Imagine a surgery that lets doctors target specific spots in the body with precision and minimal invasion. This is thanks to stereotactic surgery. It uses a three-dimensional coordinate system for accurate localization. We apply this advanced method to treat many medical conditions, mainly those affecting the brain.
The term “stereotactic” is often used the same as “stereotaxic.” Both refer to using a precise coordinate system to find targets in the body. This technique has changed neurosurgery, making complex procedures safer and more effective.
Key Takeaways
- Stereotactic surgery uses a three-dimensional coordinate system for precise localization.
- This technique is very useful in neurosurgery for treating brain conditions.
- The terms “stereotactic” and “stereotaxic” are used interchangeably.
- It allows for minimally invasive procedures, reducing recovery time.
- Accurate localization is key for the success of stereotactic surgery.
The Definition and Etymology of Stereotactic
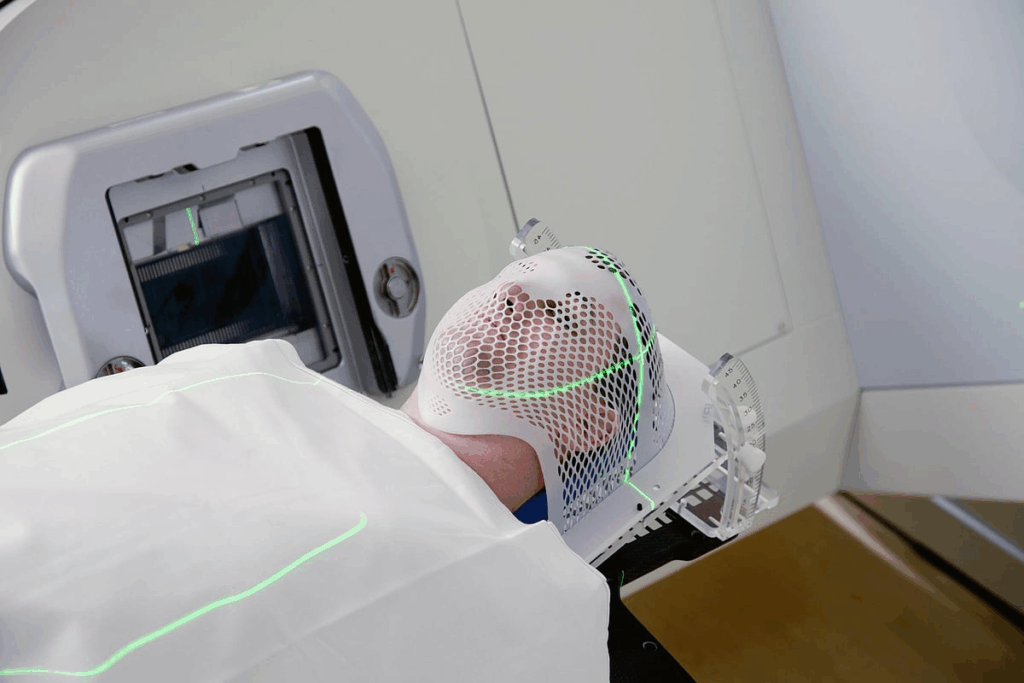

The word “stereotactic” comes from Greek. It mixes “stereos,” meaning solid, and “taktikos,” meaning arrangement or order. This background helps us see how it’s used in medicine, where exact placement in the body is key.
Origin of the Term “Stereotactic”
The term “stereotactic” comes from Greek words. “Stereos” means solid, and “taktikos” means arrangement or order. This mix shows the idea of making a precise, three-dimensional setup in the body. This is at the heart of what “stereotactic” means in medical terms.
Related Terms: Stereotaxic and Stereotaxy
“Stereotactic” and “stereotaxic” are often used the same way, but there’s a slight difference. “Stereotaxic” is more common in labs, while “stereotactic” is used in surgeries. “Stereotaxy” is the method or process of using a stereotactic device. Knowing these terms helps us understand the technology and its uses better.
