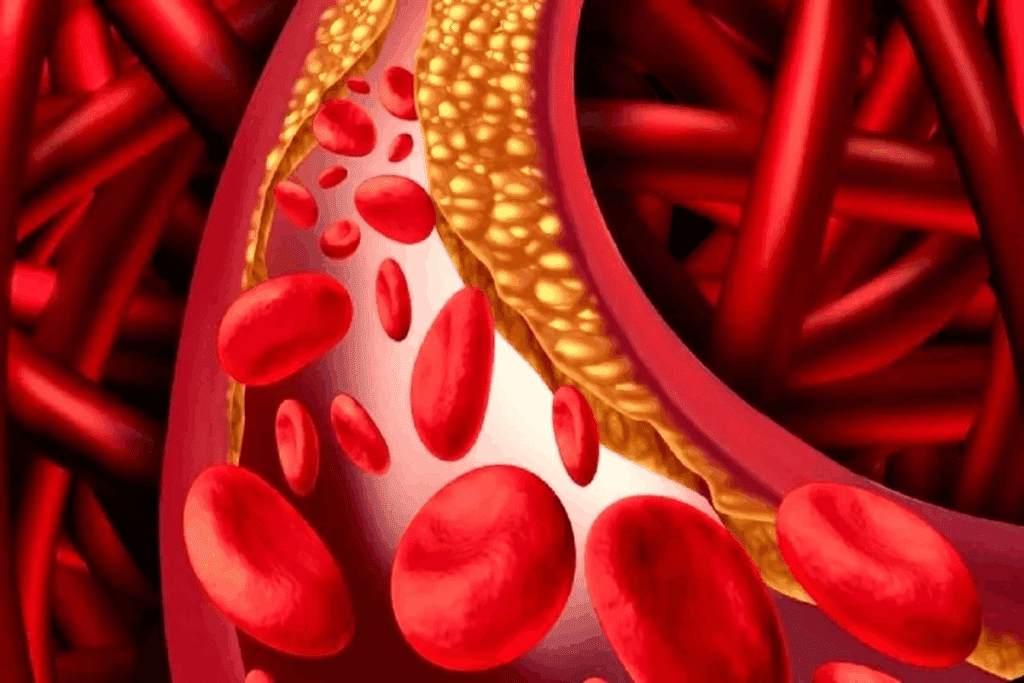
A 100% blocked artery is a serious condition that can greatly affect life expectancy. Atherosclerosis, the main cause of blocked arteries, is a big factor in heart disease. How long can you live with coronary artery calcification: can a person survive with a 100% blocked artery? Understand the body’s compensatory mechanisms clearly.
Nearly 1 in 3 adults in the United States has some form of cardiovascular disease. This includes conditions like coronary artery calcification and atherosclerosis.
It’s important to manage atherosclerosis to avoid more problems. Talking to a healthcare team about medicines and lifestyle changes can help reduce risks from a 100% blocked artery.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the risks of a 100% blocked artery is key.
- Atherosclerosis is a big factor in heart disease and life expectancy.
- Managing the condition through medical advice is vital.
- Lifestyle changes can help lessen the risks of atherosclerosis.
- Coronary artery calcification is a sign of heart disease.
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease and Blockages
It’s key to understand coronary artery disease to know how blockages form and their effects. This disease is mainly caused by atherosclerosis. It’s when fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances build up in artery walls. This buildup can narrow or block the coronary arteries, which are vital for the heart.
The Anatomy of Coronary Arteries
The coronary arteries are essential for the heart’s function. They provide the heart with the oxygen and nutrients it needs. The main arteries include the Right Coronary Artery (RCA), Left Anterior Descending artery (LAD), and the Circumflex artery. Each artery has a specific role in supplying blood to different heart areas.
How Blockages Develop Over Time
Blockages in coronary arteries grow over time due to plaque buildup. This buildup is influenced by high cholesterol, smoking, and high blood pressure. As plaque hardens, it narrows the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart.
Different Types of Coronary Arteries
The RCA, LAD, and Circumflex arteries are vital for heart health. The RCA supplies the right ventricle. The LAD provides blood to the heart’s anterior wall. The Circumflex artery supplies the lateral and posterior walls. Blockages in these arteries can cause various heart problems, depending on the area affected.
The Reality of 100% Blocked Arteries

About 15% to 20% of people with heart disease have a 100% blocked artery. This is called chronic total occlusion (CTO). It means a coronary artery is completely blocked, which is very bad for the heart.
Complete Occlusion: What It Means Medically
A chronic total occlusion means the artery is fully blocked. This stops blood from flowing. It can cause serious damage to the heart muscle if not treated.
Immediate Dangers of Total Blockage
A total blockage can cause a heart attack. This can damage or kill heart tissue. The dangers are urgent, needing emergency care.
