Nearly 30,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with a brain tumor each year. This shows how important neuro oncology is. It’s a medical field that deals with tumors in the brain and spinal cord. What is neuro oncology? Our essential, critical guide explains this amazing field, which treats awful brain and spinal cord tumors.
Neuro-oncology is a complex field. It needs a deep understanding of both neurology and oncology. A neuro oncologist is a doctor with special training in this area.
The importance of neurooncology is huge. It helps provide full care to patients with tough conditions. It also makes big steps in treatment and care for patients.
Key Takeaways
- Neuro-oncology is a medical specialty focused on brain and spinal cord tumors.
- A neuro oncologist has specialized training in neurology and oncology.
- The field is critical for improving treatment and patient care.
- Nearly 30,000 people are diagnosed with brain tumors annually in the U.S.
- Neuro-oncology requires a deep understanding of both neurology and oncology.
The Field of Neuro Oncology: Definition and Scope
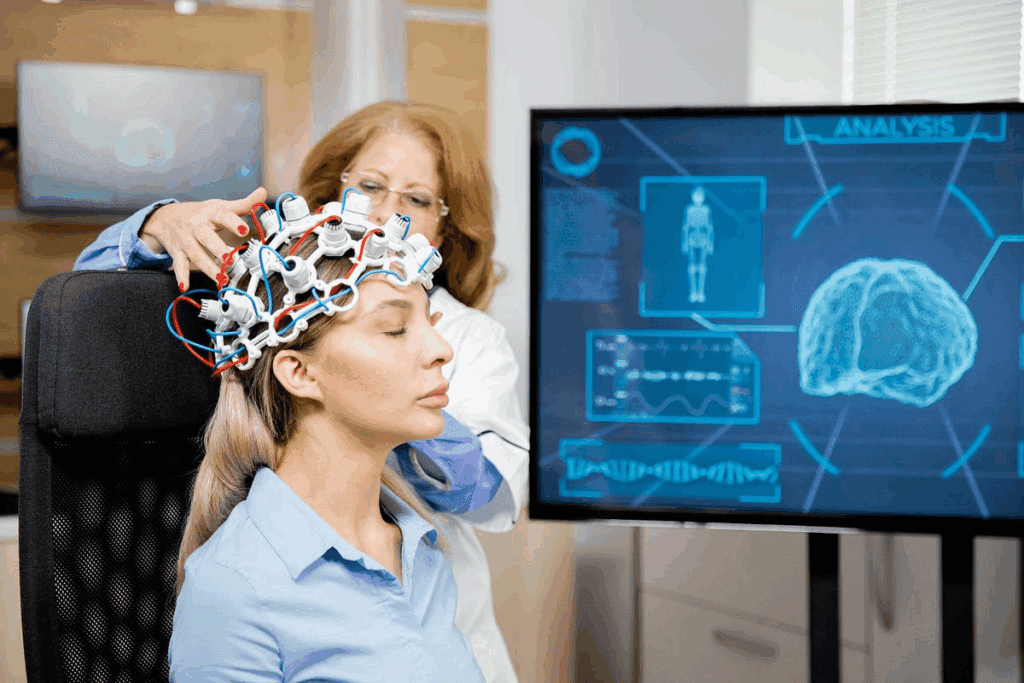
Neuro-oncology is the study, diagnosis, and treatment of tumors in the brain and spine. It combines knowledge from neurology and oncology. This field is growing because more people are getting brain and spinal tumors.
The Intersection of Neurology and Oncology
Neuro-oncology is where neurology and oncology meet. Neurologists know about the brain and nervous system. Oncologists understand tumors and how to treat them. Together, they tackle complex cases.
Key parts of this mix include:
- Diagnostic Techniques: Advanced imaging and tests to find out about tumors.
- Treatment Modalities: Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and new targeted therapies.
- Multidisciplinary Care: Working together with many specialists.
Historical Development of the Field
Neuro-oncology has grown a lot over the years. Early steps in neurosurgery and radiation therapy were key. Then, chemotherapy and targeted therapies came along, adding more options.
