Radiosurgery is a precise way to treat cancer and other conditions with focused radiation. It’s a non-invasive method that offers a highly effective treatment. This is true for many medical conditions, including neurological disorders.
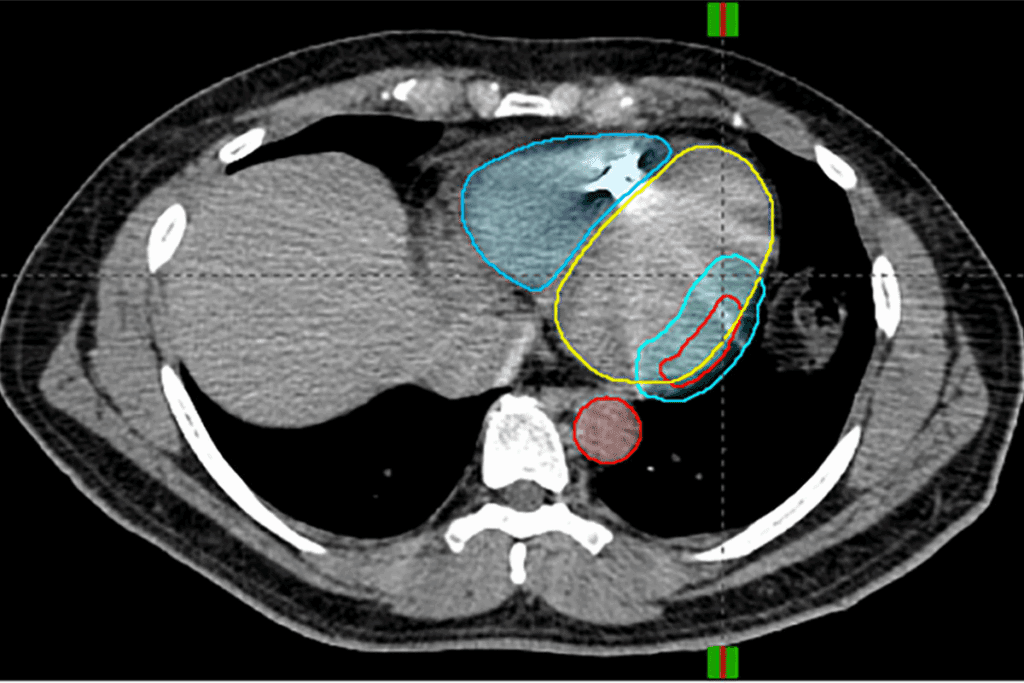
Unlike traditional surgery, radiosurgery doesn’t cut or open the body. It sends high doses of radiation directly to the target area. This helps protect the healthy tissues around it.
This advanced technology has changed how we treat some medical conditions. It gives patients a safer and often more effective option than traditional surgery.
Learn what is a radiosurgery procedure. Understand this highly precise form of radiation delivery clearly gamma knife surgery
Key Takeaways
- Radiosurgery is a non-invasive radiation therapy.
- It targets specific areas with high doses of radiation.
- Used to treat cancer and neurological disorders.
- Minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
- A safer alternative to traditional surgery for certain conditions.
The Evolution and Principles of Radiosurgery
Radiosurgery has changed a lot over time. It has become a complex medical treatment. This change is due to new technology and a better understanding of how radiation affects the body.
Definition and Core Concepts of Radiosurgical Treatments
Radiosurgery is not surgery at all. It’s a non-invasive method that uses precise radiation to treat conditions, mainly in the brain. It focuses radiation on a specific area, protecting the rest of the tissue. This method works by targeting and controlling abnormal cells or tissues with radiation.
Historical Development of Radiation-Based Surgery
The idea of using radiation for treatment started in the early 1900s, after X-rays were discovered. The 1950s and 1960s saw the beginning of radiosurgery with the Gamma Knife. This technology was a big step forward.
Today, radiosurgery has grown thanks to better imaging, radiation systems, and computer planning. It’s a story of constant improvement from early radiation therapy to today’s precise treatments.
How Gamma Knife Surgery Works
To understand Gamma Knife surgery, you need to know its technology. It involves sending precise radiation to specific areas.
The Science of Page Gamma Radiation
Gamma Knife surgery uses focused gamma radiation from cobalt sources. This radiation is aimed at the target, protecting nearby tissues. The tech behind it treats complex conditions with great accuracy.
By focusing gamma radiation, it targets tumors and abnormalities. This is done without the need for open surgery.
The gamma radiation comes from multiple cobalt sources. They focus on a single point, creating a high dose at the target site.
