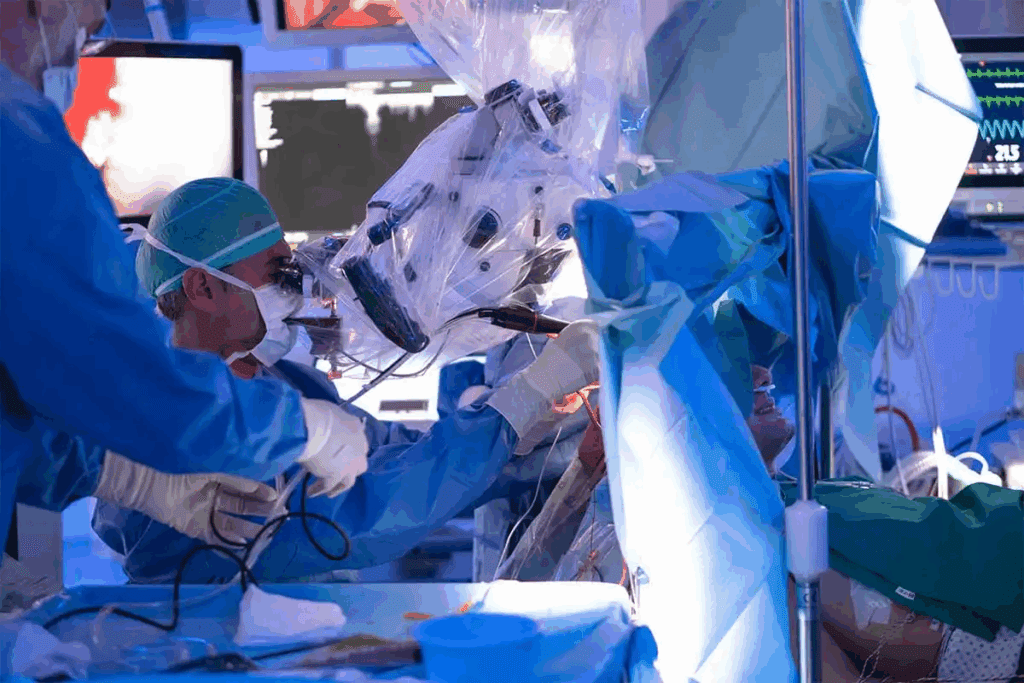
Imagine being awake and alert while a surgeon works on your brain. For some, this is their reality. Awake brain surgery, or awake craniotomy, lets patients stay awake and aware during the operation.
This new method lets surgeons map the brain as they go. It helps them avoid harming important parts. Patients can also react to what’s happening, guiding the surgeon through the brain’s complex paths.
Key Takeaways
- Awake brain surgery is a complex procedure where patients remain conscious.
- The technique allows for real-time brain mapping.
- Patients can respond to stimuli, aiding surgeons in preserving critical brain functions.
- Awake craniotomy is used for specific medical conditions.
- The procedure requires careful planning and execution.
What Is Awake Brain Surgery?
Awake brain surgery is a big step forward in brain surgery. It lets doctors do more precise work. This surgery is done while the patient is awake and can talk back, which is key for some brain operations.
Definition and Basic Concept
Awake brain surgery means the patient stays awake and can talk during the surgery. It’s used for operations where the doctor needs to see how the brain works in real-time. This way, they can avoid harming important parts of the brain.
The patient is kept comfortable with local anesthesia. This lets them stay awake and relaxed during the surgery.
Historical Development of the Procedure
The idea of awake brain surgery has been around for a long time. But, there have been big improvements in recent years. In the past, doctors had a hard time doing brain surgeries without hurting important areas.
Now, thanks to better anesthesia protocols and ways to monitor the brain during surgery, awake brain surgery is safer. It’s used for many neurological problems. This makes treatments better and reduces risks.
Medical Conditions Requiring Awake Craniotomy
Several critical medical conditions need awake craniotomy for effective treatment. This method allows surgeons to work on the brain while the patient is awake. It helps them keep an eye on and protect important brain functions.
