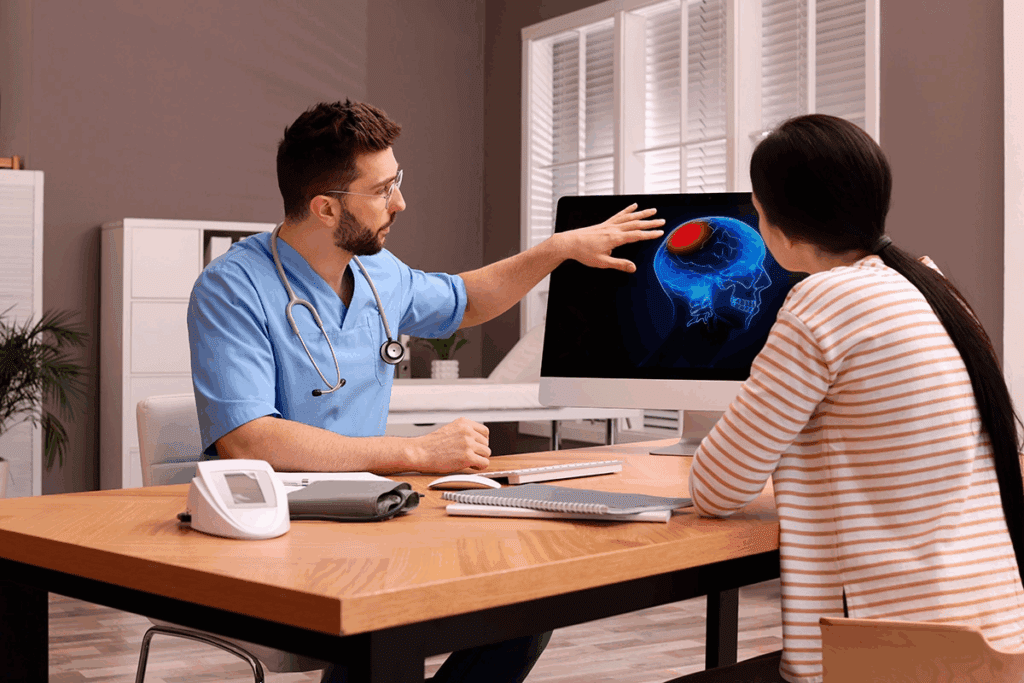
Recent studies show that about 700,000 people in the United States live with a brain tumor. These growths can be either benign or malignant. Knowing what causes them is key to better treatment and care. Don’t ignore these critical brain tumor symptoms. Our essential guide covers 7 alarming signs. Learn what causes brain tumors and when to see a doctor.
Brain tumors can greatly affect a person’s life. It’s important to find out why they happen. This way, doctors and researchers can find better ways to diagnose and treat them.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the causes of brain tumors is vital for effective treatment.
- Brain tumors can be benign or malignant.
- Approximately 700,000 people in the US are living with a brain tumor.
- Research is ongoing to improve diagnosis and treatment options.
- Identifying risk factors can help in the early detection of brain tumors.
Understanding Brain Tumors
The term “brain tumor” covers a wide range of growths in the brain. These growths vary in their characteristics and impact. They can be categorized based on their origin, behavior, and other key factors.
Definition and Basic Concepts
A brain tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue in the brain. It can be benign or malignant. The definition includes both primary tumors that start in the brain and secondary tumors that spread from other parts of the body.
Primary vs. Secondary Brain Tumors
Primary brain tumors start in the brain. On the other hand, secondary brain tumors come from other parts of the body. Knowing if a tumor is primary or secondary is key for the right treatment plan.
| Tumor Type | Origin | Typical Treatment Approach |
| Primary | Originates in the brain | Surgery, Radiation, Chemotherapy |
| Secondary | Spreads to the brain from elsewhere | Treatment of the primary cancer, Palliative care |
Benign vs. Malignant Brain Tumors
Benign brain tumors are usually non-cancerous and grow slowly. Malignant brain tumors are cancerous and grow fast. Knowing if a tumor is benign or malignant is important for its prognosis and treatment.