Looking into “stereotactic” and its roots, we learn about its history and meaning. Its Greek roots show the value of solidity and exact placement. These are key to making stereotactic methods work in medicine.
Historical Development of Stereotactic Techniques
The history of stereotactic techniques is a key part of medical innovation. It has seen many milestones and pioneering efforts. These techniques have changed medicine, mainly in neurosurgery and oncology, by making procedures more precise and less invasive.
Early Pioneers in Stereotactic Methods
Spiegel and Wycis introduced stereotactic surgery in the mid-20th century. Their work started the use of stereotactic frames and techniques. These early innovators used a three-dimensional system to target body areas with great precision.
The start of stereotactic techniques was a big step towards more precise and less invasive treatments. This was thanks to the use of X-ray and later CT scans. These imaging technologies gave the needed details for precise targeting.
Evolution of Stereotactic Technology
Stereotactic technology has grown a lot over the years. This growth came from better imaging and computer methods. MRI and PET scans have made procedures more precise by giving detailed information. Computers have also helped in planning and doing these interventions better.
These advancements have made stereotactic techniques more accurate and useful in many medical areas. Today, they are used in neurosurgery, oncology, and more. They offer patients treatments that are less invasive, with fewer complications and quicker recovery times.
Key Milestones in Stereotactic Medicine
There have been many important moments in the history of stereotactic techniques. The first stereotactic frame, new imaging tech, and applying these principles to different medical issues have all helped. The move from frame-based to frameless systems is a big technological step. It has made things more flexible and precise.
The journey of stereotactic technology shows the teamwork of pioneers, researchers, and doctors. Their work has led to ongoing improvements and better care for patients.
The Science Behind Stereotactic Coordinate Systems
Stereotactic coordinate systems are key in precise medical treatments. They help doctors target areas with great accuracy. These systems are vital in neurosurgery and oncology.
Three-Dimensional Mapping Principles
The success of stereotactic procedures depends on three-dimensional mapping. This mapping creates detailed body maps. It lets doctors pinpoint specific spots. Advanced imaging like MRI and CT scans make this possible.
We use these scans to build a detailed coordinate system. This system guides our treatments. It combines different images to understand the target area’s layout.
Reference Points and Spatial Targeting
Reference points are essential in stereotactic navigation. They act as fixed landmarks. These points help align the patient’s anatomy with imaging data, ensuring spatial targeting is accurate. By matching these points with imaging, we can find the target area.
Mathematical Foundations of Stereotactic Navigation
The mathematical foundations of stereotactic navigation are based on geometry and algorithms. These models turn imaging data into a usable coordinate system. They handle the complexities of human anatomy and the need for exact location.
Mathematical Concept | Application in Stereotactic Navigation |
Coordinate Transformation | Enables the translation of imaging data into a navigable coordinate system. |
Geometric Algorithms | Facilitates the accurate registration of reference points and target areas. |
Spatial Analysis | Allows for the precise localization of targets within the body’s complex anatomy. |
Advanced imaging, precise reference points, and complex math models make stereotactic coordinate systems reliable. They are essential for today’s medical treatments.
Components of a Stereotactic System
Stereotactic systems, whether frame-based or frameless, have key parts that make them work. These parts help achieve the precision needed for these procedures.
Frame-Based Stereotactic Systems
Frame-based systems use a rigid frame attached to the patient’s head or body. This frame is the reference point for the stereotactic coordinates. It ensures the target is accurately hit. The frame is fixed with pins or other devices, making it stable for the procedure.
Key components of frame-based systems include:
- The stereotactic frame itself, which is designed to be rigid and stable
- An arc or other mechanical system that guides the surgical instrument
- A coordinate system that allows for precise localization of targets
Frameless Stereotactic Navigation
Frameless systems don’t need a rigid frame. They use advanced imaging and markers for accurate targeting. These systems track the surgical instruments in real-time using optical or electromagnetic methods.
