expect to feel pain during awake brain surgery?
Some pain or discomfort is possible. The team aims to manage it with local anesthesia and sedation.
How will I be able to communicate with the surgical team during awake brain surgery?
You can talk to the team during surgery. This helps them monitor your brain functions and adjust as needed.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9338386/




