Survival Statistics with 100% Blockage
Survival rates for 100% blocked arteries depend on many things. These include overall health, other blockages, and how well the heart finds other paths. Here are some survival stats.
| Condition | Survival Rate | Factors Influencing Survival |
| Single 100% Blocked Artery | Higher survival rate with treatment | Collateral circulation, overall health |
| Multiple Blockages | Lower survival rate without treatment | Number of blockages, severity |
Knowing these survival rates and what affects them helps patients and doctors make better choices. This is about treatment and managing the condition.
Coronary Artery Calcification: The Silent Progression
Coronary artery calcification is a sign of atherosclerosis. It starts quietly and can lead to serious heart problems if not treated. Coronary artery calcification is when calcium builds up in the arteries that supply blood to the heart.
How Calcification Develops in Arterial Walls
Calcification in the arterial walls is a complex process. It involves the buildup of calcium and phosphate. It’s linked to aging, inflammation, and atherosclerosis.
As plaque builds up, calcium deposits form. This makes the arterial walls stiff and less flexible.
Measuring Calcium Scores and What They Mean
A coronary calcium scan is a non-invasive test. It measures the calcium in the coronary arteries. The result is a calcium score.
This score helps doctors assess the risk of coronary artery disease. A score of 0 means no calcium is found. Higher scores mean more calcium and a higher risk of heart problems.
Average Calcium Scores by Age and Gender
Calcium scores vary by age and gender. Men usually have higher scores than women of the same age. This means men have a higher burden of coronary artery calcification.
Knowing these differences is key to understanding calcium scores. It helps doctors assess cardiovascular risk.
By understanding coronary artery calcification, people can better assess their risk for heart disease. They can then take steps to prevent it.
How Long Can You Live with Coronary Artery Calcification?
Coronary artery calcification is a sign of heart disease. It shows plaque buildup in the heart’s arteries. This can shorten your life and lower your quality of life.
Factors Affecting Survival Rates
Many things can change how long you live with coronary artery calcification. These include how much calcification you have, your heart health, and other heart risks. Early detection and treatment are key to better outcomes.
Statistical Life Expectancy Data
Research shows people with high calcium scores in their arteries face more heart risks. High scores can mean a shorter life. But, each person is different, and many factors can affect how long you live. These include your lifestyle and medical care.
Differences Between Calcification and Soft Plaque
It’s important to know the difference between hard and soft plaque. Hard plaque is stable, but soft plaque can burst and cause heart attacks. Knowing the type of plaque helps doctors decide the best treatment.
In summary, managing coronary artery calcification is critical. By understanding the risks and differences in plaque, you can improve your life. This includes making lifestyle changes and following medical advice.
Survival Mechanisms: Collateral Circulation
Collateral circulation is a vital mechanism that keeps blood flowing to the heart when an artery is blocked. It creates alternate pathways to bypass the blocked area. This helps keep the heart muscle alive.
Creation of Alternate Pathways
The body grows new blood vessels or enlarges small ones when a coronary artery narrows or blocks. This complex process is a response to the blockage. It aims to restore blood flow to the heart.
Limitations of Collateral Arteries
Collateral circulation is lifesaving but has its limits. Its effectiveness varies among people. The blockage’s location, severity, and the person’s health are key factors.
| Factors | Description | Impact on Collateral Circulation |
| Blockage Location | The position of the blockage within the artery. | Affects the chance for collateral development. |
| Blockage Severity | The degree to which the artery is blocked. | Decides how much collateral circulation is needed. |
| Overall Health | The general health condition of the individual, including presence of other diseases. | Can either hinder or enhance the body’s ability to develop collateral circulation. |
Factors Promoting Collateral Development
Regular physical activity boosts collateral artery growth. Certain medical therapies and lifestyle changes also help. Knowing these factors is key for those with coronary artery disease.
In summary, collateral circulation is a vital survival mechanism for those with blocked arteries. Understanding how it works, its limitations, and what promotes it can help improve outcomes.
Multiple Blocked Arteries: Survival and Prognosis
When more than one artery is blocked, the heart gets even less blood. This can cause more damage during a heart attack.
Having multiple blocked arteries makes diagnosing and treating heart disease harder. Patients often need more intense and detailed treatment plans.
Living with Two Blocked Arteries
Patients with two blocked arteries face a tougher prognosis than those with one. The location and how bad the blockages are affect their health a lot.
For example, blockages in the left anterior descending (LAD) artery can be very serious. This artery supplies a big part of the heart.