Understanding these basics is key to dealing with brain tumor diagnosis and treatment. Getting the right diagnosis and care can greatly improve patient outcomes.
Types of Brain Tumors
It’s important to know about the different brain tumors. They are sorted by where they start and how they grow.
Gliomas
Gliomas are common brain tumors. They start from glial cells in the brain. Each glioma is different based on the cell type and growth pattern.
Astrocytomas
Astrocytomas come from astrocytes, a type of glial cell. They can be low-grade or high-grade, like glioblastoma.
Oligodendrogliomas
Oligodendrogliomas start from oligodendrocytes. They are usually found in the brain’s hemispheres. They can be low-grade or grow faster.
Ependymomas
Ependymomas come from cells lining the brain’s ventricles and spinal cord. They can happen at any age.
Meningiomas
Meningiomas are usually not cancerous. They grow from the brain and spinal cord’s membranes. Most grow slowly and can be removed with surgery.
Acoustic Neuromas
Acoustic neuromas, or vestibular schwannomas, are benign. They grow on the eighth cranial nerve. They can cause hearing loss and balance issues.
Other Common Types
There are more brain tumors beyond gliomas, meningiomas, and acoustic neuromas.
Pituitary Tumors
Pituitary tumors are usually not cancerous. They grow in the pituitary gland. They can affect hormone levels and cause symptoms.
Medulloblastomas
Medulloblastomas are cancerous and mostly found in kids. They start in the cerebellum and can spread through the cerebrospinal fluid.
Craniopharyngiomas
Craniopharyngiomas are rare and not cancerous. They grow near the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. They can cause hormonal imbalances and vision problems.
What Causes Brain Tumors: Primary Factors
The exact causes of brain tumors are not fully known. But research has found several key factors. Knowing these factors helps us find better ways to prevent and treat brain tumors.
Cell Mutations and DNA Changes
Cell mutations and DNA changes are key in brain tumor development. These genetic changes can cause cells to grow out of control. DNA damage can happen from many things, like genetics, environment, and DNA copying mistakes. Some genetic mutations raise the risk of brain tumors.
| Genetic Factor | Description | Impact on Brain Tumor Risk |
| DNA Repair Gene Mutations | Mutations in genes responsible for DNA repair | Increased risk due to impaired DNA repair mechanisms |
| Oncogene Activation | Activation of genes that promote cell growth | Potential for uncontrolled cell proliferation |
| Tumor Suppressor Gene Mutations | Mutations in genes that normally suppress tumor formation | Loss of protective mechanism against tumor development |
Growth Factor Dysregulation
Growth factor dysregulation is also important in brain tumors. Growth factors help cells grow and divide. When these factors are not working right, cells can grow too much. For example, some brain tumors have too many growth factors, helping them grow and spread.
Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) protects the brain from the blood. If the BBB is broken, harmful things can get to brain cells. Scientists are studying how this affects brain tumors and how to fix it.
Knowing what causes brain tumors is key to better treatments. Research on cell mutations, growth factor issues, and BBB problems is helping us understand brain tumors better.
Genetic Factors in Brain Tumor Development
Brain tumors often start because of genetic factors. These can be hereditary syndromes or specific gene mutations. These elements greatly affect the risk and how brain tumors grow.
Hereditary Syndromes
Some hereditary syndromes raise the risk of brain tumors. These include:
- Neurofibromatosis: A condition that can lead to the development of tumors on nerve tissue.
- Li-Fraumeni Syndrome: A rare genetic disorder that increases the risk of several types of cancer, including brain tumors.
- Tuberous Sclerosis: A genetic disorder characterized by the growth of non-cancerous tumors in various parts of the body, including the brain.
Gene Mutations
Specific gene mutations also play a key role in brain tumor development. Some important mutations include:
- IDH Mutations: Mutations in the IDH1 or IDH2 genes, commonly found in gliomas.