Precision Targeting in the Brain and Body
Gamma Knife surgery’s big plus is its precision targeting in the brain and body. Advanced imaging and treatment planning software ensure accurate delivery of radiation. This makes it a top choice for many medical conditions.
This treatment is very effective with few side effects. Its precision is perfect for treating brain tumors and other complex issues. It greatly improves a patient’s quality of life.
Gamma Knife Surgery: The Pioneering Radiosurgery Technology
Gamma Knife surgery is a leading technology for treating brain tumors and neurological conditions. It’s a non-invasive method that has changed neurosurgery. This technology offers a new way to treat without surgery.
Origins and Evolution of Gamma Knife Technology
A Swedish neurosurgeon, created Gamma Knife technology in the 1960s. The first version had one cobalt source. Now, it uses many sources for better results.
Over time, Gamma Knife technology has improved a lot. New models like the Gamma Knife Perfexion and Icon offer better precision and flexibility.
Components of the Gamma Knife Machine
The Gamma Knife machine has key parts like gamma sources, a collimator system, and a patient positioning system. The latest models, like the Gamma Knife Icon, use 201 cobalt sources for precise radiation.
The collimator system focuses the gamma rays on the target. This reduces harm to healthy tissue. The patient positioning system makes sure the patient is in the right place during treatment.
How Gamma Radiation Is Used in Cancer Treatment
Gamma Knife surgery uses gamma radiation to treat brain tumors and other conditions. The gamma rays from the cobalt sources target the tumor. This kills the tumor cells while protecting the brain.
| Treatment Aspect | Description | Benefit |
| Precision | Gamma Knife surgery delivers gamma radiation with sub-millimeter precision. | Minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissue. |
| Non-invasive | No surgical incisions are required; treatment is performed through the intact skull. | Reduces risk of infection and promotes faster recovery. |
| Effectiveness | High success rates in treating brain tumors and other neurological conditions. | Offers a viable treatment option for patients who are not good candidates for traditional surgery. |
Gamma Knife surgery’s use of gamma radiation is a big step forward. It provides a safe and effective way to treat complex brain disorders.
Types of Radiosurgery Procedures Available Today
Radiosurgery uses advanced technologies like Gamma Knife, CyberKnife, and LINAC-based systems. These treatments aim to solve various health issues with precision and less invasiveness.
Gamma Knife Technology Overview
Gamma Knife radiosurgery uses a precise delivery system to target areas, mainly in the brain. It’s great for treating brain tumors, vascular malformations, and some functional disorders. The Gamma Knife’s accuracy lets it give high doses of radiation to the target area, protecting healthy tissue nearby.
CyberKnife Radiosurgery Systems
CyberKnife technology is flexible and non-invasive, treating tumors all over the body, not just in the brain. It has a robotic arm that moves to deliver radiation from different angles. This makes it perfect for tumors that are hard to reach or near important structures.
Linear Accelerator (LINAC) Based Treatments
LINAC-based radiosurgery systems use a linear accelerator to make high-energy X-rays. These systems are very versatile and can treat many conditions, from brain tumors to some cancers. Treatments can be given in one session or spread over several, based on the case.
Each radiosurgery technology has its own benefits and is best for different health issues. The right treatment depends on the tumor’s location, size, and type.
Medical Conditions Treated with Radiosurgery
Radiosurgery is a key treatment for many brain conditions. It’s precise and effective, making it a game-changer for tough-to-treat cases.
Brain Tumors and Metastases
Brain tumors, both primary and metastatic, are treated with radiosurgery. Metastatic brain tumors are common in cancer patients. Radiosurgery is a non-invasive option.
It delivers high doses of radiation right to the tumor. This minimizes harm to the brain around it.
- Effective for treating single or multiple brain metastases
- Offers a non-invasive alternative to traditional surgery
- Can be used in conjunction with whole-brain radiation therapy
Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs)
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are abnormal brain connections. Radiosurgery is a top choice for treating many AVMs. It delivers focused radiation to close the malformation over time.
The effectiveness of radiosurgery for AVMs depends on size and location. Studies show high obliteration rates, lowering hemorrhage risk.
Functional Disorders and Other Neurological Conditions
Radiosurgery treats various functional disorders and neurological conditions. It’s used for trigeminal neuralgia to ease severe facial pain. It’s also explored for other disorders.
Radiosurgery’s wide range of applications highlights its value in medicine. As technology improves, its uses will likely grow, bringing new hope to patients.
The Complete Gamma Knife Surgery Procedure
Gamma Knife surgery is a precise treatment for brain lesions. It’s great for treating brain tumors and arteriovenous malformations. This method is very effective.