Important moments in neuro-oncology’s history include:
- The start of using CT scans and MRI for better diagnosis.
- The creation of neuro-oncology programs and clinics.
- Breakthroughs in molecular biology for understanding tumors and new treatments.
With ongoing research, neuro-oncology is set to make even more progress. This brings hope to patients and their families.
The Role of Neuro-Oncologists in Patient Care

Brain and spinal tumors are complex. They need the help of neuro-oncologists. These doctors specialize in treating tumors of the brain and spine.
Education and Training Requirements
To be a neuro-oncologist, a lot of education is needed. First, you must finish medical school. Then, you need residency training in neurology or oncology. Sometimes, you also get fellowship training in neuro-oncology.
This training is tough. It prepares them for hard cases.
Specialized Skills and Expertise
Neuro-oncologists have specialized skills in neuro oncology. They can read complex images and manage treatments. They also do neurological exams.
Their skills are key in making treatment plans for each patient.
Differences Between Neurologists and Neuro-Oncologists
Neurologists and neuro-oncologists both work with the nervous system. But, they focus on different things. Neurologists treat many nervous system disorders.
Neuro-oncologists focus on brain and spine cancers. Knowing the difference is important for the right care.
Common Brain Tumors and Neurological Cancers
It’s important to know about common brain tumors and neurological cancers. This knowledge helps in finding the best treatments. Early and correct diagnosis is key to improving patients’ lives.
Primary Brain Tumors
Primary brain tumors start in the brain. They can be either benign or malignant. Here are some common types:
- Gliomas: These tumors come from glial cells. They can be low-grade or high-grade, like glioblastoma.
- Meningiomas: Usually benign, these tumors grow in the meninges. The meninges are the membranes around the brain.
- Pituitary Adenomas: These are benign tumors in the pituitary gland. They can affect hormone production.
Metastatic Brain Tumors
Metastatic brain tumors come from cancer cells spreading to the brain. They often come from:
- Lung cancer: It’s known for spreading to the brain quickly.
- Breast cancer: Aggressive types like HER2-positive breast cancer are common.
- Melanoma: This skin cancer often spreads to the brain.
Spinal Cord Tumors
Spinal cord tumors can be benign or malignant. They are classified by where they are in relation to the spinal cord:
- Intramedullary tumors: These tumors are inside the spinal cord.
- Extramedullary tumors: These tumors are outside the spinal cord but in the spinal canal.
Knowing about these tumors helps doctors choose the right treatment.
Glioblastoma: The Most Aggressive Brain Cancer
Glioblastoma is the most aggressive brain cancer, making treatment and care very challenging. It’s a complex and highly malignant tumor. A detailed approach is needed to manage it.
Pathology and Characteristics
Glioblastoma grows quickly and spreads to nearby brain tissue, making surgery hard. Its cells are very different, which makes it hard to treat.
The World Health Organization (WHO) calls glioblastoma a Grade IV astrocytoma, the most severe type. This grade is based on how abnormal the cells look, how fast they divide, and if there’s damage to blood vessels and cells.
Standard of Care Treatment
The usual treatment for glioblastoma includes surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. The Stupp protocol, which uses radiotherapy and temozolomide, is a key part of treatment for new glioblastoma cases.
Surgery tries to remove as much of the tumor as possible without harming the brain. New techniques like intraoperative imaging help improve surgery results and reduce risks.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Even with aggressive treatment, glioblastoma patients face a tough outlook. The average survival time is about 15 months, with less than 10% surviving five years. Factors like age, how well the patient can function, and how much of the tumor is removed affect survival chances.
Researchers are working on new treatments like targeted therapies and immunotherapy to help glioblastoma patients. Understanding glioblastoma’s molecular makeup is key to finding better treatments.
Diagnostic Approaches in Neuro Oncology
Diagnosing neurological cancers involves several steps. We use imaging, histology, and molecular tests. Getting the diagnosis right is key to choosing the best treatment and helping patients.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Advanced imaging is vital in diagnosing neurological cancers. Tools like Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Computed Tomography (CT) scans, and Positron Emission Tomography (PET) give us detailed views of tumors. They show where the tumor is, how big it is, and what it looks like.