- EGFR Alterations: Amplification or mutation of the EGFR gene, often associated with glioblastoma.
- TP53 Mutations: Mutations in the TP53 gene, which is a tumor suppressor gene, leading to increased cancer risk.
| Gene Mutation | Tumor Type | Impact |
| IDH1/IDH2 | Gliomas | Associated with better prognosis |
| EGFR | Glioblastoma | Linked to aggressive tumor behavior |
| TP53 | Various | Increases cancer risk |
Knowing about these genetic factors is key for diagnosing and treating brain tumors. More research into brain tumor genetics will help find new treatments.
Environmental Risk Factors
Research has found several environmental risks for brain tumors. Knowing these risks helps in prevention and treatment.
Radiation Exposure
Ionizing radiation is a known risk for brain tumors. It has enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, creating ions.
Medical Radiation
Medical radiation, like from CT scans, adds to overall exposure. While these scans are often necessary, repeated use can raise brain tumor risk.
Occupational Exposure
People working in places like nuclear power plants face higher risks. This is due to their exposure to radiation at work.
Chemical Exposures
Chemical exposures in industrial settings increase brain tumor risk. Certain chemicals used in manufacturing can be harmful.
Industrial Chemicals
Some industrial chemicals are known carcinogens. Workers in these industries should take extra precautions.
Pesticides and Herbicides
Exposure to pesticides and herbicides, used in farming, also raises brain tumor risk.
Electromagnetic Fields and Mobile Phones
The link between electromagnetic fields (EMFs) and brain tumor risk is being studied. Mobile phones are a focus. Some studies hint at a connection, but more research is needed.
Age, Gender, and Ethnicity Considerations
Brain tumors are affected by age, gender, and ethnicity. Knowing these factors helps us understand risks and create better treatments.
Age-Related Risk Patterns
The chance of getting a brain tumor changes with age. Kids and teens often get certain tumors, while adults get others. For example, medulloblastomas are common in young people, and glioblastomas are more common in older adults.
Gender Differences in Tumor Types
Some brain tumors are more common in men or women. Menningiomas are more common in women, and glioblastomas are more common in men. This suggests there might be biological or hormonal reasons for these differences.
Ethnic and Geographic Variations
Where you live and your ethnicity can also affect brain tumor rates. Some studies show that certain tumors are more common in certain groups. For example, meningiomas are more common in some populations.
| Demographic Factor | Influence on Brain Tumors |
| Age | Risk varies across age groups; certain tumors more common in specific ages. |
| Gender | Some tumor types show gender disparities in incidence. |
| Ethnicity/Geography | Variations in tumor incidence among different ethnic and geographic groups. |
These factors show how complex brain tumor research is. They highlight the need for treatments that are tailored to each person’s situation.
Brain Tumor Symptoms: Recognizing the Warning Signs
Knowing the warning signs of brain tumors is key to better outcomes. Brain tumors show symptoms based on their location, size, and the person’s health.
General Symptoms
General symptoms of brain tumors include a mix of signs. Common ones are:
- Headaches: Often worse in the morning and may be accompanied by nausea or vomiting.
- Seizures: Can occur due to the tumor’s irritation of the surrounding brain tissue.
- Cognitive Changes: Including memory problems, difficulty concentrating, or changes in personality.
These symptoms can be quite general and may be mistaken for other conditions, making diagnosis challenging.
Headaches
Headaches caused by brain tumors are typically persistent and may worsen over time. They can be a result of increased intracranial pressure.
Seizures
Seizures are a common presenting symptom, specially in tumors affecting the cerebral cortex. They can vary in type and severity.
Cognitive Changes
Cognitive changes can range from mild memory issues to significant personality changes, depending on the tumor’s location.
Location-Specific Symptoms
The symptoms of brain tumors can also be highly specific to the tumor’s location within the brain.
- Frontal Lobe Tumors: May cause changes in personality, motor deficits, or speech difficulties.