The advantages of frameless systems include:
- Greater flexibility during the procedure
- Reduced patient discomfort due to the absence of a bulky frame
- Potential for improved accuracy through real-time tracking
Calibration and Accuracy Verification
Calibration and accuracy verification are key for both frame-based and frameless systems. Calibration adjusts the system to match the patient’s anatomy from imaging data. Accuracy verification checks if the system is working right and targeting information is reliable.
We use various methods for calibration and verification, including:
- Phantom targets to test the system’s accuracy
- Quality control checks on the imaging equipment
- Regular maintenance and updating of the stereotactic system’s software and hardware
Stereotactic Applications in Neurosurgery
Stereotactic neurosurgery uses precise targeting and is less invasive. It has made neurosurgery more accurate and safe. We will look at how these methods are used in neurosurgery, their benefits, and their importance in treatment.
Brain Biopsy Procedures
Brain biopsy is a key tool in neurosurgery for diagnosing brain conditions. It uses a coordinate system to target specific brain areas. This method is great for finding deep-seated lesions or tumors that are hard to reach.
Using stereotactic guidance in brain biopsies improves accuracy and lowers risks. Advanced imaging like MRI or CT scans helps neurosurgeons plan and perform the biopsy. This way, they can get tissue samples with little impact on the patient’s brain function.
Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) involves placing electrodes in the brain to control abnormal activity. Stereotactic techniques are key for precise placement. This is vital for treating movement disorders like Parkinson’s disease.
The stereotactic method allows for adjustments during the procedure. This ensures the electrodes are placed correctly. It makes DBS more effective and reduces side effects by avoiding nearby brain areas.
Treatment of Movement Disorders
Stereotactic neurosurgery is essential for treating movement disorders. It targets brain areas causing abnormal movements. Procedures like thalamotomy and pallidotomy help patients with Parkinson’s disease and dystonia.
- Thalamotomy: Creates a lesion in the thalamus to stop tremors.
- Pallidotomy: Targets the globus pallidus to reduce dyskinesia and rigidity.
Epilepsy and Psychiatric Applications
Stereotactic techniques are also used for epilepsy and some psychiatric conditions. For epilepsy, surgery can remove seizure foci or implant devices like responsive neurostimulation systems. In psychiatry, it’s used for OCD and treatment-resistant depression.
The precision of stereotactic methods is a big advantage in these complex cases. It allows for targeted treatments with fewer side effects than traditional surgery.
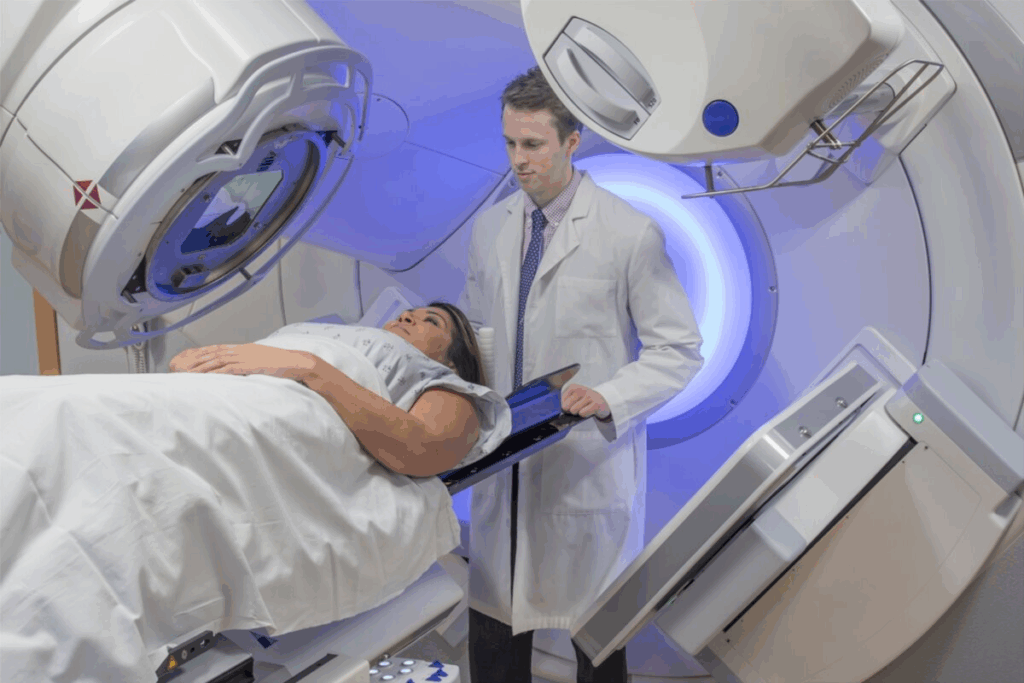
Stereotactic Radiosurgery Explained
Stereotactic radiosurgery is a top-notch treatment for patients around the world. It uses advanced tech to send precise radiation to specific spots. This is done with tools like Gamma Knife, LINAC, and CyberKnife.