Patient Preparation and Evaluation
Before Gamma Knife surgery, patients get checked to see if they’re a good fit. Doctors look at their medical history and current health. They make sure Gamma Knife surgery is the best choice.
Frame Placement and Imaging Process
Then, a special head frame is put on the patient’s head. This frame helps find the exact spot in the brain. After that, MRI or CT scans are done to get clear images of the brain and the target area.
Treatment Planning and Radiation Delivery
Next, the team plans the treatment using the images. They figure out the right amount of radiation and where to aim. The patient is then placed in the Gamma Knife unit for the radiation treatment. The whole thing is watched closely to make sure it works right.
| Procedure Step | Description |
| Patient Preparation | Medical evaluation and history review |
| Frame Placement | Stereotactic head frame secured to the head |
| Imaging Process | MRI or CT scans for precise localization |
| Treatment Planning | Personalized plan based on imaging data |
| Radiation Delivery | Precise radiation delivery to the target lesion |
CyberKnife vs. Gamma Knife: A Detailed Look
When we talk about radiosurgery, CyberKnife and Gamma Knife are two big names. They help treat different health issues but work in different ways.
Technical and Mechanical Differences
The main difference is how they send radiation. Gamma Knife uses a fixed frame and cobalt sources for focused gamma rays. CyberKnife, with its robotic arm and linear accelerator, is more flexible and can treat more areas
Treatment Applications and Limitations
CyberKnife is good for treating tumors all over the body, not just in the brain. Gamma Knife is mainly for brain tumors and some neurological issues, thanks to its high precision.
Patient Experience and Comfort Factors
Comfort levels vary between the two. Gamma Knife needs a frame on the head, which can be uncomfortable. CyberKnife, being frame-less, is more comfortable, making it better for longer treatments.
In summary, picking between CyberKnife and Gamma Knife depends on the health issue, where it is, and how comfortable the patient feels. Knowing these differences helps make better choices.
Inside Radiosurgery Equipment and Technology
Radiosurgery equipment has seen big changes, making treatments better. New tech has made radiosurgery more precise and effective for many health issues.
Gamma Knife Machine Components and Operation
The Gamma Knife machine is a top-notch tool for radiosurgery. It has a helmet system that focuses gamma radiation on the target area. The machine sends out gamma rays from many sources, focusing them on the tumor or affected area.
This precise focus allows for a high dose of radiation to the target. It also keeps healthy tissue around it safe from harm.
Using the Gamma Knife involves several steps. First, the patient gets ready and imaging is done. Then, the patient’s head is fixed in a frame to ensure accurate targeting.
Imaging like MRI or CT scans helps find the target area exactly.
Recent Technological Advancements in Radiosurgery
In recent years, radiosurgery has seen big tech improvements. One key change is using advanced imaging like MRI and CT scans in planning treatments. This makes targeting tumors more accurate and spares more healthy tissue.
| Technological Advancement | Description | Benefit |
| Advanced Imaging | Integration of MRI and CT scans | More accurate targeting |
| Robotic Systems | CyberKnife and other robotic systems | Enhanced precision and flexibility |
| Treatment Planning Software | Advanced software for dose calculation and optimization | Improved treatment outcomes |
Robotic radiosurgery systems, like CyberKnife, are another big step forward. They offer better precision and flexibility. This means they can treat tumors in hard-to-reach places.
“The integration of advanced technologies has revolutionized the field of radiosurgery, enabling more precise and effective treatments.”
— Radiosurgery Specialist
The future of radiosurgery is bright. Ongoing research aims to make treatments even better. It also hopes to treat more conditions.
Advantages of Radiosurgery Over Conventional Surgery
Radiosurgery has changed neurosurgery by giving a non-invasive option instead of traditional surgery. It’s becoming more popular because of its many benefits over traditional surgery.
Non-Invasive Nature and Reduced Complications
Radiosurgery is non-invasive, unlike traditional surgery. It doesn’t need incisions or instruments in the body, lowering the risk of problems. This is great for patients at high risk for surgery complications or with hard-to-treat conditions.
Outpatient Procedure with Minimal Recovery Time
Radiosurgery is usually done as an outpatient procedure. Patients can go home the same day. It also has a short recovery time, unlike traditional surgery. This makes it perfect for those with busy lives or big responsibilities.
Precision and Effectiveness for Specific Conditions
Radiosurgery targets the affected area precisely, protecting healthy tissue. This is very helpful for treating tumors, AVMs, and other hard-to-reach conditions. Its success in these areas makes it a valuable treatment choice.
| Advantages | Radiosurgery | Conventional Surgery |
| Non-Invasive | Yes | No |
| Recovery Time | Minimal | Significant |
| Precision | High | Variable |
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Radiosurgical Treatments
Radiosurgery, like any medical treatment, comes with risks and side effects. It’s important for patients to know about these to make the best treatment choices.