- Temporal Lobe Tumors: Can lead to seizures, memory problems, or auditory disturbances.
- Brain Stem Tumors: Often cause difficulties with basic functions such as breathing, swallowing, or controlling eye movements.
Symptoms in Children vs. Adults
While some symptoms are common across age groups, others are more prevalent in either children or adults. Children, for instance, may exhibit increased intracranial pressure symptoms like morning headaches and vomiting, while adults might more frequently experience seizures or cognitive changes.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s important to know when to get medical help for brain tumor symptoms. Some symptoms need quick attention. Knowing these can save lives.
Emergency Warning Signs
Severe headaches, seizures, and sudden vision or speech changes are urgent signs. If you or someone you know has these, act fast.
- Sudden severe headache
- Seizure or convulsion
- Loss of vision or double vision
- Difficulty in speech or understanding
- Weakness or numbness in limbs
Differentiating from Other Conditions
It can be hard to tell if symptoms are from a brain tumor or something else. Knowing the difference helps get the right medical care.
Migraines vs. Tumor Headaches
Migraines often come with nausea and light sensitivity. Tumor headaches are constant and get worse. See a doctor if you’re not sure about your headaches.
Stroke vs. Brain Tumor
A stroke causes sudden numbness or weakness, often on one side, and speech trouble. Brain tumors may have similar symptoms but get worse slowly. Both need immediate medical help.
| Symptom | Brain Tumor | Stroke |
| Headache | Persistent, worsening over time | Sudden, often severe |
| Weakness/Numbness | Gradual onset | Sudden, often one-sided |
| Speech Difficulty | Gradual | Sudden |
Diagnostic Procedures for Brain Tumors
Diagnosing brain tumors involves several steps. These include neurological exams and imaging tests. Getting an accurate diagnosis is key to choosing the right treatment.
Neurological Examination
A neurological exam is the first step in finding out if you have a brain tumor. It checks how well you think, move, and feel things. It helps doctors spot any signs of a tumor.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are essential for finding brain tumors. They give doctors clear pictures of the brain. This lets them see the tumor and what it looks like.
MRI Scans
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans are great for finding brain tumors. They show the brain in detail. Doctors can see how big the tumor is and where it is in the brain.
CT Scans
Computed Tomography (CT) scans are also used to check for brain tumors. They are fast and useful in emergencies. They give important info about the tumor and its effects on the brain.
PET Scans
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans check how active the tumor is. They help doctors tell if the tumor is cancerous. They also see how well the tumor is responding to treatment.
| Imaging Test | Primary Use | Benefits |
| MRI | Detailed brain imaging | High-resolution images, non-invasive |
| CT | Emergency situations, quick assessment | Fast, provides critical information |
| PET | Assessing tumor metabolism | Helps differentiate tumor types, evaluates treatment response |
Biopsy Procedures
A biopsy is often needed to confirm a brain tumor diagnosis. There are two main types of biopsies for brain tumors.
Stereotactic Biopsy
A stereotactic biopsy is a small procedure. It uses a computer to guide a needle to the tumor. This method is precise and safe for the brain.
Open Surgical Biopsy
An open surgical biopsy is when a part of the tumor is removed. This is done when the tumor is easy to reach and can be safely taken out.
A leading neurosurgeon says, “The choice of diagnostic procedure depends on many things. These include the tumor’s location, size, and type.” This shows how important it is to tailor the diagnosis for each patient.
“Advances in imaging technologies have greatly helped us diagnose and manage brain tumors,” said a renowned neurologist.
Understanding Brain Tumor Grading and Staging
Grading and staging brain tumors are key for making treatment plans and predicting outcomes. The grading system sorts tumors by their traits and behavior.
The WHO Classification System
The World Health Organization (WHO) uses a system to grade brain tumors. It groups tumors by their look and how they act.
Grade I-II Tumors
Grade I tumors are usually benign and grow slowly. Grade II tumors grow a bit faster but might come back or get worse. Treatment for these tumors often includes surgery and sometimes radiation therapy.
