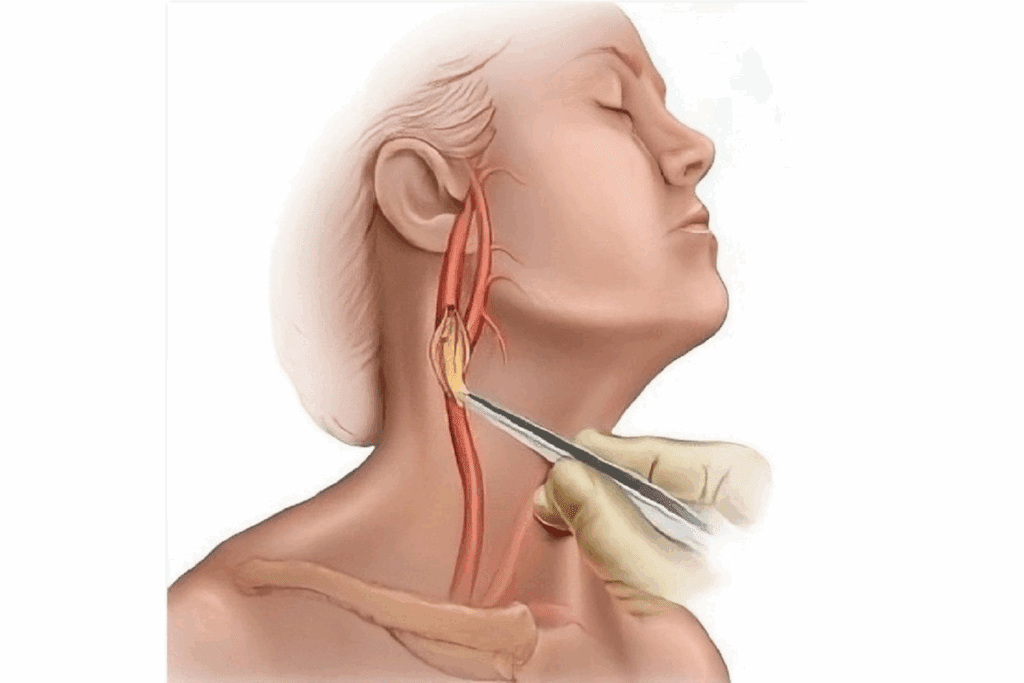
The human body has a complex network of blood vessels. The carotid arteries are key in supplying blood to the brain, neck, and face. There are two main carotid arteries, one on each side of the neck. They split into internal and external carotid arteries.Get the definitive answer: how many carotid arteries are there? Understand the anatomy and location in the neck clearly.
This structure is vital for the brain’s health and other important areas in the head and neck. Knowing how these arteries work is key for diagnosing and treating vascular diseases.
Key Takeaways
- The human body has two main carotid arteries.
- These arteries are vital for supplying blood to the brain, neck, and face.
- The carotid arteries branch into internal and external carotid arteries.
- Understanding carotid artery anatomy is essential for vascular health.
- Carotid arteries play a significant role in overall circulatory health.
The Anatomy of Carotid Arteries
The carotid arteries are key to the body’s blood flow. They carry oxygen-rich blood to the head and neck. These arteries are vital for the brain and face’s health.
Definition and Basic Structure
The carotid arteries are major neck vessels. They start in the chest and go up the neck. They split into two branches: the internal carotid artery and the external carotid artery.
The internal carotid artery goes straight to the brain. The external carotid artery goes to the face and neck.
Knowing the carotid arteries’ structure is key for doctors. It helps them diagnose and treat problems.
Location in the Human Body
The carotid arteries are in the neck, next to the trachea and larynx. They go up through the carotid sheath, a protective tube. This makes them easy to check, like feeling the carotid pulse.
| Artery | Origin | Branching |
| Common Carotid Artery | Aortic Arch (left) and Brachiocephalic trunk (right) | Divides into Internal and External Carotid Arteries |
| Internal Carotid Artery | Common Carotid Artery | Supplies blood to the Brain |
| External Carotid Artery | Common Carotid Artery | Supplies blood to the Face and Neck |
How Many Carotid Arteries Are There?

The carotid arteries are key in bringing blood to the brain. It’s important to know how many there are. The carotid system has many vessels to keep the brain well-oxygenated.