Gamma Knife Technology
Gamma Knife radiosurgery uses cobalt sources to target areas. It’s great for brain tumors and other brain issues. The precision of Gamma Knife technology helps treat areas well without harming nearby tissues.
Linear Accelerator (LINAC) Systems
LINAC systems use a linear accelerator to make high-energy X-rays. They’re very flexible and treat many conditions. The ability to adjust the radiation’s intensity and direction makes LINAC systems very effective.
CyberKnife and Other Robotic Systems
CyberKnife is a robotic system that tracks and adjusts the radiation beam in real-time. It’s perfect for tumors that move with breathing or body movements. The flexibility of CyberKnife and similar systems has opened up new possibilities for treatment.
Dose Planning and Delivery
Dose planning is key in stereotactic radiosurgery. It involves figuring out the right amount of radiation for the target area. Advanced imaging and software are used to make sure the radiation is delivered safely and effectively. The goal of dose planning is to make the treatment as effective as possible while reducing side effects.
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)
SBRT is a cutting-edge radiation therapy that targets tumors with great precision. It has changed how we treat cancer by giving high doses of radiation to tumors. At the same time, it protects healthy tissues around the tumor.
Treatment Planning Process
The planning for SBRT is detailed and involves several steps. Accurate imaging is key, using CT scans, MRI, or PET scans to find the tumor. We then use special software to make a 3D model of the tumor and the tissues around it. This helps us shape the radiation beams for the best results.
The main parts of SBRT planning are:
- Image registration and fusion
- Tumor delineation
- Organ-at-risk (OAR) contouring
- Beam arrangement and dose calculation
- Plan optimization
Target Localization Techniques
Getting the radiation to the right spot is key in SBRT. We use different methods for this, including:
- Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) using onboard imaging
- Real-time tumor tracking
- Use of fiducial markers
- Respiratory gating
These methods help us track the tumor’s movement. This ensures the radiation is delivered exactly where it’s needed.
Applications in Cancer Treatment
SBRT is used in many cancer treatments, a non-surgical option for some patients. It’s often used for tumors in the:
- Lungs
- Liver
- Prostate
- Spine
- Other extracranial sites
It’s great for patients who can’t have surgery because of health issues or where the tumor is. SBRT gives high doses of radiation in just a few sessions. This makes it a good choice for many patients.
As technology improves, SBRT’s uses and benefits for patients are growing. This is helping to make cancer treatment even better.
Image Guidance in Stereotactic Procedures
Advanced image guidance systems are changing stereotactic medicine. They make procedures more precise and safe. We use MRI, CT, PET, and functional imaging to target and treat accurately.
MRI-Guided Stereotactic Approaches
MRI-guided methods are great for neurosurgery because they show soft tissues well. High-resolution MRI images help us find tumors and important areas. This is key for planning and doing stereotactic procedures.
CT-Based Stereotactic Navigation
CT-based navigation gives us the exact location needed for precise targeting. CT scans are good for seeing bones and calcifications. This is helpful for some neurosurgery and orthopedic treatments.
PET and Functional Imaging Integration
Adding PET and functional imaging to procedures helps us target specific areas. PET imaging shows how active tumors are. This helps us plan and check treatment.