Brain Tumor Resection
Brain tumor removal is a main reason for awake craniotomy. Brain tumor surgery needs to be precise to remove the tumor without harming nearby healthy tissue. This way, the patient’s brain function can stay intact. Awake craniotomy lets doctors watch the patient’s brain responses in real-time, helping them remove the tumor more accurately.
Epilepsy Surgery
Epilepsy surgery may also need awake craniotomy. This is when seizures don’t respond to medicine and the seizure area is near important brain parts. Awake craniotomy helps surgeons find and keep these key areas safe during surgery.
Other Neurological Conditions
Other neurological issues might also need awake craniotomy. This includes some vascular malformations or lesions close to vital brain areas. The detailed work of awake craniotomy is key in handling these complex cases.
The Science Behind Functional Brain Mapping
Neurosurgeons need to understand the brain’s function for precise operations. Functional brain mapping is a key technique. It helps surgeons find and keep safe important brain parts during surgery. This is very important in awake brain surgery, where the patient is awake and can answer questions.
Critical Brain Areas and Their Functions
The human brain has different areas for different tasks. For example, some areas control movement, others handle language and senses. Cortical stimulation is used to find these areas. This helps surgeons avoid harming them during surgery.
By knowing where these areas are, surgeons can work more carefully. They can handle the brain’s complex structure better.
Why Consciousness Is Essential During Certain Procedures
Being awake during brain surgery is very helpful. It lets patients react to the stimulation, giving the team feedback right away. This feedback is key to mapping brain functions correctly.
It also helps make sure important areas are not damaged. The patient’s awareness lets the team make changes quickly. This reduces the chance of problems after surgery.
Common Misconceptions About Awake Brain Surgery
Many people don’t understand awake brain surgery. It’s a procedure where the patient is awake during parts of the surgery. This is because it’s a complex process.
One big worry is pain. But, thanks to new medical tech and anesthesia, managing pain has gotten much better.
Pain Management Realities
Pain control is key in awake brain surgery. People think patients are in a lot of pain, but they’re not. Local anesthesia numbs the scalp and skull, so patients don’t feel pain. A top neurosurgeon says, “Local anesthesia makes the procedure okay for patients.”
Level of Awareness During the Procedure
Some think patients are fully awake the whole time. But, conscious sedation keeps them comfortable and relaxed. How awake a patient is can change, based on the sedation and how they handle it.
The main aim of awake brain surgery is to remove bad brain tissue. It also tries to keep important brain functions like speech and motor skills safe. By keeping patients awake, doctors can watch how they respond. This helps make sure these important areas stay safe.
Patient Selection Criteria
Choosing the right patients for awake brain surgery is key to success. Doctors look at many factors to see if a patient is a good fit for this complex surgery.
Ideal Candidates
Good candidates for awake brain surgery often have tumors near important brain spots. They need to be able to talk and listen well during the surgery.
Being able to stay calm and not move much is also important. People with anxiety disorders or claustrophobia might need extra checks to see if they can handle it.
| Criteria | Description | Importance Level |
| Cooperation Ability | Patient’s ability to follow instructions and communicate during surgery | High |
| Medical Condition | Nature of the condition requiring surgery (e.g., tumor location) | High |
| Psychological Stability | Patient’s mental state and ability to handle the stress of awake surgery | Medium |
Contraindications and Risk Factors
Some conditions might make awake brain surgery too risky. This includes severe anxiety or psychiatric conditions that could make it hard for the patient to cooperate. Also, significant medical comorbidities could make the surgery more complicated.
Those who have had trouble with anesthesia before or can’t stay quiet are also at higher risk. A detailed check before surgery is vital to spot these risks and plan the best approach.
Pre-Surgical Preparation Process
Awake brain surgery needs a detailed preparation process. This includes physical, psychological, and educational steps. It makes sure patients are ready for the surgery, reducing risks and improving results.
Physical Assessments and Testing
Physical checks are key in the preparation. These tests look at the patient’s health and brain function. Comprehensive medical evaluations find any possible surgery risks.