Grade III-IV Tumors
Grade III tumors are malignant and grow faster. Grade IV tumors are the most aggressive and likely to come back. These tumors usually need surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
What Your Diagnosis Means
Knowing your brain tumor diagnosis means understanding its grade and stage. This info is key for knowing your prognosis and treatment options.
Prognosis Factors
Prognosis factors include the tumor grade, age, health, and treatment response. Understanding these factors helps doctors create personalized treatment plans.
Survival Statistics
Survival statistics give insight into survival chances based on tumor type and grade. Talking to your doctor about these statistics helps you understand your situation.
Treatment Options for Brain Tumors
Treatment for brain tumors varies. It depends on the tumor’s type, size, and location. Also, the patient’s health plays a big role.
Surgery
Surgery is often the first step. It involves removing the tumor.
Traditional Approaches
Traditional surgery opens the skull to reach the tumor. This way, surgeons can remove as much of the tumor as they can.
Minimally Invasive Techniques
Nowadays, smaller surgeries are used more. These, like keyhole surgery, use small cuts and special tools. They might help you recover faster.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy kills cancer cells with high-energy waves. It’s a key part of treating brain tumors.
External Beam Radiation
External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) sends radiation from outside the body. It’s precise and can be shaped to fit the tumor.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) gives a focused dose of radiation in one session. It’s good for small, well-defined tumors.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It can be taken by mouth or through an IV.
Systemic Chemotherapy
Systemic chemotherapy goes through the blood to reach cancer cells all over the body.
Local Delivery Methods
Local delivery methods, like chemotherapy wafers, are placed directly in the tumor. They offer targeted treatment.
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are new ways to treat brain tumors. Targeted therapy attacks specific molecules in tumors. Immunotherapy uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Treatment plans often mix these methods. They’re tailored to each patient. Medical technology and research keep getting better, helping brain tumor patients more.
Complementary and Alternative Approaches
More and more people are looking into different ways to manage their health. They use these methods along with traditional treatments to feel better.
Nutritional Strategies
Good nutrition is key for those fighting brain tumors. The ketogenic diet and eating foods rich in antioxidants are two popular choices.
Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet is all about eating lots of fat and very few carbs. Some research shows it might slow down brain tumor growth.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Eating foods full of antioxidants can fight oxidative stress. This stress is linked to tumor growth. Foods like berries and leafy greens are great choices.
Mind-Body Therapies
Mind-body therapies help patients deal with their diagnosis and treatment. Stress reduction and exercise are among the most helpful.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Stress reduction techniques like meditation and yoga can ease the mind. They help with the emotional toll of a brain tumor.
Exercise Benefits
Exercise is good for both body and mind. It boosts overall well-being and quality of life.
| Therapy Type | Description | Potential Benefits |
| Ketogenic Diet | High-fat, low-carbohydrate diet | Potential reduction in tumor growth |
| Antioxidant-Rich Foods | Diet rich in fruits, vegetables | Reduced oxidative stress |
| Stress Reduction Techniques | Meditation, yoga | Improved mental well-being |
| Exercise | Regular physical activity | Enhanced physical and mental health |
Living with a Brain Tumor Diagnosis
Living with a brain tumor diagnosis is a big challenge. It involves dealing with medical, emotional, and social issues. You need a plan that includes treatment, coping strategies, and support.
Coping Strategies
Good coping strategies are key to handling the emotional side of a brain tumor diagnosis. Mindfulness practices like meditation and yoga can help reduce stress. Also, keeping a positive outlook and setting achievable goals can boost your resilience.
Support Resources
Finding the right support can greatly improve life with a brain tumor. Support can be in many forms, including:
- Professional counseling
- Support groups
- Financial assistance programs
Support Groups
Support groups offer a place to share experiences and get emotional support. You can find them at local hospitals, online, or through brain tumor organizations.