Real-Time Imaging During Procedures
Real-time imaging is key for accuracy and adapting during procedures. Real-time MRI or CT imaging lets us watch the procedure. We can adjust and check if everything is right.
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy and Other Applications
Stereotactic precision is changing how we do diagnostic and treatment procedures. It’s now used in many medical fields, not just neurosurgery.
Minimally Invasive Diagnostic Procedures
Stereotactic breast biopsy is a key example of using stereotactic techniques for less invasive tests. It lets doctors take precise samples from the breast with little pain. This method is more accurate than older ways, needing fewer big surgeries.
It’s great for patients because it means less time recovering and less scarring. This makes it a popular choice for breast tissue sampling.
Expanding Applications Beyond Neurosurgery
Stereotactic technology is now used in many areas, not just neurosurgery. It’s used in oncology, orthopedics, and more. This is because it offers precise targeting, which is vital in complex surgeries.
In oncology, it helps target tumors for radiation therapy. This makes treatments more effective and less harmful.
Stereotactic Approaches in Orthopedics
In orthopedics, stereotactic methods are being tested to improve surgery accuracy. They help with bone biopsies and placing orthopedic devices. This could lead to better surgery results and fewer complications.
Using stereotactic technology in orthopedics is a big step forward. It could make surgeries more precise and less invasive.
The Patient Experience During Stereotactic Procedures
Medical technology keeps getting better, and so does our understanding of the patient’s journey. The experience of having a stereotactic procedure is very important. It includes getting ready, feeling comfortable during the procedure, and getting care after it’s done.
Preparation and Positioning
Getting ready for a stereotactic procedure is very important. Patients usually have imaging studies first to guide the treatment. Making sure the patient is in the right position is also key for the procedure to work well.
Comfort and Pain Management
Keeping the patient comfortable and managing pain is a big part of the experience. We use local anesthesia and conscious sedation to help. Our goal is to make sure the patient is comfortable and safe during the procedure.
Recovery and Follow-up Care
Recovering from a stereotactic procedure is usually quick. Most patients can go back to their normal activities soon. Follow-up care is very important to check on the patient’s recovery and handle any issues that might come up.
Aspect of Care | Description | Importance |
Preparation | Involves imaging studies and patient education | High |
Positioning | Ensures correct alignment for the procedure | High |
Comfort and Pain Management | Utilizes local anesthesia and conscious sedation | High |
Recovery and Follow-up | Includes post-procedure monitoring and care | High |
Advantages of Stereotactic Precision in Medicine
Stereotactic precision is changing medicine with its high accuracy. It’s a key part of many medical fields. It helps patients get better faster and makes healthcare more efficient.
Enhanced Accuracy and Safety
The main benefit of stereotactic precision is its enhanced accuracy. It uses advanced imaging and precise systems. This lets doctors target areas with less invasion, lowering risks and improving safety.
In neurosurgery, where success is very close to failure, this precision is vital. It helps in making accurate diagnoses and treatments. This leads to better results for patients.
Reduced Recovery Time and Complications
Another big plus of stereotactic precision is the reduced recovery time. Its minimally invasive nature causes less damage and trauma. This means patients heal faster and stay in the hospital less.
This also cuts down on complications, a big worry in traditional surgeries. With less risk, doctors can treat more patients safely.
Economic Benefits of Minimally Invasive Approaches
The economic benefits of stereotactic precision are huge. It reduces the need for big surgeries, cuts down recovery times, and lowers complication risks. This saves a lot of money for healthcare systems.
Also, treating patients as outpatients saves money for both patients and healthcare providers. In short, stereotactic precision offers many benefits. It improves accuracy, reduces recovery times, and saves money. As it keeps improving, we’ll see more uses in medicine.
Future Innovations in Stereotactic Technology
Stereotactic technology is on the verge of a new era. Breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, real-time imaging, and robotic assistance are leading the way. These advancements promise to make treatments more precise and effective, bringing hope to those needing complex medical care.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
The addition of artificial intelligence (AI) to stereotactic systems is set to change treatment planning and execution. AI can quickly analyze large amounts of data, helping doctors make better decisions. It enhances pattern recognition and predictive analytics, making procedures more accurate.