Psychological Preparation
Psychological prep is also vital. It helps patients deal with the stress and anxiety of awake brain surgery. Counseling and relaxation techniques are used to ease anxiety and comfort during the surgery.
Patient Education and Informed Consent
Teaching patients is a big part of the prep. They need to know the surgery’s risks, benefits, and other options. Informed consent makes sure patients understand and can make informed choices.
The prep process covers physical, psychological, and educational needs for awake brain surgery. By preparing patients well, doctors can get better results and make patients happier.
Anesthesia Protocols Used in Awake Brain Surgery
Anesthesia protocols are key in awake brain surgery. They balance comfort with the need for precision. The right anesthesia ensures the patient is comfortable and cooperative.
Local vs. Conscious Sedation
In awake brain surgery, two main anesthesia methods are used: local and conscious sedation. Local anesthesia numbs the surgery area, keeping the patient awake and alert. This is important for surgeries needing patient feedback, like speech or motor function tests.
Conscious sedation relaxes the patient without making them lose consciousness. The sedation level can vary, depending on the patient’s needs and the surgery.
The Asleep-Awake-Asleep Technique
The asleep-awake-asleep technique is also used in awake brain surgery. It starts with general anesthesia, then wakes the patient for important tests. After, general anesthesia is used again for the rest of the surgery.
This method makes the patient more comfortable at the start and end of surgery. It also lets the team do necessary awake tests.
Choosing and managing the right anesthesia is vital. It ensures both patient comfort and the success of the surgery.
The Operating Room Environment
Awake brain surgery needs a very special and controlled operating room environment. This environment is key for the surgery’s success. It affects the patient’s safety and the team’s ability to do the surgery right.
The operating room has the latest technology and a team of experts. This team works together to give the patient the best care during the surgery.
Specialized Equipment and Setup
The specialized equipment for awake brain surgery includes advanced imaging and monitoring tools. These tools help the team find and protect important brain areas.
The room is set up to meet the needs of awake brain surgery. It’s arranged to help the patient talk to the team and stay comfortable during the surgery.
The Multidisciplinary Surgical Team
The multidisciplinary surgical team for awake brain surgery includes neurosurgeons, anesthesiologists, nurses, and neurophysiologists. Each team member is important for the surgery’s success.
The neurosurgeon leads the team and makes important decisions during the surgery. The anesthesiologist manages the patient’s pain and comfort. Nurses provide care and support, and the neurophysiologist monitors brain activity.
Step-by-Step Procedure of Awake Brain Surgery
The awake brain surgery process is detailed and requires a team effort. It’s a precise procedure aimed at the best results for patients.
Initial Sedation and Craniotomy
The first step is sedating the patient to calm them down. Then, the team does a craniotomy, removing part of the skull to reach the brain. This step is very important to avoid harming the brain.
Awakening Process
Next, the patient is slowly brought back to full consciousness. The team watches the patient’s vital signs and brain responses closely. This is a key moment to ensure the patient can follow instructions during the surgery.
Intraoperative Testing and Monitoring
When the patient is awake, the team tests brain functions. They check speech, motor skills, and other important areas. This helps the surgeons make accurate decisions during the surgery.
| Procedure Stage | Description | Key Activities |
| Initial Sedation and Craniotomy | Patient sedation and skull opening | Sedation administration, craniotomy |
| Awakening Process | Gradual reduction of sedation | Vital sign monitoring, neurological assessment |
| Intraoperative Testing and Monitoring | Assessment of brain function | Speech and motor skill testing, brain mapping |
Speech and Motor Mapping Techniques
The success of awake brain surgery depends on speech and motor mapping. These methods are key to finding and keeping safe the brain areas for language and movement.
Language Function Assessment
During awake brain surgery, language tests are used to check a patient’s language skills. These tests might include naming pictures, reading, and counting. The team watches how the patient responds to these tasks.
This helps them spot the brain areas that handle language. Language mapping is very important for surgeries near language centers in the brain.
Motor Cortex Stimulation and Response
Motor cortex stimulation is also a key part of awake brain surgery. It uses electrical impulses to find out which brain parts control movement. The patient’s movements are watched and noted.