- MRI: Gives us clear images of soft tissues. It helps us tell different tumors apart and see how far they’ve spread.
- CT scans: Help find calcifications in tumors and check if the bone is involved.
- PET scans: Show us how active the tumor is. This helps us see how aggressive the tumor is and how well it’s responding to treatment.
Biopsy and Pathological Analysis
Biopsy is the top way to diagnose brain tumors. It involves taking a tissue sample. Then, we study it to figure out what kind of tumor it is and how serious it is.
Histopathological examination is key. It helps us see the tumor’s details, like how abnormal the cells are and if there’s any cell death. This info is vital for making a diagnosis and predicting how the tumor will behave.
Molecular and Genetic Testing
Molecular and genetic tests are now very important in neuro-oncology. They help us understand what’s driving the tumor to grow.
Tests like next-generation sequencing (NGS) and methylation profiling find specific genetic changes. This info helps us decide on the best treatment and predict how well the patient will do.
- IDH mutation status: Tells us about the tumor’s behavior in gliomas.
- MGMT promoter methylation: Helps us guess how well the tumor will respond to certain treatments.
- 1p/19q codeletion: Shows us a special genetic change in oligodendrogliomas.
By combining these methods, we get a full picture of the tumor. This helps us tailor treatments to each patient. It improves care in neuro-oncology.
The Multidisciplinary Approach to Neuro-Oncological Care
For patients with neuro-oncological disorders, a team approach is key. This strategy combines the skills of many healthcare experts. It helps meet the complex needs of these patients.
Tumor Board Conferences
Tumor board conferences are vital in neuro oncology. They gather specialists from different fields. Together, they discuss patient cases and plan treatments.
These conferences lead to better care and safer treatments. They also help in creating plans that fit each patient’s needs. Plus, they keep everyone up-to-date with the latest in neuro oncology.
Collaborative Treatment Planning
Working together is key in treating neuro-oncological conditions. A team creates a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs. This ensures all aspects of care are covered.
This team approach allows for a mix of treatments. It also helps predict and manage complications. This leads to better patient outcomes.
Patient-Centered Care Models
Patient-centered care is becoming more important in neuro oncology. It puts the patient first, focusing on their needs and values. This approach improves the quality of life for those with neuro-oncological conditions.
Effective communication and emotional support are key. Patients also need access to resources that meet their physical, psychological, and social needs. Adopting these models can boost patient satisfaction and outcomes.
Surgical Interventions for Brain and Spinal Tumors
Surgery is key in treating brain and spinal tumors. Neurosurgeons use different methods to remove or shrink tumors. They aim to keep brain function intact and improve patient results.
Craniotomy and Tumor Resection
A craniotomy is a surgery where part of the skull is removed to reach the brain. This is needed for brain tumor removal. The goal is to take out as much tumor as possible without harming nearby brain tissue.
The success of these surgeries depends on the tumor’s location, size, and type. New imaging and monitoring tools have made these surgeries safer and more effective.
Minimally Invasive Neurosurgical Techniques
Minimally invasive neurosurgery uses small cuts and special tools to cause less damage and speed up recovery. Methods like endoscopic surgery and stereotactic radiosurgery are alternatives to open surgery for some brain tumors.
These methods are great for tumors in hard-to-reach or sensitive areas. They are getting better, thanks to ongoing research.
Intraoperative Monitoring and Mapping
Intraoperative monitoring and mapping are vital in neurosurgery today. They involve checking the patient’s brain function during surgery and mapping the brain. This helps find areas that control important functions.
Monitoring can include EEG, EMG, and other neurophysiological tests. Brain mapping guides neurosurgeons through the brain’s complex structure. It helps avoid damage to critical areas, reducing the chance of neurological problems after surgery.