Short-Term Side Effects and Management
Right after radiosurgery, you might feel fatigue, headaches, or nausea. These symptoms are usually mild and go away quickly. To feel better, rest, drink plenty of water, and take medicine if needed.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: Page Regular check-ups with your doctor to watch for any side effects.
- Symptom Management: Use medicines and other treatments to help manage symptoms.
Long-Term Considerations and Radiation Effects
Long-term, radiosurgery might affect nearby tissues or cause radiation necrosis. Though rare, these issues can be serious and might need extra treatment.
Radiation Necrosis: A rare but serious problem where radiation damages brain tissue around the tumor.
Risk Factors and Important Contraindications
Some things can make radiosurgery risks higher. These include the tumor’s size and where it is, past radiation, and your overall health.
- Tumor Size and Location: Bigger tumors or those in key areas might be riskier.
- Previous Radiation Exposure: If you’ve had radiation therapy before, you might face higher risks.
Patient Selection Criteria for Radiosurgery Procedures
Radiosurgery is a precise treatment that needs careful patient selection for the best results. The choice to have radiosurgery depends on a detailed check of the patient’s health, test results, and overall well-being.
Medical and Diagnostic Requirements
To qualify for radiosurgery, patients must meet certain medical and diagnostic standards. This includes a full medical history, accurate diagnostic imaging, and a detailed check of the condition being treated. Tests like MRI, CT scans, or PET scans are key in deciding if radiosurgery is right for a patient.
The size, location, and type of lesion or tumor are closely looked at. This helps decide if radiosurgery is a good option.
Conditions That May Exclude Radiosurgery Options
While radiosurgery is a valuable treatment for many, some conditions make it unsuitable. Large tumors or those near important structures might not be good candidates. Also, patients with ongoing chemotherapy or weak immune systems are evaluated individually.
The doctor will look at these factors to find the best treatment for each patient.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery in Modern Cancer Treatment
Stereotactic radiosurgery is a key part of modern cancer treatment, mainly for brain tumors. It sends precise, high doses of radiation to specific brain areas. This helps avoid harming the healthy tissue around it.
Primary and Metastatic Brain Tumor Management
Stereotactic radiosurgery works well for both primary and metastatic brain tumors. For primary tumors like gliomas and meningiomas, it’s a non-invasive option. It can be used alone or with surgery and chemotherapy. For metastatic tumors, which start elsewhere in the body, radiosurgery improves outcomes and quality of life.
- Precision targeting of tumors
- Minimally invasive with fewer side effects
- Effective for tumors that are difficult to reach surgically
- Can be used in combination with other treatments
Integration with Chemotherapy and Other Cancer Therapies
Combining stereotactic radiosurgery with chemotherapy and other treatments is a big step forward. This approach targets both the tumor and any microscopic disease spread. It makes treatments more effective and can increase survival rates.
Recovery and Follow-Up After Radiosurgery Procedures
Radiosurgery is a non-invasive treatment that requires careful recovery and follow-up. This ensures the best results. It involves watching for side effects and checking if the treatment worked.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care and Monitoring
Right after radiosurgery, patients are watched closely for any bad reactions. Close observation is key to handle any issues quickly. Most patients go home the same day, with clear instructions for aftercare.
“The immediate post-procedure period is critical,” says a top radiosurgery expert. “Watching closely helps spot and manage side effects early.”
Long-Term Follow-Up Protocols and Imaging
Long-term follow-ups are vital to see how well radiosurgery worked. They also help catch any long-term side effects. This includes imaging tests and visits with the treatment team. How often these happen depends on the condition and the patient’s health.
A study in the Journal of Neurosurgery found, “Regular follow-up and imaging are key for checking treatment success and managing late effects.” This shows how important a detailed follow-up plan is.
Following the recommended follow-up schedule helps patients get the most from their radiosurgery. It also lets them quickly address any issues or concerns.
Beyond Traditional Approaches: Innovations in Radiosurgery
Innovations in radiosurgery are changing the game in radiation therapy. New technologies and methods are being developed to better treat patients.
Proton Therapy and Emerging Radiation Technologies
Proton therapy is a big step forward in radiosurgery. It uses protons to target tumors, which is gentler on healthy tissue. This is great for tumors close to important areas or in kids.