This helps the team make a detailed map of the motor cortex. It’s essential for safely removing damaged brain tissue without harming the patient’s motor skills. Using speech and motor mapping together helps neurosurgeons do complex surgeries more safely and accurately.
The Patient Experience During Awake Craniotomy
Being awake during brain surgery might sound scary, but it’s a safe and comfortable process. Awake craniotomy lets the patient stay awake during part of the surgery. This way, doctors can watch how the brain works in real time.
Sensations and Awareness Levels
Patients feel different things during the surgery. Some might feel a bit of pressure or discomfort. But, doctors use local anesthesia and sedation to keep them comfortable.
Motor cortex monitoring helps the team see which brain areas are important. This way, they can make sure the patient’s important functions stay safe.
A study in the Journal of Neurosurgery found something interesting. Patients who had awake craniotomy with motor mapping did better. They had more successful surgeries with fewer problems afterwards.
| Aspect | Patient Experience |
| Sensation | Varied; managed with anesthesia and sedation |
| Awareness | Conscious; able to respond to commands |
| Communication | Continuous; critical for brain mapping |
Communication Between Patient and Surgical Team
Talking well is very important during awake craniotomy. The patient needs to answer questions and tell about any feelings. This helps the team do motor mapping right and keep the patient safe.
“The teamwork between the patient and the surgical team is key to a successful awake craniotomy,” said Medical Expert, a top neurosurgeon.
The patient is not just a spectator; they are a big part of the surgery. They work with the neurosurgeon and other doctors to get the best results.
Potential Complications and Management
Awake brain surgery is very effective but has its own risks. These risks need careful management. Understanding these risks is key to keeping patients safe and getting the best results.
Medical Complications
Medical issues during awake brain surgery can include seizures and brain swelling. They can also be more serious, like stroke or cerebral hemorrhage. To manage these, we plan carefully before surgery, watch closely during it, and have a team of experts.
“The key to managing medical complications lies in anticipation and preparedness,” a leading neurosurgeon said. “Knowing the risks and having plans in place helps a lot.”
Psychological Reactions and Anxiety
Patients may feel anxiety or psychological distress because of the surgery. It’s important to talk about these feelings before and during surgery. The surgical team can use gentle words and reassurance to help calm the patient.
- Pre-operative counseling to address patient concerns
- Intraoperative support through gentle communication
- Reassurance by the surgical team
Emergency Conversion to General Anesthesia
Sometimes, the team might switch to general anesthesia because of problems or if the patient is too stressed. This is done when the patient’s safety is at risk or if the surgery can’t be done while awake. Having a well-rehearsed protocol for these situations is very important.
Medical professionals stress that “being ready for anything is key in managing awake brain surgery risks.” This means having the right tools and skills ready to go.
Recovery After Awake Brain Surgery
The journey to full recovery after awake neurosurgery has several stages. It starts with immediate post-operative care. This phase is key for watching the patient’s brain and managing any issues.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Right after surgery, care is very important. Patients are watched closely in the intensive care unit (ICU). This is to catch any problems early.
Pain management is also a big part. Doctors give medicines to keep the patient comfortable.
Doctors also check the patient’s brain function. They look at thinking, movement, and speech. This helps find and fix any problems quickly.
Long-term Recovery Timeline and Rehabilitation
How long it takes to recover can vary. It depends on the patient’s health and the surgery. Usually, it takes weeks to months to see big improvements.
Rehabilitation is key to getting better. It includes physical, speech, and occupational therapy. These help patients get back to normal life.
Success Rates and Clinical Outcomes
Awake brain surgery has seen big improvements in success rates and outcomes. It’s now a top choice for treating many brain conditions. This surgery offers better results for patients.
Tumor Resection Effectiveness
Research shows awake brain surgery boosts tumor removal success. Surgeons can watch brain functions live during surgery. This helps them remove tumors better without harming key brain areas.
This method leads to higher rates of complete tumor resection. It also cuts down on tumor coming back.