Three-Vessel Disease and Life Expectancy
Three-vessel disease, where all three major arteries are blocked, is very serious. It can greatly shorten a person’s life expectancy. Without treatment, the outlook is usually very poor.
| Condition | Average Life Expectancy | Treatment Impact |
| Single Vessel Disease | Longer | Minimally impacted by treatment |
| Two Vessel Disease | Moderate | Significantly improved with treatment |
| Three-Vessel Disease | Shorter | Substantially improved with aggressive treatment |
Comparing Different Blockage Patterns
The way blockages are spread out can affect how well a patient does. For instance, diffuse disease is harder to treat than blockages in one spot.
It’s important to understand these differences. This helps doctors create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.

Symptoms and Warning Signs of Severe Arterial Blockage
The signs of arterial blockage can be hard to spot at first. Atherosclerosis is dangerous because it can grow slowly without any clear signs. This makes it a big concern.
Recognizing a Cardiac Emergency
A cardiac emergency can happen suddenly, with little warning. Chest pain or discomfort is a common sign. It feels like pressure or tightness in the chest.
This pain can spread to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach. The American Heart Association says chest pain is the most common sign of a heart attack. Other signs include shortness of breath, feeling lightheaded, or cold sweats.
Subtle Signs of Chronic Blockages
Chronic blockages can show up in more subtle ways. These include fatigue, shortness of breath during routine activities, or swelling in the legs. These signs are important and should not be ignored.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
If you have severe chest pain, trouble breathing, or pain in the arm or jaw, get help right away.
“Acting F.A.S.T. can save lives. F.A.S.T. stands for Face drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulty, and Time to call 911,”
the American Stroke Association says. This advice is also true for cardiac emergencies.
Knowing these warning signs can save lives. If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, get medical help without delay.
Diagnosing Coronary Artery Blockages
Diagnosing coronary artery blockages requires both non-invasive and invasive tests. It’s important to get an accurate diagnosis. This helps doctors choose the best treatment and manage heart health.
Non-Invasive Testing Methods
Non-invasive tests are often the first step. They include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test measures the heart’s electrical activity. It can show signs of blockages or damage.
- Echocardiogram: It uses sound waves to create heart images. This shows how well the heart pumps and any problems.
- Cardiac Stress Test: This test checks the heart’s activity during stress. It can be through exercise or medicine, to find blockages.
Angiography and Other Definitive Tests
Invasive tests are sometimes needed for a clear diagnosis. Coronary angiography is a key one. It involves injecting dye into the arteries to see blockages on an X-ray.
Understanding Your Diagnostic Results
After testing, it’s important to understand the results. Your doctor will explain what they found. They’ll tell you about any blockages and suggest treatments based on their severity and location.
Treatment Options for Blocked Coronary Arteries
Treating blocked coronary arteries involves several steps. These include medical care, interventional procedures, and surgery. The main goal is to boost blood flow, lessen symptoms, and avoid serious issues like heart attacks or strokes.
Medical Management Approaches
Medical management uses drugs to control symptoms and slow disease growth. This includes:
- Antiplatelet drugs to stop blood clots
- Statins to lower cholesterol
- Beta-blockers to slow heart rate and blood pressure
- Nitrates to ease chest pain
Interventional Procedures (Stents and Angioplasty)
For severe blockages, procedures like angioplasty and stenting are needed. These steps involve:
- Angioplasty to open the blocked artery
- Stenting to keep the artery open
These methods are less invasive and can greatly improve blood flow and symptoms.
Surgical Solutions (Bypass Surgery)
When other methods fail, bypass surgery is considered. It creates a new path around the blockage using a graft.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Treatment
After treatment, a detailed recovery plan is essential. This includes:
- Lifestyle changes like diet and exercise
- Cardiac rehabilitation to enhance heart health
- Monitoring by doctors to adjust treatment as needed
By following these steps, people with blocked coronary arteries can greatly improve their life quality and lower the risk of future heart problems.
Can Arterial Blockages Be Reversed?
Arterial blockages, a key part of coronary artery disease, might be reversed. This idea opens up new ways to handle and treat coronary artery disease.
Lifestyle Modifications That Show Promise
Making lifestyle changes is key in managing coronary artery disease. Dietary modifications, like eating a Mediterranean diet, can help. This diet is full of fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. It helps reduce plaque buildup.
Regular physical activity, like brisk walking, also boosts heart health. It’s a simple way to improve your heart’s condition.
Medical Therapies for Plaque Regression
Some medical treatments can help reduce plaque. Statins are often used to lower cholesterol and stabilize plaques. This makes them less likely to rupture.
Other treatments might include medicines to lower blood pressure or control diabetes. These can also help manage the disease.
The Limits of Reversal: What’s Realistic
While lifestyle changes and medical treatments can help, the extent of reversal varies. It depends on the blockage’s severity, your overall health, and how well you follow treatment plans.
| Treatment Approach | Potential Benefits |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Reduces plaque buildup, improves overall heart health |
| Medical Therapies | Lowers cholesterol, stabilizes plaques, manages related conditions |
Knowing how to reverse arterial blockages is vital for those with coronary artery disease. By mixing lifestyle changes with medical treatments, patients can see better results. This can greatly improve their life quality and prognosis.