The Four Main Carotid Vessels
There are four main carotid vessels. The right and left common carotid arteries split into internal carotid arteries and external carotid arteries. The common carotid arteries are the main ones that bring blood to the head and neck.
They start from the brachiocephalic trunk on the right and the aortic arch on the left.
- The right common carotid artery starts from the brachiocephalic trunk.
- The left common carotid artery comes directly from the aortic arch.
- Both common carotid arteries go up the neck and split into internal and external carotid arteries.
The internal carotid arteries send blood to the brain. The external carotid arteries send blood to the face and neck. Knowing the difference is key for diagnosing and treating vascular issues.
Anatomical Variations and Anomalies
While most people have the typical four main carotid vessels, there can be variations. These variations can affect where the carotid arteries start, how they go, or how they branch. For example, some people might have the right common carotid artery starting from the aortic arch.
It’s vital for doctors to know about these variations. They help in planning surgeries and avoiding complications.
The Common Carotid Arteries
The common carotid arteries are vital for bringing oxygen-rich blood to the brain and face. They play a key role in keeping these areas healthy and functioning well.
Origin and Path
The common carotid arteries start from the brachiocephalic trunk on the right and the aortic arch on the left. They move up the neck, in front of the prevertebral fascia. They are inside the carotid sheath, with the internal jugular vein and vagus nerve nearby.
The right artery comes from the brachiocephalic trunk, and the left comes from the aortic arch. Knowing this helps in understanding and treating any issues.
Differences Between Left and Right Common Carotid
The left artery is longer because it starts from the aortic arch. The right artery is shorter, starting from the brachiocephalic trunk. This affects how doctors and surgeons work on them.
Both arteries split into the internal and external carotid arteries at the top of the thyroid cartilage. This split is very important in surgeries and medical imaging.
Anatomical Relationships
The common carotid arteries are close to many important neck structures. They are in the carotid sheath with the internal jugular vein and vagus nerve. They are also in front of the prevertebral fascia and the muscles it covers.
Knowing these relationships is key for surgeons and radiologists. It helps them safely and effectively work in the neck’s complex anatomy.
The Internal Carotid Arteries
The internal carotid arteries are key to the brain’s blood supply. They carry oxygen-rich blood to the brain. This is vital for the brain to work right.
Path and Segments
The internal carotid arteries start from the common carotid arteries. They split into the internal and external carotid arteries near the thyroid cartilage. Then, they go up through the neck and into the skull.
They pass through the carotid canal in the temporal bone. Inside the skull, they split into segments. These segments include the cervical, petrous, lacerum, cavernous, and cerebral segments.
Each segment has its own role. They give off branches that feed different parts of the brain. Knowing this helps doctors diagnose and treat brain conditions.
Branches of the Internal Carotid
The internal carotid arteries have several important branches. These include the ophthalmic artery, posterior communicating artery, and anterior choroidal artery. These branches are key for the eyes and parts of the brain.
| Branch | Area Supplied |
| Ophthalmic Artery | Eyes and surrounding structures |
| Posterior Communicating Artery | Part of the circle of Willis, contributing to cerebral circulation |
| Anterior Choroidal Artery | Choroid plexus, parts of the internal capsule, and other deep brain structures |
Areas Supplied by the Internal Carotid
The internal carotid arteries supply blood to a big part of the brain. This includes the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes. They also feed the eyes and other head structures.
This blood supply is vital for movement, feeling, and thinking. The internal carotid arteries are essential for brain health.
Any problem with these arteries can cause serious brain damage. This includes stroke. It’s important to know about the internal carotid arteries for diagnosing and treating brain issues.
The External Carotid Arteries
The external carotid arteries start from the common carotid arteries. They mainly send blood to the face, neck, and scalp. These arteries are key for making sure these areas get enough oxygen and nutrients.
Major Branches
The external carotid arteries have several important branches. These include the superior thyroid artery, ascending pharyngeal artery, lingual artery, facial artery, occipital artery, and posterior auricular artery. Each branch supplies a different part of the head and neck.
The superior thyroid artery mainly goes to the thyroid gland. The facial artery supplies the face, including the lips, nose, and palate.
Areas Supplied by the External Carotid
The external carotid arteries supply blood to the face, neck, scalp, and more. Their branches make sure these areas get enough blood. For example, the maxillary artery goes to the deep face, like the nasal cavity and palate.