Radiation Therapy in Neuro Oncology
Radiation therapy has changed how we treat brain tumors. It’s a key treatment that has grown a lot. Now, it offers many options for patients with brain and spinal tumors.
External Beam Radiation
External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) is a common treatment in neuro-oncology. It sends radiation from outside the body to the tumor. EBRT includes techniques like 3D conformal radiation therapy, intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), and volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT).
EBRT is great because it targets the tumor well and protects healthy tissues. This is very important in neuro-oncology. Tumors are close to important brain parts, so precision is key.
| Technique | Description | Advantages |
| 3D Conformal Radiation Therapy | Uses 3D imaging to deliver radiation beams that conform to the tumor shape. | Reduces radiation exposure to surrounding tissues. |
| Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) | Modulates the intensity of radiation beams to match the tumor’s shape and size. | Enhances precision and reduces side effects. |
| Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) | Delivers radiation in a continuous arc around the patient. | Offers high precision and efficiency. |
Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a precise radiation therapy. It gives a big dose of radiation to a small tumor. SRS is not surgery but a non-invasive treatment that uses beams to target the tumor.
SRS works well for small to medium-sized brain tumors. It’s good for some benign tumors and metastases. Its precision helps avoid damage to the brain around the tumor.
Proton Therapy and Advanced Radiation Approaches
Proton therapy uses protons instead of X-rays to kill cancer cells. It’s good because it targets the tumor well and doesn’t harm nearby tissues much.
Proton therapy is great for tumors near important structures or in kids. It’s important to avoid too much radiation in these cases.
Other new radiation methods like carbon ion therapy and boron neutron capture therapy are being studied. They might help treat certain brain tumors.
Chemotherapy and Systemic Treatments
Chemotherapy is a key treatment for brain tumors. It uses drugs to target and kill tumor cells. This approach helps manage the disease.
Standard Chemotherapy Protocols
For brain tumors, doctors often use drugs like temozolomide. This is a common treatment for glioblastoma. The choice of treatment depends on the tumor type and the patient’s health.
Table 1: Common Chemotherapy Agents for Brain Tumors
| Chemotherapy Agent | Tumor Type | Mechanism of Action |
| Temozolomide | Glioblastoma | Alkylating agent |
| Carmustine | Various brain tumors | Alkylating agent |
| Lomustine | Brain tumors, lymphoma | Alkylating agent |
Blood-Brain Barrier Considerations
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a big challenge in treating brain tumors. It blocks many substances, including drugs, from entering the brain. This barrier makes it hard for chemotherapy to reach the tumor.
Drug Delivery Challenges
Getting drugs to brain tumors is hard because of the BBB. Researchers are working on new ways to deliver drugs. They’re using things like nanoparticles to help drugs get into the tumor.
Understanding chemotherapy and systemic treatments is key to managing brain tumors. Scientists are always looking for better ways to deliver drugs and improve treatments. They aim to find new ways to fight brain tumors.
Precision Medicine and Targeted Therapies
Neuro-oncology is changing fast with precision medicine and targeted therapies. These methods make treatments better for patients. Precision medicine means treatments are made just for each person. This is often done by looking at their genes or molecular profile.
Molecular Profiling of Tumors
Molecular profiling is key in precision medicine for brain tumors. It looks at a tumor’s genes to find specific targets for treatment.
Key aspects of molecular profiling include:
- Identifying genetic mutations that drive tumor growth
- Determining the tumor’s molecular subtype
- Informing treatment decisions based on the tumor’s genetic profile
Personalized Treatment Approaches
Personalized treatments in neuro-oncology focus on each patient’s unique tumor. By using molecular profiling, doctors can create treatments that work better.
“The future of neuro-oncology lies in our ability to tailor treatments to the individual, using the latest advances in precision medicine to improve patient outcomes.”
Emerging Targeted Agents
New targeted agents are being developed for brain tumors. These new treatments could lead to better results in clinical trials.