Neurological Function Preservation Statistics
Awake brain surgery is great at keeping brain functions safe. Surgeons can see brain functions live and avoid important areas. This means patients often have better neurological outcomes.
Studies show a big drop in brain problems after surgery. The success and outcomes of awake brain surgery prove it’s a valuable treatment for many brain issues.
Technological Advances in Neurosurgical Techniques
Technological innovations have changed how neurosurgeons do complex surgeries like awake craniotomies. These new technologies have made these surgeries more precise and safer.
Intraoperative imaging technologies are key in modern neurosurgery. They let surgeons see the brain in real-time during surgery. This helps them remove tumors more accurately and avoid damaging important brain areas.
Intraoperative Imaging Technologies
Intraoperative imaging includes methods like functional MRI (fMRI), intraoperative MRI (iMRI), and ultrasound. These tools give surgeons real-time feedback. For example, fMRI shows brain function, and iMRI lets them check how much tumor they’ve removed right away.
Computer-Assisted Neuronavigation
Computer-assisted neuronavigation is a big step forward in neurosurgery. It uses pre-surgery imaging to create a 3D model of the brain. During surgery, this model guides the surgeon’s tools, making the procedure more precise and safer.
These technologies together have greatly improved neurosurgery. As technology keeps getting better, we can look forward to even better results for patients.
Conclusion
Awake brain surgery has changed neurosurgery a lot. It lets surgeons keep patients awake during some operations. This way, they can see and remove bad tissue without harming important brain parts.
This method is a big win because it balances surgery needs with keeping the brain working. It’s all about choosing the right patients, using the best anesthesia, and having the latest tech.
As tech gets better, awake brain surgery will help more people. It’s a big hope for those with tough brain problems. Patients and doctors can work together to get the best results.
In short, awake brain surgery is a big step forward in brain surgery. It focuses on keeping the brain safe and improving care. As it gets better, it will play a key role in future brain surgery.
FAQ
What is awake brain surgery?
Awake brain surgery, also known as awake craniotomy, is a surgical procedure. The patient stays awake and alert during part or all of the operation. This lets the surgical team watch the brain function in real-time. They make sure to keep critical areas safe.
Why is awake brain surgery necessary?
It’s needed for certain medical conditions, like brain tumors or epilepsy. The tumor or seizure focus is near critical brain areas. The surgery removes the affected tissue while keeping the brain function around it.
Is awake brain surgery painful?
The surgery is done under local anesthesia, which numbs the scalp and skull. Patients might feel some discomfort or pressure. But, this is usually managed with medication. The pain is generally minimal.
How is the patient’s brain function monitored during awake brain surgery?
The brain function is monitored through speech and motor mapping, electrocorticography, and functional MRI. These tests help the team identify critical areas. They ensure these areas are preserved.
What is the role of the anesthesiologist during awake brain surgery?
The anesthesiologist manages the patient’s comfort and safety. They give local anesthesia, sedation, and other medications as needed. This ensures the patient’s well-being.
Can anyone undergo awake brain surgery?
Not everyone is a good candidate for awake brain surgery. The decision depends on the patient’s medical condition, the tumor or lesion’s location and type, and the patient’s overall health.
What is the recovery process like after awake brain surgery?
Recovery involves a period of observation in the hospital, followed by a gradual return to normal activities. Patients might feel tired, have headaches, or discomfort. But, these symptoms usually go away with time.
What are the benefits of awake brain surgery?
The surgery has several benefits. It improves tumor resection rates, reduces the risk of neurological damage, and leads to faster recovery times. It also allows for more precise removal of affected tissue, improving patient outcomes.
Are there any risks or complications associated with awake brain surgery?
Like any surgery, there are risks and complications, such as infection, bleeding, and neurological damage. But, these risks are low. The benefits of the procedure often outweigh the risks.
How has technology improved awake brain surgery?
Advances in technology, like intraoperative imaging and computer-assisted neuronavigation, have greatly improved the surgery. These technologies help surgeons better see the brain and surrounding tissue. This reduces the risk of complications.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9338386/



