Clinical Importance of External Carotid Branches
The external carotid arteries and their branches are very important in medicine. They are involved in many diseases and are key for surgeries and treatments. For example, they can help when the internal carotid artery is blocked. Knowing how these arteries work is vital for treating vascular diseases.
In summary, the external carotid arteries are essential for the blood supply to the face, neck, and scalp. Their branches and the areas they cover are vital for our body’s functions. Their importance in medicine is huge.
Function of the Carotid Arterial System
The carotid arterial system is key for bringing oxygen-rich blood to the brain and other head and neck areas. It includes the common carotid arteries and their branches, the internal and external carotid arteries. This system is vital for keeping the brain, face, and neck healthy and functioning well.
Blood Supply to the Brain
The internal carotid arteries mainly carry blood to the brain. They start from the common carotid arteries and go up through the neck. They then enter the skull through the carotid canal.
Inside the skull, they split into segments that feed different brain parts. The internal carotid arteries are key for bringing oxygen and nutrients to the brain. They help the brain control movement and think.
Blood Supply to the Face and Neck
The external carotid arteries, on the other hand, supply blood to the face and neck. They split into arteries like the maxillary, superficial temporal, and facial arteries. These arteries give oxygen-rich blood to the face and neck’s structures.
These branches are vital for the health and function of facial muscles, the scalp, and other tissues. The external carotid artery and its branches help with facial expressions and blood supply to the thyroid gland.
In summary, the carotid arterial system is essential for delivering oxygenated blood to the brain, face, and neck. It supports their functions and overall health.
Clinical Significance of the Carotid Arteries
The carotid arteries are key to our circulatory system. They carry oxygen-rich blood to the brain, face, and neck. Their importance is huge, affecting blood pressure, oxygen levels, and heart health.
Carotid Pulse and Its Importance
The carotid pulse is a vital sign that shows heart rate and rhythm. It’s checked during CPR or when checking a patient’s heart. The carotid pulse is key, showing how well the heart is working.
Carotid Sinus and Baroreceptors
The carotid sinus is at the common carotid artery’s split. It has baroreceptors that sense blood pressure changes. These receptors help control heart rate and blood vessel size.
A study in the Journal of Hypertension found, “The carotid sinus baroreceptors are vital for blood pressure control. They affect heart rate and blood vessel size.”
Carotid Body and Chemoreceptors
The carotid body is near the artery split. It has chemoreceptors that sense blood oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH. These receptors help control breathing and heart rate.
A study in the Journal of Applied Physiology said, “The carotid body chemoreceptors are important for breathing in low oxygen. They help keep blood oxygen levels right.”
In summary, the carotid arteries are very important. They affect the carotid pulse, carotid sinus, and carotid body. Knowing this helps doctors take better care of patients.
Common Carotid Artery Disorders
The carotid arteries can face several issues, like disease, stenosis, and dissection. These problems can seriously affect heart health. They might lead to stroke or other severe issues.
Atherosclerosis and Carotid Artery Disease
Atherosclerosis causes plaque buildup in arteries, narrowing them. This restricts blood flow. Atherosclerosis is a big risk for carotid artery disease. High blood pressure, smoking, and high cholesterol can make it worse.
Carotid artery disease symptoms include TIAs or mini-strokes. These can cause temporary weakness, numbness, or vision problems.
Carotid Stenosis and Stroke Risk
Carotid stenosis is when the carotid arteries narrow. This is often due to atherosclerosis. It raises stroke risk by reducing blood flow to the brain.
- Risk factors include hypertension, diabetes, and smoking.
- Symptoms are similar to carotid artery disease, like TIAs or stroke.
- Diagnosis uses imaging studies like ultrasound or angiography.
Carotid Dissection and Trauma
Carotid dissection happens when the artery wall tears. It can lead to stroke or other serious issues. It might be caused by neck trauma or can happen on its own.
Symptoms include severe headache, neck pain, and neurological problems. Quick medical help is key if dissection is suspected.
Treatment for carotid artery disorders depends on the condition and its severity. It can range from medication to surgery like carotid endarterectomy or angioplasty with stenting.
Diagnostic Approaches for Carotid Arteries
There are many ways to check the carotid arteries. These methods help find problems like stenosis and atherosclerosis. They are important to prevent serious health issues, like stroke.