Some of the emerging targeted agents include:
- BRAF inhibitors for tumors with BRAF mutations
- IDH inhibitors for tumors with IDH mutations
- Other novel agents targeting various molecular pathways
Immunotherapy Advances in Neuro Oncology
Immunotherapy is changing neuro-oncology. It uses the immune system to fight cancer. This has shown great results in treating brain and spinal tumors.
Immunotherapy is bringing new ideas to neuro-oncology. We’re looking at checkpoint inhibitors, CAR T-cell therapy, and vaccines. Each aims to better target cancer cells.
Checkpoint Inhibitors
Checkpoint inhibitors help the immune system fight cancer better. In neuro-oncology, they’re being tested for brain tumors. They help the body’s immune response.
Research on checkpoint inhibitors in neuro-oncology is ongoing. Trials are checking how well they work and if they’re safe for glioblastoma and other brain tumors.
CAR T-Cell Therapy
CAR T-cell therapy changes T-cells to fight cancer. It’s shown great promise in blood cancers. Now, it’s being tested for brain tumors too.
Early trials suggest CAR T-cell therapy can target glioblastoma. This gives hope to those with aggressive brain cancer.
Vaccine-Based Approaches
Vaccine-based immunotherapy uses vaccines to boost the immune system. In neuro-oncology, vaccines are being made to target specific tumor antigens. This aims to create a strong immune response against brain tumors.
These vaccines are being tested in clinical trials. Early results look promising. Personalized vaccines, made for each patient, are an exciting area of research.
Pediatric Neuro Oncology: Special Considerations
Diagnosing brain tumors in kids is a big challenge. It needs special care from pediatric neuro-oncologists. This field is all about understanding brain tumors in children, both the neurological and oncological sides.
Common Pediatric Brain Tumors
Pediatric brain tumors come in many types. Each type has its own needs and treatments. Here are some common ones:
- Medulloblastoma: A very aggressive tumor in the cerebellum.
- Pilocytic Astrocytoma: A slow-growing tumor that can often be removed surgically.
- Ependymoma: Tumors from the ependymal cells in the ventricles and spinal cord.
- Glioma: Tumors from the brain’s glial cells, ranging from low-grade to high-grade.
Treatment Adaptations for Children
Treatment for kids with brain tumors needs to be tailored. It depends on the child’s age, tumor type, and health. Treatments include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, often together. The aim is to control the tumor while avoiding long-term harm.
| Treatment Modality | Considerations for Children |
| Surgery | Must be carefully planned to preserve neurological function and minimize impact on development. |
| Radiation Therapy | Dosage and delivery must be tailored to the child’s age and tumor type to reduce long-term side effects. |
| Chemotherapy | Regimens are designed to be effective against the specific tumor type while considering the child’s overall health. |
Long-term Developmental Concerns
Children treated for brain tumors may face long-term challenges. These include cognitive, neurological, and endocrine issues. It’s important to have long-term follow-up care to address these concerns.
Key long-term concerns include:
- Cognitive and learning disabilities.
- Neurological deficits, such as weakness or coordination issues.
- Endocrine dysfunction due to radiation or surgery affecting hormone-producing glands.
Understanding these challenges helps pediatric neuro-oncologists improve outcomes for kids with brain tumors.
Research and Academic Contributions in Neuro-Oncology
Academic contributions have been key in shaping neuro-oncology research. The field has grown a lot, thanks to the never-ending search for new knowledge and better treatments.
Major Journals and Publications
Many journals are important for sharing neuro-oncology research. Neuro-Oncology, Journal of Neuro-Oncology, and Neuro-Oncology Advances are some of them. These journals help researchers share their work, encouraging teamwork and new ideas.
Writing for these journals boosts the field’s reputation. It also helps show the value of research in neuro-oncology.
Impact Factor and Research Significance
The impact factor shows a journal’s prestige and how often its articles are cited. In neuro-oncology, top journals are seen as key sources of information. Research in these journals is often groundbreaking and can change how doctors treat patients.
High-impact research in neuro-oncology often looks at new treatments. This includes targeted therapies and immunotherapies. Such research aims to improve patient care and survival rates.