Advances in Real-Time Imaging
Real-time imaging is key for successful stereotactic procedures. New imaging technologies, like intraoperative MRI and real-time ultrasound, give doctors detailed and accurate information during surgery. This leads to more precise targeting and lowers the risk of complications.
Robotic Assistance Developments
Robotic assistance is playing a bigger role in stereotactic technology. Robotic systems improve precision, stability, and dexterity, making complex procedures easier. The development of advanced robotic systems will allow for more treatments using stereotactic techniques.
Personalized Treatment Planning
Personalized treatment planning is where future innovations in stereotactic technology will make a big difference. Advanced imaging and AI analytics enable clinicians to create treatment plans tailored to each patient. This personalized approach can lead to more effective treatments and better outcomes.
As we explore new possibilities with stereotactic technology, we can expect major improvements in patient care and treatment results. The future of stereotactic technology is promising, and we’re excited to see its positive impact on the medical field.
Conclusion
Stereotactic surgery has changed medicine a lot. It now offers precise and less invasive treatments. This was not possible before. The growth of stereotactic techniques has greatly helped patients.
This method is used in many areas like neurosurgery and radiation therapy. It makes treatments more accurate and safe. It also cuts down recovery time and lowers the chance of problems.
Looking ahead, there’s a lot more to come in stereotactic surgery. New tech like artificial intelligence and real-time imaging will make things even better. These advancements will keep improving precision medicine.
We expect to see more personalized treatments in the future. This will make care even more effective. As doctors keep improving these methods, patients will get better results. Care will also become more precise and caring.
FAQ
What is stereotactic surgery?
Stereotactic surgery is a way to do surgery with less harm. It uses a special system to find and reach specific spots in the body, like the brain.
What is the difference between stereotactic and stereotaxic?
“Stereotactic” and “stereotaxic” mean the same thing. They talk about using a three-dimensional system for precise targeting. “Stereotaxy” is the whole method or procedure.
How has stereotactic technology evolved over time?
Stereotactic technology has grown a lot. It now uses new imaging like MRI, CT, and PET. It also uses computers to get better results.
What are the components of a stereotactic system?
A stereotactic system has different parts. It can be frame-based or frameless. It includes a coordinate system, reference points, and imaging tools for precise targeting.
What are the applications of stereotactic techniques in neurosurgery?
Stereotactic techniques help in many neurosurgery tasks. They are used for brain biopsies, deep brain stimulation, treating movement disorders, and epilepsy.
How does stereotactic radiosurgery work?
Stereotactic radiosurgery uses precise beams of radiation. Systems like Gamma Knife, LINAC, and CyberKnife aim at tumors. They give high doses of radiation while protecting nearby tissues.
What is Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)?
SBRT is a treatment that gives high doses of radiation to tumors. It uses stereotactic techniques and image guidance to protect surrounding tissues.
What is the role of image guidance in stereotactic procedures?
Image guidance is key in stereotactic procedures. It includes MRI, CT, PET, and functional imaging. It helps target spots precisely and monitor treatment in real-time.
Can stereotactic techniques be used beyond neurosurgery?
Yes, stereotactic techniques are used in many fields. They are used for breast biopsies, orthopedic procedures, and cancer treatment. They offer less invasive ways to diagnose and treat.
What are the benefits of stereotactic precision in medicine?
Stereotactic precision makes treatments more accurate and safe. It shortens recovery time and lowers the risk of complications. It also saves money by being less invasive.
What future innovations can be expected in stereotactic technology?
Future advancements in stereotactic technology include artificial intelligence and better imaging. There will also be robotic help and personalized treatment plans. These will make treatments even more precise and effective.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Stereotactic surgery applications and definition in contemporary medicine. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560664/



