Non-invasive Imaging Techniques
Non-invasive tests are often the first choice because they are safe and work well. Ultrasound uses sound waves to show images of the arteries. It helps check blood flow and find blockages or plaque.
Duplex ultrasound combines traditional ultrasound with Doppler ultrasonography. It gives detailed info about the arteries. Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) uses magnetic fields to create detailed artery images.
Angiography and Advanced Imaging
Angiography is used for more detailed checks. It involves injecting a contrast agent to see the arteries on X-ray. Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) makes images clearer by removing background structures.
“The choice of diagnostic approach depends on the patient’s condition, the availability of equipment, and the expertise of the healthcare provider.” – Medical Expert
Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) gives high-resolution images of the arteries. It’s useful for planning surgeries.
Treatment and Management of Carotid Artery Conditions
Managing carotid artery conditions requires a mix of medical care and surgery. This approach helps lower risks and improves health outcomes.
Medical Management
Medical care for carotid artery issues aims to reduce risks and stop disease growth. It includes antiplatelet therapy, statins for cholesterol, and drugs for blood pressure and diabetes. Quitting smoking, eating right, and exercising more are also key.
Key components of medical management:
- Antiplatelet therapy
- Statin therapy
- Blood pressure management
- Diabetes control
- Lifestyle modifications
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is for those with severe carotid stenosis or high stroke risk. The main surgeries are carotid endarterectomy (CEA) and carotid artery stenting (CAS). The choice depends on the patient’s condition, health, and artery shape.
| Procedure | Description | Indications |
| Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA) | Surgical removal of plaque from the carotid artery | Significant carotid stenosis, high risk of stroke |
| Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS) | Minimally invasive placement of a stent to keep the artery open | High-risk patients, significant stenosis, or anatomical challenges for CEA |
Conclusion
The carotid arteries are key for blood flow to the brain, face, and neck. They split into two main parts: the left and right common carotid arteries. These then branch into internal and external carotid arteries.
The internal carotid arteries are vital for the brain’s blood supply. On the other hand, the external carotid arteries provide blood to the face and neck.
Problems like carotid artery disease and stenosis can raise stroke risk. Tests like non-invasive imaging and angiography can spot these issues. Treatment varies from medication to surgery, based on the problem’s severity.
In summary, the carotid arteries are vital for our health, mainly our brain’s function. Knowing about their structure, role, and possible issues is key for prevention and treatment. By understanding their importance, we can work on keeping our heart and brain healthy.
FAQ
Where are the carotid arteries located?
The carotid arteries are in the neck, on both sides of the trachea. They are key to the circulatory system. They supply blood to the brain, face, and neck.
How many carotid arteries are there?
There are four main carotid vessels. These are the right and left common carotid arteries. They split into the internal and external carotid arteries.
What is the function of the carotid arterial system?
The carotid arterial system is vital. It supplies blood to the brain, face, and neck. It’s essential for our overall health.
What is the difference between the internal and external carotid arteries?
The internal carotid arteries go to the brain. The external carotid arteries go to the face and neck.
What are the common disorders affecting the carotid arteries?
Common issues include carotid artery disease and atherosclerosis. Carotid stenosis and dissection are also common.
How are carotid artery conditions diagnosed?
Doctors use non-invasive tests like ultrasound and MRI. Angiography and advanced imaging are also used.
What are the treatment options for carotid artery conditions?
Treatment includes lifestyle changes and medication. Surgery like carotid endarterectomy and angioplasty are also options.
What is the clinical significance of the carotid arteries?
The carotid arteries are vital for blood pressure and oxygen level monitoring. They are key to our health.
Where is the carotid artery located in the neck?
The carotid artery is in the neck, beside the trachea. You can feel it by taking the pulse on the neck side.
What is the carotid pulse, and why is it important?
The carotid pulse shows the heart rate and rhythm. It’s a key sign of heart health.
What is carotid stenosis, and how does it affect the body?
Carotid stenosis is when the arteries narrow. It raises the risk of stroke and heart problems.
What is the role of the carotid body and chemoreceptors?
The carotid body and chemoreceptors detect oxygen level changes. They help the body respond to changes in its state.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545238/




