Current Clinical Trials and Experimental Treatments
Clinical trials are vital for finding new treatments in neuro-oncology. Today, trials are looking at checkpoint inhibitors and CAR T-cell therapy. These trials help us understand if new treatments work and are safe.
Experimental treatments, like vaccines, are also being tested. The results of these trials will guide the future of neuro-oncology care.
For more on clinical trials, researchers and patients can check out ClinicalTrials.gov. It has all the details on trial goals, who can join, and where trials are happening.
Specialized Neuro Oncology Centers in the United States
Many specialized centers in the U.S. offer advanced care for neuro-oncology patients. They have the latest technology and teams of experts. These teams work together to give patients the best care possible.
Academic Medical Centers
Academic medical centers are key in treating neuro-oncology. They focus on patient care, research, and teaching. This helps them find new treatments and improve care through clinical trials.
- Provide cutting-edge treatments through clinical trials
- Employ multidisciplinary teams of specialists
- Engage in research to improve patient outcomes
Patient Resources and Support Services
Specialized centers offer many resources and support services. These include counseling, support groups, and educational programs. They help meet the complex needs of patients and their families.
Key Support Services Include:
- Psychological counseling and support
- Educational programs for patients and families
- Access to clinical trials and new treatments
These centers aim to improve patient outcomes and quality of life. They provide all-around care and support.
Conclusion: The Future of Neuro Oncology
The field of neuro-oncology is changing fast. This is thanks to new medical tech, research, and our growing knowledge of brain tumors. Looking ahead, we see big steps in better treatments and better patient results.
New research in precision medicine, immunotherapy, and targeted therapies is leading the way. These advances help us better diagnose and treat brain tumors. This gives hope to patients and their families facing these tough conditions.
As we learn more about brain tumors, neuro oncology will focus more on personalized care. We’ll use the latest in molecular biology and genetics. This is key to improving survival rates and quality of life for those with neurological cancers.
FAQ
What is neuro-oncology?
Neuro-oncology is a medical field that focuses on brain and spinal cord tumors. It also deals with neurological cancers.
What is the role of a neuro-oncologist?
A neuro-oncologist is a doctor who specializes in brain and spinal cord tumors. They work with other doctors to create treatment plans and care for patients.
What are the common types of brain tumors?
Brain tumors can be primary or metastatic. Primary tumors include gliomas and meningiomas. Metastatic tumors start in other parts of the body.
What is glioblastoma?
Glioblastoma is a fast-growing and aggressive brain tumor. It’s the most common brain cancer in adults and has a poor prognosis.
How is glioblastoma treated?
Glioblastoma treatment combines surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. The treatment plan varies based on the patient’s needs and medical history.
What is the significance of the blood-brain barrier in neuro-oncology?
The blood-brain barrier protects the brain from the bloodstream. It makes it hard for some medicines to reach the brain, posing a challenge in treating tumors.
What is precision medicine in neuro-oncology?
Precision medicine tailors treatments to a patient’s tumor. It uses molecular profiling and targeted therapies.
What are some emerging treatments in neuro-oncology?
New treatments include immunotherapy and targeted therapies. These include checkpoint inhibitors and CAR T-cell therapy, as well as vaccine-based approaches.
What is the role of tumor board conferences in neuro-oncology?
Tumor board conferences involve a team of doctors discussing patient cases. They help ensure patients get the best care by coordinating treatment plans.
Where can I find specialized neuro-oncology centers in the United States?
You can find specialized centers at academic medical centers and cancer centers across the U.S. These centers offer a range of treatments and support services.
What is the impact factor of the Journal of Neuro-Oncology?
The Journal of Neuro-Oncology publishes research on brain and spinal cord tumors. Its impact factor shows its influence and reputation in neuro-oncology.
How can I stay up-to-date with the latest research in neuro-oncology?
Stay updated by reading major journals and attending conferences. You can also follow reputable online sources.
References
National Institutes of Health. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/diagnostic-tests/neurological-examination



