Living with Coronary Artery Disease: Quality of Life
Coronary artery disease can really change how you live, but you can stay active. To manage CAD well, you need medical care, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups.
Managing Daily Activities with CAD
It’s possible to adjust your daily routine with CAD. Pace yourself, don’t overdo it, and exercise safely. Always get your exercise plans checked by a doctor.
Eating right is also key. Eat lots of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean meats. Try to cut down on fats, cholesterol, and salt.
| Dietary Component | Recommended Intake | Benefits |
| Fruits and Vegetables | 5 servings a day | Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants |
| Whole Grains | 3-5 servings a day | High in fiber, vitamins, and minerals |
| Lean Proteins | Include in every meal | Supports heart health |
Psychological Impact and Coping Strategies
CAD can also affect your mind, causing stress or sadness. Use stress-busting activities like meditation or yoga. Having friends and support groups can help a lot too.
Long-term Monitoring and Follow-up Care
Keeping an eye on your CAD is vital. See your doctor regularly and follow their advice. This way, you can catch any problems early.
With these steps, people with CAD can live better lives. They can stay active and enjoy life, even with CAD.
Conclusion: Navigating Life with Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease is serious, but it’s not a death sentence. Early detection and the right treatment can help manage the risks. Making lifestyle changes is also key to improving life quality.
Recognizing warning signs and symptoms is important. This allows for quick medical attention. Tests and treatments like angioplasty can help the heart. Eating right and exercising regularly are also essential.
Managing coronary artery disease requires a team effort. Working with healthcare providers and making smart choices can lower risks. This journey involves regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle.
FAQ
How many arteries in the heart can be blocked?
One, two, or all three major coronary arteries can be blocked. The number affects the disease’s severity and risks.
What is the anterior circumflex artery?
The circumflex artery, or left circumflex artery, is a branch of the left coronary artery. It supplies blood to the heart’s lateral and posterior walls.
What is a normal average calcium score for a 65-year-old?
For a 65-year-old, a calcium score above 400 is high. It shows significant coronary artery calcification.
What is the heart circumflex artery?
The circumflex artery wraps around the heart. It supplies blood to the lateral and posterior walls.
What is severe CAD?
Severe CAD means significant narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries. It can lead to heart attacks and serious complications.
How long can you live with 3 blocked arteries?
Life expectancy with three blocked arteries varies. It depends on blockage severity, health, and treatment. Proper management can extend life years.
What is nonobstructive CAD?
Nonobstructive CAD means some narrowing of coronary arteries. But it’s not enough to block blood flow significantly.
What is three-vessel disease?
Three-vessel disease occurs when all three major coronary arteries are blocked. It’s serious and requires careful management.
Can calcified arteries be reversed?
Some studies suggest lifestyle changes and medical therapies can slow or halt calcified artery progression. Reversal is rare.
What causes clogged arteries in the heart?
Clogged arteries are caused by plaque buildup over time. This plaque is a mix of cholesterol, fat, and other substances.
How long can you live with collateral arteries?
Collateral arteries can improve survival and quality of life for those with coronary artery disease.
What is scattered calcified atherosclerosis?
Scattered calcified atherosclerosis is when there are calcified areas in arterial walls. It indicates atherosclerosis presence.
Can you live a long life with coronary artery calcification?
Many people with coronary artery calcification can live long with proper management and lifestyle changes.
What is the life expectancy with atherosclerosis?
Life expectancy with atherosclerosis varies. It depends on condition severity, health, and treatment. Proper management can extend life years.
Can you reverse arterial blockage?
Reversing arterial blockage is rare. But, lifestyle changes and medical therapies can slow or halt progression. Treatment can improve symptoms and quality of life.
What is the left circumflex artery?
The left circumflex artery is a branch of the left coronary artery. It supplies blood to the heart’s lateral and posterior walls.
What happens if the coronary arteries are blocked?
Blocked coronary arteries can lead to heart attacks. Heart attacks can damage the heart muscle and be life-threatening.
Can you live with 90% blockage in an artery?
Living with 90% blockage in an artery is possible. But, it’s a serious condition that needs careful management and possibly interventional treatment.
What is the right coronary artery?
The right coronary artery is one of the three major coronary arteries. It supplies blood to the right ventricle, right atrium, and other heart areas.
Can heart disease cause depression?
Yes, heart disease can lead to depression, and vice versa. Managing both conditions is key for overall health and well-being.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5882405/

