New technologies like IMRT and SBRT are making radiosurgery more precise and effective. They help create treatment plans that are more tailored to each patient, leading to better results.
| Technology | Description | Benefits |
| Proton Therapy | Uses protons to target tumors | Reduces damage to surrounding tissue |
| IMRT | Intensity-modulated radiation therapy | Enhances precision in radiation delivery |
| SBRT | Stereotactic body radiation therapy | Improves treatment outcomes for specific conditions |
Future Directions in Precision Radiosurgical Treatments
The future of radiosurgery is all about getting even more precise and personal. Better imaging tech like MRI and CT scans will help target tumors more accurately. Also, AI and machine learning will make planning and delivering treatments easier.
Researchers are looking into new radiation types, like carbon ion therapy. These advancements will be key in shaping the future of radiosurgery.
Practical Considerations: Insurance and Costs
It’s important for patients to know the financial side of radiosurgery. The cost can change a lot. This depends on the type of procedure, the technology used, and where the treatment is done.
Typical Costs of Different Radiosurgery Options
The cost of radiosurgery varies. It depends on the technology and how it’s done. Here are some key points:
- Gamma Knife Radiosurgery: This is used for brain tumors and other brain conditions. It costs between $8,000 and $14,000.
- CyberKnife Radiosurgery: It’s flexible and treats tumors outside the brain. Costs range from $10,000 to $20,000.
- LINAC Radiosurgery: This method is used for different tumors. Costs vary from $7,000 to $15,000.
Navigating Insurance Coverage and Approval
Getting insurance for radiosurgery can be tricky. Here’s how to handle it:
- Check Insurance Policy: Look at your insurance to see what’s covered and what’s not.
- Pre-Approval: Get approval from your insurance before the procedure.
- Financial Assistance: Look for financial help from the treatment center or other groups.
Knowing the costs and how to deal with insurance helps patients make good choices about radiosurgery.
Conclusion: The Evolving Landscape of Radiosurgery
The field of radiosurgery is changing fast, thanks to new tech and techniques. This means better precision, more treatment choices, and better results for patients.
New systems like Gamma Knife and CyberKnife are making treatments more accurate and effective. They help with tough conditions like brain tumors and blood vessel problems. The future looks bright, with more tech like proton therapy on the way.
As it keeps growing, radiosurgery will become even more key in treating diseases. It offers patients less invasive and very effective treatments. With its history, current progress, and bright future, radiosurgery is a big part of modern medicine.
FAQ
What is radiosurgery?
Radiosurgery is a non-invasive way to treat diseases with radiation. It focuses high doses on specific areas. This method is used for cancer and neurological issues.
How does Gamma Knife surgery work?
Gamma Knife surgery uses gamma radiation to target areas in the brain and body. It treats complex conditions with high accuracy.
What are the different types of radiosurgery procedures available?
There are Gamma Knife, CyberKnife, and LINAC-based treatments. Each uses different technology for various medical needs.
What medical conditions can be treated with radiosurgery?
Radiosurgery treats brain tumors, metastases, and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). It also helps with functional disorders and other neurological issues.
What is the Gamma Knife surgery procedure like?
The procedure starts with preparation and evaluation. Then, a frame is placed and imaging is done. Next, treatment planning and radiation delivery follow, ensuring a precise treatment.
How does CyberKnife compare to Gamma Knife?
CyberKnife and Gamma Knife differ in technology and application. They also vary in patient experience and comfort.
What are the advantages of radiosurgery over conventional surgery?
Radiosurgery is non-invasive and has fewer risks. It’s often done as an outpatient procedure with little recovery time. It’s a precise treatment for specific conditions.
What are the possible risks and side effects of radiosurgical treatments?
Treatments can cause short-term side effects and long-term considerations. There are also radiation effects and certain risks to consider.
How are patients selected for radiosurgery procedures?
Patients are selected based on medical and diagnostic requirements. Some conditions may not be suitable for radiosurgery.
What is the role of stereotactic radiosurgery in cancer treatment?
Stereotactic radiosurgery is key in managing brain tumors. It’s often used with chemotherapy and other cancer treatments.
What is the recovery process like after radiosurgery?
Recovery involves immediate care and monitoring. Long-term follow-up and imaging are also part of the process to ensure the best results.
Who are some of the pioneering specialists in radiosurgery?
Medical Expert. Major centers in the U.S. offer advanced treatments.
What innovations are on the horizon for radiosurgery?
New technologies like proton therapy are coming. Future treatments aim for more precision and better outcomes.
How much does radiosurgery typically cost?
Costs vary by procedure type.
How does radiosurgery equipment work?
Equipment, like Gamma Knife machines, use advanced tech. They deliver precise radiation doses for effective treatment.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23328437/