Financial Assistance
Financial help programs can ease the financial stress of a brain tumor diagnosis. They can cover medical costs, transportation, and more.
Quality of Life Considerations
Keeping a good quality of life is important when living with a brain tumor. It means managing symptoms, reducing treatment side effects, and enjoying activities that make you happy.
| Aspect | Considerations | Strategies |
| Emotional Well-being | Managing stress and anxiety | Mindfulness, counseling |
| Physical Health | Symptom management | Medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments |
| Social Connections | Maintaining relationships | Support groups, family support |
Advances in Brain Tumor Research
Recent breakthroughs in brain tumor research are changing how we treat and care for patients. Studies are working on new therapies and better patient results.
Emerging Treatments
New treatments are giving brain tumor patients new hope. These include:
Immunotherapy Advances
Immunotherapy uses the immune system to fight cancer. It’s showing great promise in treating brain tumors. Immunotherapy advances are making treatments more targeted and effective.
Precision Medicine
Precision medicine tailors treatment to a patient’s tumor genetics. This leads to more effective and personalized care.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are key in advancing brain tumor research. They offer new treatments and help improve patient outcomes.
How to Find Clinical Trials
Patients can find clinical trials online or through healthcare providers. It’s important to talk about options with a doctor.
Promising Research Areas
Research is ongoing, with several promising areas. These include combination therapies and new therapeutic targets.
Conclusion
It’s key to know about brain tumors for both patients and doctors. This detailed look has covered many topics. We’ve talked about what causes them, their symptoms, how to diagnose them, and treatment choices.
Learning about brain tumors shows they can be either good or bad. They can also be either the first kind or come from somewhere else. Spotting the signs early and getting help fast is very important.
In short, knowing about brain tumors is very important. It helps people understand their situation better. This knowledge makes it easier to deal with the diagnosis and treatment.
FAQ
What is a brain tumor?
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of cells in the brain. It can be benign or malignant. Tumors can start in the brain or spread from another part of the body.
What are the symptoms of a brain tumor?
Symptoms vary based on the tumor’s location, size, and type. Common signs include headaches, seizures, and confusion. You might also notice changes in speech, vision, or behavior.
What causes brain tumors?
The exact cause of brain tumors is not known. But, genetic mutations, radiation, and environmental factors might play a role.
Are brain tumors hereditary?
Some brain tumors are linked to genetic syndromes like neurofibromatosis. But, most are not directly inherited.
How are brain tumors diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a neurological exam and imaging tests like MRI or CT scans. Sometimes, a biopsy is needed to determine the tumor’s type and grade.
What are the treatment options for brain tumors?
Treatment varies based on the tumor’s type, grade, and location. It also depends on the patient’s health. Options include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or a mix of these.
Can brain tumors be cured?
The cure rate for brain tumors varies. Benign tumors might be cured with surgery. But, malignant tumors often need a combination of treatments and have a less certain outcome.
What is the difference between a benign and malignant brain tumor?
Benign tumors are non-cancerous and grow slowly. Malignant tumors are cancerous and grow faster, invading brain tissue.
How do age, gender, and ethnicity affect brain tumor risk?
Age, gender, and ethnicity can affect brain tumor risk and characteristics. Some tumors are more common in children or older adults. Others have a gender or ethnic preference.
What are the latest advances in brain tumor research?
Research is focused on new treatments like targeted therapies and immunotherapies. It aims to improve our understanding of brain tumor biology and genetics.
What are the warning signs that I should seek medical attention for a potentially brain tumor?
Warning signs include severe or persistent headaches, seizures, and confusion. Difficulty with speech or vision, and changes in behavior are also signs. If you notice these symptoms, seek medical help.
Can lifestyle changes or complementary therapies help manage brain tumor symptoms?
Lifestyle changes and complementary therapies can’t cure brain tumors. But, they can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Examples include nutritional strategies, mind-body therapies, and stress management.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35050246/



































